Origin of the species and description
Photo: Hives
The wren (Aglais urticae, Nymphalis urticae) belongs to the Holarctic genus of day butterflies Aglais, originating from the family Nymphalidae. The specific epithet urticae comes from the word nettle, and Aglais is the ancient Greek goddess of grace Aglaia. Depending on their habitat, there are several subspecies of urticaria:
- Aglais urticae var. chinensis;
- Aglais urticae var. connexa;
- Aglais urticae var. baicalensis;
- Aglais urticae var. urticae;
- Aglais urticae var. polaris;
- Aglais urticae var. kansuensis;
- Aglais urticae var. excimia;
- Aglais urticae var. stoetzneri;
- Aglais urticae var. turcica.
The insect's closest relative is the spotted wren. Externally they are absolutely identical. Their only difference is a large discal spot. It is located on the front wings and is connected to the veins. This species is not so numerous and is less common.
Interesting fact: The Scots called this subspecies “devils”; in Japan, on the contrary, hives are considered a symbol of an innocent young soul and immortality. The ancient Romans believed that these were not insects, but bouquets of flowers torn by a gust of wind, personifying love, success, beauty, and prosperity.
Butterfly behavior can predict the weather. If the flight is intermittent and restless, it means it will start raining soon. Chocolate girls sense a change in humidity levels in the near future and try to quickly find a cozy place to hide and wait out the bad weather.
What does urticaria look like (photo)
Beautiful hives butterfly.Name: Urticaria Lat.:
Aglais urticaeClass: Insects - Insecta Order: Lepidoptera - Lepidoptera Family: Nymphalidae - Nymphalidae
| Habitats: | parks, forests, edges, highlands |
| Peculiarities: | beautiful day butterfly, distinguishes several colors |
| Benefit or harm: | lives on nettles, hops or hemp, not considered a pest |
Photo and description of the urticaria butterfly: appearance and internal structure
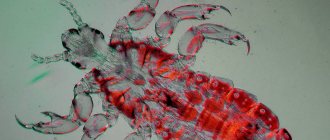
The length of the wings of the urticaria, which is also called chocolate, varies from 20 to 25 mm. In scope they reach 40–60 mm. Their color in males and females is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye. The outer surface has a brick-red hue and is strewn with black spots. At the anterior side of the wing triangle, which connects the base to the apical angle, the wings are separated by yellow intervals. There is a white spot at the top of the front wing.
The basal half of the hind wing is brownish-brown, the outer half is brick-red. These zones are clearly demarcated. Along the outer jagged edge of the wings there are bluish crescent-shaped spots. Their underside is brownish-brown. There is a transverse wide yellow stripe on the front wing.
The inner surface of the wings is brownish with light spots. Brown hairs grow on the abdomen and chest of a rich brown color. Insects have 3 pairs of legs. Shortened forelimbs without claws do not participate in the process of locomotion. They are responsible for a soft landing. There are spurs on the shins of the forelimbs. The insect cleans the snot with them.
The body of the urticaria is covered with a chitinous shell. The head is round in shape with a somewhat flattened occipital region. Compounded eyes are round or oval. They occupy most of the lateral area of the head. It also has a long black proboscis. With its help, the chocolate maker sucks out the nectar. During flight, it curls up to form a spiral.
The chest consists of 3 segments, the anterior of which is significantly smaller than the others. The elongated cylindrical abdomen is formed by 10 ring-shaped segments, each of which has spiracles. Club-shaped antennae are located on the border of the parietal and frontal regions of the head. Antennas perform important functions: they help their owner navigate in space, detect air vibrations and smell. A description of the insect would be incomplete without a photo. Below you can see what it looks like.
The chocolate butterfly has a perfect nervous system and sensory organs. The first consists of the peripharyngeal ring and the ventral nerve cord. The result of the fusion of clusters of nerve cells is the brain, which controls movements. Regarding circulation, digestion and respiration, these involuntary functions are controlled by the sympathetic nervous system.
The circulatory system is lacunar, the respiratory system consists of tracheas, through which oxygen flows to the internal organs and tissues. The excretory system is represented by a bundle of Malpighian vessels, closed at the tops, and flowing into the intestine at the bases.
The reproductive system in females is formed by 2 ovaries, which pass into a tubular oviduct. The right and left ducts are combined into a single unpaired organ, through which mature eggs are released. After fertilization, sperm accumulation occurs in the spermatic receptacle. The reproductive organs of males are formed by 2 testes, which pass into the vas deferens and are united by an unpaired ejaculatory duct through which the seed is excreted.
Treatment of urticaria
Pharmaceutical drugs used to treat urticaria should be taken as recommended by your doctor. The best treatment for this condition is to know and avoid trigger factors. The hives will probably go away on their own. But at the same time, medical supervision is a prerequisite to exclude the development of complications.
Treatment for urticaria in children includes:
- taking antihistamines to reduce the rash;
- eliminating foods that cause hives;
- prescribing diuretics to eliminate severe edema;
- using antipruritic ointments to relieve the condition.
- in some situations, hormones are used (topically and by injection).
You need to keep a diary about what the child does and eats. This approach allows us to identify predisposing factors and eliminate them.
Gradually, one can narrow down the real causes and respond accordingly.
With such a complication as Quincke's edema, coughing attacks appear and breathing becomes difficult. In this case, urticaria in children requires emergency care.
Young children often experience swelling of the gastrointestinal mucosa, which is accompanied by vomiting. In severe cases, damage to the nervous system and brain occurs. Such conditions are dangerous to health and life, so delaying a visit to the doctor is unacceptable.
Most children switched to a hypoallergenic diet recover quickly and recover even without medication.
Where does the hives butterfly live?
These insects, along with the cabbage white and peacock's eye, are one of the most common species living in Europe. The range extends to the coast of the Arctic Ocean. Chocolate girls can be found in China, Japan, Asia Minor and Central Asia, Mongolia, Vietnam, Siberia, Korea, and in the countries of the former CIS.
You can see urticaria, like its brothers, in parks, squares, meadows and fields, gardens, forest edges and other flowering areas. Moths prefer quiet and peaceful places to noisy cities. They don't like bad weather. If you feel the approach of a strong wind or rain, chocolate butterflies look for where to hide - in tree hollows, basements, attics of private houses, verandas.
You can also meet chocolate makers high in the mountains. In the Alps, this species was found at an altitude of 3 thousand meters, and in the Himalayas - 5 thousand meters above sea level. At the pupal stage, cocoons can be seen everywhere: on tree branches, leaves and stems of flowers, on fences and gates, and benches.
Butterflies do not fly away for the winter, but hide from cold weather and frosts under the bark of trees, in the basements of houses, caves, and sometimes on balconies. Urban individuals choose places closer to human houses, so that in case of bad weather it is easier to find shelter.
Chocolate Butterfly - Wish Maker
Of all the fauna living on earth, there is hardly any more mysterious and beautiful creature than the butterfly. No insect undergoes so many transformations before appearing in its true form. The life of a butterfly can be divided into four stages: egg, caterpillar, pupa, butterfly.
And it is precisely the fourth phase of the butterfly’s life that causes so many admiring glances and exclamations. There are a great variety of species of this insect: from small one-day moths to huge butterflies living in the tropics. Some of them are absolutely harmless, but there are also those that cause significant damage to agriculture, destroying the harvest of tomatoes, cabbage and other crops. In this article we will talk about such a familiar moth as the chocolate butterfly. It is very common in our latitudes, and, of course, you have seen it more than once outside the city - in the country or in the forest.
Chocolate Butterfly
The second name for this lepidoptera is urticaria. The butterfly received its first name (chocolate maker) because of its color. The wings of the butterfly are brown-orange in color, along the edge of which there is a border of pale blue spots in the shape of a crescent. They give the insect a particularly elegant appearance. And the second (urticaria) - because the food plant of this butterfly is exclusively nettle. Males differ little in color from females. Eggs are laid by those butterflies that managed to survive the winter. To do this, they hide in cracks and often overwinter in basements, attics of houses, and also in caves. The butterfly lays eggs (pale yellow) in nettle thickets on the underside of a leaf (200-300 pieces each).
The caterpillars are dark, almost black in color, with yellow stripes running along the body. Before pupation, they do not spread far from each other and intensively absorb nettle leaves. As soon as the caterpillars gain enough nutrients, the third stage of the butterfly's life begins - the pupa. The caterpillar weaves a cocoon around its body and remains in it until the butterfly forms. The doll hangs upside down. The cocoons of these butterflies can often be seen on the walls of houses and on fences.
Chocolate butterfly: habitat and life expectancy
It is known that the chocolate butterfly (photo presented in the article) lives in almost all of Eurasia and Europe. These butterflies love to fly on forest edges, in gardens and parks. They are also found in the mountains at an altitude of about 3000 meters. The question arises about how long chocolate butterflies live. The lifespan of these beauties varies from several weeks to several months. The fact is that several generations of butterflies are formed over the summer. Some of them overwinter in secluded places and then live all summer, laying eggs.
Signs
If a butterfly flies into your house, then this is considered a very good sign, since on its wings it brings happiness. There is a belief that if you catch a butterfly and, carefully holding it in your palms, make a wish, it will definitely come true. But don’t forget to release her afterwards.
Related species
The common spotted urticaria belongs to the genus Aglais. A distinctive feature of the species is that in the upper part of the fore wings a black discal spot merges with the spot located between the veins. They form a zigzag band. The butterfly is found in Japan, southern Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands.
Classification
There are the following subtypes of urticaria]
:
- Aglais urticae var. ;baicalensis - Sayan Mountains, Transbaikalia
- Aglais urticae var. ;chinensis - Northern Vietnam, China
- Aglais urticae var. ;connexa - southern part of the Ussuri Valley, South Sakhalin, Kuril Islands, Japan
- Aglais urticae var. ;eximia - valleys of the Amur and Ussuri rivers
- Aglais urticae var. ;kansuensis
- Aglais urticae var. ;polaris - Northern Europe, Siberia, Far East
- Aglais urticae var. ;stoetzneri – Chehuan
- Aglais urticae var. ;turcica - Southern Europe, Caucasus, Transbaikalia, Kopet-Dag, Central Asia
- Aglais urticae var. ;urticae - Europe, Western Siberia, Altai. Nominative subspecies
Morphological description of the species
Urticaria belongs to the genus Aglais of the Nymphalis family (nymphalids). Its species designation is urticae (nettle). A medium-sized diurnal butterfly has a wingspan of 42-62 mm. The main background of the wings is brick red. In the upper part of the forewing, three black spots alternate with yellow ones, and at the apex there is a light area. The outer edge is wavy and there is a sharp protrusion on each wing. The base of the hind wings is brown with brown scales. Next comes the orange stripe. In the description of the urticaria butterfly, one should note its characteristic feature - a pattern of blue spots on a black background along the entire outer perimeter of the wings.
Nymphalids are distinguished by protective coloring on the inside of the wings. In urticaria it is brownish-brown with light areas on the fore wings. In winter, folding its wings behind its back, the moth turns into a dry leaf. The antennae of urticaria are club-shaped, complex compound eyes distinguish red. The black chest and abdomen are covered with brown hairs.
Related species
The common spotted urticaria belongs to the genus Aglais. A distinctive feature of the species is that in the upper part of the fore wings a black discal spot merges with the spot located between the veins. They form a zigzag band. The butterfly is found in Japan, southern Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands.
Nettle caterpillars - black caterpillars on nettles
The urticaria caterpillar is one of the most common insects that can be found in central Russia and beyond. It has a fairly wide habitat. Also found in Siberia, Asia Minor and Central Asia, Japan, China, Mongolia, and Korea. Representatives of this species are often found in many CIS countries: Ukraine, Belarus, Baltics, Moldova. These are very resilient individuals, so they can be found even high in the mountains.
Pupation of urticaria
The urticaria butterfly pupates in a very interesting way. First, a caterpillar appears, hanging upside down on a leaf of a plant. It is attached to the nettle with an adhesive mass, which it produces itself. After some time, the caterpillar shell falls off, revealing an angular pupa, which remains hanging on the plant leaf for another 2-3 weeks.
Then the larva bursts and a butterfly is born. Its wings at this moment are very short. But what’s surprising is that they grow to large sizes in almost a few minutes. It is very difficult even for specialists to distinguish a male from a female. They are almost indistinguishable.
Range and habitats
The urticaria, together with the cabbage white and peacock's eye, is one of the most common butterflies in Europe and Russia. They live in Kazakhstan, are found in Asia, and are distributed further east to the Pacific coast of Russia, China, Japan, and China. Urticaria is a common sight in Siberia.
Butterflies of the species under discussion fly across the vast expanses of steppes and semi-deserts, living on forest edges, roadsides, floodplains, meadows, woodlands, gardens and city parks. In the warm summer months they are found in the mountains up to an altitude of 3000 m and above.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Hives
The wren butterfly is one of the first spring butterflies. Summer begins with the appearance of the first rays of the sun. During the day they are busy pollinating flowers and searching for food; at night they hide in shelters. Up to two generations are replaced per year, depending on the climate. You can see the insect until September.
Chocolate makers are very dependent on weather conditions. During drought, their numbers decrease significantly. The lack of precipitation directly depends on the availability of water, nitrogen and nutrient minerals in the leaves of plants. Lack of substances weakens the caterpillars and slows down their development.
Interesting fact: Chocolate girls can distinguish colors, unlike other insects. This helps to find the necessary objects.
In favorable conditions, the species can exist for up to 9 months. Compared to other moths, which can expect to live only a few days, wrens are truly long-lived. With the onset of cold weather, they do not freeze, but hibernate, like bears.
Lepidoptera do not fly away anywhere, but remain to winter in their native lands. At temperatures of 21 degrees below zero and below, butterflies freeze through, but do not die. Their metabolism slows down and energy is used sparingly. With the first rays of the sun they thaw and come to life. After wintering, they lay eggs and soon die.
Reproduction and development
Reproduction in this species is bisexual and the female needs a male to fertilize the eggs. Before mating, the male and female fly together up to 100 meters. The development of the cabbage butterfly has four stages:
- egg;
- larva (caterpillar);
- chrysalis;
- adult butterfly.
The eggs laid by the female have pronounced ribbing and an elongated barrel shape. The length of each egg is 1.25 mm. Already after 7-10 days from the moment of laying, movement is visible in them and small larvae begin to hatch. The body length of the larvae is only 1.75 mm and their first food is the egg shell. The larva of the cabbage butterfly has a green (ocher) color, a black head and is highly viable.
Compared to the rest of the body, the larva's head is very hard with serrated jaws. Immediately after hatching, the caterpillars stay in groups, eating the shell and pulp of the cabbage leaf from the back side. During this period, cabbage butterfly caterpillars eat little. However, as soon as they get stronger, they spread to the sides. Their appetite becomes insatiable, and they make entire holes in the leaf.
Cabbage larvae are voracious and become a real disaster for gardeners if they are not dealt with. With their powerful jaws, they eat cabbage leaves, leaving only hard veins. The lifespan of the caterpillar is several weeks, but during this time they are capable of completely destroying the crop. Unlike adults, larvae have very poor eyesight and see no further than one centimeter, so in search of food they rely only on their sense of smell. Their eyes are very small and do not have the complex structure of an adult butterfly.
During the caterpillar's life span, it experiences 4 molts. Usually the first three times this process lasts about a day, but the last, fourth molt can last up to 40 hours. Between molts there are 3 to 7 days. In warm and dry seasons, caterpillars develop faster than in the rainy season. Before molting, the caterpillar stops eating and moving, remaining motionless for some time after its completion.
Expert opinion
Nina Lukina
In caterpillars, the body covers do not grow with them, so molting is a very important process. The peculiarity of caterpillars is that they do not grow continuously. They can grow only after molting, while the body cover is relatively soft and capable of stretching. By the time of the first molt, the body length already reaches 1.7 cm. During the period from the first to the second moult, the caterpillar actively grows. By the fourth molt, it grows to 3.5-4 cm. Having reached this size and having eaten well on cabbage leaves, the adult caterpillars move to trees and fences.
In total, the cabbage butterfly spends from 17 to 30 days in the caterpillar stage. After the completion of the fourth molt on days 7-10, the caterpillar pupates. It secretes a web, with which it attaches to the surface of a tree trunk, climbing to a height of up to six meters. Belted with a belt made of cobwebs, it hangs freely in a vertical position with its head up. You can meet them everywhere:
- on the trees;
- fences;
- bushes;
- barn walls.
Black and orange spots are scattered throughout the greenish-yellow body of the pupa. The pupa tends to take on the color of the surface on which it is attached. On a light fence or wall of a building it will be light, on a dark tree bark it will be dark. The cabbage plant stays in this stage for 8 to 17 days, depending on the ambient temperature. The warmer it is, the shorter the transformation process lasts. Spring and summer pupae differ from autumn ones.
The most optimal temperature for the development of cabbage is in the range from 20 to 26 degrees. In addition, whites do not like high humidity. Under favorable conditions, the young butterfly appears two weeks after pupation. It differs from adult individuals in being slightly smaller in size. Butterflies that appear in summer have black markings and spots on their wings that are brighter than those of spring representatives of the species.
If climatic conditions in summer are not favorable (cold, rainy), the cabbage caterpillar turns into a diapasing pupa. The butterfly will fly out of it only next spring, when the air warms up to a temperature of at least 20 degrees. If pupation occurs early or mid-season, a new butterfly emerges from the cocoon and gives birth to another generation. If it pupates in September, the cabbage weed goes into hibernation and waits out the winter in a cocoon, awakening only in the spring.
Social structure and reproduction
Having awakened from hibernation, refreshed and gathered strength, insects begin to reproduce. In the morning, males look for food, bask in the sun, and then begin searching for a female in the afternoon. There are practically no clashes over territory.
The male flies up to the female from behind and emits a specific buzz. The next few hours will be spent in mating games. Most often, the mating process occurs in nettles. After fertilization, the female lays her future offspring on the inside of the plant.
There can be from 100 to 200 green or yellow oval eggs. Laying time is up to one and a half hours. Under favorable conditions, embryos develop within a week. Baby caterpillars stay together in one brood, and do not spread throughout the plant.
The small caterpillars are born only 1.2 mm long. At first they are green in color, with spots and black hairs. While growing up, they molt 4 times. The body of adult caterpillars is black with yellow stripes. Having shed for the last time, the individuals crawl around the bush.
They look for a place to pupate and attach vertically to a stem or leaf, forming a golden-red pupa approximately 2 cm in size. It remains in this state for about 2 weeks. After this period, the shell breaks and a butterfly is born. She needs to sit still for a few minutes so that her wings get stronger and she can fly away.
Appearance and features
The chocolate butterfly is a medium-sized insect. The wings of butterflies are dark orange, brick red. Their length is 20-25 mm, span - 40-60 mm. On the forewings there are three black spots alternating with yellow. There are large dark spots on the front wings, the top is light. There are small spots on the back ones. Females are practically no different from males. Each of the wings has a sharp protrusion, the edges are wavy. At the base of the hind wings there are brown scales on a brown background, followed by a bright orange stripe. Along the outer edge of the wings on a black background there is a pattern of light blue crescent-shaped spots. The inside is brown with light spots.
Each individual has a unique pattern, like human fingerprints. In winter, when hibernating, butterflies fold their wings and look like a dry gray leaf. The abdomen and chest are dark brown with brown hairs. The antennae of the moth are club-shaped. Chocolate girls have three pairs of legs located on the chest. The family has a characteristic distinctive feature - the front legs are so short that they do not participate in the process of walking. They don't have claws. They serve for a soft landing. Chocolate girls move on their middle and hind legs. The hives butterfly caterpillar is black with a yellow stripe on top. There are small green spines with bristles all over the body. In the pupal stage, the moth is wrapped in a cocoon, on top of which there are horns, which some people associate with a devil.
These insects, along with the cabbage white and peacock's eye, are one of the most common species living in Europe. The range extends to the coast of the Arctic Ocean. Chocolate girls can be found in China, Japan, Asia Minor and Central Asia, Mongolia, Vietnam, Siberia, Korea, and in the countries of the former CIS. You can see urticaria, like its brothers, in parks, squares, meadows and fields, gardens, forest edges and other flowering areas. Moths prefer quiet and peaceful places to noisy cities. They don't like bad weather.
If you feel the approach of a strong wind or rain, chocolate butterflies look for where to hide - in tree hollows, basements, attics of private houses, verandas. You can also meet chocolate makers high in the mountains. In the Alps, this species was found at an altitude of 3 thousand meters, and in the Himalayas - 5 thousand meters above sea level. At the pupal stage, cocoons can be seen everywhere: on tree branches, leaves and stems of flowers, on fences and gates, and benches. Butterflies do not fly away for the winter, but hide from cold weather and frosts under the bark of trees, in the basements of houses, caves, and sometimes on balconies. Urban individuals choose places closer to human houses, so that in case of bad weather it is easier to find shelter.
Thanks to their long black proboscis, moths obtain food in the form of nectar from plant inflorescences. At the caterpillar stage, chocolatiers are very fond of eating nettle leaves, which served as the main criterion in choosing the name for the butterfly. Also, insects are not averse to eating: Dandelion; Blackberries; Marjoram; Thistle; Primrose; Elecampane. Imago (adults) are not as picky eaters as caterpillars. The choice of the latter comes down to the use of: Stinging nettle and stinging nettle; Hops; Hemp. The newly hatched caterpillars weave together a common web and eat young leaves. When one plant runs out of greenery, the young growth moves to the next one. As soon as a butterfly is born from a pupa, it immediately goes in search of flowers.
At the end of summer, lepidoptera begin to feed especially actively. To maintain the vital activity of a small insect during the cold season, the body of hives needs to stock up on lipids. Flower juice helps them a lot with this. While butterflies are looking for nectar, they fly from one plant to another, pollinating them. Their wings contain delicate pollen, which they carry to flowers. Thanks to this, they take second place in the ranking of pollinating insects. Only bees are ahead of them. Sometimes during the February thaws, moths wake up from hibernation ahead of time and fly into houses or apartments. Until spring, the insect can be kept at home, feeding it with a solution of sugar or honey. To do this, moisten a cotton swab with syrup and place it on a saucer. 10-15 minutes of feeding per day is sufficient for hives.
The wren butterfly is one of the first spring butterflies. Summer begins with the appearance of the first rays of the sun. During the day they are busy pollinating flowers and searching for food; at night they hide in shelters. Up to two generations are replaced per year, depending on the climate. You can see the insect until September. Chocolate makers are very dependent on weather conditions. During drought, their numbers are significantly reduced. The lack of precipitation directly depends on the availability of water, nitrogen and nutrient minerals in the leaves of plants. Lack of substances weakens the caterpillars and slows down their development.
In favorable conditions, the species can exist for up to 9 months. Compared to other moths, which can expect to live only a few days, wrens are truly long-lived. With the onset of cold weather, they do not freeze, but hibernate, like bears. Lepidoptera do not fly away anywhere, but remain to winter in their native lands. At temperatures of 21 degrees below zero and below, butterflies freeze through, but do not die. Their metabolism slows down and energy is used sparingly. With the first rays of the sun they thaw and come to life. After wintering, they lay eggs and soon die.
Having awakened from hibernation, refreshed and gathered strength, insects begin to reproduce. In the morning, males look for food, bask in the sun, and then begin searching for a female in the afternoon. There are practically no clashes over territory. The male flies up to the female from behind and emits a specific buzz. The next few hours will be spent in mating games. Most often, the mating process occurs in nettles. After fertilization, the female lays her future offspring on the inside of the plant. There can be from 100 to 200 green or yellow oval eggs. Laying time is up to one and a half hours.
Under favorable conditions, embryos develop within a week. Baby caterpillars stay together in one brood, and do not spread throughout the plant. The small caterpillars are born only 1.2 mm long. At first they are green in color, with spots and black hairs. While growing up, they molt 4 times. The body of adult caterpillars is black with yellow stripes. Having shed for the last time, the individuals crawl around the bush. They look for a place to pupate and attach vertically to a stem or leaf, forming a golden-red pupa approximately 2 cm in size. It remains in this state for about 2 weeks. After this period, the shell breaks and a butterfly is born. She needs to sit still for a few minutes so that her wings get stronger and she can fly away.
Natural enemies of the hives butterfly
Like all insects, this species of butterfly has many natural enemies. Among them are amphibians in the form of frogs; reptiles – steppe vipers, lizards, snakes; birds - marsh harrier and many others; small rodents.
To protect themselves from enemies, chocolate makers have protective coloring on the inside of their wings. When they fold their wings, the camouflage color from the outside resembles a dry leaf. But often it does not save the butterflies, and the birds, having declassified their camouflage, eat them, sometimes up to half of the wintering ones.
There is also a chance of being attacked by parasites. Hymenoptera insects, such as flies, can lay eggs on plant leaves, which are then eaten by caterpillars. The larvae will grow in the caterpillars' bodies and eat the organs from the inside. After a painful death, up to 100 riders can crawl out of the body of the future butterfly.
It can be difficult to catch chocolate, so individuals at the egg, pupa or caterpillar stage are most vulnerable. Birds constantly feed their chicks hundreds of caterpillars a day. Birds account for about 20% of the caterpillars eaten. Birds grab feeding or resting moths, rub them against a tree so that the wings fall off, and eat only the body.
Caterpillars can become prey for beetles, dragonflies, mantises, and wasps. Spiders can catch butterflies in their webs or lie in wait in flowers. Humans play an important role. Due to the destruction of landscapes, chocolate makers are losing their habitats. When harmful insects are destroyed, many butterflies die from poisoning.
Development
The crop that the urticaria caterpillars feed on is also their home. Pests live in families and rarely spread out. After the time comes for pupation, they place their pupae directly on the same plants.
Hives caterpillar
There are 2 periods when the urticaria caterpillar appears. The first generation hatches in late spring early summer. This is May-June.
Important!
In southern latitudes, during the warm period, 2-3 generations of urticaria caterpillars manage to grow.
The second generation is born in July-August. Adult butterflies go to winter and hide in hollows and under the bark of trees. Only fertilized individuals survive the cold. The butterfly may even freeze through, but this will not kill it. With the onset of warmth, she will return to life again.
The caterpillar of the nettle butterfly is not afraid of stinging nettles and actively occupies it for its place of residence. During the period of growing up, she goes through several stages of molting. After each one it increases in size. In 30 days, it can grow up to 5 cm. The transformation time from a pupa to an adult is a couple of weeks.
Black caterpillars on nettles can be found in parks, meadows, near summer cottages and private houses. They also often choose valleys and mountainous areas as their habitat. If a nettle leaf is covered with a large number of black caterpillars, it means that these are urticaria and after 2-3 weeks you will be able to see very beautiful butterflies.
Rating( 1 rating, average 5 out of 5 )
Description and characteristics of urticaria butterflies
Urticaria is a member of the Nymphalidae family and has about nine subspecies.
She has several distinctive appearance features:
- wings are red-brown;
- reach with a span of 50 mm;
- there are white spots on the front wings;
- basal areas of rich brown color;
- along the edges there are teeth and protrusions in the form of crescents with blue splashes;
- pin-shaped antennae;
- dark chest with gray hairs;
- a long proboscis for sucking nectar, which curls into a spiral during flight.
Chocolate caterpillars are almost black in color, and their surface is strewn with spines. Over the summer they molt and increase in size.
The chocolate butterfly is a diurnal butterfly that sleeps in the dark, hiding in a shelter. She appears early in the spring and is fertilized throughout the summer. She moves on her hind and middle legs.
The front ones are much shorter than the others and perform the following functions:
- touch objects;
- help to move;
- guarantee a comfortable takeoff;
- promote a soft landing.
Females are practically no different from males. Only specialists can find out who is who. Based on the description of the species, the female is often larger than the male.
It is no coincidence that the butterfly was named so.
She leaves eggs on the inside of nettle leaves. The chocolate maker does this several times over three months. At this time, the plant looks like a Christmas tree, decorated with yellow garlands.
According to popular belief, if hives fly into the window, happiness and the fulfillment of a dream are coming. You should take the butterfly in your hands and make a wish. It will definitely come true soon. The main thing is to release the insect into the wild.
What does the hives butterfly eat?
Urticaria butterflies eat only liquid food, namely the flower nectar of nettles, hops, hemp and other crops. Flying from one plant to another, moths pollinate them. At the caterpillar development stage, the main food is young leaves.
Crops that serve as food:
- nettle;
- dandelion;
- primrose;
- blackberry;
- thistle.
After eating the leaves on one plant, the caterpillars move to another. They have a particularly intense diet at the end of summer in order to make provisions for the winter.
Population and species status
Fortunately, the species is not listed in the Red Book, so there is no need to protect it. Urticaria is definitely not in danger of disappearing in the coming years. Thanks to the ability to adapt to any living conditions, butterflies reproduce well and their habitat is very wide. You can't meet them except at the North Pole.
Since the species does not cause any harm to agriculture, there have never been any attempts to exterminate chocolate makers. No country sees butterflies as negative images. Individuals exist in sufficient numbers everywhere, do not need protection, and according to scientists, the species will not become extinct in the next 20 years.
Record high air temperatures in recent years, according to researchers, have led to a high increase in the number of moths. Weather conditions have recently been ideal for the existence and reproduction of these beautiful creatures.
During 2010-2011, the number of chocolate makers increased by 60%. But during the period when the summer was quite cold, the population again decreased significantly. Scientist from the Center for Ecology Mark Botham emphasized that it is necessary to locally maintain a favorable environment for lepidoptera without interfering with their habitats.
Forest conservation, so necessary for this species, greatly helps to increase butterfly numbers. Insects live in their usual environment and the slightest changes in the habitat can be destructive for them. Preserving the environment helps the species feel better and reproduce more actively.
During thaws you can often see butterflies in the snow. Caring people take them home to save them from the cold. The life of a moth at home will be affected by several factors, such as room humidity, nutrition, and energy reserves. In favorable conditions, the insect can live for several weeks.
The chocolate butterfly is undoubtedly a cute and beautiful creature. From time immemorial, different nationalities have treated them with respect and prejudice. In all cultures, butterflies have been associated with a symbol of prosperity, success, love and well-being. Moths performing a mating dance are compared to a happy couple in love and serve as a symbol of family happiness.
Harm and benefits of insects
The benefit of these insects for humans is that they pollinate plants, which directly affects the amount of future harvest. In search of nectar, butterflies fly from one plant to another, pollinating them along the way. On their wings, nymphalids carry delicate pollen to flowers. Wrens have firmly established themselves in second place in the ranking of pollinating insects. First on this list are bees.
There is no information about the damage that adult individuals can cause to agricultural plants. These are absolutely non-venomous creatures. They do not bite and do not pose a threat to human health. Only caterpillars can be considered pests. By feeding on plants, the larvae can damage agricultural crops.
If there are too many caterpillars on a personal plot, their large number is most likely due to a violation of the rules for alternating crops and fallow during placement on plots or fields, or the abuse of chemicals. To prevent them from damaging the plantings, you need to maintain a natural balance in the garden.
How hives butterflies overwinter
From the beginning of autumn, butterflies begin to feed intensively. They need to make a significant supply of lipids to survive several cold months. Urticaria overwinter in the adult phase. Tree hollows, cracks in the bark, root litter, cracks in the walls of outbuildings, and attics serve as shelter from frost for fragile insects. When the temperature drops below 0°, the moths enter a state of diapause. It is similar to a long sleep, during which all processes in the body slow down. Energy reserves are used sparingly.
Information. Nymphalisurticae butterflies are extremely resistant to low temperatures. They freeze at -21°, but thaw in the spring and continue their life cycle.
For insects in winter, natural enemies are more dangerous than frost. Camouflage coloring helps moths survive the winter. She hides them from numerous enemies looking for food. But half of the wrens do not survive until spring, eaten by rodents or birds.
Keeping at home
Urticaria often wakes up when there is a thaw in winter. The butterfly can be seen in the snow. In the entrance, attic, loggia. Insect lovers take them into the house to save them from frost.
How long does a hives butterfly live at home? Its lifespan is influenced by many factors: nutrition, room humidity, energy reserves and others. With good care she will live for several weeks.
What does the hives butterfly eat at home? In nature, they feed on flower nectar and drink birch sap. For lepidopterans, prepare a sweet solution in a proportion of 6 tsp. water for 1 tsp. honey The treat is offered in a small lid, on a saucer, or with cotton wool soaked in syrup.
The urticaria has receptors on its front legs; when it touches the solution, it will sense food. Feeding occurs during the day and takes from 5 to 15 minutes. The butterfly unwinds its proboscis and drinks the offered honey solution. Actively flying insects are fed daily, passive ones - after 36 hours.
Information. When feeding, the butterfly is taken by the base of the wings; if necessary, the proboscis is straightened with a toothpick.
Is it possible to keep a hives butterfly at home?
Representatives of this type of nymphalids can be kept at home. If a butterfly has chosen a balcony for wintering, it can be left dormant until spring, when it awakens, or taken home, where it will quickly warm up and wake up. If she wakes up from sleep during the winter thaw, she can be fed sugar syrup.
The lifespan of a hives when kept at home is influenced by several factors: how such an unusual pet feeds, what is the humidity in the room in which it is kept, etc.
Nutrition is the main condition for the life of a butterfly in an artificial environment. You need to feed the insect taking into account the following recommendations:
- give hives honey diluted with water in a ratio of 1:6;
- feed your pet only during the daytime;
- for ease of feeding, pour the sweetness into a small flat container (saucer, jar lid) or present the butterfly with a piece of cotton wool moistened with a sweet solution, carefully taking it by the base of the wings and, if necessary, straightening the proboscis with a toothpick;
- Feed actively flying insects every day, passive ones - once every 1.5 days.
When keeping such an unusual pet, one must take into account that even in ideal conditions it is not able to live long. With proper nutrition, optimal air humidity in the room and a sufficient supply of energy, the butterfly lives at home for only a few weeks.
Is it possible to keep a hives butterfly at home?
During periods of thaw, moths wake up from hibernation and can fly during the daytime. To save insects from frost, some enthusiasts take them into their homes. At home, the hives butterfly can survive for several weeks.
To do this, it needs to provide a temperature within +24...300C and a humidity of 70-90%. If the air is too dry, the insect should be sprayed from a spray bottle from a distance of 25-30 cm with plain water.
At night, the hives should be placed in a cardboard box, along with a damp sponge or cloth. She should be released every morning. You can only pick up the insect by its body, or place your finger close under its front paws and sit it on it.
The butterfly should be fed with sugar or honey syrup in a ratio of 1:10, moistening a cotton pad with it. To feed, the insect should be brought to the disk, the front legs should be moistened, or the proboscis should be gently unscrewed with a toothpick. You can use baby juices and fruit purees as food, pouring them into a bottle cap.
Interesting Facts
Butterfly hives, why is it called that? The name of the species in Russian and Latin (Nymphalisurticae) is associated with the food plant of the larvae - nettle. Adults are often seen fluttering above the bushes of the plant during oviposition. The close connection between the butterfly and nettle was the reason for choosing the name.
By observing the behavior of hives, you can predict the weather. If on a clear day a butterfly rushes about in search of shelter, it means that in a few hours it will rain heavily.
How many legs does a hives butterfly have? Lepidopteran insects have three pairs of legs attached to the chest. The family of nymphalids, to which the urticaria belongs, has a characteristic feature. The front legs of moths are reduced. They are greatly shortened and are not used when walking. The limbs are devoid of claws. The modified legs are covered with long bristles that serve as organs of touch. Butterflies move on two pairs of legs - middle and hind. But the limbs are used for moving short distances, as well as landing and taking off.
- Tasyaa what do butterflies eat hives
comment from: 03/01/2018 at 8:22 - Lera I got hives. The only thing that scares me is when she sits on my hand she can pull out her proboscis and look for food on my hand
comment from: 09/30/2018 at 15:31 - Read carefully the article What does the hives butterfly eat at home?
In nature, they feed on flower nectar and drink birch sap. For lepidopterans, prepare a sweet solution in a proportion of 6 tsp. water for 1 tsp. honey The treat is offered in a small lid, on a saucer, or with cotton wool soaked in syrup. The urticaria has receptors on its front legs; when it touches the solution, it will sense food. Feeding occurs during the day and takes from 5 to 15 minutes. The butterfly unwinds its proboscis and drinks the offered honey solution. Actively flying insects are fed daily, passive ones - after 36 hours. comment from: 08/10/2018 at 8:43 - Tanyusha I counted a lot of hives butterflies (about 20 of them) overwintering on my veranda. I collected them in a jar and they all came to life. Now it’s the end of March and I don’t know what to do with them
comment from: 03/17/2019 at 16:08 - Sasha and Milana Milana is my butterfly, she sits in one place all the time until she is moved, why?
comment from: 05/25/2019 at 9:23
Literature
- Joseph Mocha Butterflies. - Prague: Artia, 1979. - P. 124. - 191 p.
- Kurentsov A. I. Club-bearded Lepidoptera of the Far East of the USSR. (Determinant). - L.: Nauka, 1970. - P. 26. - 163 p.
- Lvovsky A. L. 23. Sem. Nymphalidae - Nymphalidae // Insects and mites - pests of agricultural crops. Volume III. Lepidoptera. Part 2 / Ed. Kuznetsova V.I.. - St. Petersburg: Nauka, 1999. - 216 p.
- Morgun D. V. Club-bearded lepidoptera of European Russia and neighboring countries. Determinant-directory. - M.: MGSYUN, 2002. - P. 118. - 208 p.
- Nekrutenko Yu. P. Club-bearded Lepidoptera of Crimea. Determinant. - Kyiv: Naukova Dumka, 1985. - P. 85-86. — 152 s.