Causes of itching and burning after a bite
Proteins and minerals contained in the blood of warm-blooded mammals, which include humans, are necessary for insects for further reproduction.
When the skin is punctured, enzymes that increase blood clotting enter the body along with the mosquito’s saliva. Anticoagulants contain a protein that is not found in the human body. The immune system, having detected foreign elements, produces antibodies, resulting in an allergic reaction, which causes itching and burning in the affected area.
Another reason that the bitten area itches and becomes inflamed may be an infection that enters the bloodstream through contact with an insect.
Usually mosquito bites go away after a few days, but sometimes, with a weakened immune system, the allergic reaction takes on more severe forms and causes hospitalization.
Normal and pathological reaction
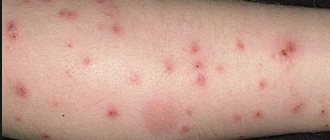
Based on the individual characteristics of a person, a mosquito bite can manifest itself in different ways. A normal reaction to insect saliva is a wound on the body, accompanied by a round, slight redness. Sometimes a small hole may appear in the center of the lesion - a mark from a sting. Often a blister appears at the site of redness, which resembles a nettle burn. As a rule, a mosquito bite becomes very itchy a few minutes after the saliva hits the skin.
- 10 habits that make our brains age faster
- What diagnostic procedures are included in the compulsory medical insurance policy?
- Free medical examination in 2021
A pathological (allergic) reaction to mosquito bites is called culicidosis. The protein contained in insect saliva leads to sensitization (increased sensitivity to irritants) of the body. The human condition is characterized by various manifestations: from severe skin rashes to swelling of the upper respiratory tract. In addition, a pathological reaction may be accompanied by:
- the appearance of sneezing, rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal mucosa), lacrimation;
- increased temperature;
- the appearance of a rash, soreness and itching;
- cough, feeling of lack of air;
- the appearance of conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye);
- swelling of the limbs;
- the appearance of hives, spots all over the body;
Simultaneous multiple bites are considered the most toxic. They can cause large infiltrations (compactions), which can last up to 30 days, painfully affecting a person’s well-being. Severe culicidosis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- suffocation;
- drowsiness;
- stomach ache;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- increased heart rate;
- weakness;
- shortness of breath with symptoms of bronchial asthma;
- headache;
- decreased blood pressure (blood pressure);
- dizziness;
- generalization of edema (severe redness and rapid increase in size of the affected area, more than 3 centimeters);
- high fever;
- Quincke's edema;
- anaphylactic shock;
- fainting states.
Why you shouldn't scratch a bite
The itching from an insect bite can be quite severe, but despite this, you should not scratch the affected areas of the skin. At the site of the bite, the skin cells are especially fragile. Scratching causes their walls to burst and the allergen substances that enter the body during a mosquito bite spread further.
Most often, children suffer from scratching. This is due to the fact that a child’s immunity is weaker than an adult’s, and the likelihood of complications from contact with a mosquito in this case is higher.
In addition, when scratching, bacteria and microorganisms from the external environment enter the wound. This causes the development of various diseases, ulcers and abscesses appear at the site of scratching, and subsequently scars and cicatrices remain on the skin.
Reasons for the body's reaction to a mosquito bite
Few people know that only female mosquitoes bite. This is due to the fact that their instincts are tuned to the survival and reproduction of the entire species. To lay eggs, insects need lipids (organic compounds) and proteins found in the blood. Therefore, these parasites look for their prey, literally sniffing it out. As a rule, their olfactory receptors are tuned to the sweat of warm-blooded animals, because of this, in one room some people will be bitten from head to toe, while others will simply not be noticed by mosquitoes.
Having found the victim, the female pierces the skin with her proboscis and tries to feel the small capillaries. Before sucking blood, it injects an anticoagulant (a special substance) under the skin that prevents blood proteins from clotting. In this case, the human body recognizes it as a foreign body and begins to produce antibodies to eliminate it, which is why swelling and redness appear at the site of the bite.
The insect's saliva is not poisonous, but at the same time it causes unpleasant consequences - swelling, redness, itching, hyperemia (redness). Injecting an anticoagulant under the skin results in an allergic reaction. At the same time, some people do not feel any consequences, but a sensitive person suffers greatly - his mosquito bite itches, the affected area swells and begins to hurt.
- Banana pancakes - step-by-step recipes for preparing dough and filling with photos
- Codelac Broncho for children and adults - release form, instructions for use, indications and side effects
- Corn in the microwave
How to reduce itching after a mosquito bite
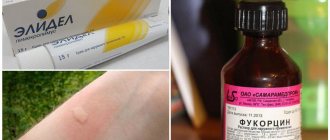
You can reduce itching and forget about the discomfort that occurs when an insect bites you with the help of anti-inflammatory and anti-allergenic medications. These include:
- Fenistil gel is an antihistamine with a cooling effect. Relieves itching and inflammation, can be used by both adults and children up to one year old.
- Gardex is a balm based on plant components and D-panthenol. Removes swelling and itching at the bite site, cools and soothes the affected area.
- Rescuer is a balm that contains natural ingredients (beeswax, vegetable oils, calendula) and vitamins (A, E). It has not only an anti-inflammatory and disinfectant, but also a healing effect.
- Vitaon is an oil-balm made from natural ingredients. Relieves itching and allergy symptoms. Contraindicated for people with hypersensitivity to substances contained in Vitaon.
- Zinc ointment – has an anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and drying effect. Can also be used to heal and disinfect areas damaged during combing.
Products not only for external use, but also for internal use (Claritin, Diazolin, Suprastin and other antihistamines) help get rid of itching.
How to get rid of or reduce itching after a mosquito bite?
If the site of the insect bite does not give you peace, then there are several ways to help get rid of the itching:
• You can use regular ice. Cold, in this case, will relieve the itching from a mosquito bite and reduce swelling.
• You can also wipe the mosquito bite area by dissolving baking soda in water. This procedure needs to be carried out several times. To prepare a relief solution, you can also use boric alcohol, calendula, lemon, tomatoes, kefir and sour cream.
• In addition, ointments that reduce allergic reactions are good for itching after a mosquito bite.
Folk remedies against insect bites
Sometimes there are situations in which it is impossible to use medications. In addition, many of them have age restrictions and are not suitable for children. You can replace ointments and balms with folk remedies, including:
- ice – to reduce itching and relieve redness, apply an ice compress to the affected area of the skin for a short (up to 5 minutes) period of time;
- soda - the bite area is wiped with a solution (1 tablespoon of soda is stirred in a glass of water);
- lemon juice – a wound treated with lemon juice stops itching and itching;
- aloe – a small piece of aloe leaf should be cut in half and the inside should be applied to the inflamed area;
- essential oils – clove and tea tree oils reduce inflammation and destroy bacteria;
- mint, plantain, parsley - before applying plant leaves to the site of inflammation, they must be thoroughly mashed (the juice contained in the leaves has a healing effect);
- dairy products (kefir, sour cream, yogurt) - when applied to the skin, it becomes softer, swelling and inflammation are relieved, and itching goes away.
Timely treatment of a mosquito bite with disinfectants and anti-inflammatory agents not only relieves itching and burning, but also reduces the risk of developing diseases transmitted by mosquitoes.
Why does the skin itch from a bite?
Histamine is a substance that is responsible for a number of vital processes for the body, including recovery from illness. In a healthy body, it is bound and inactive. When any irritants appear - be it internal (bacteria) or external (mosquito bites) factors - it is free, enters the bloodstream and begins active activity.
The flow of blood with a high histamine content to the area damaged by a mosquito bite produces itching. This is how histamine tries to repair the damage. And if you scratch the bite, there will be no benefit from its work, and the blood with the “itching” substance will continue to flow to the puncture site. Remember that the reaction to insect bites is individual: for most people it is itching, but there is a large percentage of those who complain every summer that the bite is swollen and swollen and has not gone away for a week now. If such reactions occur, you should consult a physician: most likely, this is a sign of an allergy.
If an insect bite simply itches, then you can relieve the nasty itch quickly and without harming the functioning of your own body. Here are the best and proven treatments for insect bites.
Folk remedies
If there are no special means at hand to alleviate the consequences of a bite, you can use improvised drugs. Suitable for you:
- A few drops of lemon juice or lime juice, once on the wound, can relieve itching;
- Aloe is a remedy for all ills. And here it is suitable, squeeze a little juice onto a piece of bandage or cotton wool and apply, or use the pulp of the plant;
- Banana peel, press it on the inside for a couple of minutes;
- A piece of ice wrapped in a cloth (handkerchief). Press it onto the inflamed skin, the discomfort will go away in 20 minutes;
- Soda with warm water. Apply the resulting paste to the wound for a couple of minutes, then rinse. The alkali will work as an antidote.
If you are severely bitten and the body’s reaction is violent, you will have to use antihistamine ointments or drops. It also happens that it is difficult to cope without them.
Why do mosquito bites itch for several days?
Everything would be fine, you don’t seem to feel how they bite, but then this place itches unbearably, sometimes even swells. Why is this happening?
It's all about the saliva that females secrete. It contains anticoagulants - chemicals that prevent blood from clotting. It is this substance that causes irritation, itching, and sometimes severe allergies.
The body responds to foreign elements that enter the bloodstream and produces histamines that can eliminate foreigners. That's why the redness and itching begins.
By scratching the sore, you introduce other pathogenic microorganisms into the wound. The immune system begins to react to them, sending an additional squad of histamines and leukocytes. It turns out to be a vicious inflammatory circle.
Then you begin to suffer from your own incontinence, and there is nothing left of the mosquito saliva there.
But this problem can be easily dealt with using both folk remedies and those sold in pharmacies or stores.
Protect yourself from midges with vanillin solution
For the future: to avoid having to deal with itching, protect yourself from midges in advance. A repeatedly tested and objectively best means of protection against insect bites is a vanillin solution. It’s easy to do: a sachet of the substance, which is sold in most grocery stores, is poured into a small (0.5 liter) plastic bottle, half filled with warm water and shaken well. Spray the solution on clothing and skin before going outside.
If the insect does find its victim, to relieve itching and redness from the bite, we recommend using the classic La Cree cream, which soothes the skin in a couple of minutes with the help of tonic natural ingredients: string and violet extracts, avocado oil and others. The cream will also help with peeling skin of the hands and feet.