Order Lepidoptera
Representatives of this order - moths, butterflies, moths - are distinguished by the presence in adult individuals of a thick cover of chitinous scales located on the front and hind wings.
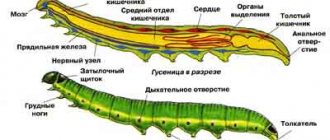
These insects go through four stages of development. These are eggs, larvae (or caterpillars), pupae and adults. Caterpillars (larvae) of Lepidoptera are worm-like, with a thick sclerotized head cover. The similarity with worms arises from the fact that insects in this phase of development have underdeveloped abdominal legs. Particularly worth highlighting is the well-developed gnawing mouthparts. Moreover, it is different for each species, since the larvae feed differently.
Navigation
Moths never simply move anywhere, as many of our readers may believe. Actually, like no other living organism, with the exception of humans. Everything in the animal and plant world is interconnected, and cannot happen just like that, out of nothing to do. In particular, moths always fly either in search of a mate or food, or for the purpose of laying eggs.
There is a lot of debate today about why moths are so attracted to light, but in fact, this information remains a mystery. One of the hypotheses, which can also explain why butterflies are more active in the light, says that the heat of the light warms up the muscles of the moth’s wings, since moonlight does not warm at night. However, this idea has not yet been scientifically proven. Another, also quite well-known theory is that light, in particular its ultraviolet part, emits energy similar to that given off by night flowers, the nectar of which is the main food for insects.
The course and speed of the moth's flight are determined by the moon and stars, and when these are not available, the insect is guided by geomagnetic clues from the earth.
Other interesting information
- Adult clothes moths and kitchen moths, which are well known as household pests, do not feed at all. The main harm they cause to humans comes from the larvae, which have extremely high gluttony. People often ask: where do moths come from? The answer is very simple - it flies in from the street.
- The science that studies moths and butterflies is known as lepideroptology, and biologists who specialize in this discipline are called lepidopterists.
- Often moths are pests. Various species, especially in the larval stage, are major agricultural and household pests in many parts of the world. The gypsy moth caterpillar, for example, causes severe damage to forests. In temperate climates, the codling moth causes significant damage to fruit production. In tropical and subtropical climates, the cabbage moth is perhaps the most serious pest of cruciferous crops - the mustard and cabbage families. Read more about cabbage moth.
- Insects are able to “hear” sounds through their wings, thanks to the vibration of pollen on them.
- Many species of moths and butterflies have a well-developed special organ, called Johnston's organ, located at the base of the antennae. This organ is responsible for maintaining a sense of balance and orientation during flight.
Distinctive features of the moth butterfly from other Lepidoptera
These insects appeared supposedly 190 million years ago. Their modern descendants have changed, many new species have appeared.
All representatives of the order Lepidoptera are divided into day and night butterflies. Those that lead a predominantly crepuscular and nocturnal lifestyle constitute the family of moths. But such a division cannot be called scientific.
Modern entomologists divide Lepidoptera into suborders. According to one classification, there are three of them today: lower homoptera, higher homoptera and heteroptera. The first subspecies includes Lepidoptera with a primitive wing structure. Both wings have almost identical veining. These small butterflies either lack a proboscis or have one, but it is very short. There are spurs on the shins. These butterflies are called primary moths.
The second classification divides Lepidoptera into four suborders, distinguishing primary toothed moths, proboscis moths, heterobatmyans and proboscis moths.
So, to answer the question of how a moth differs from a butterfly, you can do this:
- small size;
- the primitive structure of the wings, which the moth at rest folds behind its back not like a “sail”, but like a “house”;
- pale, mostly gray in color;
- nocturnal lifestyle.
The opinion that moths harm humans and butterflies decorate the world is not true. Both of them can cause significant damage to the human economy. But mainly it is not the adults themselves that cause harm, but the larvae of butterflies and moths. Actively feeding, caterpillars eat plants, grains, fruits, fabrics, wax honeycombs and other products and materials. Adult butterflies, moths, and moths often do not need food. Their harm is that they lay eggs, from which voracious larvae then emerge.
Features of reproduction
The answer to the question of how moths reproduce will help you take preventive measures and more effectively combat the pest. 5-6 hours after mating, the female lays eggs, their number varies between 50 -100 pieces. In most cases, moth eggs are found in the same substrate where the entire family lives. Under favorable conditions, after 6-7 days, small worm-like moth larvae with a whitish transparent body, the size of which does not exceed 1 mm, appear. Optimal conditions for the development of eggs are a temperature of 30-33 ° C; at a temperature of 15 ° C, the duration of maturation can increase to 35 days.
Pregnant females hardly fly and lead a sedentary lifestyle. Mostly males fly in the apartment.
Caterpillars are also not prone to travel and are characterized by low mobility. At this stage of moth development, they molt several times, and the duration of the period can range from 40 days to 2.5 years. The developed caterpillars begin to weave a cocoon in which it will pupate. The inside is absolutely smooth, the outer part can be covered with small debris, insect excrement, and dust particles. The pupal development stage lasts 8-28 days depending on the ambient temperature.
Stages of moth development
The complete development cycle from egg to adulthood can range from 60 days to 2-3 years. How long an adult lives depends on its gender. Females live 7-10 days, and the lifespan itself can reach 30 days.
Small butterflies that look like moths
Watching insects in nature can be both pleasant and funny. But completely different feelings arise when they occupy a human home as uninvited guests. For example, sometimes people notice that small butterflies, similar to moths, appear on the curtains in their houses in the evenings. The owner will inevitably have a feeling of anxiety. What if this small lepidopteran did not just appear in the house? What if it is a lover of carpets, fur coats, flour, dried fruits or something else that the owner does not intend to share with it?
It is possible that in this situation the anxiety is not at all groundless. After all, a small butterfly that looks like a moth may turn out to be a mill moth. But you can’t expect any good from this gluttonous guest: once she shows up, she will very soon get into the flour, cereals, and other products, laying her eggs everywhere. And very soon caterpillars will hatch from them, which will eat and grow, grow and eat, spoiling food with waste products and eating them.
It’s a completely different matter if fenestrated moths come to visit. These insects do not pose a danger to food and household items. So, we got the wrong address, as they say. Leading a nocturnal lifestyle, a moth flew into the light, crawled through a crack into the house, but did not know how to get out.
Quite small moths are leaf rollers. They also sometimes end up in human habitation. This is a terrible pest for gardens and vegetable gardens. But in the house there is no harm from them. You can distinguish a leaf roller from a moth by its size, which is still almost 2 times larger than that of a moth.
Where do moths come from in the kitchen and how to get rid of them?
The principle of combating kitchen moths should combine the following actions:
- complete liquidation of affected stocks;
- destruction of flying moths;
- processing of kitchen furniture.
We can immediately conclude that in order to eliminate the harmful insect, it will be necessary to develop a whole range of measures. It is worth noting that it is simply impossible to withdraw it with one action.
Check the products in the store; they should not contain even a hint of moth larvae or cobwebs. Check the expiration date and general appearance of the products.
Very often, when housewives see a moth in the kitchen, they begin to wonder where it came from. There is no need to guess - moths always enter the house with affected products from the store. These are mainly cereals, sugar, and less often pasta. Kitchen moths cannot simply fly in from the street; they multiply and spread through larvae. More often, products that have expired and have not been treated for pests are susceptible to damage.
Types of agricultural moths
Many people think that worms bother them in their gardens and gardens. But in fact, these are caterpillars - the larvae of butterflies or moths. They are the ones who devour the fruits and foliage of plants, destroy them and deprive people of their harvest.
There are many types of moths. Part of this suborder are agricultural pests. For example, you can distinguish potato, cabbage, apple, and rye moths. The damage caused by the larvae of these pests is significant, since they are capable of completely destroying the entire crop in a vegetable garden or garden.
But in houses these insects are helpless, since there is nowhere for them to even lay eggs in the home. Unless, of course, the owner happens to have forks of cabbage or a freshly picked potato bush readily available in his room.
Preventing or reducing infestations
Periodically cleaning "danger" areas in the home that may harbor moths can completely prevent the insects from appearing. These areas include not only hidden areas on woolen clothing, but also areas outside the closet itself, such as under heavy pieces of furniture, along baseboards and in cracks where hair, dog hair and other debris accumulate.
It is worth paying attention to the space behind the heating radiators and inside the ventilation openings.
A vacuum cleaner is the best tool for most basic methods of such processing. After using the device in areas known to be infested, the contents of the bag should be removed as quickly as possible from the home, since there may be many eggs, larvae or adults inside that can quickly return to the living environment.
Moths may initially establish themselves on woolen items or wool scraps that have been stored for long periods of time. In addition to storing woolen items properly, they should be periodically exposed to the sun and cleaned most thoroughly, especially along seams, inside folds and pockets. A natural fiber brush removes eggs and exposes larvae. In addition, the larvae do not like bright light, so they themselves will try to fall off the clothes as soon as possible.
If the infestation is observed in a closet, be sure to remove all clothing and fabrics stored inside. You should then thoroughly vacuum and wash all interior surfaces, especially cracks and crevices, before returning clean items. Powdered insecticides containing pyrethroids or pyrethrins, such as 0.05% Deltamethrin or 1% Pyrethrin, can be applied to cracks and crevices. Before using chemicals, you should always comply with the requirements indicated on the label.
Winged pests in human homes
Usually, when we hear the word “moth,” everyone thinks of a small, inconspicuous butterfly that climbs into places where clothes are stored and leaves its eggs there. And after some time, the housewife discovers that the pile of the coat has bald spots, and the woolen blouse is completely full of small holes. And the clothes moth larvae did their best.
In fact, many moths in an apartment are a real disaster. In addition to the already mentioned clothes moths, fur moths, furniture moths, grain moths, and wax moths annoy people in their homes. Moreover, sometimes it is quite difficult to determine by appearance whether this pest belongs to one species or another and to guess its taste preferences. Although there are differences between them.
Impact of the pest on human health
Once in the kitchen and getting into the cereals, the moth begins to multiply. One adult insect can lay about 300 eggs during its life. It is clear that the remains of the vital activity of the voracious larvae increase significantly every day. The amount of contaminated food quickly spreads throughout the kitchen.
Within 60 days, the larvae manage to change the skin 3-4 times, which remains in grocery products. Plus, the pest actively feeds, so feces are present in the cereals.
Eating foods that contain moths is prohibited and even dangerous to health. The consequences can be depressing:
- intoxication;
- decreased protective functions of the body;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- allergic manifestations.
Fur moth
This Lepidoptera is colored clay-yellow with a sheen. The wings below are light gray in color, with a slightly yellowish tint. In their front part, near the middle, there are small dark dots, and a little further there is a larger spot. The wingspan is approximately fifteen to sixteen millimeters. This is quite a beautiful moth butterfly. The photo shows how peculiar the insect looks.
Their caterpillars are worm-like, whitish in color and almost naked. They have eight short abdominal legs, transparent skin through which the stomach is visible.
The larva of the fur moth feeds mainly on natural fur, which is why it got its name. Crawling along the skin, the caterpillar gnaws all the hairs it comes across on its way. Moreover, this process is not always caused by hunger. So, having hung a brand new fluffy fur coat in the closet, you can after a while take out a completely bald little thing, provided that the fur moth has been in the wardrobe and managed to breed there.
Protecting things in the closet
Moths often damage improperly stored items. When storing pest-sensitive fabrics, make sure the items are clean and free of pests, then place them in a sealed plastic bag. Additionally, before sealing the bag, you can place repellents inside, for example, spray with lavender essential oil.
Naphthalene or crystals containing 1,4-dichlorobenzene, also called paradichlorobenzene, are also widely available to protect clothing during storage.
Since these materials are toxic, be sure to keep them away from children and pets. These products have other disadvantages as well. For example, they leave an unpleasant odor on clothing and other objects, so if such products come into contact with plastic snaps, grab bars or garment bags, they can deteriorate the plastic and soften and melt synthetic fabrics.
When such chemicals evaporate, they produce fumes that, in sufficient concentration, will slowly kill insects. Vapors accumulate to the required concentration only in a sealed container. If the container is not airtight, the chemicals will only slightly repel adult moths, but they will be useless against the larvae.
The effectiveness of cedar wood is a controversial issue. Aromatic eastern red cedar, or Juniperus virginiana, contains an oil that can kill small grubs, but it has no effect on large grubs. In addition, after several years, cedar loses this quality, so using pressed essential oil is always more effective than a chest or cabinet made of cedar wood.
Clothes moth
The body length of an adult insect of this species ranges from 5 to 8 ml, and the wingspan reaches 1.6 cm. The wings of the moth are narrow and devoid of spots. But on their edges there is a long fringe of hairs.
The body of the moth is beige in color with golden hairs. Reddish-golden hairs grow on the head.
Clothes moth caterpillars are similar in appearance to coat moth larvae. They live in natural tissues, eating those places of matter that are not visible from the outside, because they most often do not even taste the top layer. Having developed, the larva stops feeding and weaves a spindle-shaped hard silk cocoon. The outside of this sarcophagus is covered with feces and food waste.
Female clothes moths are poor fliers. Therefore, they move by jumping, trying to hide in the folds of clothing. If you notice a flying clothes moth in your home, you can be sure that it is a male.
Differences from other species.
Externally, clothes moths are very similar to furniture moths - until the middle of the last century, they were even considered the same species. Despite such great similarities, these insects still have clear differences from each other. The furniture moth is larger; its wingspan can reach 18 and even 20 mm.
It is also slightly different in color - this butterfly is yellowish in color, while the clothes moth is almost white. The furniture moth's head is most often covered with yellowish-brown rather than reddish-brown hairs.
Photo of furniture moth.
Food moths are the name given to all granary pests belonging to the fire family. It is quite simple to distinguish food moths from clothes moths. These are small butterflies, the wingspan of which usually does not exceed 1 cm. Most species of moths are gray in color, their wings are covered with spots (unlike the wings of clothes moths, which are colored uniformly).
You can see what food moth looks like and learn about it here.
Ways to get rid of moths in the house
If you don’t pay attention in time to the fact that these insatiable gluttons have taken up residence in your apartment, then very soon you will discover that the pests have multiplied simply monstrously! Running around the house trying to swat flying creatures is useless, since getting rid of moths does not mean anything. The greatest harm is caused by the larvae. And flying insects eat practically nothing. Their concern is to lay eggs in a convenient place so that the babies have something to eat after they are born.
There are several types of getting rid of moths.
- Items that are overly infested with moths are best thrown away.
- Those things in which there is not much moth can be dried on the stove, in the oven, in the sun.
- Cabinets in which moths lived should be washed with soapy water. Adding white to the liquid will not be superfluous.
- Things affected by moths must be treated with dichlorvos.
- Ultraviolet irradiation will help get rid of moths.
- You can put special tablets or powders that repel insects in wardrobe drawers, on closet shelves, in the pockets of outerwear. Naphthalene has always been considered the best in this direction.
- It is very important to regularly shake out folded clothes, dry them, iron them with a hot iron, and rewash them.
- You should not store a lot of old junk - it is precisely such deposits that attract moths.
How to get rid
If a moth butterfly flies around the apartment during the daytime, then most likely it is a male. Swatting an insect is not the best way to protect your living space from this pest. This is due to the fact that the female is already quietly laying eggs somewhere, from which hungry larvae will soon hatch. Therefore, in order to get rid of uninvited guests, you need to find the most effective folk remedies for moths.
In the closet
Quite often, the presence of a pest in a wardrobe is discovered after holes appear on expensive woolen items. The larvae of such insects can be brought from the street. It is possible to avoid the proliferation of moths if you put into the closet only those clothes that have been pre-washed or thoroughly cleaned after use.
But even if, despite carefully caring for things, pests still appear in the closet with clothes, then everything needs to be reconsidered again, washed and ironed. And fur products should be taken out into the fresh air several times a year under direct sunlight or frost, which this insect is so afraid of.
It must first be treated with a solution of laundry soap. After all the compartments and shelves have dried, you can return the wardrobe items to their original place. For moths in the closet, it is advisable to place repellent folk remedies on the shelves.
This effect is achieved by:
- laundry soap in the cupboard;
- orange peels;
- lavender, mint, chamomile, tansy, wormwood
If there are no folk remedies at home to protect against this insect, then you can use any scented toilet soap. Bars of soap along with wrappers are laid out in cabinets.
In the apartment
To destroy carpet or furniture moths, you need to prepare a concentrated soap solution, which is used to treat the damaged carpet on both sides, as well as upholstered furniture. After such cleaning, the pile of the products becomes tougher, but this method is guaranteed to get rid of unpleasant insects.
To repel carpet moths, you can use high or low temperatures (sun or frost). Experienced housewives know that folk remedies for moths in an apartment include taking carpets out into the cold in winter to thoroughly clean them with snow. In summer, it is recommended to hang carpets in the sun and dry them thoroughly, which will allow you to confidently get rid of pests.
Moths can not only be localized on carpets; they also love down pillows, blankets and rugs. Some people get out of this situation by regularly sending such items to the dry cleaner or drying them in the fresh air. In any case, pillows and blankets that are not used daily should be checked regularly so that insects do not have time to breed in them. They can also be arranged with pieces of soap or bags of herbs.
Among the plants that repel the pest are coleus and geranium. The smell of tobacco, pepper, dried orange peels, and strawberry soap also repels such insects. In addition to plants, most well-known spices also have a pungent odor - allspice, cloves, vanilla, cinnamon. To repel the pest for a long time, it is recommended to fill bags with spices and place them around the apartment.
In the kitchen
The grain species is capable of multiplying very quickly. He can easily do this in sealed bags or glass jars with lids.
When faced with food moths in the kitchen, where they can be found in many cereals, the first thing you should do is throw away everything that is already spoiled. Cereals without larvae must be sifted and fried in a hot frying pan to ensure the destruction of the pest. In addition, cabinets and kitchen surfaces must be thoroughly washed with a solution of laundry soap, rinsed with clean water and dried.
Folk remedies for moths in the kitchen include the use of garlic. Slices of this phytoncide are stored in bedside tables, kitchen cabinets or pantries along with food products. When the clove dries out, it is advisable to replace it with a fresh one.
You can scare away pests in the following popular ways:
- Place lemon, orange or grapefruit zest, bags of lavender or other herbs next to the food.
- Essential oils (lemon, rosemary, lavender) have a good repellent effect. Some people also use laundry or scented soap.
- Spices that have a strong aroma (cloves, allspice, cinnamon, oregano, mint) will help repel. Spices can be poured onto a saucer and placed inside the kitchen cabinets.
Since groceries actively absorb odors, not all folk recipes are suitable for use.
Ways to fight
How to deal with the American butterfly? There are a number of special measures that will indirectly help prevent the appearance of an uninvited guest or reduce its population:
- Quarantine measures: inspection of supplies, new seedlings, etc.
- Planting monitoring.
- Removing dead bark from trees, in which pest pupae can hide in anticipation of spring warmth.
- Destruction of excess and dry branches.
- Regular weeding of the area;
- Plowing the rows between trees and shrubs in the fall.
But these measures are more prevention than a way to combat. There are special remedies for the American butterfly that help destroy it and save fruit and berry crops.
Chemicals
American moth control products should be used with caution because they are toxic. It is very important to follow safety precautions. But these remedies show good results:
You can also use systemic insecticides such as Aktara or Karate. They are applied to trees by spraying them with a garden sprayer before flowering, so as not to harm the future harvest.
It is necessary to treat not only the affected trees, but also all plants located within a radius of 50 m. The consumption rate is indicated in the instructions for each drug and depends on the concentration of active substances in it.