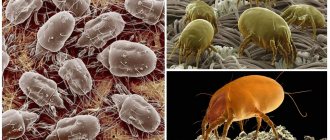
Description of the tick
The mealy mite is considered one of the most harmful insects.
It not only spoils cereals, seeds, herbs, and food, but can also cause the development of serious human diseases. In order to fight it, it is necessary to study in detail information about the pest. This is one of the insects that exhibit sexual dimorphism (differences in the appearance of the female and the male). The male individual has a body length of no more than 0.43 mm, so it is quite difficult to notice with the naked eye. The main distinguishing feature of males is their thickened front legs, which have a conical tooth. The female mealy mite is approximately one and a half times larger than the male. The length of the female’s almost colorless body can reach 0.67 mm. The head of such an insect is pale brown, and the legs are yellowish.
The body of both individuals of the grain mite has a slight rounding at the end. There are 4 pairs of legs on it, each having approximately the same length. They have microscopic suction cups that help the insect stay on the plant.
What is a flour mite?
There are pests of plants, grains, and other food products, which are quite problematic to get rid of. Among them we can distinguish the flour mite or, as it is also called, the granary mite. It would seem, what harm can an insect whose size is less than a centimeter cause? In fact, with the appearance of this arachnid, food begins to deteriorate and rot.
It is quite difficult to notice the flour mite due to its small size and color. The body is white, the legs are brown. He has quite strong and powerful paws, thanks to which he calmly moves on a flat vertical surface (for example, glass).
Females live relatively short lives. In summer 2-3 months, in winter up to 6 months. During this period they are able to lay up to 200 eggs. The flour mite feeds on wheat grains, flax seeds, legumes and others. The most delicious food for him is the one that is rich in fatty compounds.
What does a flour mite look like?
The flour mite is a microscopic insect that can adapt to any conditions. Scientists believe that these parasites will survive even after radiation exposure! Due to their small size (0.32-0.67 mm) and special color (white body with brown limbs), it is almost impossible to notice flour mites. They have a primitive structure and breathe over the entire surface of the body. These insects are able to move very quickly not only on horizontal, but also on vertical surfaces (for example, glass).
In summer, females live for two to three months, in winter – up to six months. During this time they can lay about 200 eggs. Despite its name, this parasite feeds on foods of both plant and animal origin. That is why the habitat of the flour mite can be completely different:
- Barns and warehouses in which grain is stored;
- Stacks of hay and straw, leftover fodder;
- Grain flows;
- Bakeries;
- Barns where livestock live;
- Burrows of wild animals and rodents;
- Plant remains;
- Litter of fields and forests;
- Fields where corn and cereals grow;
- Kitchens;
- Flour mills;
- Grocery stores;
With high magnification, you can see that dozens of flour mites have settled on one grain of wheat
Parasites enter barns, storage facilities and warehouses along with contaminated equipment, rodents, crops, equipment and even workers’ clothing.
general description
A small bug that a person can notice due to its color. The size of the bug is no more than 1 millimeter, the body is white or gray, but the legs are red-brown. They lack organs of vision, but this does not at all prevent them from moving quickly and achieving their goal. It is worth mentioning studies in which it was found that exposure of a tick to radioactive radiation does not lead to its death.
These insects move very well on horizontal and vertical surfaces. Regarding the life cycle, it is quite short, but during this short period, females are capable of laying several hundred eggs. They adapt perfectly to any climatic conditions and are not afraid of either low or high temperatures.
Where do they live?
Generally speaking, their habitat is where there is any food. Since they can easily adapt to any conditions, it doesn’t matter to them exactly where they settle, the main thing is that they have something to eat. Insects infest warehouses, shops, factories, and kitchens. Quite often found in barns and pens where livestock live, since rotting wood, remains of straw and plant food are a favorable environment for reproduction and life.
Colonies of flour mites are very dangerous, since a large number of parasites can harm not only all food supplies, but also will not disdain medicines and even tobacco. Therefore, the fight against them must begin as soon as they are noticed.
How does it reproduce?
If they can live in any room, then special conditions are required for reproduction. For example, there must be enough organic substances, the ideal temperature is 1827°, the humidity level plays a big role, it should be at least 15% and no more than 18%. In addition, there should be no direct exposure to sunlight.
Under these conditions, the female lays eggs when the incubation period ends and a larva emerges from each egg. Already at this stage, the larva has a good appetite, and it needs to eat regularly and a lot in order to develop and grow into a young individual. The development process includes two molts. The larva does not have a shell or bristles, and its size is very small.
Several days pass from the time the egg hatches until it transforms into a first instar nymph. It increases in size and becomes more like an adult. After a week, molting occurs, the time of the second generation comes, and after a few days a full-fledged young individual appears that can reproduce.
Characteristic
The flour mite, or Acarus siro, belongs to the class of arachnids and is a representative of the order Acariform mites. This is a microscopic pest of grain products, as well as dried fruits, nuts, and sometimes cheese and meat.
It is impossible to examine a flour mite with the naked eye, only with the help of a microscope, as shown in the photo. Its body dimensions are very small: in females - from 0.35 to 0.65 mm, in males - from 0.3 to 0.4 mm. The integument is almost colorless, having a faint white or pale gray tint. The body is divided by a transverse groove, which is located in the area between the second and third pairs of legs, while the front part will be slightly darker than the back.
Habitats
In nature, the flour mite lives where there is an abundance of plant debris, for example, in stacks of straw, heaps of hay, in forest litter, and can also settle in bird nests and rodent burrows. It is often found both in livestock buildings and on agricultural lands where corn, vegetables and grain crops grow.
The spread of flour mites in granaries and other warehouse buildings occurs according to the simplest scheme - the pest gets there with freshly harvested crops, on containers, equipment used in warehouses, and on grain cleaning machines. As a result, the parasite finds itself in optimal conditions for existence that meet all the necessary requirements - there is an abundance of food, suitable humidity and air temperature.
Nutrition
The meal mite's diet may include food such as:
- processed grains, such as flour, bran and animal feed;
- yeast;
- powdered milk;
- mold spores;
- cheese;
- dried vegetables and fruits;
- sausages;
- meat and bone meal;
- fish flour;
- egg powder;
- raw tobacco;
- spices.
Optimal conditions for life and development
The habitats of the flour mite are always warm and humid, since these are the conditions that are most suitable for the rapid development of the population of this pest. The optimal temperature for its normal functioning ranges from +21...27°C, relative humidity 65...80%. At the same time, the moisture content of food products on which this species parasitizes should not be lower than 13%.
On a note! Under such conditions, the female alone is capable of laying about 800 eggs!
This parasite tolerates a temporary drop in temperature relatively easily - when the thermometer drops to -5°C, it can survive for about 18 days. If the temperature rises to +55°C, the flour mite will die after 10 minutes, at +60°C – after 5 minutes.
Under normal conditions, the full life cycle of the parasite takes about 14 days, but despite the relatively short life span, the colony grows quite quickly. Overpopulation pushes flour mites to search for other food sources, and often this process is quite noticeable without the use of auxiliary equipment - a dust-like layer consisting of tiny mites seems to flow over the surface of shelves or bags of food.
Stages of development
The entire pest development cycle can take about 2 weeks. During this time, the born insect turns into an adult, which is capable of mating and laying eggs.
The life cycle of such a tick begins with mating. This whole process is quite lengthy and takes several hours. During it, you can observe a “mating walk”, in which a larger female leads a backing male. As soon as fertilization occurs, individuals move away from each other.
The development cycle of an individual mealy mite:
- Egg. A few days after mating, the female begins to lay 3 or 4 eggs per day. In most cases, the laying place is grass seeds and various grains. If there are none nearby, then the female scatters the eggs on food. Over a full season, a female is capable of laying from 20 to 150 eggs. This large difference is due to the presence of different environmental conditions. As a rule, the incubation period lasts 3-4 days.
- Larva. She emerges from the egg looking very much like her parents. The only difference from an adult is the presence of only three pairs of legs. The larvae grow in size very quickly as they continuously eat available food. After about three days, the developing insect becomes motionless. It stays in this state for 1-2 days, and then reincarnation occurs. The protective layer of skin on the back breaks and the insect moves on to the next stage of development.
- Nymph. The duration of this stage is 7 days. At this time, the individual continues to actively feed, and then goes into a stationary state. The result of this process is the appearance of an adult.
Features of reproduction
Like most arthropods, these mites require special conditions. They can only reproduce if there is enough organic matter and no direct sunlight. The optimal conditions for the continuation of the species of these pests are considered to be a temperature of 18 to 27 degrees and humidity within 15-18%.
The females of this insect are capable of laying several hundred eggs during their short life. At the end of the incubation period, a tick larva emerges from each of them. It has three pairs of limbs, and its size is so small that it can be compared to a poppy seed. Before turning into an adult, it feeds intensively and goes through two molts. There are no bristles or membranes on her body.
After a few days, the tick larva transforms into a first-generation nymph, whose lifespan is only a week. During this time, it manages to increase significantly in size, acquire an additional pair of limbs and become similar to an adult insect. Under favorable conditions, after the next molt, she turns into a second instar nymph. After a few days, it becomes an adult insect capable of reproducing offspring. The entire development cycle lasts two weeks.
Where do ticks start?
This parasite can be found almost everywhere where there is plant food. The largest colonies live in large agricultural barns with grain for livestock or further cultivation of seeds. Straw is also one of the favorite places for ticks.
They come from the field during harvesting. A person may well bring ticks stuck to shoes inside a storage facility or with tools that were used for processing in the field. If stored improperly, food ends up on store shelves and carries parasites further down the chain. This is how they end up on the shelves of kitchen cabinets.
Thus, it lives and reproduces where food products are stored:
- kitchen cabinets;
- warm basements;
- warehouses;
- barns;
- sheds.
The following foods are especially welcome in the diet of ticks:
- pasta;
- legumes;
- whole grain cereals;
- dried fruits;
- nuts;
- flour;
- yeast;
- sugar.
The worst thing is that ticks are also spread by rodents and other insects. They easily cling to everything that comes their way. This happens during a certain phase of tick development, when they do not feed, grow or develop, being in a kind of capsule, in a dormant state. The fact is that they have special suction cups that allow them to firmly adhere to any hard surface. If such a capsule enters the stomach of a rodent, it does not dissolve, but is carried along with its excrement.
Further development of the parasite occurs when it eventually finds itself in ideal conditions for life and development:
- abundance of food;
- relative humidity 65–80%;
- temperature +21-+27 °C;
- no direct sunlight.
If the temperature drops to below zero, the tick will survive, although it will not be able to reproduce. Only a decrease in temperature below -5°C and above 55°C kills both the adult tick and its eggs.
The life cycle of a tick until it becomes sexually mature is only 14 days, but it reproduces rapidly. Only one female lays hundreds of eggs.
Development cycle and reproduction of ticks
Adult fertilized females and eggs overwinter under the bark, in its cracks, and also in fallen leaves. In spring, females leave hibernation when the air temperature warms above +12°C and move to the leaves and buds of plants, where they feed intensively and lay new eggs.
Autumn eggs begin a new development cycle, which from egg to adult, depending on the ambient temperature, can take from 6-7 to 20 days. Over the course of a year, ticks in enclosed spaces form up to 25 generations. In garden plots during the warm season (especially in the southern regions) they form from 6 to 10 generations. The female lives up to a month and during this time is capable of laying up to 200 eggs.
Signs of damage to leaves by gall mites.
One generation goes through the following temporary stages of development:
- eggs remain viable for up to 5 years,
- the larva hatches from the egg on the third day, its life expectancy is 1 day,
- nymphs develop for 4 days and degenerate into adults, characterized by sexual dimorphism.
That is, under optimal conditions in any region, one generation takes only 8-9 days. Females are larger than the male. Each stage of tick development is accompanied by molting. As you can see, the tick's fertility is very high, and the short development cycle contributes to its rapid reproduction. Suspension of reproduction occurs only in cold winter weather and with the onset of spring it resumes and continues without interruption until the next cold snap.
What harm does the flour mite cause?
- While the tick eats the supplies, it infects them with dangerous microbes, so at home it is recommended to immediately throw away such products in order to avoid poisoning and prevent further spread of the parasite. Of course, temperature treatment can help, that is, you can freeze it and warm it up strongly. But will the taste and beneficial qualities of the products remain in this case?
- Entering the human body with food, the flour mite affects the gastrointestinal tract, causing nausea, or leading to an allergic reaction, including anaphylactic shock.
- As a result of constant contact with products affected by plant mites, grocer's scabies develops, which is accompanied by rashes, itching and other skin inflammations.
Danger and harm caused
The barn mite got its nickname for a reason. Most often it can be found in barns and warehouses, and from there it spreads to kitchens. The pest easily adapts and is able to “wait out” long periods of lack of food. Over time, it ends up in home preparations.
Grain eaten by mites, like other products, is dangerous for processing and consumption. May cause an unexpected allergic reaction, making the human or animal body hypersensitive to allergens. The chitinous membranes left after molting provoke skin allergies, or flour scabies, which is especially acute in children. In addition, tick waste contains dangerous bacteria and infections, such as E. coli. Among the consequences of eating food spoiled by mites are various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidney diseases.
Flour mites are easily detected: a layer of flour is scattered on the table and leveled with your hand or a spoon. If after some time the smooth surface becomes loose, a pest has settled in the flour. There are other signs: a bitter taste, a slight minty smell and a grayish tint.
How to identify a pest
The flour mite is smaller than a millimeter, so it is quite difficult to notice with the naked eye. The following steps will allow you to determine whether you have a flour mite:
- Open the package and take a sniff. Usually the smell changes.
- Spread the flour in a thin, smooth layer and leave for a while. Unevenness should appear.
- Take a closer look: on non-white grains that are stored in large quantities, a light film appears on them that resembles sand.
Signs of a pest
- It is almost impossible to detect the flour mite as soon as it appears, and this is due to the fact that it is very small in size and is well camouflaged in food supplies. As you can understand from the name of the mite, the first place to look for it is in flour. In addition, there are several signs that will help identify the parasite.
- The first thing you should pay attention to is the smell. Where they live, a rather specific smell appears, it resembles the aroma of mint. If you notice that, for example, flour or cereal has an unnatural odor for the product, then most likely they are infected with mites. Products also change their taste characteristics and a sweetish taste appears.
- In addition to smell and taste, we can identify them visually. It is necessary to take a good look at flour products and cereals. If there is a bug, but something similar to a coating in the form of small grains of sand appears on them. To identify the parasite in flour, you can perform the following steps. Pour a little flour onto the table, spread it over the surface in a thin layer, leave for 20 minutes. If there are noticeable small bumps on the surface of the flour, it means there is a mite in it.
- Another way we can detect flour mites is with tape. We take double-sided tape and stick it on the doors of the cabinet where food supplies are stored. After a few days, we take a magnifying glass and look at the tape; if this parasite lives in your home, you will see it (photos will help you recognize it).
Control measures and prevention?
Control measures and prevention of the appearance of this dangerous pest should begin as early as possible. They consist in the proper preparation of premises for storing grain:
- Clean barns or warehouses well;
- Take out all leftovers;
- Treat walls and floors with insecticidal sprays;
- Do wet cleaning;
- Process the grain - dry it until dry or medium dry;
- Go through your supplies and eliminate all rubbish and questionable grains;
- Monitor constantly - signs of tick infestation may appear later;
- Make sure there are no rats or mice in the room - these are the main carriers of pests.
Attention! In one winter season, a tick can damage half of all stocks. That is why it is necessary to combat these pests even before the grain is placed in the warehouse.
If flour mites infested during grain storage, use effective control methods:
Method 1. Warming the grain to a temperature of 50 degrees or more.
Method 2. Cooling the grain. During the winter, regularly open the doors and windows of warehouses to ensure the premises are well ventilated. Ticks will die at a temperature of -4 degrees.
Method 3. Use of products containing hydrogen phosphide. The stocks processed by it are covered with a thick film. Ticks die within a day.
Method 4. Use of insecticides against ticks - “Fostoxin”, “Detia-EX-B”, “Fostek”.
The rooms where ticks live should become dry and cool. Fans and air conditioners will help control climate control.
How to get rid of flour mites?
To get rid of pests, you need to use the following methods to combat them:
- The temperature in rooms where grain, flour, and products are stored should be reduced to -4° and below. Cereals and grain need to be stirred, moisture should be prevented, and ventilation should be provided in the rooms. At home, food can be taken out into the cold or placed in the freezer.
- Contaminated food should be thrown away. Dry the room and perform wet cleaning.
- Sort out the remaining products, dry them, and constantly monitor their condition.
Insecticidal and acaricidal preparations are used to treat premises against ticks.
Phostoxin
A preparation based on aluminum phosphide. It is produced in the form of pills or tablets, which are placed in silos or used for processing warehouses and granaries.
According to consumer reviews, this is an excellent drug that acts not only on ticks, but also on all pests of agricultural products. The constantly released gas penetrates even through sealed packaging.
Cost - 1 kg from 2,000 rubles.
Fostek
The drug is also available in tablets and contains aluminum phosphide. Effective in controlling stock pests.
The disadvantage of such means is that it is necessary to ventilate the premises before loading them and admitting people, otherwise poisoning with chemicals is possible.
Cost - from 1,300 rubles.
Detia-EX-V
The product contains natural ingredients and is harmless to the soil and the environment. Available in the form of granules, aerosols and powders. Lavender extract, essential oils, and active natural substances repel pests that cannot stand their pungent odor.
Cost - from 650 rubles.
Clean barns are the key to grain preservation
In order to prevent flour mites from infesting, it is necessary to properly store food and grain crops, especially in warehouses. There are several tips on how to avoid this pest in barns:
- Maintain the correct temperature and moisture. From time to time the room must be ventilated. Provide climate control. This can be done using air conditioners and fans. If the products allow, it is better to keep them at low temperatures, in which case granary mites are unlikely to appear.
- Keep warehouses perfectly clean. If debris, dust, or other waste appears, it must be removed.
- Make sure there are no mice in the room. They are carriers of such ticks.
- Quality control. Weekly check of stored products for the presence of small scales of the pest.
In addition, you need to keep the vehicle and containers in which grain and other products of interest to the flour mite are transported clean.
Fighting methods
First, the safest methods are considered, for example, temperature exposure. In case of severe infection, it is advisable to use toxic substances. This method is used provided that the probable benefit outweighs the possible harm that the chemicals can cause to the products.
Fumigation of grain
It is recommended to use this method for processing large areas, as well as large volumes of inventory. It is based on gas mixtures. To implement the fumigation process, special equipment is used, which allows the entire object to be processed in a short period.
This method cannot be used in everyday life.
Fumigation of grain against mites
Insecticides
Mealy mites are susceptible to the effects of drugs based on toxic substances. Most commonly used:
- Aktelik;
- Arrivo;
- Decis;
- Fozalon;
- Karate.
The preparations are used for wet cleaning of empty granaries. The consumption rate of the substance varies and depends on the type of construction material being processed and the properties of the chemical.
Treatment with insecticides to protect against ticks
Calcination
This method is more often used at home, as it is easy to implement: the products are exposed to high temperatures (more than +60°C), for example, in an oven. In addition, you can clean the room in a similar way. However, a steam generator or boiling water is used as a source of high temperatures (wet cleaning of various surfaces is done).
Soil treatment with high temperature
Freezing
The mealy parasite does not tolerate prolonged exposure to extremely low temperatures (from -10°C and below). You can put the food in the freezer for 1 night. The air temperature in it is more than -20°C, so even tick eggs will die. In winter, food can be taken out onto the balcony.
This option
considered if the temperature outside the window is below -10°C.
Ticks cannot tolerate low temperatures
Folk remedies
Such methods are not used for processing grains on an industrial scale, since they are not effective enough and have little effect. For this reason, improvised means can be considered as an auxiliary measure at home.
Used as an aid at home
Aromatic herbs: lavender, bay leaf, garlic
Such products have a similar effect on pests - they repel ticks. Moreover, it is enough to hang bay leaves or lavender around the room or in places where bulk products are stored. The garlic can be spread out after cleaning the cloves first. Some even put peeled garlic in containers with bulk products.
The intense odor of this plant
is unpleasant for parasites, they cannot live in such conditions, so they tend to choose other places to live.
Folk remedy for ticks
Cleaning with bleach
Pure chlorine is used; it is used to prepare a solution, which will later be used for wet cleaning of the room where food is stored. It is not recommended to use such a product for cleaning cabinets; it should be remembered that chlorine is an aggressive substance, as are its fumes. Chlorine-based detergents (for example, White) are also used.
They also have a strong smell,
therefore, a repellent effect will be provided.
Fighting ticks with bleach
Preventing the appearance of flour mites
Proper prevention helps prevent the appearance of mealy mites in a barn, granary or home kitchen. Basic methods of prevention:
How to get rid of food moths in the kitchen
- The room must be regularly ventilated, especially in winter. Pests are very heat-loving, so they die at low air temperatures.
- Grain, flour and other food supplies must be regularly inspected, and all spoiled products must be disposed of immediately.
- You need to carefully ensure that cabinets and shelves for storing food are perfectly clean, free of crumbs and dirt.
- You should not buy flour, cereals and other food products in damaged packaging, as well as those that visually seem slightly damp.
- It is best to replenish food supplies as needed to prevent pests.
- Pet food must be stored separately from food.
To prevent the appearance of pests, you can use effective folk remedies - for example, place bay leaves or several peeled and slightly crushed garlic cloves in the closet. Lavender has a similar repellent effect.
Infected products acquire a slight minty odor
Preventive actions
In order to avoid the appearance of flour mites, it is necessary to take preventive measures. These simple steps will significantly reduce the risk of grain infection by dermatophages and prevent their rapid reproduction.
For large enterprises
The most important task of large agricultural enterprises in winter is to protect grain reserves that will be used for sowing. If flour mites infest them, most of the grains will lose their ability to grow. This will lead to poor yields and loss of investment.
Necessary measures aimed at combating barn pests:
- Thorough inspection of barns and grain warehouses. Agricultural workers must regularly monitor the condition of the cereals and carry out the necessary checks.
- Spraying containers used for storing and transporting grain with chemicals. If you do not do this, you can create favorable conditions for the development of insects.
- Preparing premises for grain storage. Before storing grains, it is necessary to carry out cleaning and disinfestation. This will not only help get rid of existing pests, but also reduce the risk of their occurrence.
- Manipulations with grain. Before storing it, you need to dry it and remove all impurities.
- Treatment of cereals with chemicals. During storage, grain should be periodically sprayed with insecticides to kill emerging insects.
- Creating unfavorable conditions for the reproduction of flour mites. Regular ventilation and maintaining a certain temperature and humidity will prevent pests from multiplying and destroying the crop.
- Conducting laboratory tests. During long-term storage, it is recommended to frequently check the grain in laboratories. This will help identify not only the insects themselves, but also the microscopic eggs laid.
In a house or apartment
Very often, grain mites can appear in a city apartment or private house. In most cases, this occurs due to improper storage or use of food. In order to avoid the appearance of pests, the following measures should be observed:
- It is not recommended to buy or bring low quality flour into your apartment. Infected flour has a grayish tint and emits an unpleasant odor, and also collects in lumps that do not crumble when touched.
- Be extremely careful with flour and other goods purchased at very low prices. In most cases, such products were stored incorrectly or have expired.
- Mealy mites only appear in large accumulations of cereals and flour. Because of this, it is recommended to buy small quantities of products and store them in an airtight container.
- Products intended for pets (dry food, leftover food) must be kept away from human animals.
- Places where food is accumulated (pantries, kitchen cabinets) should be regularly washed and treated with insecticidal agents.
- Experts advise regularly drying the foods that mealy mites most like to be in (flour, cereals, dried fruits, medicinal herbs).
- Products intended for long-term storage should sometimes be taken out into the cold or placed in the refrigerator. A few tens of minutes will be enough to kill all pests.
- The flour mite is afraid of the smell of bay leaves and garlic. In order to prevent the appearance of this insect, you can put 1 clove or leaf in a container with food.
The flour mite is a harmful insect that can destroy large grain reserves and reduce yields. These pests settle not only in barns, but also in people’s homes, posing a threat of infection with serious diseases. In order not to be afraid of the negative impact of this parasite, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of specialists and carry out preventive measures.
Prevention of infection
Preventing flour mite infestation is very important.
It is better to prevent its appearance and spread than to then spend a lot of effort and money fighting the pest:
- Do not purchase products with expired expiration dates, damaged packaging, or high humidity.
- Products must be stored in jars with airtight lids or in tightly closed bags.
- Storage areas must be kept clean, and especially dry.
- Use old products first, then new ones. Do not add new products to old ones; check their quality regularly.
- Products with a strong odor - garlic, bay leaf, lavender - repel flour mites. You can place them on the shelves of food cupboards - and you definitely won’t get ticks.
- Barns and warehouses should also be dry and clean. The walls are treated with lime before filling the grain.
- Scattered flour or grain is collected and burned.
- Dirt, landfills, and garbage heaps should not be allowed in the area near granaries.
- Make sure that there are no rodents or birds in the barns.
- Suspicious products are fried at temperatures above +50°C. The tick cannot withstand this temperature and dies.
Any owner can take preventive measures. Fighting a pest such as the flour mite will prevent the pest from appearing in your home and warehouse
Preventive actions
To prevent ticks from appearing, you need to keep your cabinets clean and clean them regularly. Carry out wet cleaning as often as possible to avoid drinking and get rid of food crumbs. Cereals must be stored in hermetically sealed containers and jars; they must be dry. It is advisable to choose cool places for storage, so that there are no heat sources nearby.
Avoid shopping at reduced prices and various sales. Most often, goods at a reduced price are of very poor quality and may be expired. Often these are the products that are infested with larvae. In this case, it is not worth saving, since you can acquire new tenants who will bring huge problems.
You should not purchase large quantities of products so that they can be stored for a long period of time. It is correct to buy supplies for 2 weeks. If you have pets, you should note that this parasite is often found in food, so keep them away from food.
Old and new stock must not be mixed. Maintain the correct microclimate in the room, ventilate the apartment, it should be clean and, of course, not hot.
Tips and tricks
In order to get rid of these mites, it is very important to detect where they accumulate. The product in which they are located must be disposed of. Products that were stored nearby are also subject to destruction, since we may not notice the parasites, but they have definitely settled nearby.
At home, you can use folk remedies that are quite effective, but at the same time absolutely safe. As mentioned earlier, they lack visual organs, but their sense of smell is very well developed. They do not tolerate the bright aromas of lavender, bay leaf, garlic, so you can put them in cabinets with supplies. They do not kill parasites, but serve as a good repellent. It is effective to use a chlorine solution to wash surfaces, after which the room is ventilated.
Sources
- https://kleshun.ru/muchnoj-kleshh/
- https://GdeKlop.ru/kleshchi/muchnoj-kleshh-mesta-obitaniya-i-metody-borby/
- https://beetlestop.ru/muchnoy-kleshh/
- https://glisty24.ru/parazity/muchnoj-kleshh-dlya-cheloveka/
- https://dezvredexpert.com/kleshhi/vidy-kleshhej/kleshh-muchnoj/
- https://misterklop.ru/klesshi/muchnoj-kleshh-acarus-siro-kak-vyglyadit-chem-pitaetsya-metody-borby-v-domashnih-usloviyah
- https://KlopVred.ru/kleshhi/muchnoj-kleshh/
[collapse]
Prevention measures
Tick eggs are extremely small and can remain dormant for a long time until the surrounding microclimate changes to favorably humid and warm.
- Store food in airtight containers to prevent bugs from spreading.
- Do not mix fresh and old/expired foods.
- The kitchen should be dry and cool, so ventilate the room often.
- Regularly go through your cabinets so that not a crumb is left unpacked, and wash the shelves with soapy water. All corners and cracks must be clean and dry.
- Bugs cannot tolerate strong aromas such as lavender. It won't kill, but it will scare you away.
Such measures will protect you not only from ticks, but also from other insects.