Many people have parasitic microorganisms in their bodies. Some patients do not even suspect that they are carriers of the infection. Parasitic microorganisms can affect any part of the body. They can also affect the scalp. Such parasites bring a lot of discomfort to the patient. Let's find out what microorganisms can affect the scalp and whether hair can fall out due to parasites living in the body.
Parasites, in addition to various organs, can live in human hair
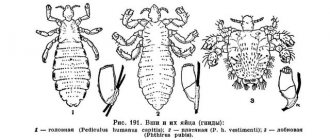
Appearance of lice
Parasites have a faded, whitish, and sometimes grayish color.
They have three pairs of legs. They are easy to notice visually on the scalp, but lice are very agile and are able to quickly move from one place on the head to another. Nits are the specific membranes in which lice eggs are located. They consist of a sticky substance, so they are quite difficult to separate from the hair. Any nit contains only one egg. As a rule, they are attached to individual hairs.
If a person has lice, the first thing you might notice is the nits. They are small oblong white balls that stand out especially against a dark background - dark hair.
When there are a huge number of lice on the hair, even after careful hygiene procedures, in particular, washing the scalp, it seems that small white grains have been scattered on the hair.
Features of the appearance of nits:
- The size of the nit is approximately one millimeter.
- Outwardly, it looks like a round and oblong ball.
- When examined under a microscope, you can notice the adhesive component in the shell.
It is worth noting that nits have a “small cap”, which, when the egg matures and turns into an adult, easily opens and releases parasites into the hair.
Insect species
Depending on the structural features and place of residence, lice are divided into three groups.
Living on the head (head)
The most common variety, the appearance of which depends little on human living conditions.
Reference. Parasitizes the scalp. In men, larvae can be deposited on sideburns or stubble.
Clothes (linen)
Outwardly it resembles a head parasite, but settles exclusively on dirty clothes or bedding used on a regular basis. This species is not able to live on the human body or hair, so it is the easiest to fight.
The body louse is a variation of the other two and has a similar genome. It appeared as a result of evolution and spread due to human fault.
Pubic
It parasitizes the intimate area, but with severe infection it can spread to the eyebrows or eyelashes.
Important! This variety is most often transmitted through sexual intercourse, less often through water in the pool or the use of other people's things.
Equated to sexually transmitted diseases.
Distribution and reproduction
How do lice appear? In order for an insect to move onto the head, it must be in close contact with the contaminated surface. Contact can occur when using a comb, wearing hats, or sleeping on pillows. Such contacts especially often occur among children when visiting kindergartens and schools, since they, as a rule, are not attentive enough to personal hygiene.
It is believed that dirty hair is more conducive to the spread of parasites. This is wrong. Lice only care about blood; they do not feed on any other tissues of the body. A clean head and hair are just as attractive to insects.
The correlation between uncleanliness and the frequency of infection has another reason: people living in poor sanitary conditions are more likely to have physical contact with each other and use the same hygiene items, which increases the risk of disease.
The belief that a nervous condition makes infection more likely has no serious scientific basis.
But indirectly, stress can increase the risk of lice - nervous people sweat more often, and their immune system is weakened, which attracts insects.
Lice in the head begin to multiply immediately after settling. The female lays two to four eggs per day; during her entire adult life (a month), their number can reach 140 eggs.
It is not difficult to calculate that in a few weeks a colony of lice on the head can grow to such a scale that it becomes unbearable for a person to endure their vital activity with a high frequency of bites. In the early stages of the disease, only a few parasites live on the head, later their number reaches tens and even hundreds.
REFERENCE: Head lice live only on the surface of the head. There are no “subcutaneous lice” - these are scabies mites, which are often confused with the pathogens of lice because of their external similarity and the same way of feeding.
Why do they appear and how are they transmitted?
Lice can be transmitted from person to person. And in this case, lifestyle and attitude to hygiene procedures do not play a special role. Even someone who is completely healthy can become infected.
Lice are transmitted in the following ways:
- Contact. Parasites reach a healthy person through direct tactile contact with the host. Infection can occur in crowded places, in public transport, in a gym, etc.
- Bytovym . Namely due to the sharing of hygiene items (combs, hairpins, etc.), linen (towels, pillowcases), clothes (especially hats).
- Water. Lice can live in liquid for a long time. Therefore, when visiting a swimming pool or public bath and using the same water with a carrier, infection is inevitable. Most often, as a result of such “bathing”, pubic lice are transmitted, because they retain their viability in water the longest.
- Sexual. Pubic parasites are also transmitted after sexual contact, settling in the groin and armpits. This disease is equated to a venereal disease.
Attention! Linen lice's natural habitat is fabric fibers. Therefore, they can be transmitted to humans only through contaminated clothing, climbing onto the skin only to feed.
Through direct contact or shared hygiene items, this type of parasite is transmitted only as an exception.
Causes and symptoms
Since parasites appear in places with poor sanitary and hygienic conditions, the main reason for their appearance is failure to comply with basic hygiene rules.
Lice can be transmitted through underwear or bedding, through hats and other personal items. An interesting fact, but lice can exist freely in open bodies of water, and even in a swimming pool where sanitary and hygienic requirements are not met. Swimming in them can cause you to become infected with lice.
In a number of situations, parasites can “hide” in the folds of clothing, where they lay their eggs; it is almost impossible to detect them. However, they crawl onto human skin to feed; in this case, areas of the skin such as the armpits, groin area, and back are affected, that is, in those places where clothing fits most closely to the human body.
Lice can also appear under the following conditions:
- Long journeys, trips when it is not possible to fully comply with hygiene rules.
- Seasonal work with large crowds of people.
- In children's institutions where children closely communicate and make contact.
- In other places where there are large crowds of people (sanatorium, hospital).
It is in such places that you should follow all the rules of hygiene and do not forget about preventive measures, which will avoid infection, thereby eliminating subsequent treatment.
As practice shows, the appearance of lice is quite difficult to notice. In some cases, parasites can manifest themselves immediately after a couple of days from the moment of infection; in other situations, they can remain on a person’s head for a couple of weeks, and there will be no signs of their presence.
As a rule, lice especially affect the back of the head and temples of a person's head. The following signs may be observed in this area:
- Severe itching sensations, as a result of which a person scratches the scalp, sometimes until blood appears.
- The affected parts of the head can fester, resulting in the formation of ulcers, boils and other pathological phenomena.
- With a prolonged course of the disease, the scalp becomes denser and pigment spots appear.
In good lighting, you can visually observe nits on human hair that are attached to them. Usually they are located as close as possible to the root structure of the hairline.
Lice love... clean heads and expensive perfume
Moreover, among adults, pediculosis is detected five times more often than in children.
Elena Belova, an epidemiologist at the Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology of the Pervomaisky District of Minsk, agreed to talk about these unpleasant insects and comment on the most common myths about head lice.
Myth 1. Animals carry lice
Only fleas, which are not dangerous to humans, live on the body of animals. Therefore, in this case, there is no point in slandering our smaller brothers.
Myth 2: Second-hand clothes are contagious.
Before arriving to us, consignment goods undergo thorough chamber processing. But to be on the safe side when buying second-hand clothes, be sure to wash them at home.
Myth 3. Those with long hair are more vulnerable
It doesn’t matter at all whether you have a haircut or a waist-length braid. True, long flowing hair is an excellent bridge for the travel of these parasites. In transport, where there is a lot of crowding of people, it is advisable to hide your hair. Long-haired people, in addition, have a really harder time fighting the disease.
Myth 4. Lice cannot live outside their host.
Without food (outside a person), a head louse can live for a day, a nit can live from 10 to 14 days (and then a louse can emerge from it!). The pubic louse does not live without a person - this is true. A body louse can survive for a whole week without food.
Myth 5. The head louse gnaws the keratinized scales of the epidermis
All lice feed only on blood.
Myth 6. Pediculosis is dangerous for all people
Experts do not dare to say so categorically. There are people who are absolutely immune to these insects and do not become infected with them even in a lice-infested environment. It is unknown why this is so. Most likely, they have individual metabolic characteristics - for example, lice are repelled by a specific smell of sweat.
Myth 7. When moving, the louse tickles the skin with its paws, so everything itches
Severe itching is caused by the saliva that the louse secretes when biting. Scratching appears, the skin at the bite sites becomes covered with bloody crusts. In advanced cases, the hair becomes sticky with the exudate that is released. Concomitant dermatitis often develops.
Myth 8. Pediculosis is difficult to diagnose at an early stage
Diagnosis of difficulties is usually not provided. Head lice manifests itself as severe itching, leading to scratching. It itches especially behind the ears and on the back of the head. Upon examination, it is difficult to notice an adult louse, but a small, teardrop-shaped nit can be detected for sure.
The pubic louse also causes severe itching with its bites. The pubic skin becomes covered with a rash with a reddish-bluish tint.
Myth 9. Pediculosis is a disease of homeless people
Rather, one can even say the opposite - the louse is especially dangerous for wealthy people, since it is attracted by the smell of good perfume. And lice will also choose from all the heads the one that is washed often. There are fewer substances that the sebaceous glands secrete. This makes it easier for insects to suck blood.
Myth 10. Dandruff is difficult to distinguish from lice
Of course not. Dandruff is easily removed from the hair, but nits are not. It can only be removed with a very fine comb using acids and alkalis. And in appearance they are very different.
YOU NEED TO KNOW THE ENEMY BY FACE
1. The greatest likelihood of becoming infected with lice is in places with the largest concentration of people: public bath, swimming pool, hairdresser, train, etc.
2. The louse cannot stand the smell of tea tree and lavender. Parasites will bypass you if you apply a little of this liquid to the back of your head and behind your ears.
4. Lice are excellent swimmers. They can stay in water for up to three days. This is why swimming pools are dangerous if sanitary standards are not observed in them.
5. Body louse is less common than head and pubic louse; it lives in the folds of clothing and lays nits there. It comes to the skin only to feed with blood. It feeds mainly in places where clothing fits tightly to the skin. By the way, clothes made of natural silk and linen become a kind of obstacle to body louse infection.
6. Pubic louse - as the name suggests - lives in the groin, sometimes under the arms, on the eyelashes and eyebrows, and on the hairy chest of men. But not your head! It is transmitted mainly through sexual contact, as well as through shared bedding and hygiene items.
7. To get enough, lice don’t care whether it’s day or night, dark or light. It is especially good for them if the owner’s body is at rest or the person moves little.
DO YOU KNOW THAT…
...Mummified lice were found during the study of mummies of Egyptian pharaohs. They were no different from their current descendants. It turns out that even the pharaohs suffered from this disease.
...If you collect all the lice of the planet in a heap and weigh them, then the total mass will exceed the mass of all the elephants on Earth by 15 thousand times.
...Lice select the most “appetizing” smelling host using their sense of smell. Short antennae not only replace their eyes, but also help them navigate in space. Moreover, a louse removed from a person - given a choice - will always return to him.
...Human blood is a specific food for lice. In extreme hunger, they can feed on the blood of a rabbit or guinea pig, but such food is harmful to them.
...Under normal conditions, a louse feeds 2 to 3 times a day and, on average, spends 3 to 10 minutes feeding. Food (blood) gradually fills the intestine and sometimes comes out. If a louse's stomach becomes overfilled, the stomach wall may rupture and the louse will die.
BY THE WAY
As long as there is at least one pair of lice on the planet, they will not disappear. Every day the female lays 4 eggs (nits) and glues them to the bottom of the hair. Nits are oval in shape and gray-white in color. From these, after 8 - 13 days, a louse appears, which becomes sexually mature after 10 - 14 days. The lifespan of a head louse is 38 days. They are transparent or grayish-yellow, up to 4 mm long. They parasitize mainly in the area of the temples and the back of the head, from where they can spread to the entire scalp.
STAY IN TOUCH!
For any type of lice (head lice, body lice, pubic), you can choose an effective drug and get rid of the parasites. Everyone who is near the patient should be treated. Moreover, treatment should take place simultaneously with disinfection of clothing, bed, and premises. A visit to a doctor (or a local therapist) cannot be postponed. Otherwise, self-medication may take a long time.
Which parasites can live in the brain?
Most parasites enter the human body through the digestive tract. From there, they are carried throughout the body through the blood or lymph flow, but each of them has its own favorite localization sites.
The human brain is one of the vital structures that is well supplied with blood and the slightest malfunction in its functioning will immediately manifest itself in various symptoms. Not many parasites choose to live in the brain; cysticerci and echinococci are found there most often.
Cysticercosis
Cysticercosis of the brain is a parasitic disease caused by the ingestion of pork tapeworm (worm) larvae. These larvae are called cysticerci.
The disease develops when larvae of the pork tapeworm enter the digestive tract. Under the influence of gastric juice, the shell of the eggs dissolves, and they enter the brain tissue through the bloodstream, and less often into the eyes and muscles.
In the brain they turn into bubbles filled with colorless liquid. Most often, tens and hundreds of such bubbles are found in the brain, but single cysticerci are also found. Clinical signs of the disease:
- mental changes;
- paresis and paralysis;
- visual impairment;
- sleep problems;
- headaches and vomiting;
- convulsions, epileptic seizures, etc.
Symptoms and treatment of such parasites in the human head depend on their location and number. Anticonvulsants, hormones, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. If there are only a few accessible cysts, surgical intervention is performed and the parasites are removed. With widespread cysticercosis, the prognosis is very serious, since the disease can quickly lead to death.
Echinococcosis of the brain
This worm (echinococcus) does not often affect the brain, preferring to settle in the liver and other organs. Infection occurs when echinococcus enters the brain tissue, where it forms cysts of various sizes: from a small pea to the size of a fist. Clinical symptoms are similar to a brain tumor. The patient experiences vomiting, headaches, seizures and convulsions. Mental disorders and decreased mental abilities are noted.
Treatment is carried out surgically. If possible, remove the hydatid cyst. With numerous cysts, such removal is impossible and the prognosis for life is very unfavorable.
What you need to know about the microflora of the scalp?
The content of the article
Microbiome* or microbiota are recently popular terms that we associate mainly with the bacterial flora of the intestines, oral cavity or genital tract. But microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea (small single-celled cells), eukaryotes, fungi, inhabit almost the entire body, regardless of whether we feel it, whether we like it or not.
Microorganisms are essential for maintaining balance and proper functioning of the body, including maintaining immunity.
The discovery that microbes are a physiological element in the human body was made in 1880 by the Austrian pediatrician Theodor Escherich. He observed the positive effect of E. coli on the intestinal microflora of healthy children and children with diarrhea. In subsequent years, a number of other microorganisms were isolated from the human body. Among other things, the bacteria Veilonella parvula were discovered in 1898, and Bifidobacterium spp. in 1900. and others located on the skin, in the digestive tract and genitourinary system.
* The term “microbiome” was first used by Nobel laureate Joshua Lederberg, who proposed using it to describe the collective genome of all commensal (that is, indifferent to us) symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms living in the human body.
Demodex: causes and symptoms
Demodex is a mite that can live and parasitize on the human scalp, in the sebaceous glands and glands of the cartilage of the eyelids.
The parasite is small in size, not exceeding two tenths of a millimeter. The main symptom of the presence of the parasite is redness of the edges of the eyelids, with painful sensations present, the eyelids are constantly irritated and itchy. This condition intensifies at night, and it is very difficult to endure; sometimes there is discharge from the eyes - it can be mucus or a foam-like liquid.
Demodex in women can lead to a white coating on the eyelashes or their complete loss. In addition, patients complain of constant lacrimation, redness of the eyeballs, and a feeling of “garbage” in the eyes.
Demodex can appear in any person, for example, due to the abuse of cosmetics that contain hormones, or when the skin is damaged, as a result of which an infection gets into the wound.
If there is a high number of demodex mites in humans, the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Acne and pink spots appear on the skin of the face.
- Itching in the hair.
- The skin of the face becomes lumpy and uneven.
- Individual symptoms - excessive expansion of pores on the nose, forehead, cheeks.
If the hair follicles are infected and treatment is not carried out, then over time the hair begins to fall out, and the person slowly but surely goes bald. It is worth noting that demodex, due to the release of a special substance, can provoke a malfunction in human metabolism.
There are two types of mites - one lives in the hair, and the second parasitizes the sebaceous glands. If the patient's eyes are affected, a microscopic examination of the eyelashes is performed. When there are lesions on the skin of the face characteristic of this parasite, a scraping is taken from the affected area.
Treatment of such a problem is difficult, and its duration can be up to six months. Treatment of the disease is aimed at the following goals:
- Increase the body's defenses, strengthen the human immune system.
- Eliminate parasitic microorganisms.
During therapy, antihistamines are prescribed to get rid of allergies. These can be a variety of ointments, gels or tablets. Treatment for mites on the face includes the following medications:
- Demalan (ointment) promotes increased tissue regeneration and is applied to the affected areas of the skin.
- Prenacid reduces the manifestations of an allergic reaction.
If a purulent manifestation of blepharitis has developed, the doctor recommends antibacterial medications. The most proven ones are Colbiotsin and Eubetal.
It is worth noting that you cannot get rid of such a mite on your own, and alternative medicine will not give the required effect, although there are options for treating demodex on the face at home, but they must be supported by traditional medicine.
Only the attending physician will draw up an adequate treatment regimen and help get rid of the problem.
Types of parasites in hair and symptoms
There are entire classes of organisms that parasitize human hair. A component of their nutrition is human tissue, that is, skin, sebum, blood. By feeding on tissues, parasites make themselves felt by itching, scalp pain, hair loss and creating significant discomfort. It is difficult not to detect such parasites; they are extremely dangerous to human health.
Head lice
Pediculosis or, in other words, lice is known to every parent and every child. The main risk group is school-age children. The main danger of lice is that they are invisible to the naked eye. They look like tiny bugs that can masquerade as the light skin of a person’s scalp, thanks to the pale color of their body. Nits are lice eggs that stick tightly to the hair roots, making them often difficult to get rid of. The nits contain larvae. Lice are able to run quickly and are transmitted through direct contact between people, that is, when their heads touch, with hats or clothing. They leave bites behind, and feel most comfortable at the temples and on the back of a person’s head.
The flea is an omnivorous parasite
The flea in the past was a carrier of plague and typhoid. Most often found in animal fur, but also found in humans. These are bugs of different shades - from yellowish to dark brown. The classification of fleas corresponds to the type of carrier. They are divided into the following types:
- Household: linen;
- sexual
- canine;
Human fleas are universal. They are able to feed on the blood of humans, dogs or cats. In addition, there are species that choose habitats in the form of rugs and upholstered furniture. Such fleas are called house fleas. Earth fleas live in the yard, which do not pose a danger to humans because they do not feed on blood. The main danger of fleas is that they carry infectious diseases.
Parasites under the scalp
Scheme of human infection with dirophyllaria.
Subcutaneous parasites are often found in hot, tropical countries. Getting rid of them requires much more time and effort than those that live on the surface of the skin. Under the skin of the head, wrists, armpits, and between the fingers, microscopic scabies mites parasitize, causing the disease scabies. It feeds on human skin tissue, gnawing paths under the skin and causing unbearable itching. Another dangerous subcutaneous pest is dirophyllaria. This parasite develops under the mucous membrane of the eye, which can impair vision or even make a person blind. It can only be removed surgically.
Hair mites
The hair mite or demodex lives in human hair and eyelashes. Having a detrimental effect on the scalp and hair structure, it causes excessive hair loss. At first they feed on dry scales - pieces of dead skin, then they get into the follicles and cause serious damage, resulting in hair loss. Mites on eyelashes provoke the formation of white or yellowish scales between the hairs, as well as their loss. This parasite often causes bright red acne on the face. For a long time, it may not remind you of itself in any way, but when the immune system weakens, it makes itself felt by the reactions described above. https://cryptosnews.info.
Classification
Partial or complete baldness is caused by the following types of pathogenic organisms:
- Psoriasis or lichen is not infectious, caused by pathological processes inside the human body.
- Asbestos lichen, resulting from organ dysfunction.
- Fungi.
- Worms.
- Fleas.
- Lice.
- Ticks.
Fungus
There are several types of parasitic fungi that affect people's hair, causing hair loss. Fungal diseases are always infectious in nature, so you will have to disinfect all personal hygiene items. Let's look at the types of diseases:
- Microsporia is a fungal disease that causes hair loss. If several people live in a house, then the risk of re-infection is very high. In the process of inflammation of the skin, areas swell, the hair follicle weakens and, as a result, baldness appears.
- Scabs or yellow crusts on the skin. There is a small area of skin where there is no hair, some area is affected by crusts.
- Trichophytosis is a complex fungal pathology that causes complete hair loss. The disease is transmitted by contact. The lesion leads to brittle hair at the base, bare areas of skin become covered with plaque. The skin is hyperemic and swollen.
Fungi cause serious pathologies of internal organs. Only a qualified doctor can determine which fungus caused the skin lesion and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
The danger of the presence of nits and lice in human hair
When settling in human hair, these insects and their eggs can cause a lot of trouble. The main diseases caused by pediculosis:
- Allergy, as a result of lice biological waste getting into wounds;
- Eczema;
- Dermatitis;
- Ulcers on the skin;
- Blepharitis of the eye;
- Relapsing fever;
- Pigmentation of the scalp in advanced forms.
Lice must be removed immediately. It will take several weeks to get rid of nits.
What's happened
Dandruff is a flaking of the skin underneath the hair. Its causes are malfunctions of the sebaceous glands or excessive drying of the skin. Of course, such manifestations do not pose a particular threat to the health of the owner, but they give the hair an unkempt and completely unnatural appearance.
Therefore, dandruff needs to be combated with various cosmetic methods and through proper nutrition.
They produce oily dandruff, which involves gluing of scales. Men and women experience severe scalp itching, and after washing, their hair looks dull and dirty. But there is one positive thing about this type of dandruff - it is hardly noticeable.
Important point! If oily dandruff covers large areas of the scalp, the scales begin to flake off and damage the curls. This situation can cause excessive hair loss.
The dry type of dandruff is accompanied by severe itching and the abundant appearance of white powder, which directly falls out of the hair at the slightest movement or combing.
The causative agent of severe peeling of the skin is Pityrosporum oval. This microorganism begins to actively multiply during malfunctions of the sebaceous glands, since favorable conditions are created for its existence.
The distinctive signs of dandruff are:
- small scales on the curls, which somewhat resemble white snow;
- peeling is noticeable on the scalp, accompanied by itching;
- hair color loses brightness and curls begin to fall out;
- hair acquires excessive gloss, becoming greasy (in some cases);
- if dandruff is not treated, the process of keratinization of the dermis becomes more intense, so the number of white grains increases;
- with a severely advanced form, dandruff spreads to the eyebrows and interlash space.
The appearance of dandruff is caused by the fact that little subcutaneous fat is secreted. Therefore, if you have dry skin, split ends and brittle hair, be prepared for dandruff.
It is important to distinguish dandruff from other dermatological diseases, namely:
- psoriasis, which appears along the edge of the hairline;
- ringworm, which has clear boundaries and local foci;
- streptoderma, which at first is very similar to dandruff, but over time manifests itself as ulcers and the formation of a yellow crust;
- seborrhea pemphigus.
Dandruff is very easy to confuse with lichen , especially at first. But over time, the latter turns into a circle or oval, at the location of which curls fall out and pus appears.
Microbiota (microflora) of the scalp
What happens on the scalp? This is a unique place, equipped with a large number of sebaceous glands and characterized by a rapid rate of sebum production. It is also a living microbial ecosystem, meaning it is home to hundreds of millions of bacteria, fungi and viruses.
More than a million commensal microbes live on the scalp in every square centimeter (for comparison, on the skin of the hands there are about 100,000 / cm2). Bacteria from the subfamily Propionibacterinae, various species of Staphyloccocus spp. live in the area of the nose, ears and hair. One and many other microorganisms that play a key role in protecting the skin from external infectious agents or toxic substances.
Staphylococci
How to get rid of lice?
Pediculosis will not go away on its own. Over time, the number of insects increases, the number of bites increases, and the itching becomes constant and unbearable. Control methods are divided into two types - mechanical and chemical. Folk recipes can also be classified as chemical methods, but we will consider them separately.
Mechanical methods
Typically, mechanical methods mean hair cutting, shaving and combing out parasites with a comb, but they can also include thermal treatment with a hair straightener or tongs. Hair cutting at the root is the cheapest and most effective treatment method, but it is not suitable for everyone. Women and girls will not want to lose their hair, and not all men are ready to go bald.
Chemical and mechanical methods must be combined. Just treating with a drug from a pharmacy will not be enough; you need to comb out dead lice and their larvae from your hair. The fact is that most drugs are not capable of destroying nits; their shell reliably protects the offspring from chemical exposure.
Don't expect to get by with a regular comb. Nits must be combed out with a special comb with very frequent teeth located almost close to each other.
Chemicals
There are a large number of modern drugs for head lice; they differ in cost, consistency and method of application. The most common types of medicinal formulations can be distinguished:
- Shampoos are the most popular, inexpensive and quite effective products when used correctly and following all the procedures specified in the instructions. Here are some of them: Hygia, Paranit, Lavinal. Shampoos specifically designed for children are sold separately.
- Sprays are more effective than shampoos, but are more difficult to use, are difficult to wash off and can cause unwanted allergic reactions. Usually a comb is included. The most famous: Paranit, Lavinal, Nyuda, Para Plus.
- Aerosols used to treat contaminated clothing. Someone even uses Dichlorvos against lice.
- Creams are less common than shampoos and sprays, but they are not inferior to sprays in effectiveness. Among them: Nix, D-95.
- Combs - designed for combing out bloodsuckers. They differ from ordinary ones in that they have very frequent teeth that detach the nit from the hair using mechanical pressure. But this is an auxiliary product used in combination with chemicals, most often included with the product.
Linen lice are removed by thoroughly washing and ironing bedding or clothing. Temperatures above 60 and below -10 °C are destructive for parasites.
Size
Human dreams have a subtle connection with reality. Everything that seems frightening and bad in night dreams can in reality mean something good. If you dream of huge lice, so will your profit and success. If you see several large insects in your hair, a person gets a chance to make his dreams come true.
If the parasites are small, this portends favorable changes. A head full of parasites promises to overcome any difficulties. A person is ready to overcome any obstacles and go towards his goal. This is a favorable time for any endeavors.
How are lice transmitted from person to person?
The dangerous thing is that the causes of lice are so commonplace that anyone can become infected with lice. It doesn’t matter what kind of life a person leads and how much he maintains hygiene. Lice can be everywhere, so you can never predict their appearance. Where do lice in human hair come from and how can they be transmitted?
How are parasites transmitted?
- In kindergartens, when children play and interact with each other;
- Using the same comb or pillow with an infected person;
- Water procedures in the bathroom and sauna without changing the water. Lice can live in liquid for a sufficient amount of time, so after bathing an infested person, the lice will float in the water for some time. They can easily end up on your hair.
- Using hats with a person who is infected with lice.
- Places where there are a large number of people, especially on public transport. Lice can easily crawl onto another person's hair.
Many people notice parasites after sexual intercourse has occurred. Typically, pubic lice are located only on the pubic area and armpits. If parasites occur, it is necessary to begin treatment so as not to worsen the situation.
Prevention
Maintaining personal hygiene is the main principle of preventing disease. It is not recommended to use other people's combs or wear other people's hats. When visiting unfavorable places, insect repellent products are applied to the hair. During epidemiological periods of increased risk of infection, regular head examinations are carried out. Particular attention is paid to monitoring the condition of children's hair when they visit kindergartens and schools in the autumn and spring.
Thanks to this article, you learned what kind of disease this is - pediculosis, how lice get, and got acquainted with photos of lice and nits on the head.
Our website has many useful articles about pediculosis:
- Do lice grow on dyed hair - the specifics of selecting anti-pediculosis agents;
- how to remove nits and lice from long hair without resorting to a “zero” haircut?
- what to do if lice appear on your head? First and subsequent actions!
- a cloudy pool of your eyes, or lice on your eyelashes;
- what to use to combat parasites on the head: what are lice and nits afraid of?
How to protect yourself from lice infestation?
Unfortunately, there is no absolutely effective way to avoid infection. The main method of preventing head lice is keeping a distance from people who may be infected and thoroughly checking the head for possible contacts.
Children attending kindergartens and schools are regularly checked for the presence of parasites in their hair. This is carried out as planned by medical workers in order to prevent mass casualties. Parents should also be attentive to the health of their children.
Are there black nits?
Since an adult insect differs from larvae and eggs in having the ability to move quickly, it is difficult to visually detect the appearance of parasites. A characteristic external sign of lice infection is the appearance of black dots and nits on the hair, while the former are waste products of insects.
There are no black nits, since the color of parasite eggs can vary from white to gray, dark shades are excluded.
Diagnosis of pediculosis: how to independently detect the disease?
During the feeding process, the insect injects substances under the human skin that reduce sensitivity and prevent blood clotting, so during the bite the victim does not feel pain; unpleasant symptoms appear after some time. The following symptoms are characteristic of pediculosis:
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- constant itching;
- the appearance of pustules on the skin;
- sleep disturbance;
- irritability.
Pediculosis can be diagnosed by detecting insects. At the initial stage of the disease, there are not many parasites yet, so inspection will require a fine-toothed comb. First, comb the hair in the usual way. When the comb slides freely along the entire length of the hair, you can use a comb.
In addition to the fact that lice cause significant discomfort to the victim, it is believed that they can infect a person with typhus or relapsing fever. They can, but it's very unlikely. There are currently no typhus epidemics, so there is no need to worry.
But lice can cause dermatitis and severe itching, which in rare cases can lead to allergic reactions and inflammation.
Where do lice live at home (apartment)
Body lice as a species have not been around for very long - they appeared at the same time as people began to cover their nakedness . It is noteworthy that it was the DNA of this insect that helped scientists establish the approximate date of the creation of clothing.
They cannot live in hair - their limbs are not tenacious enough for this. But these parasites feel quite comfortable on “stale” clothes. They can be found:
- in folds and pleating;
- in turns;
- under the seams;
- in your pockets.
Compared to head lice, they are more resilient and harder to detect, which makes their habitat more comfortable and safe. In addition, clothing maintains a much more stable microclimate than hair.
Can lice live in things, on clothes, bedding and pillows?
When the problem of lice arises again and again, it makes sense to check and treat everything that regularly comes into contact with human skin . All textile items, from bed linen to furniture upholstery, are quarantined.
But at the same time, it often happens that lice are confused with bedbugs and fleas. You can distinguish some parasites from others by the following characteristics:
- A louse, unlike a flea, is not capable of jumping.
- A bedbug, unlike a louse, can be seen with the naked eye.
“A louse is bad, but not a flea”
Photo from dinocro.info
These two insects are often confused: both belong to the group of ectoparasites that live on the surface of the body of a person or animal (as opposed to endoparasites that live inside), both feed on blood. From this confusion two myths arise.
Myth one. Lice can jump from person to person.
Myth two. Lice can be contracted through close contact with cats and dogs.
Both are wrong.
The types of lice that parasitize humans do not live in the fur of animals, and therefore they can only crawl onto you from another person. And specifically crawl, because these insects do not know how to jump and fly.
If you see that a louse has fallen from your child’s head, then it is, if not yet dead, then a very weakened insect that does not pose any danger.
The human louse comes in three morphological types: head, pubic and body louse. Subspecies differ from each other, although they can interbreed and produce offspring. But this is just an interesting feature that in itself does not threaten us with anything.
But as for troubles from different subspecies, each of them has its own specifics, which are important to understand.
Now we will deal with this, and let's start with infestation.
Treatment of pediculosis in children
Once you have identified lice, you should think about what treatment for head lice to choose. Increasingly, parents are choosing pest control shampoos, but some opt for folk remedies.
On a note!
Not every drug from the pharmacy is suitable for a child. Children are sensitive to chemistry. A toxic product can cause severe allergies or burn the scalp.
If the disease is detected at an early stage, then a comb will help to cope with it.
Pharmacy products
Most often, the pediatrician prescribes a special anti-lice shampoo or spray for children. Before using it, you should read the instructions. It is better not to buy this product without a doctor's prescription. After all, a poisonous drug can poison a child.
The following medications are usually prescribed to children:
- NOC;
- Hygia;
- Nyx cream;
- Nuda spray;
- Para Plus remedy for lice and nits;
- Paranit;
- Veda shampoo;
- Lavinal;
- Full Marx.
On a note!
Nyuda is the only spray that can be used to treat children's hair. It does not contain insecticides and does not cause allergies.
After the first treatment, parents sometimes turn to the pediatrician because white lice remain in the head. But these are not the insects themselves, but their eggs. After seven days, the parasites will come out of them. Therefore, treatment with the drug is repeated after a week.
Nude product
Folk remedies
An effective insect repellent can be prepared in your own kitchen. The most commonly used recipes are:
- Hydrogen peroxide is mixed with water 1:1. The mixture is applied to damp hair. The head is wrapped in a bag and then a towel. After 40 minutes, the product is washed off.
- Tar soap is applied to wet hair, kept under the bag for 40 minutes, and then washed off.
- Vinegar 9% is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:3. Each strand is treated with vinegar solution. The head is covered with a towel and a scarf is put on top. After 40 minutes, the hair is washed.
Important!
It is prohibited to use kerosene or Dichlorvos to treat head lice in a child. These products can cause severe burns and poisoning.
Special comb
A lice comb helps get rid of insect nits. It is used both after pediculosis has been recognized and for the purpose of preventing the disease.
Before combing out lice and nits, it is recommended to treat the hair with water and citric acid: 5 g of powder per 250 ml of warm water. The composition softens the sticky mass, with the help of which the nit is attached to the hair and lice eggs become easier to comb out.
Fine-tooth comb
Review
I treated the child’s head with everything. The insects appeared again and again. The pediatrician advised me to purchase a special lice comb. They managed to comb out the nits, and the lice no longer bothered us.
Larisa, Ekaterinburg
The comb also helps to determine whether a child has lice. If nits and insects remain on it, then it is worth checking your hair and treating your head with an anti-parasite product. Hair is combed 4 times a day for 5 days. After combing, the comb is washed and treated with alcohol.
Red dandruff (dermatitis)
Red dandruff is called so conventionally. In fact, this is nothing more than particles of epithelium that fall from an area of skin affected by fungus or dermatitis. Why is it red? Because the irritated area becomes inflamed, causing discomfort and, often, itching.
Scratching the area will only make the problem worse, as scratches and deep depressions in the affected area are a quick easy way for other infections.
The reasons for this are as follows:
- Fungal diseases.
- Predisposition.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Frequent stress.
- Lack of sleep and excessively long sleep.
- Alcohol consumption.
Getting rid of parasites
Hitting malicious insects on your own body in a dream means victory over troubles. Luck is on the dreamer's side. Any thoughts and actions of hostile individuals will be ineffective. Combing parasites out of your head means getting rid of problems. Pests leave a person’s head, and his life becomes easier and happier. This interpretation is given to dreams in which fleas are combed out from oneself or from other people.
Catching, squeezing with your hands and killing parasites means an improvement in your financial condition and positive changes in your work. The interpretation is true if the dreamer is a man. If another person succeeds in killing an insect on the head, someone from the environment will become successful.
Some dream books claim the opposite. The English interpreter says that intentionally killing parasites leads to negative changes. If you dream that you are crushing lice, your significant other or close friend will betray you.
“Pediculosis brings us a parasite and a bloodsucker”
Photo from the site licebustersnyc.com
More precisely: pediculosis is, in fact, an infestation with lice.
Lice feed on the host's blood and, being extremely fertile, lay numerous eggs (nits). The head louse glues nits to a person's hair, the body louse hides them in the folds and seams of clothing, and sometimes glues them to the hair on the body of its victim.
Key question: how to understand that an infestation has occurred? How to identify head lice in yourself or your child?
Here are the most important symptoms:
- skin itching;
- small grayish-bluish spots on the skin;
- nits in hair.
It is not so easy to notice lice or nits in the hair because of their small size, and itching on the skin may not matter at first.
People often attribute strange spots on the neck, behind the ears and on the rest of the body to allergies, mosquito or flea bites. It is important to know! If you take an antiallergic drug during itching or give it to a child, it can blur the picture and lull your vigilance, while the parasites, meanwhile, will continue to feed on the host’s blood and actively colonize his head or clothes.
The best thing you can do if you experience itching is to see a professional, but just in case, here are some guidelines.
- unlike an allergic rash, lice bites have a pronounced puncture point in the center of the inflamed area;
- since the parasite, when bitten, introduces a special enzyme into the blood that destroys hemoglobin, the color of the skin in the area of the bite becomes bluish;
- lice bites can resemble flea bites, however, fleas bite a person in open areas of the body, and body lice, on the contrary, attack those places that come into contact with clothing: shoulders, back, armpits, hips, stomach, lower back; and in addition, flea bites line up in a characteristic chain, and lice bites are chaotic.
Remember the most important thing! Lice bites themselves are not dangerous, but scratching them can lead to bacterial infection, boils, or even abscesses if the infection goes deep inside. Nausea, headache, fever, and regional lymphadenitis (swelling of the lymph nodes) may develop. Immediately after discovering lice, especially in a child, it is necessary to begin fighting parasites in the victim himself, and also check all household members for lice.
What do they eat?
Lice feed exclusively on blood (mainly human), their oral apparatus is adapted specifically to pierce the skin and pump out blood. Other power sources are not available to them. They cannot feed on hair, skin or dandruff as some people believe.
Lice feed about 5 times a day every 2-3 hours. In one suction, a louse can drink approximately 0.5 mg of human blood. Saturation with blood allows parasites to reproduce and lead an active life.
Parasites lay eggs close to the skin. How long do nits live? The incubation period before lice hatch from the egg is about 10 days. Females require blood feeding to reproduce. Nits do not need nutrition, since their shell contains all the necessary nutrients. A constant ambient temperature is very important for egg maturation. The scalp provides the ideal level of warmth that allows lice to develop and hatch.
After this, the cocoon shells remain on the hairs, and the lice begin to feed, biting through the human skin. From the moment the larva emerges from the nit until the louse reproduces independently, nine days pass. The louse can move to other people from the tenth day of life. Parasites live on average about 30 days, during which time they lay from 100 to 300 eggs.
People actively destroy parasites using pharmaceutical and folk remedies, but insects can also die from natural enemies. In nature, they are threatened by certain types of ticks, false scorpions.
Comfortable conditions for life and reproduction
There are social and sanitary conditions in which parasites multiply at a faster rate and their numbers increase exponentially. These include:
- low cultural level of society;
- lack of understanding of personal hygiene;
- lack of knowledge about this disease;
- close contacts between people from the same social circle;
- spontaneous sexual contacts with unreliable partners;
- trips during which there is no possibility of carrying out hygiene procedures;
- air temperature above +20 degrees Celsius, at which lice actively reproduce;
- frequent presence in rooms with large crowds of people, including confined spaces of public transport.
Important! Lice infestation is most active during the cold season. In frosty weather, people more often find themselves in crowded places, where the likelihood of contact with infected people increases several times.
Dreamer
Lice promise a man success in his career
The fact that lice dream of money is not always true. The gender and position of the dreamer matters:
- Pregnant woman. Seeing parasites in your hair means profit. Squeezing them means health problems. It is better for the expectant mother to consult a doctor.
- Married woman. Dreaming of a louse in your hair means your significant other is cheating. There is another meaning - the need to pay attention to hobbies and creativity.
- Unmarried girl. If a girl is lonely, such a dream will mean fear of meeting a young guy. If a girl is in a relationship, it means she needs to share her fears and secrets with her other half.
- Man. Such a dream symbolizes favorable changes in your career, success in business, and more money.
Having seen lice in a dream, you will need to figure out what type of parasites they were. This also affects the interpretation.
Worm infestation
Can worms cause hair loss? With a strong proliferation of worms in the human body, a decrease in protective functions (immunity) occurs, which indirectly can provoke thinning of the hairline: the hair begins to fall off. In addition to thinning hair, other undesirable changes occur in the human body.
However, trichologists claim that hair loss can be caused not by all worms, but only by bovine tapeworm. Infection with tapeworm not only changes the microflora in the intestines, but also negatively affects the composition of the blood. A decrease in the protein components of the bloodstream leads to baldness.
Neither the presence of lice nor the presence of worms in the human body are the causes of thinning hair. However, a decrease in the body's protective functions can lead to significant hair loss. This should be remembered.
How to protect yourself from bovine tapeworm and other worms? To do this you need:
- always wash your hands with soap;
- do not eat poorly cooked meat;
- treat pets for worms.