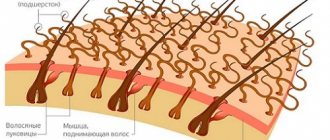
Main routes of infection by head lice
The main route of infection is through household contact. Most often it is close contact with another person that occurs when hair touches. Since lice move very quickly, it only takes a few seconds for them to move from another person and settle on the scalp.
There are other ways you can become infected with lice, although the likelihood of such infection is low:
- • using other people's combs, hairpins, hair decorations;
- • hats;
- • staying on public transport during rush hour;
- • poorly processed accessories in hairdressing salons
- • pillowcases on the pillows of an infected patient.
The main methods of infection with body lice
This type of parasite lives in the folds of clothing, bed linen, and mattresses. They move onto the human body to obtain food. The bites themselves are invisible, but cause severe itching with the formation of wounds after scratching.
Not only people leading an asocial lifestyle can suffer from body lice. The route of infection is through close contact with an infected person. The risk increases in crowded places: boarding schools, prisons, army barracks. Infection requires prolonged contact
Lice and personal hygiene: addiction
One of the most common misconceptions about lice is that only people who do not pay enough attention to personal hygiene become infected. Since infection occurs through close contact with another person, cleanliness of hair or body does not matter. The disease can occur even in the cleanest people.
Danger for children
The louse feeds on human blood.
To do this, she bites the skin on the head and injects a substance that prevents blood clotting. This creates a wound at the site of the bite. Then insect excrement gets into this wound, causing unbearable itching. The more the baby scratches his head, the larger the wound and the more painful the irritation. As a result, children often:
- sleep is disturbed;
- concentration deteriorates;
- anxiety and nervousness appear;
- purulent wounds form in places where scratching occurs;
- dizziness is observed.
In more rare cases, the following may develop:
- allergy;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- fever;
- nausea;
- phobias.
Yes, sometimes children who have had head lice develop entomophobia (fear of insects) or parasitophobia (fear of parasites). In these cases, even after recovery, the baby will be haunted by the feeling that someone is crawling on him. Or he will react in panic to any insects. To prevent this from happening, it is important to correctly tell the child about the disease, without exaggerating.
Myths about lice infestation
Despite the fact that head lice is a well-studied disease, it is still associated with many misconceptions and myths. Let's look at the most common of them.
Lice can fly or jump over
This type of insect can neither fly nor jump, so they are transmitted only through close contact. By being at a distance with a person whose cleanliness you doubt, you can completely protect yourself from infection.
Lice can appear as a result of emotional shock
Parasites in the head area are the result of their transfer from another person. Infection does not occur due to a nervous breakdown, strong emotions, or in people weakened by illness if they have not been in contact with infected patients.
You can get rid of lice only by shaving or cutting your hair short.
For many years, when lice were found, boys' heads were shaved bald, and girls' hair was cut as much as possible. It was believed that only their absence would help quickly and reliably eliminate parasites.
Indeed, it is much easier to eliminate parasites on a head without hair. The most difficult task is to get rid of lice on long hair, which will have to be combed out very carefully. However, this does not mean that you cannot do without shaving and a short haircut. Modern means allow you to quickly get rid of unwanted insects in just one application without the need to use radical methods.
There is nothing more reliable than traditional methods
Lice have been known to man for many centuries. It is not surprising that during this time many ways to get rid of parasites have been found. But many of them are highly toxic and can be dangerous to humans, for example, causing scalp burns.
Modern remedies are much more effective and safer than folk remedies. They do not pose a risk of skin damage or poisoning, allergic reactions or other side effects.
You can get rid of lice using hair dye
Some chemicals that are part of hair dye can actually have a detrimental effect on parasites. But this does not mean that it is advisable to use them to get rid of lice. The effectiveness will be low, but there is a risk of damaging your hair.
Lice carry dangerous diseases
The parasites themselves are not carriers of dangerous diseases, in particular typhus. The risk of disease increases as a result of scratching the scalp, which creates wounds through which infection can penetrate. But in our time, infection with typhus is unlikely
Pediculosis is a disease of antisocial individuals
This is the main myth associated with lice infestation. Indeed, many people with low levels of cleanliness, such as homeless people or antisocial individuals, are affected by lice. But most of us rarely come into close contact with them.
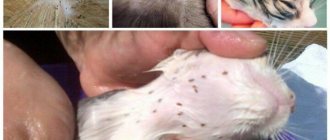
How can you tell if there are lice on your head?
Many people believe that the main symptom of head lice is itching of the scalp. In fact, itching appears only in 14-36% of cases, and sometimes does not occur at all. Moreover, itching cannot be considered as an early sign of lice. As a rule, the bites begin to itch only in the fourth to sixth week of infection. Therefore, it is better to diagnose pediculosis using the following recommendations:
- • Carefully check your child's or adult's scalp for lice. Remember that in some cases, lice can adapt to the color of the owner's hair. That is, if the host is blond, the insects can be pale brown, if the bearer is dark-haired, they can be almost black.
- • Inspect the hair close to the scalp for nits. Live nits are usually a deep brown color. The nit shells remaining after lice hatch are lighter in color. Despite the fact that nits are very small, they are quite easy to distinguish from dandruff or skin particles. The latter are easy to remove while the nits are tightly attached to the hair shaft.
- • Comb your hair with a fine comb. Keep in mind that lice move very quickly and are not easy to spot. Try this tip: grab a fine-tooth comb and a white sheet. Comb your hair thoroughly. Carefully inspect the sheet. There may be live parasites on it.
How to avoid infection
Unfortunately, there is no 100% protection against lice infestation. But if you follow certain precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of infection:
- • keep your head and body clean;
- • avoid close contacts with unscrupulous people and teach children this;
- • avoid sleeping on other people's bedding, especially pillowcases;
- • keep your clothes clean to prevent infestation with body lice;
- • avoid casual relationships - in order to prevent infection with pubic parasites;
Parents of a child attending kindergarten or school should regularly examine the child's head, without waiting for symptoms of infection (itching and nits on the hair) to appear. Early detection of parasites will help get rid of them as soon as possible.
If parents find lice on their child, they should notify the teacher or educator. The infection occurred in a children's group, therefore, to prevent further spread of infection, it is necessary to identify the source of infection. If this is not done, the child may become infected again.
It is easier for lice to switch to long, flowing hair, so girls should give preference to neat hairstyles - ponytails or braids.
Quintan
The carrier of this disease is body lice. Pathogens enter the human body through saliva or insect excrement.
The incubation period of the disease lasts from 7 to 17 days, symptoms appear abruptly. A person experiences:
- fever and severe chills;
- pain in the eyes;
- joint pain and general weakness;
- a papular rash appears;
- disruptions in the functioning of the heart, liver, blood vessels, spleen.
Recovery occurs as quickly as the onset of the disease. No deaths due to Volyn fever have been recorded and it occurs quite infrequently.
Folk remedies if infection does occur
If you find lice on yourself or your child, there is no need to be scared, much less make a tragedy out of it. Infection with parasites is unpleasant, but fighting them is quite possible. For this purpose, both pharmaceutical products and traditional methods are used.
Over the years, traditional medicine has accumulated many effective recipes that are traditionally used to get rid of unpleasant insects. Let us give examples of the most common and safest of them.
Combing
For this purpose, you need to use a special comb with fine teeth. This is a rather labor-intensive and time-consuming method. It involves thoroughly combing your hair strand by strand for 40-45 minutes. To enhance effectiveness, the comb is periodically moistened in vinegar.
The disadvantage of this method is that even with the most thorough combing, you can miss parasites, and even a small amount of them will provoke the disease again.
Vinegar
9% vinegar is dissolved in water in a ratio of 1:2 and the mixture is applied to the head, wrapped in plastic and a towel and left for 30-40 minutes. After this, wash your hair with regular shampoo and comb your hair with a comb to remove nits.
The disadvantage of this method is the risk of scalp burns.
Cranberry
Apply cranberry juice to your hair and wait half an hour. In an acidic environment, insects die, and nits peel off from hair more easily. This is a safe method, but not always effective enough.
Kerosene
Typically, a mixture of kerosene and a vegetable or soap solution was used to get rid of lice. The mixture is applied to the head for 1-1.5 hours, then rinsed off and washed with regular shampoo.
The kerosene-based mixture effectively removes parasites, but is highly toxic. It should be noted that there is a high risk of skin burns and negative effects on hair condition.
All home remedies can only be beneficial in the early stages of the disease, when the number of active individuals is small. But since lice are rarely found at this stage of infestation, more effective remedies should be sought for greater effectiveness.
Modern drugs against head lice are safe and reliable. They allow you to get rid of parasites quickly, reliably, without risk to health.
Effective treatment
A reliable and effective remedy for lice is the Paranit line of modern products. It allows you to get rid of parasites in just one application without the risk of side effects and allergic reactions.
A pediculicidal agent based on the active substance dimethicone and mineral oils blocks the respiratory tract of insects, which causes their death. “Paranit” is produced in the form of a spray, lotion, and shampoo. It belongs to the class of low-hazard compounds, so it can be used both for children (Paranit Sensitive from 1 year old) and for adults.
Advantages of the drug:
- • kills lice in 15 minutes;
- • non-addictive, repeated use is possible;
- • suitable for pregnant and lactating women - Paranit Sensitive is recommended;
- • does not harm hair;
After treating the head, rinse off the product and comb the hair with a comb, which is included in most forms. The product is very economical; one bottle is enough to remove lice from several people, so it can be recommended for family use.
Relapsing fever
The carriers of this disease are body lice and head lice. The causative agents of the disease are Borrelia.
Once in the human blood, bacteria cause disruption of the circulatory and nervous systems, as well as:
- fever with heat;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- disorders of the liver and spleen;
- disruption of the heart and lungs;
- hemorrhagic infarctions.
The immune system produces antibodies to fight bacteria, so the disease alternates between remission and new outbreaks. Stable immunity to the disease is not developed. There are vaccinations to prevent typhus.