Today, approximately 500 specific species of fleas live in the Russian Federation. The most common of them are those insects that live on pets (cats, dogs - Ctenocephalides canis, Ctenocephalides felis, etc.), as well as on rats or humans (for example, Pulex irritans).
About 30 species of these small pests live in private households or apartments. The size of 1 insect is 1–5 mm.
Most people do not know how the different types of fleas reproduce. This and other nuances are discussed in detail below in this article.
How fleas are fertilized and reproduce
How are fleas fertilized and reproduce? They have a specific reproductive system.
Mating of similar insects Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis or Xenopsylla cheopis lasts a maximum of 10 hours. They almost always copulate with each other after they have drunk a large amount of blood from a particular host.
What is the reproduction rate of various flea species (Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides canis, Xenopsylla cheopis, etc.)? After mating with the male, the female flea begins to lay eggs. Then she puts away up to 10 pieces at a time.
The total number of flea eggs from 1 female is more than 500 pieces per 1 life cycle. Such small pests copulate with each other in comfortable conditions.
Females breed in dust, on various rags, certain woolen products, genital crevices, dog kennels, clothes or other places hidden from prying eyes.
Flea eggs are covered with a white shell and also have an oval shape. They are similar to grains of rice, but are significantly smaller in size.
Appearance of a flea
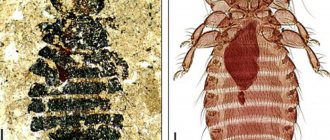
The adult specimen has an interesting structure. It is flattened on the sides and can be from 1 to 5 millimeters. Usually the female is larger than the male, and under favorable conditions her body can increase up to 1 centimeter. The body is covered with small bristle hairs, thanks to which the flea is easily held in the fur. The eyes are almost invisible, but there are special antennae with which the insect searches for food. Large paws allow it to easily move on the surface by jumping. There is also a special organ on the body that can recognize danger and the slightest change in temperature.
This is interesting: do fleas bite people?
The appearance of a flea has interesting features
Flea eggs are virtually invisible: almost transparent, barely reaching one millimeter in size. After hatching, the larvae reach 3 mm and are whitish-transparent.
After the larva goes through the molting stage, it begins to create a cocoon that is difficult to see. After the formation of the cocoon, the adult appears, thus beginning the adult life of the insect.
Flea lifespan
How long does the most common human flea, Pulex irritans, live? In a favorable environment, this insect lives for about 3 months.
During this period, 1 female of this bloodsucker lays 400–600 small eggs, and each such small pest makes about 100 bites. Only after this minimal “plan” is completed does this parasite die naturally.
An important condition for comfortable living of fleas is compliance with specific air humidity and temperature. Thus, rat-like insects Xenopsylla cheopis live quietly inside any room at 14 degrees Celsius and 55% humidity or more.
Bloodsuckers that live in a private household or apartment (Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis) also feel good there. However, they die quickly without immediate access to blood.
If these insects live in places with elevated temperatures, then all their phases of reproduction and development pass much faster. Thus, adults become very large.
Typically, flea larvae of pulex irritans degenerate into an adult in 30 days, while at elevated temperatures the fleas multiply and then grow much faster - in 7 days. The development of flea eggs ends after 14 days, and then for another 14 days this small pest is in the pupal phase.
These bloodsuckers, who live not in a warm home, but in nature, die quickly. After all, they are destroyed by the carriers themselves (dogs, cats, etc.). Then the animals bite the bloodsuckers out of their fur.
Also, many such bloodsuckers die from various infections. There are fleas that change several hosts during their life when the animal dies.
Fleas Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis immediately leave a dead dog or cat because they cannot feed on the blood of a dead animal.
How long do these insects live?
How long do various species of bloodsuckers live (for example, Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis, Xenopsylla cheopis, etc.)?
The lifespan of all types of fleas is directly related to these 3 factors:
- specific temperature regime;
- living conditions - apartment or street;
- air humidity.
On average, these small pests live 18–90 days. Throughout its life, 1 bloodsucker makes about 10 bites and, thus, it injures its owner.
Over the course of her entire life, a female flea lays about 500 eggs.
However, these bloodsuckers often die from various infections that they themselves spread, as well as from the teeth of a domestic cat or dog, from human hands or any disinfectant.
Can parasites live without food?
How long do fleas live without food? Approximately 2–3 months. the parasites Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis or Xenopsylla cheopis can live without consuming blood.
Especially those individuals that often bite humans. At the same time, they remain mobile.
However, if these insects do not feed for a long time, they do not reproduce in any way. After all, only after a hearty lunch do they mate with each other, and then the female flea lays many small eggs.
Do these bloodsuckers live in a private household or apartment if there are no animals or people there? Yes, but not indefinitely. Sooner or later they still die.
What determines the lifespan of a flea?
At the moment, it is the sharp change in air temperature that greatly affects the lifespan of fleas.
In addition to it, the lifespan of such bloodsuckers Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis or Xenopsylla cheopis is directly related to the following factors:
- air humidity. Low (but not too low) humidity is comfortable for bloodsuckers;
- source of food. Small pests that do not receive fresh animal or human blood for a long time live longer;
- the invariability of specific temperature and humidity conditions.
Bloodsuckers that live in areas with constant sharp changes in humidity and fluctuations in street temperature often quickly become numb. This significantly increases the life span of a flea.
An important factor for fleas is the number of offspring produced from 1 female, and not the rate of formation of flea larvae. As a rule, such a process is continuous.
Thus, while fighting various bloodsuckers, the lodger not only removes these parasites from the pet’s fur, but also destroys flea larvae hidden in secluded places.
Imago - adult individual
The cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis) is a wingless parasitic blood-sucking insect with complete metamorphosis (metamorphoses of appearance during maturation include a sedentary pupal stage).
Type: arthropods.
Order: fleas (Siphonaptera).
What do fleas look like on cats during the period of active reproduction? Adult individuals (imagoes), parasitizing on the skin of an animal, have a strongly laterally flattened body, consisting of an abdomen, a head and 3 pairs of powerful limbs. The length of a mature insect is 0.75-5 mm. The female is larger than the male and can reach a length of 15 mm during the period of gestation.
The segments of the insect's body are covered with a hard chitinous shell (cuticle) of a brownish-brown color and bristles directed backwards. The scutes of the segments overlap each other, which gives the adult a streamlined shape. This body structure facilitates the rapid movement of the imago between the hairs of the host animal, but complicates the physical removal of the insect (biting and combing out).
The body has no wings. In the chest area, 3 pairs of strong limbs are attached, with the rear pair of legs being more developed and having 2 sharp claws at the end. The five-segmented legs provide insects with strong jumping ability, allowing them to move long distances and actively crawl from pupation sites onto the fur of the host animal. Fleas have pronounced gender differences. In females, in addition to the anus, in the back of the abdomen there is a spermatheca; in males, there is a complex reproductive apparatus.
On the small head there is a pair of simple eyes, a piercing-sucking mouthparts with a proboscis. Holding itself on the animal's fur with the help of bristles, the insect subcutaneously inserts its proboscis into the host's body and feeds on its blood.
You can suspect the presence of fleas in cats based on the following signs:
- the animal is worried, constantly itches, tries to bite parasites out of its fur;
- the coat becomes faded, “dirty”, bald spots appear;
- Inflammation may develop at the bite sites, the skin turns red;
- on the stomach, behind the ears, in the armpits, under the head, both the flea individuals themselves and their waste products are visualized.
Since flea excrement consists partly of processed blood, a test on a wet piece of paper (the excrement turns the water brown) proves the presence of parasites.
Habitats of bloodsuckers in the apartment and in nature
Where do fleas live?
In an apartment, the parasites Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis settle and live for a long time in the following places:
- in bedding for domestic cats, dogs or other pets;
- on carpeted surfaces. Then flea eggs accumulate on the carpets;
- on sofa upholstery and outer covering of chairs;
- on a variety of soft toys for children;
- on old clothes;
- on mattresses;
- in bed linen;
- behind room or other apartment skirting boards;
- under the linoleum.
Outdoors, these small pests live close to a variety of animals (hamsters, rabbits, rats, etc.), which provide them with a source of food.
Fleas infest and lay their eggs and larvae in trash cans, basements, sand piles, bird nests, or inside the burrows of various animals.
Household fleas that live near people are divided into the following types of insects:
- bloodsuckers from pets - Ctenocephalides felis and Ctenocephalides canis;
- rat or mouse parasites - Xenopsylla cheopis, etc.;
- ground or basement bloodsuckers - for example, Vermipsylla alakurt;
- bed insects, etc.
Such bloodsuckers are small insects that cause a lot of problems for animals or humans. Their bites are very painful, after which itching and skin irritation form on the fur of a cat or dog, as well as on human skin.
In addition, the bloodsuckers Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis carry many unpleasant ailments. Therefore, it is important for a person to get rid of them in a timely manner - to destroy not only the fur of pets, but also to remove them from open or hidden corners of the apartment.
Can small pests live on the sofa and on clothes?
At home, the most common human flea, Pulex irritans, often lives on sofas, carpets, clothing or bedding. They also live behind room and other baseboards, as well as in wall cracks.
These small pests Pulex irritans like to live in comfortable conditions.
These bloodsuckers love to live and copulate on the warm carpet pile, where they sit out after satiation.
In ancient times, rich people made such anti-flea traps: they hung small pieces of natural concrete wool on their bare legs to lure bloodsuckers Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis, and then burned them.
Can bloodsuckers live on the body and on human hair?
Unlike various lice, human fleas Pulex irritans, which are infested in a private house or apartment, do not live on the skin or hair for a long time. After all, after being saturated with human blood, they immediately leave the human body.
If the bloodsucker is distracted while eating, it lingers for some time on the clothing on the underside.
Sometimes these small pests remain on summer or other clothing for 1–2 days. Then the Pulex irritans fleas periodically bite the person. However, they do not use humans as their daily hosts because little hair grows on them.
Laboratory studies by biologists have shown that bloodsuckers Pulex irritans live and reproduce quietly after consuming human blood. But more often, these small pests rarely attack people, and also do not copulate on their body.
The fact is that these insects are immediately very noticeable on human skin, and people immediately shake them off. In addition, it is difficult for them to move around a person, because their bristly small body is adapted to a comfortable life only on thick animal fur.
Human fleas, Pulex irritans, do not typically lay multiple eggs in hair. Firstly, these small pests often simply do not reach the head - they jump at most to ankle level.
And secondly, when they come into contact with a person, such bloodsuckers immediately bite him, and then immediately get out of the way.
Where do fleas live?
Strong, hardy and very tenacious, fleas are found on all continents, including Antarctica.
Most flea species live in temperate and subtropical climate zones of Europe, Asia and North Africa. Fleas are active at any time of the year, and their habitats are tied to the nests and burrows of warm-blooded animals living underground (gerbils, jerboas, gophers and other rodents), on the ground (wild and domestic animals: cats, dogs, rats, horses, cows , rams, camels, etc.) and above ground (birds, squirrels). Some fleas live on humans. The main hosts of most flea species are mammals, whose life at any time of the year is inextricably linked with the presence of shelter. Animals that periodically live in burrows and nests are less susceptible to flea attacks. Parasites do not live on the host’s body permanently, but jump on to suck blood and then descend into the nest’s litter. Some fleas are associated with artiodactyls and marsupials, which generally do not build or use nests and burrows. These types of fleas are stationary parasites that do not leave their hosts.
Fleas of both sexes suck blood, and the process can last from 1 minute to several hours. Fleas of some species are saturated with blood in reserve; as a result, they do not have time to digest everything, and the remaining blood is excreted in excrement.
Species of fleas that need frequent feeding live on the animal’s body constantly, and in between meals they wander in the fur of the owner. Fleas, which do not have the need to frequently suck blood, spend most of their lives in the substrate of the host's nest. In the absence of a food source, insects can starve for several months. Most flea species do not have a specific host choice and can exist on different animal species, with the exception of bat fleas.
How bloodsuckers get into an apartment
Will fleas live in the apartment in winter or not? Most likely not, because they are more likely to start in residential areas in the summer or autumn. At the same time, they often inhabit the lower floors of apartment buildings or private households.
Ground-like insects inhabit very dusty rooms or abandoned various buildings.
The fleas Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis or Ctenocephalides canis enter an apartment or private house in this way:
- from the entrance of an apartment building;
- enter the home from neighbors;
- they are brought in by domestic animals;
- They infect a certain home with various rodents.
If the basement is always damp, then flea breeding often begins in this place. After all, the most common human flea, Pulex irritans, loves dampness. Also, these small pests multiply quickly inside well-heated living spaces.
If a person does not ventilate his apartment for a long time, and there is always a lot of garbage in it and sunlight does not enter inside, then the bloodsuckers Pulex irritans quickly infest and multiply in this home.
Due to their small size, these parasites enter the home through small cracks in the apartment.
In addition, various species of fleas (for example, Ctenocephalides canis, etc.) do not always live on their host. They live comfortably on baseboards, floor crevices, linoleum, carpet, as well as on pieces of furniture, clothing or a variety of soft toys.
Video
Flea infestations of your pet and home
How to get rid
Sedentary worms are not difficult to destroy. Even the usual treatment of their habitats with boiling water or a steam generator will destroy all offspring. At any stage of their development, flea eggs cannot tolerate too high or low air temperatures. In winter, bedding and beds for pets can be periodically taken out into the cold. In summer - for drying in places exposed to direct sunlight. The death of the larvae occurs at temperatures of 15 degrees below zero and 45 degrees above zero. The reproduction stage of parasites stops at a temperature of 10 degrees below zero. Therefore, it is advisable to periodically wash and boil bedding, on which fleas prefer to lay eggs.
Why are these bloodsuckers needed?
At the moment, there are many species of fleas (Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis, Xenopsylla cheopis, etc.). Without these small pests, many animals would simply die out.
After all, these bloodsuckers are part of the specific food chain of various animals. Also, these bloodsuckers transfer various diseases from one carrier to another.
Thus, blood-sucking insects (fleas) are useful not for people, but for certain viral microorganisms.
The role of such a bloodsucker in nature comes down to the fact that it is a parasite. Thus, this insect shortens the life of its “carrier” (cat, dog, etc.).
In general, fleas have a positive meaning in nature, but they are more likely an epidemic. Often these small pests are the causative agents and first carriers of various epidemiological infections.
According to numerous laboratory studies by biologists, this bloodsucker simultaneously carries 30 types of specific viruses and bacteria.
Fortunately, not all such insects have the same ability to transmit various pathogens (plague, typhoid, etc.). It all depends on the diet, type and physical condition of the bloodsucker.
Ways of infecting an animal with fleas
An animal can become infected with fleas in the following ways:
- In direct contact with a sick animal.
- Walking in the same places where a flea-infested dog walks. Larvae and adult fleas that have fallen from the fur of a sick pet can wait for their prey anywhere: in the grass, on paths and bushes. The jump of an adult reaches up to 40 cm in length and the same height. Therefore, when passing by the place where a flea is waiting, a healthy pet has practically no chance of not becoming infected with this parasite.
- It often happens that flea eggs and larvae get into the house, sticking to the soles of shoes.
- Our Jackusik once picked up fleas just by walking through the entrance. As it turned out, the insects lived in the basement of the house.
Do not forget that even if your beloved pet is completely free of fleas, there is a high probability of re-infestation if, in parallel with treatment of the dog, the places where it is most often found, in which flea larvae and eggs can live, are not treated for these blood-sucking insects: the bed, toys, rugs, upholstered furniture and so on.
Life cycle of a flea
On average, fleas Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Ctenocephalides canis, Xenopsylla cheopis or other types of similar bloodsuckers live 1-1.5 years. Moreover, they remain in the pupal stage for a very long time - under not the most favorable temperature conditions, bloodsuckers remain in this state for several months.
Even when this small pest becomes an adult and enters the adult stage, it continues to live in its small cocoon and waits for a specific moment for further hatching.
The life span of a flea directly depends on their type and size of the flea, food and living conditions in the natural or other environment. Most often, such bloodsuckers live for about 6 months. During this time, this small pest bites its “carrier” more than 200 times.
The life cycle of a human or other flea consists of 4 stages of development:
- the birth of a bloodsucker in an egg;
- the appearance of flea larvae;
- transformation of an insect into a pupa;
- hatching from the pupa into an adult flea - “imago”.
These small pests, like certain other parasites, also go through the 2nd above-mentioned stage of development of a cat or other flea - the appearance of a larva.
What do the larvae of these bloodsuckers look like? The flea larva has sharp small jaws that gnaw the egg from the inside.
Larvae of small pests Pulex irritans die due to the following factors:
- low or high air temperature - about -50 or above +40 degrees Celsius, respectively;
- constant exposure to water;
- daily exposure to direct sunlight.
Development and nutrition of larvae
In general, the process of flea development from egg to adult lasts from three weeks to several months.
The eggs hatch into larvae after two days or two weeks. The length of the period depends on humidity and temperature conditions.
Externally, the larvae have the shape of white worms. Through the translucent body you can see the esophagus, which looks like a dark blotch. The length of flea larvae reaches 5 mm as they grow.
Parasites move like all worms - in segments. They cannot bite or drink blood like adults. Therefore, they get its dried remains, excrement of adults, and organic waste.
REFERENCE: The habitats of adults and larvae are noticeably different. If adults can often be seen on the animal’s fur or near its bedding, then the larvae can even breed close to the trash can.
While the larva is growing, it molts three times. Then a cocoon is formed. In terms of size, the flea pupa can be mistaken for a dark-colored speck. Its dimensions do not exceed 5 mm. Over time, the cocoon increases.
When an adult insect emerges from it depends on temperature conditions. Sometimes development can slow down during the pupal stage for up to a year or more. The young individual is initially light in color. With active feeding, it becomes stronger, and its integument darkens.
REFERENCE: Adults and pupae can withstand temperatures down to minus 40 degrees, but eggs and larvae die in light frost.
The life cycle of an adult lasts no more than three months. During this time, the flea makes about a hundred bites on average. At relatively low temperatures, fleas can live up to two years. In the cold, their growth slows down, and in the warmth, fleas become stronger and differ in size.
Insects of complete metamorphosis vary at different stages. Flea larvae are not similar in appearance to their adult relatives. They have a different food source and behavioral characteristics. When fighting fleas, you should treat not only the animal’s fur, but also the pet’s habitat.
This will help destroy the parasite eggs. After some time, it is recommended to re-process. Since fleas can spend a long time in the pupal state. And only after waiting for favorable conditions do they quickly develop, turning into an adult.
What do parasites eat?
What do the fleas Pulex irritans, Ctenocephalides felis, Xenopsylla cheopis and other species of these insects eat every day? These small pests have a small mouth proboscis through which they drink blood from a particular animal or person.
Compared to many other bloodsuckers, for these insects blood proteins are the main food.
Both females and males are parasites. After puncturing the skin, the bloodsucker releases special specific substances that simultaneously stop blood clotting and activate blood flow.
Blood addiction threshold
When eating the blood of their “carrier” (cat, dog, etc.), at a certain point in time, fleas pass a specific point, after which they then need blood every day. This is similar to a person becoming addicted to drugs or alcohol.
How long do fleas live without blood? Removed from an infected cat or dog and after 5 days of feeding, male fleas quickly die after 48 hours, and females - 96 hours.
Such bloodsuckers live 14 days after leaving their owner, if the initial feeding time was 12 hours. After all, then the threshold for flea dependence on blood is not reached.
How to kill flea larvae
You can get rid of parasite larvae using:
- aerosols and sprays;
- powders;
- dust;
- concentrated products;
- microcapsule preparations.
How to get rid of flea larvae - remedies and folk methods
You can get rid of insect caterpillars using the same means as against fleas. Spraying substances – sprays, aerosols. Particularly convenient in hard-to-reach places. "Dichlorvos", "Raptor", "Clean House".
Concentrated products that are diluted with water - “Executioner”, “Cucarachi”, “Tetrix”, “Karbofos”. It is used to treat furniture, floors, and baseboards.
Powders and dusts are the most effective preparations. They must be placed in the habitats of worms. They eat the insecticide along with their food - organic waste. The disadvantage is that it is difficult to use in hard-to-reach places - under the floor, for example. "Clean house".
Suspensions help get rid of parasites and their larvae in the shortest possible time. The popular Get product is effective and safe for people and animals.
Folk methods for getting rid of caterpillar parasites include:
Boric acid mixed with vegetable powder. Mistaking this for food, the worms become poisoned. This mixture is not dangerous for people, but you should still avoid inhaling it and wear a protective mask. It is necessary to treat the lower surfaces - floors, carpets, furniture, bedding and animal litter. Vacuum after 12 hours. Using bait. Pour water and any detergent into a bowl. Place overnight in a dark room with a low lamp on. Insects will jump into the light and become trapped.
Spray the affected areas with lemon water.
Herbs - wormwood, tansy, eucalyptus, cedar sawdust are useless against caterpillars. Finely ground salt. Sprinkle the floor and carpet well with it and leave for 5-7 days. Then vacuum it. Over time, salt crystals damage the soft body of the caterpillar through friction and it dies. Be sure to throw away the bag in the vacuum cleaner and buy a new one. Along with treating the premises, it is necessary to carry out disinfestation of pets.
How to get rid of flea larvae in cats and dogs?
Parasites do not reproduce in the fur of pets. They lay eggs in other places. Animals can be charged only in extreme cases. Bathing a dog or cat with regular, even non-insecticidal, shampoo washes out not only eggs and worms, but also fleas. Their paws are not designed to hold on to hairs or fur like lice.
For prevention, you can wash the animal with tar soap. It does not kill parasites, but it repels them with its smell.
Do flea larvae bite?
Caterpillars do not attack humans or animals and do not feed on blood from the victim. They eat organic waste and excrement, including that of adults. For warm-blooded creatures, at this stage of development, they are safe.
Briefly about the anatomical process of mating in fleas
The continuation of the genus of ectoparasites always depends on the female, since fleas reproduce by laying eggs. The features of this biological process can be explained by the physiological structure of the insect’s body.
Male fleas have two testes, at the end of each of which there is a reproductive claw - it is from this that the seed comes out when the female is fertilized. The female individual has a more complex structure of the reproductive system. Together with the ovaries, which are located in place of the uterine cavity, there are oviducts.
Mating takes a lot of time. It takes several hours for fertilization to occur. In this case, the contact between the female and the male lasts about 15-20 minutes - during this time the female climbs onto the partner’s back and absorbs seminal fluid from his genital claw.
Adult fleas have a rather unusual appearance: their body is flattened laterally, and its length can vary, depending on the type of parasite. Cat fleas grow up to 4-5 mm, and males can be much smaller than females. After feeding, the size of the fertilized female can reach 1 cm.