How can you get infected from mice?
Diseases transmitted to humans from mice can be very dangerous and even cause death.
For many centuries, mice and rats were carriers of dangerous diseases, plague and typhoid. However, in the 21st century, these terrible infectious diseases are almost no longer encountered. But the list of what you can get infected from mice, i.e. infectious and parasitic diseases is still quite long. Diseases acquired from mice
Salmonellosis
A disease caused by the bacterium Salmonella. A person can become infected through mouse droppings or by eating contaminated food. Mice carry salmonella and can transmit it to pets, and an infected person can spread the bacterium to healthy people.
Symptoms of the disease are similar to signs of intestinal disorders:
- within 6-48 hours after infection, dizziness and fever appear;
- vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea;
- liver and heart failure, urinary tract infection and even infectious-toxic shock can develop very quickly.
Salmonellosis is now successfully treated with antibiotics, but there are forms of it that require long-term treatment and recovery from the disease.
Leptospirosis
The causative agent of the disease is the Leptospira bacterium, which is transmitted through the urine of sick animals into the ground and water. This type of infection is carried by different types of mice, wild rats, cats, dogs, livestock and some wild animals. A person can become infected after direct contact with a mouse that carries the disease, or by swimming through water or dirty products.
Leptospirosis is deadly to humans and is most often found in countries with tropical and temperate climates.
Important!
In Russia, several dozen cases of leptospirosis infection are recorded annually in the summer. The Leptospira bacterium can remain viable for several weeks in water and soil under favorable conditions: high humidity and heat.
Clinical symptoms of the disease usually appear 2 weeks after infection:
- feverish condition;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, redness of the eyes;
- nausea and vomiting;
- inflammatory process in the kidneys, sometimes in the brain.
Treatment of leptospirosis is possible only in a hospital under the constant supervision of specialists, otherwise a serious complication may occur - Weil's disease, which manifests itself in renal and liver failure, possible bleeding and swelling of the brain, which can lead to death.
Tularemia
This disease is transmitted from mice to humans through blood-sucking pests: ticks and fleas that live in their fur. Having bitten a person, a tick transmits an infection to him, which is caused by the bacteria Francisella tularensis. In rare cases, tularemia can be transmitted through raw meat, causing mouth ulcers.
Signs of the disease: an ulcer at the site of the insect bite, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and in severe cases, chest pain, cough and breathing problems.
Diseases transmitted by rodents
Hemorrhagic fever
This disease is one of the most severe types; according to statistics, 5% of sick people die. Foci of infection in natural conditions are found in the Far Eastern regions of Russia and China. Fever is transmitted to humans by inhaling dust, which contains infection from a large number of field mice and rats, while working in the fields or at a construction site. Sometimes infection can occur through food contaminated by mice.
Distinctive signs of the disease: headaches, fever, digestive disorders, insomnia, severe thirst, redness and swelling of the face, possible hemorrhages on the skin, the kidneys are severely affected.
On a note!
Nearly half of people who suffer from mouse fever are subsequently treated for severe complications in the heart, lungs and brain.
Yersiniosis
Another name for the disease is pseudotuberculosis, which is widespread throughout Russia and is found in the Far East. Yersiniosis is very difficult to diagnose due to the wide variety of clinical manifestations.
The causative agent is Eirsinia - a bacterium that settles on fruits and vegetables, withstands frost well, and dies only when boiled. The disease can be contracted from wild and domestic rodents through urine, mouse and rat droppings.
Important!
Outbreaks of pseudotuberculosis are regularly recorded from late winter to early spring; most often, bacteria multiply well in warehouses and vegetable stores with high humidity.
Symptoms of yersiniosis may appear after 20 days: weakness and fever, muscle pain, abdominal and joint pain, sore throat, loss of appetite, digestive problems, skin on the upper body becomes covered with pimples.
Tapeworms
These parasites live in the bodies of mice and rats and can be transmitted through food or water that has come into contact with mouse feces. Worm eggs and larvae penetrate the human digestive system, become adults and begin to reproduce, which negatively affects human health.
Rabies
It is a fairly common infection and can also be contracted from mice. Without proper intervention, such a disease always ends in death. An attack by an infected animal can also be fatal for your pet, which in turn will bite you.
The pathogen does not make you wait long; soon the bitten person develops inflammation of the brain, which causes him to behave inappropriately and, as a result, will easily kill him.
Interesting! This infection is especially common in summer, during the dry season, when water is difficult to obtain. Its lack can cause pathogen activity. Such cases were often recorded in wood mice during the dry months.
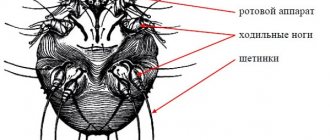
Bartonellosis
The infection is obtained from parasites that inhabit the fur of mice. The disease is often contracted by pets. It is important to take your furry friends to the veterinarian at least once a year, possibly even at the same time as your medical examination, to rule out any suspicion of infection.
Symptoms can be completely ambiguous, to the point that they can indicate inflammation of the heart muscle, so-called endo- or myocarditis. Antibiotics, previously agreed upon with the attending physician, fight the infection effectively.
Pseudotuberculosis
The person begins to suffer due to liver failure and intestinal damage. The infection enters our body through contact with the feces of rodents, which, if care is not taken care of at home, can rummage around in food packages and leave their feces there. The disease makes itself felt after a week.
Symptoms vary - it can be nausea, rash or severe fever. The disease mutates into pneumonia, polyarthritis and other dangerous diseases.
Hantavirus infection
Hantaviruses enter the human bloodstream after direct contact with contaminated saliva, urine and feces, as well as inhalation of dust containing mouse hair.
The symptoms are similar to those of ARVI and influenza, which complicates timely diagnosis.
Most often, hantavirus infection affects residents of China, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea and eastern Russia. Europeans are commonly affected by a type of hantavirus called Puumala. It is worth noting that in the western regions the disease appears to be in a relatively mild form.
Rat typhus
Also one of the ancient diseases that poisoned millions of people. The causative agent is an infection called rickettsia. This infection is not caused by the rodents themselves, but by the fleas that live in the fur of these pests. Symptoms of infection are:
- Enlargement of vital organs.
- Rising temperature.
- Pain in joints and muscles.
If they occur, you should immediately consult a doctor who will make a diagnosis. It is better not to delay contacting a doctor, as complications of the infection have serious consequences and sometimes death.
Yersioniosis
Yersioniosis or pseudotuberculosis is a disease that occurs in the Far Eastern regions of Russia. A large number of clinical manifestations make early identification of infection difficult and prevent a correct diagnosis. Massive outbreaks occur from the beginning of winter to spring, when high humidity is observed in fruit and vegetable warehouses - optimal conditions for the proliferation of pathogens.
Symptoms of yersioniosis appear after 18-20 days:
- sore throat appears;
- pain occurs in the joints, abdomen and muscles;
- there is a feverish state and weakness;
- problems with the digestive system.
The causative agent of pseudotuberculosis is a bacterium with high resistance to negative temperatures. It settles on vegetables and fruits and dies only when boiled. The most likely routes of transmission are through mouse droppings and animal body fluids.
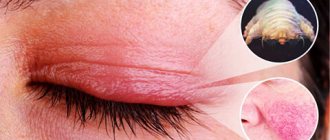
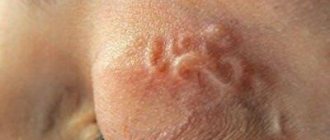
Fungal infections/ringworm
In medicine, these pathologies are classified as trichophytosis or microsporia. As the name suggests, the infection destroys the hair follicles under the skin and also disfigures the surface of the infected area of the epidermis. Most often, this disease is accompanied by severe itching of the affected skin.
The infection spreads quite quickly, so you shouldn’t delay seeing a doctor. Prevention includes careful protection of the home from pest mice, as well as annual diagnostics.
Diseases caused by arenaviruses
There are eight main subtypes of arenaviruses that cause similar diseases. Each of these seven types of virus affects only one species of rodent, living in a specific geographic region.
| № | Name of the disease | Type of mouse vector | Distribution region |
| 1 | Lymphocytic choreomeningitis | Ordinary brownie | The whole world |
| 2 | Lassa fever | Natal polymammalis | Central Africa |
| 3 | Luyo hemorrhagic fever | Not exactly defined | South Africa, Zambia |
| 4 | Argentine hemorrhagic fever | Calomys laucha | Argentina |
| 5 | Bolivian -//- | Calomus | Bolivia |
| 6 | Venezuelan -//- | Short-tailed reed | Venezuela |
| 7 | Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever | Field | Europe, Congo |
Fever pathogens are transmitted to humans during consumption of contaminated food or during agricultural work. Some of the arenaviruses can be transmitted from a sick patient to a doctor if the latter had direct contact with infected blood.
Arenavirus
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma. Although the main carrier is the domestic cat, mice are considered intermediate carriers of the virus. Most people may not experience symptoms for the rest of their lives. In 90% of cases, Toxoplasma is found in pregnant women during standard blood tests. The disease can lead to miscarriage, stillbirth and other health problems in the fetus.
Of course, these are not all diseases transmitted from mice to humans. But it is the above diseases that are most often diagnosed after contact with rodents.
Not everyone knows what diseases mice carry, otherwise people would be more careful when spring cleaning their dachas, working with soil or processing vegetables. For some housewives, information about what can be infected from mice becomes something out of the ordinary.
Diseases carried by rodents are severe and often lead to death.
Pet store mice can also become a source of dangerous infection.
Rat endemic typhus
Other names for this disease are typhus and flea typhus. Its symptoms are fever, headache, persistent temperature within 39-40°C, severe malaise and characteristic skin rashes.
In severe cases, the pathological process of typhus involves the meninges, which leads to certain nervous disorders. In addition, the disease is dangerous due to complications in the blood vessels, which can cause myocarditis, thrombophlebitis and cerebral hemorrhages.
However, today endemic rat typhus is successfully treated with accessible and inexpensive antibiotics, and its complications are prevented with the help of blood anticoagulants. Deaths are rare and occur mainly in developing countries.
It is important that fleas are the carriers of rat typhus. Neither ticks nor lice can carry this disease. The mechanism of transmission of its pathogen is not the same as in the plague: rickettsiae do not penetrate the human blood through the saliva of a flea, but are simply found in its excrement. A person infects himself when he scratches the bite, simultaneously crushing the flea secretions remaining on the skin. The bacteria themselves penetrate into microscratches on the skin, and from them into the blood, with which they spread throughout the body.
Is mouse droppings dangerous?
There is no need to explain why you should not eat the feces of any creature. Mice and rats are carriers of infections and dangerous infections. Their insides and, accordingly, everything they secrete is a deadly poison for humans and their pets. And if they have already appeared, then we must immediately begin to fight them.
The danger is not only that you can become infected yourself. Whether by accident or unintentionally, you may also infect your pets, friends, and loved ones.
Why are you standing there, swaying, you skinny girl? There is no Reelin in the brain - that's the whole reason
The shaking rat Kawasaki (SRK) was first described in 1988 in the Land of the Rising Sun [6]. The rat's trembling is caused by a mutation in the gene encoding the protein Reelin. This protein is responsible for the migration of neural stem cells - future neurons - during fetal maturation, as well as for some time after birth. In the adult brain, Reelin plays a large role in memory formation.
In Kawasaki rats, due to a mutation, the level of Reelin is reduced. Its deficiency leads to abnormalities in the structure of the brain, abnormal behavior and a trembling gait (Fig. 3). Interestingly, humans have a homologous protein that performs the same functions as in rats. Therefore, rodents with the described mutation are a good model for studying the role of Reelin in the pathogenesis of various brain malformations due to impaired neuronal migration. Thus, it has already been shown that schizophrenia and autism are associated with a lack of Reelin; Alzheimer's disease, on the contrary, is accompanied by its excess. This makes it possible to predict future human pathologies at the early stages of development and begin disease prevention.
Figure 3. Comparison of the organization of layers of the cerebral cortex in normal and pathological conditions. Drawing from Wikipedia.
Etiology (routes of infection)
There are several ways of contracting various infections that are transmitted through mice and rats. Almost all of them are reduced to direct contact with rodents or the results of their vital activity.
Interesting! Mouse fever cannot be transmitted from person to person. There is one bad habit through which, most likely, you will catch such an infection. Many people have the sin of biting their nails. An incredible amount of malicious infections accumulates underneath them.
Prevention is to wipe your smartphone with wet alcohol wipes, since it also collects a large number of infections during a day of use.
Airborne path
Infection through the respiratory tract, for example, from dust raised from the floor in an old house, on which rodents often defecate a lot. Often this exposure affects workers whose profession is directly related to contact with dusty, contaminated premises, warehouse workers, for example, or cleaners.
Prevention is inextricably linked with protecting the respiratory tract from raised dust, which contains particles of excrement and dried remains of animal urine. It is best to wear respirators when cleaning or working in such areas. Of course, it’s hard to imagine spending your entire working day with a huge mask on your face.
It may be easier to limit ourselves to the medical mask worn by surgeons. If you do come into contact with an infection, you should thoroughly treat the affected areas with water and make an appointment with a doctor for an examination.
Nutritional route
Direct consumption of products contaminated with mouse feces or contact of excrement with mucous membranes (in the eye, for example) and open wounds. Most often, excrement can be found in the same place as food or next to the trash can.
When these uninvited guests appear in your home, you need to carefully inspect all shelves, bags and packaging of food, as well as kitchen household items, since the path of the mouse may lie through it.
Prevention of nutritional contamination is simple: wash your hands and dishes more often and inspect food for contamination. And most importantly, get rid of the very source of infections: rats and mice.
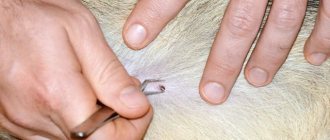
Bites and scratches
An infected mouse contains disease-causing bacteria and viruses on its teeth, in its saliva and under its claws. Therefore, scratches and mouse bites are often potential sources of infection for fever.
Contact with carcass
Mouse fever is an acute infectious disease, the active virus of which lingers in the tissue of a rodent even after its death. Contact of an adult with a mouse carcass without proper protection can cause infection transmission.
On a positive note. Mouse fever is a “one-sided” disease. This means that it is transmitted only from mice to people. An infected person is not the source of the mouse fever virus. Mouse fever infection is not spread from person to person.
But for all this time, a single case of transmission of the disease from person to person was recorded in Argentina during the virus outbreak.
Insect bites
This refers to the reptiles that inhabit the body of parasites, for example, fleas, which bite and leave infections in micro-wounds, just like ordinary lice. Thus, you can get infected through direct contact with an uninvited tailed guest, for example, by picking her up. This can happen if you start catching a mouse with your bare hands, without gloves or other skin protection.
Let's start with the fact that you shouldn't catch pests with your hands at all, as they can wriggle out and bite you. For this, there are a large number of homemade and professional traps that are sold in stores.
Prevention of this method of infection is simple - destroy rodents at the initial stage, do not let this incident take its course. Do not handle mice - it is very dangerous. In places where there is a large concentration of these pests, protect exposed skin. If contact occurs, immediately go to your doctor.
Contact with a dead mouse or rat
Even when these animals are caught in traps and die, they continue to be potentially dangerous to the human body. Infections living in the carcass of a dead animal continue to actively multiply. Therefore, you should not handle the corpse with your bare hands. Get some basic protective equipment, such as gloves.
Prevention is simple: make sure that there is no direct contact with the body of the dead rodent, as this can lead to unpleasant consequences. If this happens, go to the hospital, they will definitely help you.
Methods of transmission of diseases
As you know, not all diseases are transmitted by air and droplets, and the above can only affect a person if:
- bites from infected animals. Rats and mice can only scratch you when attacking, but this will already be enough to sound the alarm.
- Eating waste products of infected animals as food: fruits or vegetables that may have animal droppings or urine on them.
- Contact with waste from sick animals.
- Contact with domestic cats and dogs on which infected bedbugs and fleas live.
- Open wounds and infection.
- Frequent inhalation of fumes from the excrement of infected animals, as well as corpse fumes if a large rat or mouse has died somewhere in the house.
mouse sitting on a bun in the apartment
Diagnostics
Difficult diagnosis of the disease hinders its treatment. Experienced doctors recommend paying attention to the color of urine, as well as the quantitative indicators and frequency of urination (sharp changes in “habitual” indicators clearly signal illness).
Fever goes through four stages of its manifestation:
- Initial (nucleation phase or prodromal phase).
- Oligouric (phase of disease progression).
At this stage of the development of the disease in an adult, the kidneys are affected and hemorrhagic syndrome begins its active phase.
- Polyuric phase
- Convalescence stage (passive phase of the disease).
The second and third periods are distinguished by the obvious progression of the disease. New symptoms appear, which are characterized by intense development.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of mouse fever in adults:
- mouse fever is always accompanied by an increase in temperature;
- the mark is located within 400;
- severe dizziness and pain;
- the entire body is overcome by weakness and malaise;
- the mucous membrane of the pharynx becomes red;
- Pain in the kidneys and lumbar area becomes noticeable.
Sometimes the warning symptoms are supplemented by:
- decreased heart rate;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- acute reaction to bright light (the patient’s negative reaction to light fluxes is accompanied by the formation of a “grid” in front of the eyes);
- redness on the face, neck;
- the appearance of flat rashes in the axillary area and on the body.
initial stage
The initial (prodromal or febrile) phase is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- trembling and chills;
- headaches;
- muscle pain;
- blurred vision (eyes turn red);
- hemorrhagic rashes on the neck and shoulders due to vascular damage;
- inability to concentrate.
Symptoms of mouse fever in men at the initial stage are usually more pronounced than in women. During examination, the doctor very often detects Pasternatsky's symptom (pain in the kidneys when tapping). If the disease is advanced, then signs of meningitis may also be observed.
This phase takes 3-7 days and usually occurs 2-3 weeks after the bite.
Hypotensive phase
In addition to the above symptoms, the patient experiences tachycardia, hypoxemia (lack of oxygen) and impaired blood clotting. This occurs because the level of platelets in the blood drops. This condition can last for 2 days.
Oligouric stage
The oliguric stage (impaired kidney function) begins its active phase after 4-7 days and is accompanied by:
- a decrease in the patient's temperature;
- the appearance of sharp unbearable pain in the lumbar region;
- dehydration. The volume of urine decreases significantly (urine becomes reddish in color, and its daily amount fluctuates between 200-500 ml). Symptoms of dehydration include dry mucous membranes, sunken eyes, and decreased urine output in most people.
- lack of proper sleep;
- decreased appetite (possible severe vomiting);
- heart rate is not normal. His figure is significantly lower.
Hemorrhage becomes pronounced:
- possible hemorrhage into the skin (fragility of small vessels)
- various types of bleeding.
Despite the drop in temperature, the patient feels just as bad.
The duration of the stage is usually 3-7 days.
Polyuric (diuretic) stage
Symptoms:
- frequent urination (symptoms of diuresis) 3-6 liters per day;
- the proper functioning of the kidneys is impaired;
- eyelids and face swell;
- bothered by headaches;
- no sleep.
May take from several days to several weeks.
Convalescence stage (rehabilitation stage)
Signs:
- general health improves;
- urination indicators are normalized;
- a good appetite appears;
- pain in the lumbar region is less pronounced.
This stage lasts 4-5 days, and indicates an improvement, but not yet a complete recovery. In an adult, the process of convalescence lasts much longer than in children and can take more than one month to fully recover.
Complications – what to worry about?
Mouse fever is dangerous due to its side effects. Bacterial microorganisms can affect almost any organ system.
Extreme temperatures (usually greater than 105.8°F or 41°C) can be devastating. High body temperature can lead to poor performance of most organs. Such extreme heights of body temperature entail serious illnesses (for example, sepsis, malaria, meningitis).
The first symptoms of mouse fever in an adult are similar to acute respiratory illness, but the condition gets progressively worse. In this case, there may be pain in the joints, the bite site, and a rash on the arms and legs (flat, reddened areas).
Signal symptoms cannot be ignored. They are harbingers of a dangerous disease. Treatment is carried out in a hospital under strict bed rest, so the patient should immediately consult a doctor
Plague
The plague once claimed the lives of millions of people. But there is still a possibility of contracting this extremely dangerous infectious disease. This infection is spread mainly by rodents.
Severe disease affects the lymph nodes, lungs, and other organs.
Severe symptoms:
- fever;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- pain in muscles and head;
- dizziness;
- confused consciousness.