Description and differences
Cyclamen or strawberry mites (lat. Phytonemus pallidus) are distinguished by their smallest sizes (100-250 microns), so they can only be examined with a microscope. According to the classification, they do not belong to insects, but to arthropods of the arachnid class.
Mites have a translucent light yellow body and 4 pairs of legs; they live on young shoots of green shoots and in buds. Their main diet consists of plant cell sap. In addition to indoor flowers, they also attack garden strawberry and wild strawberry bushes, which is why they received their second name.
Ticks are capable of reproducing very quickly: each female lays 12-16 eggs daily, from which larvae appear within 3-7 days, they quickly mature and turn into adults within a week, ready to reproduce further.
The most important stimulator of their reproduction is dry air and warmth, which are a favorable environment for development. Therefore, the peak activity of cyclamen mites occurs in dry, hot weather in the summer months and during the heating period in winter.
Signs of damage to violets
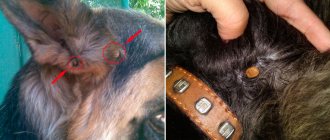
You can determine that parasites have settled on indoor plants by the following external signs (see photo of mites on violets):
- the appearance of a “dusty” coating in the folds of young green leaves, in the nascent buds and in the apical shoots of violets;
- the growth of the flower slows down and its deformation occurs, the leaves turn yellow, fade and become brownish-gray, then curl;
- leaves and petioles become brittle and dry;
- the buds wither and fall off before they have time to open;
- Long hairs appear on young leaves, which signal the appearance of the cyclamen parasite.
Cyclamen mite on violets
If such signs of mites are detected on violets, cyclamen and other house plants, it is necessary to immediately isolate them from other flowers. Then you need to start treating it.
How to treat violets against mites
Mite on violets: photo
If the plant has been attacked by mites, then controlling mites on violets will be problematic. It is better to take preventive measures in advance to ensure that the plant remains strong and healthy.
When purchasing plants, it is better to store the plant for some period of time separately from other types of plants until the acclimatization period has passed. The plant is a lover of cleanliness. Wilted flowers, rotted and yellowed foliage must be removed.
You should not bring cut plants into the room where the plant is grown. This applies primarily to roses, which are constantly accompanied by mites. As well as indoor plants, which can become a good place for insects to breed.
If you properly care for the plant, you can reduce the risk of encountering mites and prevent a long battle with mites on violets
The plant tolerates fertilization, watering, lighting and temperature conditions well - they should be kept at the optimal level. If you will be growing several plants, then the containers should be placed away from each other. This will help prevent the pest from moving from one plant to another.
Methods for controlling mites on flowers
The fight against cyclamen mite on violets can be done in various ways:
- use of folk recipes;
- use of chemicals.
Related article: Araliaceae family of plants: list, description, genera and species
The most popular folk remedy is to immerse the affected violet bush in hot water at a temperature not lower than 45°C. All affected parts of the flower must first be removed. The duration of the “bathing” is 15 minutes, but it is necessary to maintain a constant water temperature at the desired level.
After the water procedure, the bush is placed in a shaded place to allow it to recover for several days. Then it can be returned to its original place.
This article will discuss the smallest, and at the same time, perhaps the most dangerous pest in relation to indoor plants, the destruction of which is not an easy task. We are talking about the cyclamen mite. It is very difficult to recognize, because its size does not exceed the size of dust particles. Adults pose a huge threat to plants, and the larvae do not lag behind their parents, sucking all the vitality from the plants along with the juices on which they feed.
Do not be misled by the name cyclamen mite and think that it only affects cyclamen. No, unfortunately, it is widespread on azaleas, kalanchoes, fuchsias, saintpaulias, impatiens and a number of other plants. If the mite is detected too late, the plant cannot be saved. To prevent such situations, we want to teach you how to recognize this pest on your flowers.
You should know that the most conducive factor for the development of this pest is elevated temperature. The first sign of the appearance of a cyclamen mite is a dusty coating stuffed into the folds of young foliage, emerging flower buds, as well as the apical growth points of plants. Flower growth gradually fades, and the foliage becomes yellow and curled. Tick reproduction occurs very quickly, because it only takes three weeks for each new generation to appear, and if the conditions for this process are favorable, reproduction accelerates even more.
Having identified a plant affected by the disease, it must be immediately isolated from other flowers. There are flower growers who are trying to overcome this pest using the same methods as the strawberry mite - they immerse the entire plant in hot water, keeping it in it for fifteen minutes so that it warms up thoroughly. Before such a procedure, all affected parts of the plant must be removed. To kill ticks, only a temperature of forty-five degrees is enough. Make sure that the temperature remains constant throughout processing. After heating the plant, it must be placed in a shaded place and allowed to stay there for several days. Then you can safely return your pet to its rightful place.
| Actellik protection product Buy | Fitoverm Ogorodnik Buy | Fufanon 5ml Buy |
Sometimes the gardener has no choice but to throw away the damaged plant to prevent the spread of mites to other plants. If you see that there are still living parts left on the plant, you can try to graze it using cuttings. First of all, treat all cuttings with an acaricidal solution or rinse it in water with the addition of zoo shampoo.
It will not be possible to defeat ticks with the help of insecticides , since ticks are not insects. In addition, mites quickly become resistant to various drugs, so they have to be changed quite often. In addition, not every drug is capable of killing not only adult individuals, but also their larvae. Each treatment must be repeated with an interval of ten days, otherwise there can be no confidence that the tick has been completely destroyed. When purchasing a pesticide, be sure to check whether it affects tick eggs, as they remain viable for several years.
When using chemicals, it is imperative to take all precautions. To dilute the solution, you must prepare a bottle of clean water in advance. Under no circumstances prepare the solution in a food container! The addition of soap is strictly prohibited, since substances with an alkaline reaction are not compatible with avermectins. All prepared solutions should be used as quickly as possible.
Never treat flowers that are located in residential areas, as the effects of the drugs pose a threat not only to ticks, but also to people.
Return to list
Use of chemicals
The first step in treating mites should be the complete elimination of all affected parts of the plant and infected flower stalks. Then it is necessary to wipe the leaves and other green parts of the violet using acaricidal agents: Actofit, Fitoverm, Akarin, Agravertin. To completely get rid of ticks, the procedure must be repeated every 3 days, and then every 5 days. If the damage is severe, it is recommended to completely dip the violet bush into a solution with acaricide or avermectin agents.
Popular chemical insecticides have no effect on ticks at all. Arthropods very quickly develop resistance to the poison, and it does not destroy their eggs - they can remain viable for several years.
Chemical measures to combat ticks involve frequent changes of drugs to increase the effectiveness of the fight and reduce addiction to them. Therefore, treatment with acaricides should be carried out in several stages, changing the drug each time.
Such drugs as Kleschevit, Antiklesch, Neoron, Sunmite, Omite have a good effect on ticks. However, the treatment should be carried out in a non-residential area, and after spraying the violets should be covered with polyethylene for 8-24 hours.
Chemical pest control
Due to the high toxicity of these drugs, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment (respirator, gloves and protective clothing).
Precautions when processing violets:
- Do not prepare the solution in containers intended for food;
- there is no need to add soap, since alkalis are incompatible with avermectin products;
- all prepared solutions should be used quickly, and then the remains should be destroyed;
- Treatment cannot be carried out in a residential area - it is dangerous for the health of people and pets.
After processing and treatment, the violet bush must be quarantined, that is, isolated from healthy specimens. And only after 3-4 weeks, after the appearance of fresh shoots and the obvious absence of signs of mites, the flower can be moved to its usual place.
Basic methods of struggle
Traditional methods do not destroy mites on violets, but only stop their development. However, before treating violets against mites with chemicals, make sure they are properly cared for.
In order to completely rid Saintpaulias of pests, it is necessary to provide them with optimal conditions:
- temperature no more than +24 °C;
- air humidity more than 45%;
- lighting about 2500 Lux;
- daylight hours 10-12 hours;
- optimal watering;
- loose soil not overfed with nitrogen.
In cases where it is impossible to provide the flowers with a lower temperature and high humidity, it is necessary to provide the violets with weekly water treatments. Except for those specimens that have rotten leaves or the plant has lost turgor.
The leaf blades of adult violets should be washed from the underside with warm running water. You need to feel the small tubercles, which are nothing more than egg-laying sites, and remove them. The leaf plates bent inward must be carefully straightened and washed, as mites are located there.
Try to avoid getting water into the growing point. If this happens, blot the moisture well with paper napkins. Washed plants should be allowed to dry in a warm, dark room.
Running water helps get rid of tick nests.
But the most reliable and effective way to get rid of ticks is to treat Saintpaulia with acaricides. These drugs are divided into 3 groups:
- contact acaricides that penetrate the tick’s body through the skin;
- intestinal acaricides acting on insects through the mouth;
- systemic acaricides impregnate the roots and leaves of plants, making it poisonous to pests.
It is best to use a drug that immediately affects adults, nymphs and eggs. In this case, one tick treatment is enough.
It has now become possible to purchase drugs that are responsible not only for the complete destruction of pests in one treatment , but also do not pose a danger to people and pets. In addition, they are completely odorless. Here's how to treat violets against mites using the following preparations:
- Sunmite;
- Starmite;
- Mobento;
- Doni getter.
How to get rid of a tick if you couldn’t buy such drugs? In this case, it is necessary to take acaricides with different active ingredients , since mites very quickly acquire resistance to one drug.
In this case, violets will have to be processed at least 3-5 times every 7-10 days.
In addition to processing the Saintpaulia, it will be necessary to process not only the place where it was located, but also the other plants standing next to it.
Other types of ticks
Spider mites belong to the superorder Acariformes, with more than 1,200 species. The size of the parasites is less than 1 mm, the color is green in summer, and red in spring and autumn. The mite is a dangerous pest that attacks berry and fruit crops in the garden. Settles on the lower parts of leaves, covering them with small cobwebs. Small parasites suck out all the juices from violet shoots, which quickly leads to their browning and drying out. You can fight spider mites on indoor plants with acaricides and folk remedies.
The flat beetle mite on violets differs from others in its ovoid body shape and color (yellow-orange or brick). Such parasites settle on domestic ficuses, cacti, citrus fruits and other indoor plants. The leaves begin to wither, which leads to rapid death. Their danger lies in their adaptability to rapid reproduction at normal room temperature (+18...+24°C), due to which they are able to lay eggs all year round. Control is carried out using acaricidal chemicals.
Flat beetle mite on violets
Root or bulb mites - damage the underground parts of plants, mainly bulbous species (gladioli, tulips, orchids, etc.). They multiply at high air humidity, so the main preventive measure is to store the bulbs dry in a cool room at a humidity of up to 60%.
Description of ticks
Mites are the tiniest of houseplant pests and are therefore very difficult to control. Not only mature individuals, but also larvae extract juice from plants. Since they are very small (the largest ticks are approximately one millimeter in size), they are very difficult to detect. And while spider mites can still be identified by the presence of cobwebs, some are difficult to distinguish from dust.
Common varieties
Below are the most common types of ticks, with a brief description of them, which will allow you to correctly identify the threat and take appropriate measures.
Spider mites
Spider mites are a family of mites from the superorder Acariformes. Found in all regions, including Antarctica. More than 1270 species, 95 genera. Tiny mites, less than 1 millimeter long. There are two pairs of eyes, the legs consist of five segments. Herbivores (including dangerous parasites of cultivated plants) secrete cobwebs. The most famous member of the family, the common spider mite (Tetranychus urticae), is widespread.
The mites are quite small. The color of the female is green in summer, orange-red in spring and autumn. The eggs are spherical, colorless, small. Settling on the underside of young leaves and covering them with cobwebs, mites draw juices from them and within 2-3 days provoke browning, curling and drying.
Plants are completely entangled in cobwebs. In the presence of warmth and food, ticks multiply until mid-September, especially strongly in dry and hot weather. Coolness and rain have a painful effect on ticks.
Flat pliers
Flat mites are extremely small mites, with a body length of 0.25 to 0.4 millimeters. The body of the tick is ovoid, brick or yellow in color. The most commonly found are the Red Flat Mite (or Orange Flat Mite) Brevipalpus obovatus, and similarly the Cactus Flat Mite Brevipalpus russulus. They attack cacti, citrus fruits, ficus, aucuba and other domestic plants.
These very small parasites are very difficult to detect and also do not make webs. A sign of the occurrence of these pests is the slow drying of leaves, and subsequently the death of the plant. Flat mites can also pose a danger because at normal room temperatures from 18 to 24°C they can reproduce throughout the year.
Cyclamen mites
Cyclamen mites (Phytonemus pallidus) are microscopic mites that cannot be seen with the naked eye. The size of an adult female Cyclamen mite is approximately 250µ (microns), and eggs are no more than 150µ.
One female lays up to three eggs every day, the total number of eggs in a clutch is from 12 to 16. The eggs are formed within three to seven days, the larvae need another 3-4 days to develop before pupation, the tick lives in the pupa for no more than a week, after which completely ready for reproduction.
The cyclamen mite is a parasite of many ornamental shrubs and flowers, such as cyclamen, violets, begonias, gerberas, ivy, chrysanthemums, geraniums, fuchsias, delphinium, petunia, snapdragons, and others. It also affects strawberries. Because of this, it has another name - strawberry mite.
The cyclamen mite mainly lives in the growing points of young shoots and emerging buds. High humidity and warmth favor the emergence of cyclamen mites, reducing the formation of new generations to two weeks.
Preventing ticks
To avoid the proliferation of mites on violet bushes, you should create optimal and favorable conditions for them: timely feeding, watering, maintaining the required temperature and lighting conditions that are necessary for this species.
Weakened specimens are more likely to be attacked by parasites.
Experts recommend carrying out prevention in the form of regular bathing of violets in dry and hot times, and also not combining them in the room with other plants that are easily infected with parasites (roses, etc.).
Tips on how to properly wash violets:
- carry out the procedure only in running water, and not in a basin;
- hold the pot and violet in your left hand, holding the rosette between your middle and index fingers, and the other fingers holding the container itself;
- Direct a stream of water onto the underside of each leaf;
- do all procedures with your fingers, since sponges and rags only contribute to the spread of infection;
- try to prevent water from getting into the center of the outlet, onto the flowers and the container itself;
- if the violet is blooming, then it is permissible to use slightly warm water; if not, it is better to make it hotter (up to +40°C);
- Bathing should not be carried out if the leaves are rotten or there is a suspicion of rotting of the roots;
- you cannot bathe violets during the autumn-winter period in the absence of heating;
- After the water procedure, remove moisture with a soft paper napkin, moving from the center of the outlet.
general information
The cyclamen mite is almost impossible to see without additional tools, because... its body length reaches a maximum of 0.3 millimeters. The body is almost completely transparent, oval in shape, and has 8 legs. Typically, this pest builds colonies on the underside of the leaf, and when a large number of individuals are collected, they look like a layer of dust.
The cyclamen mite most often affects pelargoniums, cyclamens and violets (Saintpaulias). When attacked by the pest, the stems bend, the leaves curl, and the buds begin to wither. In Saintpaulias, infestation by the cyclamen mite is indicated by increased pubescence of the cuttings and leaves. High humidity increases damage to the plant and accelerates mite reproduction.
Preserving beauty: the main pests of cyclamen and how to combat them
Cyclamen is a rather delicate flower that requires especially careful care and increased attention of owners to the emergence of diseases and pests.
This plant, unlike many indoor counterparts, does not stop growing and flowering in the winter, therefore it is attacked by insects even in the winter months.
The rest of the article will discuss the main diseases caused by various pests and methods of treating them.
Cyclamen mite (Tarsonemus pallidus)
Home / Plant damage, pests and diseases / PestsIt mainly affects cyclamens, but is also found on ivy, schefflera, Uzambara violets, Kalanchoe, pelargonium and some other plant species. Loves moist air.
Tiny ticks. When there are a lot of them, they look like a layer of dust on the underside of the leaf. They affect cyclamen, balsam, pelargonium and saintpaulia. The affected plant's growth stops, the edges of the leaves curl, the stems twist, and the buds wither. Unlike the red spider mite, this pest prefers moist conditions. Spraying with conventional insecticides does not bring results. Remove affected leaves.
Cyclamen Mites - Compared to red spider mites, these mites are much more difficult to detect on plants because they are much smaller and hide in the corners of leaves. In addition, unlike the former, they prefer high air humidity and cooler temperatures.
It affects cyclamens, balsams, pelargoniums and gloxinias. This is a monophagous pest, i.e. it does not attack other plant species. It is impossible to see individual insects with the naked eye. A large cluster of mites appears as a layer of dust on the underside of a leaf. Unlike spider mites, this pest prefers to live in damp conditions. Symptoms of damage to the above plants are slow growth, wilting of buds, curling of leaf edges, and twisting of stems.
| Damage by cyclamen mite: curled, drying leaves | Abnormal growth may also indicate a tick infection. | Infection with the cyclamen mite disfigures the flowers and causes the buds to wither |
External signs of damage
Damage to plants by the pest is indicated by brown or dried out shoot tips, twisted, deformed and drying leaves. Saintpaulias have thickened leaves, and yuccas have a flour-like coating on the leaves. Spots appear on the flowers, they become deformed or dry out while still in buds.
| Cyclamen mite: can be accurately recognized under a microscope |
It is impossible to see individual insects with the naked eye.
A large cluster of mites appears as a layer of dust on the underside of a leaf. Unlike spider mites, this pest prefers to live in damp conditions. Symptoms of damage to the above plants are slow growth, wilting of buds, curling of leaf edges, and twisting of stems. Preventive actions
Practically only regular inspection and control, timely start of pest control.
Ways to fight
Pruning the affected parts of the plants; if the plant is heavily infected, it is better to throw it away.
You can use systemic insecticidal preparations - Neoron, Karbofos, Intavir, Decis, Fitoverm, but they do not always bring effective results. "Aldicarb" (or "Temik") is a potent granular preparation for application directly into the soil.
Based on materials from the book by Engelbert Ketter “Houseplants. Diagnostics. Treatment. Care"
Reasons for the appearance of insects on a flower
The most common reasons for the appearance of pests on cyclamen are improper care and unfavorable conditions for keeping it.
- Pests attack the flower when the temperature, lighting and humidity are incorrect.
- Excessive or insufficient watering of plants, an incorrectly selected substrate, the presence of drafts, and unbalanced feeding also provoke the appearance of insect pests.
- Pests often enter a room on a flower purchased in a store. Therefore, it is so important to inspect all parts of the plant for insects before purchasing.
- In spring and summer, indoor flowers are often taken out onto the balcony and loggia, where they can also become infected with insects.
- Soil for replanting taken from open ground can be dangerous for the plant, as it may contain pupae and larvae of pests.
Related article: List of flowering garden plants: names and photos, planting and care
Main parasites: description, photos and fight against them
Aphids are the most common and annoying pest, which can be relatively easily dealt with if you immediately notice and take all the necessary measures to destroy it. Most often, aphids enter the plant from the street through a window or window during ventilation.
This is a small wingless insect 1.4 - 2.5 mm in length. The color of their body can be gray, green, orange and black. Aphids feed on sap from the soft tissues of cyclamen.
Most of all, insects love buds, young leaves and shoots of flowers.
Signs:
- The flower stops growing.
- The leaves begin to deform and curl, turn yellow and fall off.
- Buds and flowers begin to dry out and fall off.
- A sticky coating appears on all parts of the plant. Thanks to this liquid, a sooty black fungus forms on the underside of the leaf blades, which greatly impairs gas exchange and greatly spoils the entire appearance of cyclamen.
Fighting methods:
- Isolate cyclamen from other indoor flowers.
- Wash the plant under running warm water, wipe the leaves with a damp cloth dipped in soapy water.
- Treat with insectids: “Aktara”, “Aktellik”, “Confidor” or “Agravertin”.
- You can spray the plant with folk remedies: decoctions of onion peels, orange peels, Christmas tree needles, nettles, yarrow, etc.
Shchitovka
This is a very small insect, similar to a drop, with a diameter of 2 to 5 mm with a hard shell (shield), due to which it is often compared to a turtle. This parasite spreads throughout the plant: stem, leaves, buds.
The scale insect sucks the juices of the flower, depriving it of the microelements necessary for proper growth and development.
Adult female scale insects are motionless, and young larvae without shields actively move, crawling from one plant to another. They are difficult to detect in the early stages of plant infection, as they hide in leaf axils and under leaves and camouflage themselves as specks.
Males of this species are even more dangerous. Thanks to their wings, they fly, easily covering tens of meters and spreading the population to neighboring plants. They resemble lumps of white dust.
Weakened flowers that have an excess nitrogen content and have a metabolic disorder due to improper care are infected with scale insects:
- improper watering;
- insufficient lighting;
- too hot or cold air.
Signs:
- A sticky honeydew appears on the leaves of cyclamen.
- The leaves turn yellow and dry out. You can find out about other reasons for yellowing leaves and lethargy of flowers here.
- Young shoots stop growing.
- Flowers and buds fall.
Fighting methods:
- Clean the flower from insects using a cotton swab soaked in soapy water. It is necessary to carefully process all parts of the plant and remove all shields.
- Apply insecticides - Aktar or Bankol and place the plant under the film for 1 hour.
- This procedure must be repeated every 3-4 days for two weeks.
- Place the infected plant in quarantine, and wash the infected area thoroughly with soap and water.
Thrips
Quite often, cyclamens are attacked by thrips, small black insects about 2 mm long, which in their shape resemble a spindle and have growths in the form of bubbles on their legs. They are also gray and brown.
These pests attack the entire above-ground part of the plant: buds, flowers, leaves and stems. These are very hardy and persistent creatures and very ancient; some entomologists consider them to be the ancestors of bedbugs. Their appearance is promoted by hot air and low humidity.
Signs:
- Dots, dashes, punctures and small light spots are clearly visible on the leaves and stems.
- The plant becomes discolored.
- A grayish-brown tint appears on the upper side of the leaf blades, and brown-brown spots appear on the underside.
- The edges of the leaves are deformed and curled (for what reasons can leaves curl and what to do about it?).
- Flowers and buds wither, dry out and fall off.
Control measures:
- The diseased plant must be urgently isolated and transplanted into a new substrate, having previously washed the roots and tuber in a light solution of potassium permanganate.
- Treat cyclamen with insecticides: Aktara, Intavir, Aktelik, Fitoverm, Karbofos. Treatment should be carried out once a week, 3 times a day.
- Thrips cannot stand the smell of garlic, so you can spray the plant with the appropriate infusion or simply place cut cloves next to it.
Cyclamen mite
Microscopic insect 1-3 mm long. It has a yellowish body and 4 pairs of legs. Appears when the air is too dry and the temperature is too high.
Signs:
- A dusty coating appears on different parts of the plant, which is clearly visible in the folds of young leaves and on flowering buds.
- The edges of the sheet plates are deformed.
- The buds wither and drop.
- The stems are twisted.
Fighting methods:
- All affected buds, flowers and leaves are removed.
- Chemical preparations: “Fitoverm”, “Inta-vir”, “Decis”, “Iskra”, “Neoron”, “Kinmiks” or “Karate”.
- Folk remedies: ash-soap solution, infusions of potato tops, citrus peels, onion and garlic peels and others.
If time has already passed and the mite has multiplied greatly, you can try to save the plant by cuttings.
Control measures
The greenhouse transparent mite develops much faster than the cyclamen mite. At high temperatures, in the first species the generation develops in 4-5 days, in the second - 7-8 days. This must be taken into account when drawing up a processing schedule. In non-residential premises, Actellik can be used - 2 treatments with an interval of 5 days. In apartments it is better to get by with Fitoverm (Aktofit, Akarin) - 3-4 treatments with an interval of 3 days. Spray especially carefully the growing points, the bases of rosettes, and the bases of leaf petioles. It is advisable to remove the flower stalks.
Text and photographs by Mishustin R.I.
Prevention of flower diseases
To avoid unpleasant situations with the appearance of pests on a flower, follow these rules:
- Carefully inspect existing and newly acquired plants for pests.
- Buy only healthy and high-quality planting material from trusted suppliers in specialized stores.
- Isolate damaged flowers from healthy plants.
- Disinfect dishes and soil before planting and replanting a flower.
- Significantly increase the resistance of cyclamens to pests by regular and proper watering, ventilation of the room, and proper feeding and lighting.