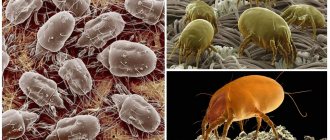
Some insects can cause an allergic reaction. One of them is dermatophagoides pteronyssinus or farinae. This is a dust mite. This is one of the most common parasites on the planet. Allergies are the result of substances that parasites secrete. The microorganism lives in a human home. The creature is also capable of triggering asthma. Ticks lead to the development of many other diseases. The insect feeds on dead particles of the skin. For a long time, a person cannot determine the cause of an allergic reaction. Examinations are required.
Dust mites live in every home
Who is dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and what is the history of discovery
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus is one of the subspecies of dust mites. Being around such a parasite can be dangerous. The insect increases the likelihood of developing diseases, including those of the respiratory system.
Dust mites were discovered in the 60s of the last century. This was done by scientists from Holland and Japan. Experts have tested how parasites affect patients.
Scientists have found that patients with a tendency to allergies have a reaction to mites. After this, a large-scale study of parasites was begun in order to be able to get rid of microorganisms.
Detailed description of the study
The main role of the immune system is to fight infectious agents (antigens). In some people, immune cells, for some unknown reason, perceive some harmless substances as foreign, similar to antigens, and produce antibodies to them. Such reactions are classified as allergic, and the substances that provoke this reaction are called allergens. They are proteins that come from plants or animals.
The first encounter with an allergen is not noticeable to a person, since in most cases no symptoms appear. At the same time, the formation of class E immunoglobulins, specific to a particular protein, occurs. Subsequent contact causes a chain of reactions with the release of chemically active substances - histamine, bradykinin. Their secretion provides the main symptoms of allergies.
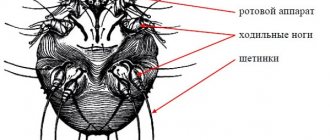
Among household allergens, one of the most common are proteins from house dust mites Dermatophagoidesfarinae (D. farinae). These creatures belong to the arachnids; their small size does not allow them to be seen without special equipment.
The basis of food for mites are scales of the epidermis (skin), which accumulate daily as part of house dust, settling on carpets, bedding, clothes, furniture and toys. These creatures reach their greatest numbers in the cold season, since during this period the temperature and humidity in the room are optimal for them, and people spend more time at home. However, in spring and summer, ticks still remain indoors.
These creatures are not carriers of diseases and are not capable of biting humans. However, D. farinae proteins, especially their excrement, are potent allergens. Contact with human skin and mucous membranes can cause the following symptoms:
- Redness and itching of the skin
- Itching and burning eyes
- Tearing
- Nasal congestion
- Itchy nose
- Nasal discharge
- Sneezing
Inhalation of dust mite allergens contributes to symptoms related to the respiratory system, such as:
- Dry cough
- Feeling of shortness of breath
- Chest congestion
House dust mites are considered to be provocateurs of bronchial asthma attacks. Manifestations of allergy to D. farinae can occur throughout the year, in contrast to reactions to pollen. This makes it difficult to identify the causes of allergies; laboratory confirmation of excessive activation of the immune system in response to contact with a certain protein is required. The ImmunoCAP method serves as the standard for diagnosing house dust mite allergy. It is highly sensitive and safe and is approved for use in pregnant and lactating women and small children. The test does not require discontinuation of treatment, which is convenient for people who regularly take therapy for allergies.
What are the general characteristics
This mite is the most common parasite. It is found everywhere and is not picky about external conditions. The pest is an insect that grows up to 0.5 mm in length. Each individual lives up to 3 months. During this time, the female lays up to 70 eggs.
Mites live in dust
In total, there are 100 subspecies of parasites. Representatives live in large groups. Insects do not exist alone. There can be 20-1000 individuals per 1 gram of dust. The numbers may vary, especially if good breeding conditions are present.
The greatest number of pests is recorded in autumn and late summer. The presence of a parasite in the house leads to an exacerbation of asthma.
Comfortable temperature for parasites is 18-26 degrees. Parasites leave behind the products of their vital activity. It is also an allergen. Ticks live in: pillows; mattresses; upholstered furniture; carpets; soft toys.
Read on topic:
Appearance of gamasid mites and the fight against them
14.11.2020
Signs of knemidocoptosis and ways to eliminate the disease
14.11.2020
Selection of the best tablets and anti-tick products for dogs in 2020, as well as drops, shampoos, sprays, collars
06.10.2020
Purpose of Reftamide and methods of its use
20.06.2019
Parasites occupy everything where particles of human skin can be found. Humidity for parasites to reproduce must be 60%. Children and people with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to allergic reactions.
Ticks do not penetrate the skin and do not parasitize humans. If you look closely, you can see the pest, but it's not that easy. The insect has a translucent body. Over the course of its life, the creature produces about 2,000 fecal particles.
Mites can cause allergies, especially in children
Description of ticks
Dermatophagoides Farinae (or Derm Farinae) is a dust mite. This arthropod is very small in size (from 0.1 to 0.5 mm) and cannot be seen with the naked eye. Parasites love moisture and warmth. They cannot tolerate too high or too low temperatures, exposure to ozone and ultraviolet radiation.
Derm Farinae mites cannot live long on the human epidermis. They live in large numbers on carpets, upholstered furniture, plush toys, and woolen blankets. These surfaces are dust collectors. The parasite feeds on exfoliated human skin cells found in house dust.
Another type of dust mite, Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus, is often found indoors. What kind of parasite is this? This arthropod is otherwise called the feather mite. It can live not only on dusty soft surfaces, but also on feather pillows and mattresses. However, feather mites can also live on bedding with synthetic fillers. After all, particles of human epithelium also remain on their surface, which serve as food for the parasite.
The mites Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides Farinae live in large groups. 1 gram of house dust can contain from 20 to 10,000 parasites. Their number increases in the summer-autumn period. A parasite concentration of more than 500 individuals per 1 g of dust is considered dangerous and can lead to allergic reactions
What are the reasons for the appearance
It is believed that the parasites originally appeared in the nests of migratory birds. Over time, the parasite spread to chickens and geese. It is for this reason that ticks often enter a human home along with feather pillows.
The insect enters human housing along with clothing and furniture, as well as bedding. A person can bring parasites on himself after visiting hotels, kindergartens, beauty salons and various public places.
The causes of parasites also include:
- keeping pets;
- irregular ventilation of clothes;
- lack of personal hygiene.
The appearance of the parasite often goes unnoticed.
What are the symptoms of an allergy to parasites?
Most often, dermatophagoides pteronyssinus or farinae leads to allergies. This is the most common complication. It can occur in different forms of severity, each of which is described in the table.
| Lightweight | There are minor rashes on the skin. Itching appears periodically. Worried about weakness and loss. Symptoms are often present at the site of contact with the allergen. Other parts of the body are not affected. Signs may become more intense after just a few minutes. Ignoring the current state is strictly prohibited. |
| Average | The itching becomes widespread and affects all parts of the body. Breathing is impaired. |
| Heavy | Symptoms of severe form include: • widespread itching throughout the body; • spontaneous and severe swelling of the body; • painful sensation in the abdomen; • colic in the abdomen; • gagging; • bowel dysfunction; • dizziness; • loss of consciousness. |
One form of gravity can instantly be replaced by another. Treatment and consultation with a doctor should be immediate.
If you have any alarming symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor immediately
What are the varieties?
There are 3 categories of dust mites. The first group lives, feeds and breeds in the dust. Insects feed on skin scales, as well as microflora particles. Some of the individuals consume mold and human products. It is these representatives that often cause allergic reactions in agricultural workers.
The number of such ticks began to increase rapidly since the 90s of the last century. This is due to the storage of products in unsuitable premises.
The second category of insects is predators. The basis of nutrition is parasites of the first group.
There is also a 3rd category of mites that fall into dust randomly. Reproduction is impossible. They do not cause an allergic reaction, and they do not settle in bed linen. They pose no danger.
Dust mites: how to get rid of them at home?
To control the number of ticks, various methods are used: mechanical, physical, chemical.
In any case, treatment against ticks should be carried out after a specialist has examined the apartment and found out the exact number of ticks. The use of household chemicals in the apartments of patients suffering from allergies should be extremely careful.
Special acaricidal products are produced that are recommended for the fight against house dust mites. A specialist can help you choose the right one. Such preparations guarantee the rapid death of all ticks in the apartment.
Washing bedding at high temperatures and baking them in the summer sun helps in the fight against ticks. Weak solutions of bleach or salt, which are used to treat surfaces, are also recommended as folk remedies.
So, we found out that it is Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. This is the most common type of house dust mite. The study of this issue remains relevant for patients who have a similar type of allergic reaction in the body.
What is the danger to humans?
Ticks pose a serious danger to humans. The insect produces large amounts of protein and other substances that are allergens. Upon contact with the waste products of the parasite, there is a possibility of developing:
- allergic rhinitis;
- atopic dermatitis;
- bronchial asthma.
In rare cases, angioedema may occur. After contact with the parasite, the human body begins to produce antibodies. Additionally, conjunctivitis occurs. There is lacrimation and fear of light.
Ticks can cause asthma
In the morning and evening, symptoms similar to bronchial asthma appear. The patient is bothered by a severe cough and difficulty breathing.
Allergen d1 - house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus, IgE (ImmunoCAP)
Quantitative determination in the blood of specific antibodies of the immunoglobulin E class that appear in the presence of an allergic reaction to the house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus.
Synonyms Russian
Specific immunoglobulin class E for the pyroglyphic mite D. pteronyssinus; pyroglyphid mites.
English synonyms
ImmunoCAP d1 (House Dust Mite, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus), IgE; Allergen d1: Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Mites), IgE - ImmunoCAP; Specific immunoglobulin E to the D.pteronyssinus, Spec. IgE to the dust mite D.pteronyssinus (serum).
Research method
Solid phase immunofluorescence (ImmunoCAP).
Units
kUA/l (kilounit of allergen per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
An allergen is a substance that causes an allergic reaction. In atopic diseases, allergens stimulate the formation of IgE class antibodies and are causative factors in the development of clinical symptoms of allergic diseases. The detection of specific immunoglobulins E in the blood for a specific allergen confirms its role in the development of type I allergic reaction (reaginic), and therefore allows us to determine the possible “culprit” of the allergy and prescribe appropriate therapeutic and preventive measures.
House dust mites are one of the main sources of indoor allergens and make up the majority of house dust. Clinical manifestations of allergies to house dust mite proteins are symptoms of year-round allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma, and atopic dermatitis.
These arthropods, about 0.3 mm in size, are not visible to the naked eye. House dust mites feed on human dander, which accumulates in mattresses, pillows, floors, carpets, stuffed toys and upholstered furniture. Their quantity is maximum at temperatures above 20º C and relative humidity above 80%. For people sensitized to house mites, the optimal indoor humidity should be no more than 50%. Among the representatives of domestic mites, the most significant for the development of allergic reactions are Dermatophagoides farinae and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. D. pteronyssinus prefers a more humid environment than D. farinae. In tropical countries, the Blomia tropicalis mite is an important source of allergens. It is believed that about 50% of patients with allergies and about 80% of children with bronchial asthma are sensitized to dust mites. With sensitization to the D. pteronyssinus mite, cross-reactions with allergens from D. farinae and other pyroglyphid mites, as well as with proteins of some crustaceans, are possible.
The purpose of this study is to determine specific IgE to D. pteronyssinus mite allergens using the ImmunoCAP method. Allergy diagnostics with ImmunoCAP technology is characterized by high accuracy and specificity, which is achieved by detecting even low concentrations of IgE antibodies in a small amount of the patient’s blood. The technique is revolutionary and is based on the immunofluorescent method, which allows it to increase sensitivity several times compared to other diagnostic methods. WHO and the World Allergy Organization recognize diagnosis using ImmunoCAP as the “gold standard”, as this technique has proven its accuracy and consistency in independent studies.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of sensitization to the dust mite D. pteronyssinus in patients with allergic diseases (allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis);
- to assess the risk of developing allergic reactions to the dust mite D. pteronyssinus;
- to resolve the issue of allergen-specific immunotherapy.
When is the study scheduled?
- If you have the following symptoms indicating an allergic nature upon contact with dust: redness and itching of the eyes, lacrimation; rhinorrhea, itching and/or nasal congestion; redness and itching of the skin, rash; laryngeal swelling, cough and bronchospasm;
- with polyvalent sensitization;
- with questionable results of skin testing and provocative tests;
- when deciding whether to conduct ASIT.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 0.00 - 0.35 kU/l.
| Indicator value, kUA/l | Class | Level of allergen-specific IgE antibodies |
| 0 – 0,35 | 0 | Absent |
| 0,351 – 0,69 | 1 | Short |
| 0,70 – 3,49 | 2 | Average |
| 3,5 – 17,49 | 3 | High |
| 17,5 – 49,99 | 4 | Very tall |
| 50,0 – 100,0 | 5 | Intensely high |
| More than 100.0 | 6 | Extremely high |
Reasons for increased levels of specific IgE:
- the presence of allergic reactions to the dust mite D. pteronyssinus;
- allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis caused by sensitization to dust mite D. pteronyssinus allergens.
Reasons for decreased levels of specific IgE
With repeated research (over time), the level of specific IgE may decrease for the following reasons:
- limiting or eliminating contact with the allergen;
- carrying out treatment, ASIT.
Cross reactions
Cross reactions are allergic reactions to components of the same structure present in different allergens. To avoid unnecessary tests that are unnecessary for the patient and to individually select possible cross-reacting allergens, consultation with an allergist is necessary.
Important Notes
Performing this study is safe for the patient compared to skin tests (in vivo), since it eliminates the patient’s contact with the allergen. Taking antihistamines and age characteristics do not affect the quality and accuracy of the study.
Also recommended
[21-673] ImmunoCAP ISAC allergy chip (112 allergy components)
[21-675] Fadiatope
[21-676] Fadiatop for children
[08-017] Determination of total immunoglobulin class E
[21-707] Allergocomponent d202 - House dust mite nDer p 1, IgE (ImmunoCAP)
[21-708] Allergocomponent d203 - House dust mite rDer p 2, IgE (ImmunoCAP)
[21-709] Allergocomponent d205 - Tropomyosin, house dust mite rDer p 10, IgE (ImmunoCAP)
[21-632] Allergen h1 - house dust (Greer), IgE (ImmunoCAP)
[21-633] Allergen h2 - house dust (Hollister), IgE (ImmunoCAP)
[21-631] Allergen d2 - house dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae, IgE (ImmunoCAP)
[21-662] Mixture of household allergens hx2 (ImmunoCAP), IgE: house dust, house dust mite D.pteronyssinus, house dust mite D.farinae, red cockroach
+ determination of specific immunoglobulins class E for other allergens
Who orders the study?
Allergist, pulmonologist, otorhinolaryngologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist, pediatrician, therapist, general practitioner.
Literature
- Pittner G, Vrtala S, Thomas WR, Weghofer M, Kundi M, Horak F, Kraft D, Valenta R. Component-resolved diagnosis of house-dust mite allergy with purified natural and recombinant mite allergens. Clin Exp Allergy 2004;34(4):597-603.
- Thomas WR, Smith WA, Hales BJ. The allergenic specificities of the house dust mite. Chang Gung Med J 2004;27(8):563-9.
- Mary CL, Lopez-Malpica F, Diaz AM. Analysis of cross-reactivity between group 1 allergens from mites. PR Health Sci J 2008;27(2):163-70.
How to fight
First of all, it is recommended to regularly wet clean the house. The struggle will bring a positive result if:
- furniture made of fabric will be replaced with analogues made of leatherette;
- All carpeting will be removed from the house;
- things are regularly washed and dried outside;
- the indoor microclimate will be normalized;
- All shoes are cleaned regularly;
- Feather pillows are periodically replaced;
- all soft toys will be removed from the house;
- a vacuum cleaner with a water filter is used.
Be sure to ventilate the room.
How dust allergies occur due to mites, see this video:
What is a mite allergy?
Approximately 150 species of dust mites have been discovered, preferring damp, dark and warm corners of living spaces. Dust mites of the species Dermatofogoides of the genus farine and pteronyssinus are the most common house mites. Moreover, the farina mite is resistant to low indoor humidity. About 80% of the total number of mites that cause allergies are precisely the varieties “farina” and “pteronissinus”, which prefer the home’s beds and carpets. Allergy to farina mites and pteronyssinus mites is an immune reaction of the body to the type of excretory secretions of dust mites, which include: larval skins, secretion of lateral glands and excrement.
What kind of prevention
For prevention it is recommended:
- throw away all old and unnecessary things;
- wash the floor frequently;
- take out everything that collects dust;
- ventilate the room;
- replace all feather sleep products with those consisting of synthetic materials;
- monitor the humidity level;
- bathe pets periodically.
Parasites can appear in any home. For this reason, it is important to adhere to prevention to reduce the likelihood of ticks.