Tick activity period
Ticks begin to wake up from hibernation in early spring and remain active until autumn. Previously, the first complaints were received around the end of April. But last year, the first complaint of a tick bite was received in March. Many associate this with the coming global warming. We don’t know whether this is true or not, but it is a fact that ticks began to wake up earlier.
Despite their early activity, ticks still prefer the sun. The ideal air temperature for them is 20 degrees. At night they hardly hunt, only certain species. For example, representatives of the ixodid group. They can migrate over short distances and do this at night.
It is ixodid ticks that are carriers of dangerous diseases.
But despite the love for warm temperatures, spring is still the peak. Waking up from hibernation, you need to take care of food. And for them, food is you and me. That's why attacks are very frequent. In addition, ticks do not favor hot weather. Ticks prefer a moist environment. Therefore, if there has been a light rain recently, this is not the time to go for a walk in the forest. It is at this time that they crawl out of their hiding places.
Periods of maximum tick activity
Ticks are very tenacious; they are able to withstand difficult climatic conditions, provided that the air temperature is above +6-8 °C. Parasites are only afraid of frost. No, at sub-zero temperatures they do not die - they go into hibernation, as they become unable to lead an active lifestyle. When frost is replaced by warming, ticks wake up and begin to actively search for food sources.
How dangerous are blood-sucking insects?
- Ticks can transmit dangerous diseases, and this does not depend on the time of year - you can “catch” tick-borne encephalitis or borreliosis both in May and October. Many tick-borne infections can have serious consequences, sometimes resulting in death. Not all ticks are infected with dangerous infections, but it is impossible to determine this by the appearance of the parasite - the presence of infection can only be confirmed or refuted in the laboratory. That is why doctors recommend not throwing away a tick if you managed to get it, but bringing it in for analysis - if it is infected, you can take timely measures to protect your health.
- In addition to infection, you can expect other troubles from ticks - allergic reactions, irritation and inflammation. Ticks have a piercing-sucking mouthparts, thanks to which they pierce the skin and stick to a blood vessel with their proboscis. The bite itself is quite traumatic, although painless (together with saliva, the parasite releases an anesthetic substance), so the skin can become irritated, inflamed, and if parts of the tick’s body are not removed in a timely manner, suppuration can occur.
Arthropod bloodsuckers do not have visual organs, but this does not at all prevent them from perfectly orienting themselves in space and easily finding victims. Ticks have sensitive receptors that respond to odors and heat - when a potential victim appears nearby, the parasites become active and raise their four upper legs - this is a posture of readiness to cling to a passing victim. As soon as a person or animal is nearby, the tick clings to clothing/fur and begins to crawl along the victim’s body, looking for a suitable area to bite. This search can take from a few seconds to 2 hours. Males quickly eat enough and fall off on their own, and females can drink blood for up to 10 days, all this time being on the “host’s” body.
Table of tick activity by month
| Months | Tick activity | Phase description |
| April | 100% | First phase of activity. Ticks begin to wake up after hibernation when the air warms up to +6-8 degrees. It is impossible to name the exact date of mite activation; it directly depends on temperature and climatic conditions. After hibernation, bloodsuckers are most aggressive because they are hungry. They begin to actively search for the food they need for development and reproduction. |
| May | 98 % | |
| June | 87 % | In summer, the activity of bloodsuckers decreases, and temporary physiological rest occurs. Parasites can attack people, they just do it less often. Since they do not like heat, they usually wait for victims in the shade. |
| July | 75 % | |
| August | 85 % | |
| September | 92 % | Second phase of activity. During this period, the aggressiveness of ticks increases again, as they prepare for hibernation - before winter they need to be completely satisfied, so the parasites search for food with diligence. |
| October | 97-100 % | |
| November-March | <10 % | Hibernation. Provided that the air temperature does not rise above +6 °C. |
Important: a tick can bite even in January under certain conditions. Parasites can get into the heat, warm up and begin to become active - for example, ticks can be brought into a house on a Christmas tree from the forest, and parasites can also hide in the hay that is stored in villages for the winter.
When to be wary of ticks
When do ticks appear? As we have already found out, ticks appear in the spring and you should be wary of them until the end of autumn. But she does not lead an active lifestyle throughout the warm period. The life of a tick is cyclical, each time moving from one stage to another, the tick needs blood for food and growth. Therefore, there are months that are especially dangerous. During their short life, ticks go through several stages: embryo, larva, nymph and adult. The embryo does not need nutrition; the female provides it with the necessary supply of food, and the larva feeds on the blood of small rodents.
The tick is a carrier of the virus , but it is initially born healthy.
Those. it can become a carrier if it bites a victim with the virus. But there is another way of infection - through a female who has laid a clutch. In this case, if the female tick has already been infected, then the larvae are also infected. They cannot attach themselves to humans, but they can be eaten by livestock. In this case, it will become infected and if you eat raw food from an infected animal, you risk getting sick. The development of different stages of a tick takes time. First of all, the speed depends on climatic factors: temperature and humidity. If the larva does not have time to be satisfied before the onset of cold weather, then it simply leaves for the winter, hiding in a nest or rotten foliage. The peak activity of individuals that have not reached sexual maturity is autumn. If they did not have time to attack the victim before winter, then spring is such a period. In this regard, summer is not really the peak of activity. But this applies to the middle zone. After the larva has become a nymph, development to a mature individual occurs very quickly.
On average, the entire development cycle can take up to 3 years. During these three years, the individual is not particularly dangerous to humans; the little thing prefers to parasitize small animals. But this does not mean that under favorable conditions they will not attack a person. Plus, don't forget about the risk of infection from livestock.
When are ticks especially active?
Ticks “wake up” and become most active when the first warm days after winter arrive.
If the soil has warmed up to 5 degrees, we can assume that the peak of parasite activity has begun. Regardless of the regions in Russia, the most dangerous months for visiting forests and forested park areas are April (from the very beginning), May and June. It is during this season that mass mating and reproduction of ticks occurs, when they especially need “feeding” in the form of blood. It is important that tick activity is not so much a calendar phenomenon (clear time limits for activity cannot be established) as a weather phenomenon. Warm (from 7 to 22 degrees) days and sufficient humidity (preferably about 80%) are the ideal time when ticks feel comfortable
This is the average temperature that is maintained in Russia during the period from the second half of April to June. Ticks do not like extreme heat and cold, so their activity at this time is somewhat lower. But before the rain, when it’s not so hot and the humidity is just right, going into the forest is fraught with consequences.
In addition to the May period, there is also a second peak in the fall - in August-September. However, few people think seriously about it, since this period is not so dangerous for several reasons:
- Most ticks are already full; their reproduction process takes longer;
- the number of parasites has noticeably decreased thanks to birds happily feeding on ticks.
In general, regardless of the stage of development of ticks, it is quite possible to be attacked by them in the period from April to October, the main thing is that the weather is suitable. If the spring is early, ticks become active earlier; if the Indian summer is prolonged, the parasites will not go to winter for a long time. This is especially noticeable in taiga regions and forest climatic zones.
If we talk about the time of day when ticks are more active, then it is morning (around 8-9 hours) or evening (19-22 hours).
Precautions when visiting dangerous areas and places
You can pick up a tick anywhere, even in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kyiv, Minsk or any other city. But most often they occur:
- in a forested area;
- in a forested area;
- on a summer cottage.
For forest walks and outdoor recreation, choose closed clothing; the collar of your outerwear should fit close to your neck, and it is advisable to tuck in your T-shirt. Sleeves and trouser legs should be long. It is better to wear rubber shoes, preferably high boots. Cover your head with a headscarf or cap. If the clothes are light, then it will not be difficult for you to see a tick crawling on it.
For stops and parking in the forest, choose dry pine meadows without tall thickets. Don’t sit on the ground, much less lie down on the grass. Before and after spending the night, be sure to inspect your entire body.
From time to time, inspect yourself and your loved ones for the presence of bloodsuckers. This issue should not be taken lightly. If you find a tick that has not yet attached itself, remove it from yourself. If it has stuck, then the faster you remove it, the less the risk of contracting a serious disease.
Forest clothing must be stored separately from regular clothing so that ticks do not transfer to it. Upon arrival from the forest, inspect your clothes, shake them out in a place away from populated areas and put them in a bag and tie it tightly. Another good way to protect your clothes from ticks is to treat them with an acaricide before and after a walk in the forest.
Use products that repel or kill ticks. The drugs can be purchased at pharmacies and hardware stores. Before purchasing and using, be sure to read the instructions.
Remember! There are three main types of tick sprays:
Repellent
– repels ticks, can be applied to exposed skin. They last for about 2-5 hours, then disappear.
Acaricidal
– kill ticks, applied to clothing, not applied to skin. The effect lasts up to several days.
Acaricidal-repellent
– at the same time they repel and, in case of contact of the parasite with the substance, paralyze it.
First aid for a bite
Make sure that when you remove the tick, you do not leave its head in the body. Wash the wound with a disinfectant solution. The tick must be submitted to a laboratory to be examined for diseases. An immunoglobulin injection must also be given within 24 hours.
Security measures:
- Wear the right clothing to prevent ticks from gaining access to your body.
- Treat clothing with repellent. Pay special attention to your feet.
- Check yourself periodically.
Pharmacies and stores offer a wide variety of anti-tick treatment products for children and adults. The most popular are products from the DEET line of domestic manufacturers.
DEET products are the simplest and most affordable way to protect against ticks. Modern and certified products are suitable for both adults and children. They effectively cope with their task, and their price is quite affordable and affordable for everyone.
When do ticks appear?
Already in April - May, patients with tick bites come to the hospital. Because it is during this period that they appear on the soil surface. Somewhere from mid-April, when the weather is warm and the sun warms the ground well, thawed patches appear. And at this time the ticks wake up.
Due to the fact that these insects are constantly in search of food, the number of victims increases sharply. Please note that in the future their activity does not depend on the weather. Even if the summer is quite cool, dangerous insects will continue their “hunt”. Therefore, care must be taken even in rainy weather.
When does a tick go hunting?
Warm sunny weather appeals not only to people, but also to representatives of arthropods, which include ticks. The main thing for them during this period is to find a victim in order to nourish their body with blood. Ticks do not like cold, frosty or rainy weather. They hide in tree crevices and wait for good weather.
Ticks have very developed receptors that allow them to sense prey at a distance of 10 m. During hunting, they can rise to a height of up to half a meter.
When a hungry tick awakens from winter hibernation, its activity increases sharply and continues until mid-summer. The peak occurs in the months of May and June. Their activity also changes throughout the day, increasing in the morning and evening.
When does tick season end?
We are talking about the summer period, so when going on vacation, a person wants to be sure that he will be completely safe. This issue becomes especially relevant in August. When the heat subsides, it begins to seem that it is more difficult to meet a tick in the forest or in the park.
This is due to the number of ticks, because it is rapidly decreasing. And therefore, in the middle of summer, people who have been bitten practically do not turn to doctors for help. Such a decrease in numbers is associated with the death of insects. The cause of death is the lack of reserve nutrients in their body.
But this does not mean at all that in August or September you can not worry and relax calmly. Experts assure that parasites can be found in parks and forests even in October. Provided the weather is favorable. That is why it is generally accepted that the tick season ends with the first noticeable cold weather.
Dangerous hobby
The maximum number of bites occurs from the first half of spring to mid-summer. But you can catch the parasite even at a temperature of +5 degrees. Peak activity is in May and June. If we are talking about the time of day, then most of them are in the morning and evening.
It is worth noting here that even in summer there may be a time when ticks disappear completely. If the season is too hot and dry, then the parasites can hide from the sun until September. But as soon as the temperature drops, they will appear again and terrorize people until October and November, after which they will fall asleep for the entire winter.
This little nuisance can befall mushroom pickers who spend a lot of time in the forests, fishermen doing what they love on the banks of reservoirs, and summer residents working in their gardens.
But people whose hobbies are not related to nature can also suffer from ticks. Sometimes you just need to walk under a tree or touch a bush with your sleeve. The small parasite will cling to the skin quickly and painlessly. But just because these creatures are everywhere does not mean that you can only go into the forest when the ticks disappear. In autumn there are usually fewer of them, but no one is safe from their bite.
First tick activity
The first activity of ticks is observed during the period when the soil surface warms up by 6.7 degrees. That is why the first cases of bites occur at the end of March, beginning of April. They live on the soil surface, on the first sprouts of grass, and on the branches of small shrubs.
There is an opinion among people that ticks are able to climb high and hide in the crowns of trees. This is a misconception, since this parasitic insect does not climb to a height of more than three meters. Bright sun rays and winds are not entirely favorable for him. For the same reason, on hot summer days they hide in holes and only after rain, at times of high humidity, can they appear outside. Therefore, we can say with confidence that tick activity lasts from April to October .
Tick activity by month
Ticks are members of the arachnid family, which are increasingly expanding their habitats and periods of activity. Most of them do not cause any harm to humans, with the exception of certain individuals - these are carriers of dangerous diseases.
The appearance of ticks in Russia
There is an assumption that ticks came to Russia from China. The first scientist to realize that these animals pose a danger was Lev Aleksandrovich Zilber. He and his expedition went to the taiga in the summer (at the height of tick activity).
The reason for the expedition was that other scientists, while exploring the natural resources of the taiga, encountered an unknown disease. The disease was severe, often ending in disability or death.
The scientist was able to find the carrier of this disease - a tick. Next, a lot of work was done to study the disease, treatment methods and develop a vaccine.
Habitats of disease-carrying ticks
Ticks are heat-loving insects, so they are more often found in the southern regions of Russia and the Far East. Also often found in Siberia and the Urals.
But due to climate changes (increasing temperatures) and ticks’ adaptations to new habitats, ticks are increasingly found in areas where they were not previously found.
Types of ticks
There are a large number of different types of mites. Disease-carrying ticks include:
- gamasaceae;
- argasaceae;
- Ixodes.
In Russia, the most common ticks are ixodid ticks (encephalitis).
Ixodid ticks
These insects have a size of 0.5-1.5 mm. Their heads have chelicerae (jaws). With their help, the tick pierces the skin of the victim and attaches itself to the body.
Subspecies of ixodid ticks:
- Taiga or forest;
- Black-legged tick;
- Armor mites;
- Barn mites;
- Red mites;
- Scabies mites.
Determining the months of tick activity varies by region. In places where the temperature does not drop below 0 degrees, ticks can be active all year round.
Start of activity
occurs during spring warming up to 3-5 degrees.
Peak activity
occurs at temperatures of 5-20 degrees. For the middle zone this is the end of April, May and June.
What diseases can you get?:
- Encephalitis;
- Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease);
- Relapsing tick-borne typhus;
- Q fever;
- Hemorrhagic fever;
- Tularemia.
First aid for a bite
Make sure that when you remove the tick, you do not leave its head in the body. Wash the wound with a disinfectant solution. The tick must be submitted to a laboratory to be examined for diseases. An immunoglobulin injection must also be given within 24 hours.
Security measures:
Wear the right clothing to prevent ticks from gaining access to your body. Treat clothes with repellent
Pay special attention to your feet. Check yourself periodically.
Pharmacies and stores offer a wide variety of anti-tick treatment products for children and adults. The most popular are products from the DEET line of domestic manufacturers.
DEET products are the simplest and most affordable way to protect against ticks. Modern and certified products are suitable for both adults and children. They effectively cope with their task, and their price is quite affordable and affordable for everyone.
Vaccination against ticks
Vaccination is an effective means of preventing diseases transmitted by ticks. Therefore, if you are in regions with increased tick activity or simply like to be outdoors, then you should not neglect vaccination.
There are more ticks in the east than in the west
The degree of danger of contracting tick-borne encephalitis within the main tick habitat increases from west to east. Cases of disease are recorded especially often in the southern regions of the Far East. Most likely, this is due to humid, warm summers and the presence of mixed forests.
The most dangerous regions of the Far East:
- Amur region;
- Sakhalin;
- Khabarovsk region;
- Jewish Autonomous Region;
- Primorsky Krai.
What is characteristic: following warming, ticks move from east to west, and the peak of their numbers and activity in different regions varies throughout the season.
How parasites behave at night
As you know, some species of animals, reptiles, and arachnids are more active at certain times of the day. For example, some species of spiders prefer to go hunting in the dark. But does this rule apply to ticks? Perhaps at night or early in the morning a person can feel relatively safe?
Studies that have been carried out repeatedly have shown that ticks have no connection to the time of day. They can be dangerous both at night and during the day. However, it is necessary to make a small clarification. On hot summer days, when the temperature reaches 30 degrees, the activity of parasites decreases. They prefer to stay in their hiding places and not attack victims.
But as soon as night falls, bringing with it coolness, they leave their shelters. And that is why the illusion is created that periods of their activity may depend on the time of day. But in reality this is not the case. The only thing that can affect the activity of ticks is weather conditions. If they are favorable, the ticks will begin searching for food.
Peak tick activity by time of day
Dog owners are more aware than anyone else that tick activity is very high during walking hours with their pet - early in the morning from 7 to 9, and late in the evening - from 7 to 10.
It is at this time that the humidity and air temperature are comfortable for the parasite. During the day, when the sun burns with particular intensity and the air temperature exceeds 22°C, ticks prefer not to leave their shelters.
When does tick activity stop?
Depending on the region, the decline in tick activity occurs at the end of June - mid-July. In the middle of summer, the parasite behaves as if sleepy, measuredly looking for a suitable place to bite on the skin of the victim. This allows you to detect and remove the tick in time.
To a greater extent, the activity of ticks is influenced by the climatic zone of their habitat. For example, on the sea coast (Taman Peninsula) in a warm and very humid climate, the risk of catching a tick persists until the beginning of October, while residents of the Urals can breathe a sigh of relief as early as July.
The photo shows the tick season by month
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that ticks do not rest at night - their activity noticeably decreases, but does not stop completely, so evening walks in the park should end with an inspection of clothing, body and personal belongings for the presence of an attached parasite. Most often, pets and children walking in tall grass suffer from arachnid attacks, so a thorough examination of children and our little brothers should be carried out after each walk.
Most often, pets and children walking in tall grass suffer from arachnid attacks, so a thorough examination of children and our little brothers should be carried out after each walk.
How do you know if ticks are awake?
To find out if ticks are active in your area, take a white piece of cloth the size of a hand towel and run it over the ground or the first green area where insects are likely to be present. If ticks are awakened, several individuals will most likely end up on the material. The original version of this method recommends using a waffle towel placed on a pole like a flag, but you can limit yourself to any fleecy fabric that the insect can cling to.
If you do not want to experiment on your own or are interested in the question purely theoretically, the easiest way to find out about the awakening of ticks is to look through the local media or your regional Rospotrebnadzor website for the first reports of bites.
Danger to humans - diseases that ticks can infect
While the parasites are active and at the stage of preparation for wintering, they can carry diseases that can cause a number of serious consequences:
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- borreliosis;
- monocytic ehrlichiosis;
- tularemia;
- hemorrhagic fever;
- piroplasmosis (found in dogs);
- hematozoonosis;
- Tyleriosis.
Despite the variety of dangerous diseases, parasites most often carry bacteria that cause borreliosis. Encephalitis develops less frequently. However, when ranking the most common diseases, this does not indicate widespread infection. In fact, such diseases are not diagnosed very often (6 cases out of 100).
It's about
that of the listed diseases, borreliosis is determined more often, encephalitis is in second place.
Erythema from a tick bite is a symptom of borreliosis (Lyme disease)
The danger of infection with tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis depending on the time of year
Ixodid ticks are specific carriers of pathogens of many vector-borne natural focal diseases that are dangerous to humans and domestic animals.
The most dangerous are tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. The causative agents of these diseases can be present in the tick body at all stages of its development - from egg to adult.
Most often, taiga ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases - their degree of infection reaches 10-15% of the total population.
Infection of a person with tick-borne encephalitis can occur in two ways:
- Transmissible - through direct contact, bite or crushing of an infected parasite;
- Alimentary – when consuming milk from sick animals or dairy products that have not undergone heat treatment.
Goats and sheep can asymptomatically carry tick-borne encephalitis and are a source of increased danger to humans.
The likelihood of encephalitis in humans directly depends on the size of the parasite population in the area of residence, the degree of their aggressiveness, as well as the size of the natural focus of pathogens.
During periods of summer diapause, the chance of becoming a victim of an infected tick is significantly lower. However, pasture animals often ingest tick larvae along with grassy vegetation and themselves become carriers of a dangerous disease.
In Russia, regions that are epidemic for tick-borne encephalitis include Siberia, the Far East and Karelia. In the center of Russia, including the Moscow region, the incidence of this disease is low. Below is a map of the distribution of tick-borne encephalitis:
Another, no less dangerous disease transmitted by ixodid ticks is borreliosis (Lyme disease). The distribution area of this disease covers the entire territory of the Russian Federation, from Kaliningrad to Sakhalin. Borreliosis is registered in all regions of the country with a frequency of two to four cases per hundred thousand inhabitants.
The likelihood of contracting tick-borne borreliosis directly depends on natural and climatic factors and the size of the tick population in the area.
It is important to know
Transmission of the Lyme borreliosis pathogen to humans can occur not only through a bite, but also when the parasite is crushed while being removed from pets (through damaged skin).
The most dangerous epidemic periods coincide with periods of seasonal activity of ticks and have obvious pronounced jumps from April to June and from August to October.
During the hot period, ixodid ticks make daily migrations between grass layers, so at night there is an increased likelihood of becoming a victim of the parasite . All ixodid ticks are active around the clock outside of the diapause period.
Also a serious factor that increases the number of foci of the causative agent of borreliosis is the number of small vertebrates within the habitat of the parasite. In some climatic zones, the maintenance of natural Borrelia reservoirs is ensured solely by voles and shrews. With a decrease in the number of these rodents, the number of registered diseases of tick-borne borreliosis among the local population decreases significantly.
The season of increased risk of tick-borne infections, as a rule, directly depends on the activity of the parasite. And although humans are an accidental component of the parasitic system of ixodid ticks, it is important to always remember preventive safety measures, especially during those periods when the seasonal activity of the parasite reaches its maximum.
The danger of infection with tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis depending on the time of year
Ixodid ticks are specific carriers of pathogens of many vector-borne natural focal diseases that are dangerous to humans and domestic animals.
The most dangerous are tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. The causative agents of these diseases can be present in the tick body at all stages of its development - from egg to adult.
Most often, taiga ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases - their degree of infection reaches 10-15% of the total population.
Infection of a person with tick-borne encephalitis can occur in two ways:
- Transmissible - through direct contact, bite or crushing of an infected parasite;
- Alimentary – when consuming milk from sick animals or dairy products that have not undergone heat treatment.
The likelihood of encephalitis in humans directly depends on the size of the parasite population in the area of residence, the degree of their aggressiveness, as well as the size of the natural focus of pathogens.
During periods of summer diapause, the chance of becoming a victim of an infected tick is significantly lower. However, pasture animals often ingest tick larvae along with grassy vegetation and themselves become carriers of a dangerous disease.
In Russia, regions that are epidemic for tick-borne encephalitis include Siberia, the Far East and Karelia. In the center of Russia, including the Moscow region, the incidence of this disease is low. Below is a map of the distribution of tick-borne encephalitis:
Another, no less dangerous disease transmitted by ixodid ticks is borreliosis (Lyme disease). The distribution area of this disease covers the entire territory of the Russian Federation, from Kaliningrad to Sakhalin. Borreliosis is registered in all regions of the country with a frequency of two to four cases per hundred thousand inhabitants.
The likelihood of contracting tick-borne borreliosis directly depends on natural and climatic factors and the size of the tick population in the area.
The most dangerous epidemic periods coincide with periods of seasonal activity of ticks and have obvious pronounced jumps from April to June and from August to October.
During the hot period, ixodid ticks make daily migrations between grass layers, so at night there is an increased likelihood of becoming a victim of the parasite. All ixodid ticks are active around the clock outside of the diapause period.
Also a serious factor that increases the number of foci of the causative agent of borreliosis is the number of small vertebrates within the habitat of the parasite. In some climatic zones, the maintenance of natural Borrelia reservoirs is ensured solely by voles and shrews. With a decrease in the number of these rodents, the number of registered diseases of tick-borne borreliosis among the local population decreases significantly.
The season of increased risk of infection with tick-borne infections, as a rule, directly depends on the activity of the parasite
And although humans are an accidental component of the parasitic system of ixodid ticks, it is important to always remember preventive safety measures, especially during those periods when the seasonal activity of the parasite reaches its maximum
How long can mites live on clothing?
Without food and water, ticks can live up to 3 years. But the likelihood of bringing an arthropod home is low. They usually dig in or fall off. However, if the bloodsucker gets tangled in the folds of clothing, it may end up in a city apartment. There is a possibility of bringing the parasite in a bouquet of flowers, berries or mushrooms.
Human housing is not suitable for the life of arachnids; it has low humidity and lacks other usual components. Therefore, forest ticks do not reproduce in apartments. However, a tick that gets home can bite any member of the household. How long an arthropod parasite can be active depends on specific conditions - humidity, temperature.
To get rid of the danger of a tick bite at home after a walk in the forest, you need to thoroughly shake up your clothes outside and wash them. Also carefully check bags, tents, forest products and other things that travelers took with them into nature.
Ticks on clothes Everyone who went for a walk should be examined for bites. Pay special attention to the favorite places of arachnids - armpits, neck, groin, chest, head. Comb your hair with a fine comb.
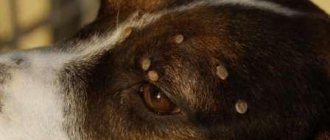
Tick attacks on pets
Among the victims of tick bites are a huge number of pets. In Moscow parks and squares, ixodid ticks most often attack cats and dogs, especially stray ones. A serious disease that a pet can contract from a tick is called “pyroplasmosis.” At the same time, vaccination is too expensive and ineffective. It is best to treat your pet with drops against ticks and fleas, or give special tablets from March to November. There are also cases of animals being infected with leptospirosis, toxoplasmosis or chlamydia.
If the tick has not had time to attach itself to the animal, it can easily crawl onto a person in close contact with the animal, for example, if it sleeps in your bed.
If you are bitten by a tick
1.Contact the ambulance
Seemingly following all the “safety precautions”, but in the end not having provided for some little detail, you found a tick already “attached” to yourself - don’t panic. Contact the ambulance by local telephone by dialing 103 or by mobile phone to number 112 or 03*. Find out from the experts what measures you should take first.
If you are unable to contact an ambulance by phone, and there is no emergency room or any other medical facility nearby, you will have to remove the tick yourself. This should be done carefully and slowly. If you crush it, there is a risk of direct infection through microcracks in the skin.
2.Remove the tick
Specialists from Rospotrebnadzor in Moscow advise grasping the tick with tweezers or fingers (gloved/wrapped in cloth) as close to its mouth as possible and holding it strictly perpendicular to the surface of the bite and turning the insect’s body around its axis. After the tick is removed, the bite site must be disinfected with any alcohol-containing product, and hands must be washed thoroughly with soap.
The removed tick must be left alive and brought safely to the laboratory, where it will be known whether there is a risk of any infection. The insect can be transported in a closed container with a small piece of slightly damp cotton wool or cloth. If you do not have the opportunity to conduct research on the tick, you should burn it or pour boiling water over it.
3.Seek help from a specialist
After you notice an “attached” tick, seek help from a medical facility as soon as possible.
Those who have not been vaccinated will be urgently administered immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis at an appointment with an infectious disease specialist. It is important that the injection is given no later than the 4th day after the tick has been sucked on. Also, the doctor may recommend taking a course of antiviral drugs.
If the insect was a carrier of borreliosis, the infected person will be prescribed a course of antibiotics. It is possible to find out what exactly the tick “suffered” from through a blood test 10 days after the bite. Thus, even a vaccinated person needs to go to a medical facility.
What should I do if bitten by a tick
The tick should be removed immediately. The more time a tick sucks blood from the body, the greater the risk of getting an infection.
There are several ways you can remove a tick. The general rule for them is that the parasite should be removed completely, without leaving the tick head in the skin:
Unscrewing the pliers. You can use tweezers, if these are not available, then use cotton wool or a bandage
I carefully grasp the body of the arthropod and carefully but forcefully turn it in a circle, “screwing” it out of the skin. Usually after a few turns the tick is easily pulled out
The specimen should be held perpendicular to the bite site.
Removing ticks using thread. For this method, take a regular sewing thread, tighten it on the pliers, in the area of the proboscis, lift it up and twist it several times. Then the thread is sharply pulled out along with the insect. This method requires skill, as you can leave part of the tick under the skin.
If, nevertheless, part of the tick remains under the skin, it is necessary to remove it:
- To do this, the bite site should be treated with iodine - sometimes this is enough for the proboscis to fall out of the wound on its own.
- If this does not happen, then use a disinfected needle and pull out the remaining part in the same way as a splinter.
- The remaining wound should be treated with alcohol.
The removed tick should be placed in a closed container - a jar, bottle, etc. If the tick died in the process, it should be poured with boiling water or burned. A live specimen can be taken to the laboratory for examination, but only within 2 days from the moment of capture.
Fighting methods
You can repel them with cologne with a strong smell, essential oils of citronella, lavender, and cloves. They use sprays and aerosols - Gardex, Reftamid Antiklesch, Raptor, Raid, Taiga, Off, Moskitol. Spray clothes thoroughly; some products can be applied directly to the skin.
To rid your land of parasites and ensure safe outdoor recreation, they use smoke bombs - Quiet Evening, Whirlwind, Fomorian. Use solutions for spraying grass and trees based on insectoacaricides. You can poison with the drug Cifox, Sinuzan, Executioner, Medilis-Ziper, Forsyth.
Ticks are not poisoned en masse, as this increases the chances of death of natural enemies - birds, animals, insects. This explains the fact why there are a lot of ticks. Initially, after using chemicals, pests disappear, but along with them, natural enemies. Over time, the population of pests increases, but there are no “exterminators” of them. A situation arises when people say, before there were no ticks, now there are a lot of them.
Pests can become active at the end of March and end their activity in November. Therefore, you should always remember about safety, but you should not be afraid of panic. Not all ticks are contagious; if you consult a specialist in a timely manner, the risk of the disease is reduced or the disease proceeds without complications. You should protect yourself in advance with clothing, anti-tick medications, and get vaccinated when visiting dangerous territories or areas.
Cloth
When going on vacation, first of all, it is important to ensure that you have the proper clothing. And it doesn’t matter where exactly you are going, to the forest, to the nearest park or to the country - ticks can be found absolutely anywhere where there is at least some vegetation. And to prevent the bloodsucker from sucking on, it is necessary to cover the entire body. Moreover, close it correctly, and this can be done if you know the structural features of the tick, due to which it can only crawl upward.
- For the upper body - something with long sleeves. This could be a shirt, jacket, raglan, etc. In this case, it is desirable that the collar covers the neck.
- For the lower body, trousers are a must. It is better to refrain from wearing shorts.
- Pants should be tucked into socks, and the top of clothing should be tucked into the bottom. For added protection, you can tighten the belt around your waist.
- It is important that all clothing is made of dense materials. As for its tones, light ones are preferable, since such ticks are quite easy to notice.
On a note! Surprisingly, the thinnest nylon tights can stop ticks. Although this is far from the most suitable item of clothing for outdoor recreation, although on the other hand they can be worn under trousers!
On sale today you can find special suits called anti-encephalitis, popularly known as encephalitis. They are made of durable, dense fabrics and equipped with drawstrings that provide additional protection against ticks. But if you don’t like this suit, then you don’t have to buy it. It’s quite possible to limit yourself to your everyday clothes, but you just need to tuck them all in!
How to protect yourself while hiking
When hiking at rest stops or while walking, you should not sit down or lie down to rest in the grass; it is better to choose places where the soil is bare or tear out all the grass within a radius of several meters. A barrier in the form of a cleared area will create good protection - ticks do not leave areas covered with grass.
It is better to choose places for overnight and rest away from the paths in dry, bright places (there are more ticks in the damp corners of the forest). The camp site should be cleared of grass, leaves, dead wood and sprayed with acaricidal agents (special preparations for ticks).
For hiking in the forest and mountains, you must wear closed shoes and trousers, jackets or long-sleeve T-shirts. Clothing should fit snugly to the body at the wrists and ankles. A hat or hood is required. There are also special anti-encephalitis suits that you can use. Exposed areas of the body should be treated with repellent ointments or sprays.
While hiking in the forest, you must periodically inspect your body and clothing. When a tick lands on a person, it begins to look for areas of thin, delicate skin and often attaches itself in the area of the abdomen, groin, scalp, throat, armpits, so these parts of the body need to be examined more carefully - the tick is small, sometimes it is difficult to notice it the first time. Upon returning from the forest or park, clothes should be carefully inspected, and it is better not to enter the house in them, but to leave them outside in the sun for several hours.
Pet owners may be bitten by a tick carried into the home on their fur. Therefore, dogs and cats need to be treated with special protective sprays or drops, and carefully examined after walks.
Basic safety rules. How to avoid meeting them
The best tick repellent for people: how to choose
There are several groups of means to protect humans from ticks. They differ in the principle of influence.
Repellents – have a repellent effect, prevent insects from landing on the skin, including mosquitoes, mosquitoes, etc. It is possible to apply to human skin, treat (spray) clothing. As a rule, these are drugs based on the active substances (a.i.) diethyltoluamide (deta), or methylbenzamide, less often alphacypermethrin, cypermethrin. They belong to protection classes III and IV, the effect is due to an odor that irritates mites - it was previously assumed that parasites temporarily lose their sense of smell.
The duration of action of repellents depends on the concentration: for example, a product with 30% active ingredient content. retains the effect for up to 5-6 hours, about 100% - up to 12 hours or more.
Acaricidal drugs have a nerve-paralytic effect. They belong to the group of neurotoxins-peretroids. The drugs affect the central nervous system by blocking nerve impulses. When paralyzed ticks come into contact with treated areas of human clothing, they fall off and die.
Compared to repellents, they are more toxic. Contact of human skin with the products is highly undesirable.
Among the drugs used to protect against ticks, the active ingredient is an insecto-acaricide (active ingredient alphacypermethrin (alfametrin), cypermethrin, alpha-cypermethrin, permethrin).
According to reviews from tourists, foresters, fishermen and other people, the best anti-tick remedy for humans in terms of price-quality ratio is based on the insectoacaricides cypermethrin, alphacypermethrin.
These products for protecting people from ticks are used both for treating skin and clothing (the least toxic and less effective), as well as for treating exclusively clothing, shoes, equipment, items of uniform and equipment, mosquito nets, etc.
The optimal concentration for a pronounced effect of a product based on cypermethrin is about 0.02%.
Insecticidal-repellent agents have a combined effect: they repel ticks from human skin and have an acaricidal effect. They protect people not only from all types of ticks, but also from blood-sucking ones, united under the general name “midge complex” - many types of midges, biting midges, etc.
Products for humans that combine the two effects are based on two components: most often diethyltoluamide and alphamethrin.
Tick vaccination
If you spend a lot of time outdoors, then using various creams and sprays is not what you need. It will cost a pretty penny and you will have to spray it all the time. In this case, it is better to get vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis. But before you do it, you need to find out what it is.
The vaccine protects you from the disease, but not from the bite. Those. you will also be attacked by parasites. The vaccination can be done at any age. The only exception is children under one year old. The vaccine is safe, but each body reacts individually, and side effects are possible.
There is little point in vaccinating those who visit nature once or twice during the summer. The vaccine is given to those who work in areas of high parasite activity, to children before going to camps, and to outdoor enthusiasts. 95% of vaccinated people do not get sick when bitten. But there are still 5% who can, despite the vaccine, contract the disease. But it will occur in an extremely mild form. And therein lies the danger. You can attribute a slight malaise to completely different diseases. Therefore, even if you are vaccinated after a tick bite, it is still worth getting your blood tested. The vaccination is effective even with multiple bites from infected individuals.
The vaccination is given in medical institutions. The vaccination is done not once, but three times at intervals. The first is done in the fall, the second a month or two later, and the third a year later. Afterwards they repeat it once every three years.
After the full course, you can donate blood for analysis to detect antibodies in the blood. This way you can be sure that the vaccination works. There are also contraindications, so you should consult your doctor before vaccination.
When should you take out tick insurance?
It is worth purchasing insurance coverage against tick bites in advance, before the start of the season.
If a tick bite occurs, insurance provides a free set of measures, such as prevention, laboratory tests, treatment, and the purchase of medications. Like other types of voluntary health insurance, this type of insurance helps to provide high-quality medical care in a clinic verified by the insurance company and protect not only your health, but also your budget.
Sources
htps://kleshei-net.ru/sezon-kleshei/ htps://TaraKlop.ru/kleshchi/sezon-aktivnosti-kleshhey/ htps://kleshun.ru/sezon-kleshhej/ htps://combat-dez. ru/kogda-poiavliautsia-kleshi-i-kogda-zakanchivaetsia-sezon-ih-naibolshei-aktivnosti/ htps://usatym.net/kleshhi/karta-rasprostraneniya-kleshhevogo-encefalita-v-2021-godu/ htps:// animashka.info/kleshchi/karta-kleshchej.html htps://Dezoff.ru/kleshhej/kleshchi-v-2020/ htps://misterklop.ru/klesshi/sezon-aktivnosti-kleshhej-v-rossii-kogda-nachalsya -i-kogda-zakonchitsya htps://chistiy-dom35.ru/kleshchi/kogda-aktivny.html htps://dezbox.ru/dezinsekciya/odezhda-dlya-zashhity-ot-kleshhej-vybiraem-luchshij-variant/ htp ://www.medicus.ru/wellness/patient/rekomendacii-po-zaschite-ot-ukusov-kleschej-166295.phtml htps://stopklopu.com/sezon-klesej-2020-periody-aktivnosti-klesej-po- mesacam/ htps://beetlestop.ru/meryi-zashhityi-ot-kleshhey/ htps://usatym.net/kleshhi/est-li-v-krymu-encefalitnye-kleshhi-kak-izbezhat-ukusov-posledstviya/ htps: //parazitdoma.ru/sovety/sredstva-ot-kleschey-dlya-lyudey-kak-vybrat-i-kakie-schitayutsya-luchshimi htps://kleshei-net.ru/zaschita-ot-kleschey/ htps://kaplife .ru/life-insurance/stop-klesch/sezon-kleshchey/
When ticks appear in spring - the beginning and end of the active season, how to protect yourself
Rospotrebnadzor warned about unusual behavior of ticks
“It’s an unusual year and the behavior of these arthropods is also unusual,” Natalya Shashina, a leading researcher at the FBUN Research Institute of Disinfectology of Rospotrebnadzor, explained to Rossiyskaya Gazeta. According to her, ticks, as a rule, become active in early March or earlier in the southern regions of Russia. In the middle zone, ticks traditionally showed activity after winter only in early April. “They begin to move already at +5 degrees, and at +10 degrees they already go hunting,” says the specialist.
But since the winter this year is abnormally warm and there is practically no snow, the first ticks have already been noticed on thawed areas of the soil. “On the southwestern slopes the snow melts earlier, so they can appear there first. This applies to the Moscow region. Pet owners should be extremely careful. Do not walk pets that have not been treated with special anti-tick products on land where there is last year's grass. Ticks can hide in this grass and crawl out during the day to bask in the sun,” Shashina clarifies.
Ticks are known to be carriers of encephalitis, borreliosis and piroplasmosis (the latter affects animals). Last year, the most disadvantaged in terms of incidence of tick-borne encephalitis were the Northwestern, Ural, Siberian and Far Eastern federal districts, and those adjacent to the Moscow region were the Tver and Yaroslavl regions. In the Moscow region, encephalitis ticks were most often found in the Dmitrovsky and Taldomsky districts.
Tick-borne viral encephalitis is a very serious viral disease that affects the central nervous system and can lead to disability and death. Its incubation (hidden) period most often lasts 10-14 days. In some cases, signs will begin to appear after a couple of months.
The disease begins acutely, accompanied by chills, severe headache, a sharp rise in temperature to 38-39 degrees, nausea, and vomiting. Worrying muscle pain, which is most often localized in the neck and shoulders, thoracic and lumbar back, and limbs.
Animal piroplasmosis is an equally dangerous disease. If the vaccine is not administered in time and treatment is not started, the animal will die within a few days from anemia (lack of oxygen in the blood). But even after suffering from piroplasmosis, animals often develop liver diseases. The main signs that an animal has been bitten by an infected tick are the pet's apathy, vomiting, and loose stools with blood. We need to urgently run to the vet.
The easiest way to protect yourself from ticks is to cover exposed areas of your body with clothing as much as possible. When going outdoors, it is also advisable to purchase special repellents that you can use to additionally treat your clothes. Pets also need to be treated with special products. Additionally, you need to purchase a flea and tick collar.
If a tick does get on the body of a person or animal and there is no way to quickly get to the emergency room, you need to remove it yourself. This should be done very carefully so as not to tear off the tick's proboscis. Using tweezers or fingers wrapped in clean gauze, you need to grab the part of the tick visible on the surface and, holding it strictly perpendicular to the surface of the bite, rotate the body of the tick around its axis. Immediately disinfect the bite site with any suitable product (70% alcohol, 5% iodine, cologne). After removing the tick, you should wash your hands thoroughly with soap. If a black spot remains in the body (the head or proboscis of an arthropod), treat this area with 5% iodine.
The removed tick must be taken for examination to the microbiological laboratory of the Federal State Healthcare Institution Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology or other laboratories conducting such research.