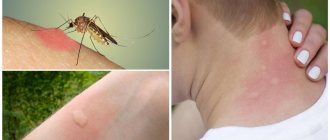
Everyone knows about ixodid ticks. Instructions on what to do if you are bitten by an ixodid tick can be found at any medical facility. Few people have heard of Gamasidae. Even fewer people have thought about how dangerous these ticks are to humans. They are so small. Gamasid bloodsuckers usually do not tolerate tick-borne encephalitis, but they can also cause a lot of trouble. The rat mite is especially dangerous. It was he who previously carried typhus from rats to humans. Today his main “specialization” is tick-borne dermatitis.
Gamasid mites next to a person
In total, there are about 6 thousand species of gamasid mites. The main part of the infrasquad does not come into contact with humans at all. But there are 3 species that today live next to people, as they are parasites of synanthropic animal species:
- chicken;
- rat;
- mousey.
Chicken gives people problems only in economic terms. But not everyone on the planet keeps chickens. Two other species pose a significant threat.
Interesting!
According to statistics, there are 10 rats per metropolitan resident. Their parasite can appear not only in a village house, but also in any apartment. The mouse mite is outnumbered only by the number of hosts. There are more rats.
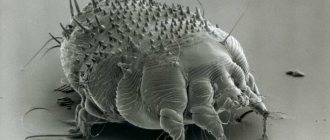
Rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti)
An obligate temporary ectoparasite of rats, capable of feeding on the blood of other mammals. It was first discovered in Australia. But rats are not endemic to Australia. It’s just that some diseases were not previously associated with this type of tick. The rat mite was later identified in the United States as a source of dermatitis in humans. A few years later, it caused people to become ill in Hamburg.
The parasite was first discovered in 1913 due to its size. The length of its body is only 0.75-1.44 mm. If you look at the photo of a rat tick, it turns out that it is very similar to the common ixodid tick. There are also differences:
- there is no segmentation between the body and chelicerae;
- oval genital shield;
- cranial anus;
- pointed tail apex.
Rat mite
On a note!
The color of sucked ticks is not light gray, but dark red in females or yellow in males. Hungry parasites are gray in color. After feeding, they are unable to move; when hungry, they are very active.
Lifestyle
Hungry rat ticks are very active creatures and can travel several hundred meters in search of a host. This explains the appearance of rat mites in an apartment in the complete absence of rodents. Rat parasites are also capable of existing for a long time without a host and in a hungry existence. Such abilities make it much more difficult to diagnose arthropod-borne diseases.
Rat mites have 5 stages of development:
- egg;
- larva;
- protonymph;
- deutonymph;
- adult.
The parasite feeds only 2 times in its entire life: at the protonymph stage and as an adult. After feeding, the arthropod falls away from the host either for further molting and transformation, or for laying eggs.
On a note!
The rat mite is a species capable of parthenogenic reproduction. In the absence of a male, the female is able to lay eggs, from which offspring will hatch.
Egg development takes only 1.5 days. The general life cycle of a rat mite is 7-16 days. The hatched larva is the only form that has only 3 pairs of legs. The egg-to-egg maturation stage usually takes 13 days.
Diseases
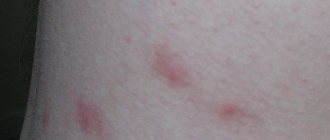
The parasite's bites cause an itchy skin irritation in humans called rat mite dermatitis. Children may have an eczematous or vesicular reaction to the sting. Rat mite attacks must be differentiated from other insect bites or skin irritations caused by the body's reaction to an allergen.
Treatment of rat tick-borne dermatitis is symptomatic. To alleviate the condition of the victim, use:
- oral antihistamines;
- topical corticosteroids;
- benzyl benzoate;
- gamma-benzene hexachloride;
- Crotamiton.
But often the irritation goes away on its own or people simply do not react to the saliva of rat bloodsuckers.
Rat mite
The reaction to rat parasites must be separated from the symptoms:
- scabies;
- bacterial folliculitis;
- pediculosis;
- dermatitis herpetiformis;
- mosquito bites and other insect bites;
- allergies.
Laboratory studies have also shown that rat mites can carry dangerous diseases:
- typhus;
- plague;
- tularemia;
- Q fever;
- rickettsiosis;
- Coxsackie.
On a note!
In unfavorable times, rat ticks, along with fleas, were the main carriers of typhoid and plague from rodents to people.
Harm to humans and animals
Despite their microscopic size, fleas bring a lot of discomfort to both animals and people. Their bites are very painful, and their saliva irritates the skin at the bite sites and can cause an allergic reaction.
In addition, rat fleas are carriers of such dangerous infectious diseases as plague, brucellosis, encephalitis, tularemia, and rat typhus.
Domestic parasitic insects cause a lot of trouble, so it is necessary to begin exterminating the insects immediately after their detection. Insect bite ointment will help relieve itching and swelling from the bite site. Read tips on choosing an ointment here.
Mouse mite (Liponyssoides sanguineus)
Previously its Latin name was Allodermanyssus sanguineus. Another type of gamas tick, dangerous to humans. It looks very similar to a rat and a layman can easily confuse them. This is an obligate parasite belonging to the nest-burrow group. It has 5 developmental stages, of which only the first two do not feed: the egg and the larva.
Contacts the owner while feeding. Spends the rest of the time in the nest litter. Once in an apartment, it can attack a person, infecting people with vesicular rickettsiosis. While dermatitis caused by attack by mouse parasites is treated with antihistamines, rickettsiosis requires antibiotic therapy.
When infected, a swelling first forms at the site of the bite, which then turns into a black, clumsy scab. As the disease progresses, a person develops:
- fever;
- chills;
- weakness;
- muscle pain;
- rash all over the body.
The last symptom is most characteristic of this type of rickettsiosis. The disease is treated with tetracycline antibiotics.
On a note!
Observations of poor urban areas, most susceptible to this disease, have shown that if untreated, rickettsiosis usually goes away on its own after 2-3 weeks. No deaths were recorded.
Mouse mite
Main ectoparasites of rats
Decorative rats are affected by several types of parasites. These include:
- mites;
- lice eaters;
- fleas.
The listed types of ectoparasites do not live on humans, but some can bite humans. Fleas and lice eaters, as well as the rat mite Ornithonyssus benoiti, are carriers of infectious diseases. They often become the cause of worm infection. Therefore, if you suspect the presence of ectoparasites in a domestic rat, treatment should be started as quickly as possible.
Ticks
These parasites belong to the order Arthropods. Several types of mites infest rats:
- cutaneous Radfordia ensifera;
- scabies Notoedres muris;
- sarcoptoid Sarcoptes anacanthos;
- subcutaneous Demodex.
Unlike lice eaters and fleas, such parasites cannot be seen with the naked eye. Firstly, because they are embedded in the skin. Secondly, rat mites are small in size - from 0.3 to 0.6 mm.
The main symptoms of infection are baldness and incessant itching. When a rat mite bites through the skin, the rodent experiences pain. Then the puncture site begins to itch. The rat bites itself and tears its body with its paws. Over time, she becomes nervous and loses her appetite.
Wounds and crusts appear on the skin, which are concentrated in the head, neck, shoulders and ridge. Some people think it's an allergy, but rats are omnivores and rarely suffer from food intolerances. Therefore, if symptoms of scabies appear, you should take your pet to the veterinarian and take a skin scraping.
Attention! Rat ticks Ornithonyssus benoiti are dangerous to humans. They cause severe dermatitis and transmit infectious diseases - tick-borne encephalitis, icteric leptospirosis, tularemia and Lyme disease.
Lice eaters (lice)
Most often, rats suffer from head lice. This disease is caused by lice - blood-sucking lice Polyplax spinulosa. They live in the animal's fur and feed on blood, secretions of the sebaceous glands and skin cells.
Lice eaters in rats can appear after contact with a sick animal. The owner may also be involved in infesting the pet with lice. Parasites can be on shoes or clothing. Also, a domestic cat or dog can bring lice eaters into the apartment on its fur.
Rat lice are small insects with elongated bodies that are yellow or light brown in color. Its dimensions do not exceed 1 mm. The lice eater has 3 pairs of limbs. The head has a piercing-type mouthparts. With its help, the louse pierces the skin to get food. During a bite, she injects a special substance into the dermis that prevents blood clotting.
The female lice eater is slightly larger than the male. She produces up to 60 eggs at a time. Nits attach to the hairs of the fur at their base, right next to the skin, because it is warm there. The eggs of lice eaters hatch into larvae, which then molt three times and turn into sexually mature individuals (imago). The full development cycle of the parasite occurs within 3-4 weeks.
The incubation period after lice infection until the first symptoms appear in a rat can last about 30 days. When a lice beetle lands on a rodent's body, it attaches itself to the hairs using mites that are located on the parasite's legs. The louse burrows into the rat's skin and begins to drink blood. A secretion from the salivary glands of the lice eater gets into the bite site. This liquid irritates the skin and causes itchy spots and nodules to appear.
Parts of the body on which rat lice infest:
- head;
- withers;
- parotid region;
- neck;
- area around the anus.
At an early stage, lice eaters in rats with dark fur are quite difficult to detect, since there are few of them and they blend in against the background of the fur. In rodents with light coats, mature lice are clearly visible. They are located on the skin and resemble moving red dots.
In dark-colored pets, it is easier to detect lice eggs. They are oval in shape and whitish in color. Nits are not found on the skin, but on the hairs of the fur.
Symptoms of lice beetle infestation:
- the rat itches frequently;
- scratches and reddish spots appear on the skin of the muzzle, neck and shoulders;
- the fur begins to fall out;
- the animal becomes irritable and loses appetite;
- The rat is losing weight.
Important! Lice eaters do not attack people, so they do not pose any danger to the owner of the rodent.
Fleas
Fleas are very rare in domestic rats. These parasites can use the rodent as a temporary source of food.
Like lice eaters, rat fleas live on the surface of the skin. They also feed on blood. The parasite's body is flattened on the sides, which allows it to move deftly and quickly in the thick hair.
The flea has a head and a rounded abdomen equipped with a piercing-sucking mouthparts. The entire body is covered with a durable chitinous layer with bristles; it protects the parasite from mechanical damage. The flea has 6 long limbs, thanks to which it can jump up to 1.5 m. Each leg consists of 5 segments.
Parasites do not live on the animal's body, but use it only as a source of food. They lay eggs in hard-to-reach places - behind the baseboard, in cracks on the floor. The flea is larger than the lice eater. The size of its body varies between 0.5-1 mm. The parasite is colored brown.
You can detect fleas in a rat by the following signs:
- the rodent becomes nervous and itches;
- his coat is thinning due to mechanical damage to the skin;
- bite marks appear on the body;
- adult parasites that move quickly can be seen in the fur;
- If you part the fur of a rat, it will contain arthropod excrement - brown lumps that look like poppy seeds.
Important! Fleas can bite people. They carry diseases dangerous to humans - some types of helminthiasis, tularemia, listeriosis, plague, brucellosis, typhus and encephalitis.
How to notice the appearance of gamas mites in an apartment
The saliva of parasites causes skin irritation and the appearance of nonspecific itchy dermatitis in humans. The sites of attacks are not localized to any one area of the body and can occur anywhere. Since the main habitat of bloodsuckers in the natural environment is the litter of the nest, they prefer to live on beds in the apartment.
It is rat and mouse blood-sucking parasites that are the culprits of dermatitis attributed to dust mites. The small size of rat parasites misleads people. But a rat or mouse mite can be seen with the naked eye, a dust mite cannot. If a small moving gray dot appears on a white sheet, this is a rat or mouse bloodsucker.
On a note!
Bite sites are usually clustered because rat mites feed in stages. At the site of the bite, papules with a diameter of 1-4 mm are formed.
How to get rid of rat fleas in an apartment?
The best solution is to call professional exterminators. Only specialists can guarantee you complete relief from these dangerous insects in just 1 day. But if you don’t have such an opportunity, you’ll have to start fighting on your own and don’t hesitate. Follow the plan:
If you have pets (rodents and others), you need to treat them with special insecticidal drops against fleas, or use shampoo or spray. Effective products: shampoos Celandine, Mr. Kiss, Barsik drops.
What are the most effective methods for removing fleas from pets?
- Clear hard-to-reach areas for treatment: move furniture, cover food, remove animals from the premises.
- Try to find flea nests.
You can start processing the premises.
Choosing a remedy for rat fleas
Among the many modern insecticides, give preference to proven drugs that have proven themselves in the fight against rat fleas:
GET for fleas
The drug GET (GET) is the most powerful microencapsulated insecticide of the latest generation. It is capable of not only completely destroying adult fleas, but also coping with the offspring.
Price – from 800-850 rubles
The rat flea larva dies upon contact with this product. Get penetrates the body, interrupting the transmission of nerve impulses, has a contact effect, and does not have a pungent odor. Chlorpyrifos is the main component and is low toxic.
Medilis Cyper for fleas and bedbugs
Medilis Cyper is a liquid concentrate with powerful characteristics that quickly kills fleas and protects against re-infection for a long time.
Cost – from 220 to 250 rubles
The poison enters the body through the skin of the insect, with food, and kills it in any case. Fleas do not develop immunity to it. Economical, easy to use.
Delta Zone
Delta Zone is an ideal remedy that will help get rid of even a heavily infested room with rat fleas.
Price – from 600 to 640 rubles
Deltamethrin quickly affects the insect's body and acts for another 8 weeks after application to the surface, reducing the reappearance of fleas to zero. The granules retain their properties, killing even newly appeared fleas.
Cifox
a universal drug that has a prolonged effect and gets rid of different types of fleas. Economical, does not have a strong odor, the emulsion does not leave marks on furniture and other surfaces.
The cost of an effective insecticide is from 260 to 320 rubles.
Ram
a concentrated insecticide that can kill rat fleas and their offspring in the shortest possible time. The price of the drug is from 380 to 400 rubles.
An excellent preventive measure that protects for a long time from the reappearance of insects and not just fleas.
Protecting yourself from fleas
If you are going to be in places where there is a high risk of flea infestation, follow these simple rules:
- Use insecticides - special aerosols that will repel insects. For example, sprays based on the substance DEET.
- When going outdoors or working in basements, protect exposed areas of the body (boots, gloves, etc.).
- Avoid cheap hotels and dubious accommodations that may be infested with fleas. Do not locate near burrows of wild animals or rodents.
Risk or guarantee?
Remember, no matter what methods of dealing with rat fleas you choose, no one will give you a 100% guarantee that you will forget about the unpleasant neighborhood! Fleas have adapted perfectly to our homes and have learned to hide in the most secluded places, multiplying quickly. And at this time you are risking your health.
Only a professional team will properly treat the room and use not just one insecticide, but a whole arsenal of effective means. It will destroy the larvae and put up a reliable “barrier” against their re-infection. Just one day and you are free from bloodsuckers. It’s up to you to decide: fight to no avail or seek the help of professionals.
Published: 11/07/2015
Fighting rat mites
Trying to fight these bloodsuckers on your own is useless, since complex treatment is required. Often, the independent use of potent acaricides is dangerous for a non-specialist, since in such cases they use drugs that are toxic to people:
- hydrocyanic acid;
- chlorphenothane (DDT);
- chlordane;
- permethrin;
- pyriproxyfen;
- lindane
Hydrocyanic acid is the starting “raw material” for cyanide, and DDT is the infamous dust.
First, decarization is carried out, and then deratization of the home, basements and adjacent outbuildings. It is possible to be sure that the premises are free of rat parasites only after several weeks due to the high ability of bloodsuckers to survive in the external environment without feeding on blood.