As the disease progresses, there is a risk of scarring on the skin, as well as secondary infection. Therefore, the sooner you start treating demodicosis, the shorter the treatment time will be and the better the results.
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist without queues and at a time convenient for you at the Otradnoe Polyclinic. You will be referred to the necessary studies and prescribed complex therapy, the results of which will help you return the quality of your life to its previous level.
Demodex of the skin - what is this disease?
Demodex (its other name is acne gland) is a parasitic mite that is an opportunistic microorganism. It lives on and under the skin of more than 90% of healthy people and does not cause them any harm. The food for this microscopic (less than 0.5 mm) mite is keratinized skin particles, sebum (sebum), and hormones. Under normal conditions, the parasite is found on the skin in very small quantities (1-2 pieces per square centimeter, and with clinical manifestations of the disease - up to 60 individuals per square cm.). However, with hypersecretion (increased production of fat) of the sebaceous glands, Demodex actively multiplies and begins its destructive activity. Increased sebum production can occur under various conditions, such as poor diet, stress, and excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The mite Demodex folliculorum was discovered in 1842. And to date, 65 species of this parasite have already been identified. However, the human body is attractive to only two varieties:
- Demodex folliculorum - it lives in hair follicles.
- Demodex brevis - lives in the sebaceous glands.
Parasites are often localized in areas rich in sebaceous glands:
- forehead;
- nose;
- nasolabial folds.
The causative agents of demodicosis can be found in other areas of the face, for example, in the external auditory canals. If the tick “favors” the eyelids, this leads to the development of blepharitis. Sometimes it lives on eyebrows, eyelashes, and can also settle on the skin of the back or chest, and scalp.
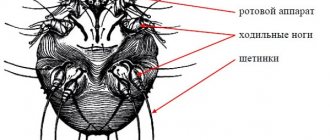
Demodex folliculorum has a worm-like shape, its transparent body (0.3-0.4 mm) consists of two segments. In the upper segment there are 4 pairs of limbs. Demodex brevis is similar in appearance to its “brother”, but its body is slightly shorter.
Thanks to the scales on the body, parasites are firmly attached to the skin and hairs. In women, demodex mites are observed on the face a little more often than in men - the latter regularly shave their faces, removing visible parts of the hairs and the surface layer of skin.
Reference! Demodex folliculorum is more common than Demodex brevis. However, the first one lives only on the skin of the face. The second one can live on the skin of the body.
The life cycle of a tick is 14-18 days and is divided into 5 phases:
- Egg – Adults emerge from the hair follicles and sebaceous glands to the surface of the skin, mate, and then the female returns to the skin and lays eggs.
- The larva emerges from the egg after 60 hours and after 1.5 days turns into a protonymph.
- Protonymph – stage lasts 3 days.
- Nymph - after 60 hours it turns into an adult.
- An adult - after a day or even half a day, she is ready to mate.
One female usually makes several clutches of eggs during her life cycle. At the end of the cycle, the adult dies directly in the hair follicle or sebaceous gland, then decomposes.
Demodex is unable to survive for a long time outside the human body. The disease can develop from “its own” microflora (if the parasite is part of it), and can also be transmitted from person to person.
The route of transmission of the parasite is through household contact. Most often it is transmitted:
- through dirty hands;
- someone else's cosmetics;
- towels;
- bed sheets.
Reference! In children, demodicosis occurs extremely rarely (mainly in the form of blepharoconjunctivitis). Usually this pathology occurs after 18 years of age.
The tick is most active at night, since ultraviolet radiation has a detrimental effect on it. Therefore, it is at this time of day that the patient’s skin itching intensifies.
Shampoos and ointments
The most convenient and effective way to combat subcutaneous mites is the use of shampoos, ointments, and balms. The convenient form of release in the form of a finished product, packaged in a plastic bottle, allows you to use this medicinal cosmetics in the everyday rhythm of life without prior preparation.
Manting Acarus-removing
Demodicosis shampoo from a well-known Chinese brand occupies not the last place in the ranking of remedies for demodicosis. The company produces natural cosmetic and medicinal products. Shampoo and conditioner fights demodicosis and seborrhea. It has a pleasant aroma and good foaming.
One plastic bottle with a volume of 280 ml with a frequency of use 2-3 times a week is enough for 2 months of use. Manting helps destroy demodex mites, heal the scalp, and reduce oily roots. The cost of one bottle of any product is 650-800 rubles. The subcutaneous mite series also includes soap, cream, milk and other products.
Demodex complex
Cosmetic kits from the Chinese company Demodex Complex were the first examples of an integrated approach to the treatment of demodicosis. The acaricidal composition has a gentle effect on damaged scalp, but kills all parasites. The series of products against demodicosis for hair includes shampoo and conditioner.
Both products are available in tubes of 200 ml each. In addition to the acaricidal component against subcutaneous mites, the products contain herbal extracts that have a healing and soothing effect. Prices for shampoo start from 1,700 rubles, and for conditioner – from 1,400.
Shampoos for demodicosis
Stop Demodex
The active ingredient in Ukrainian shampoo is metronidazole. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, destroys fungal formations, bacteria and mites themselves. The drug also reduces skin oiliness, eliminates itching, heals and restores the upper layer of the epithelium.
The product is available in a 100 ml bottle, but its consumption is economical due to abundant foaming. One bottle is enough for 2-3 weeks of treatment. The average price of a bottle of Stop Demodex is 800 rubles. You can purchase it in the online store.
Shampoo reviews
I recently encountered serious problems - demodicosis of the scalp developed. First itchy pimples appeared, and then my hair began to fall out. I was terribly scared and called a friend who deals with medicinal cosmetics. She immediately brought me a bottle of Stop Demodex for ticks. It is small, but for my short hair it lasted me almost a month of use. The itching went away, and the hair became silky and healthy.
Ekaterina, Kostroma
My sister had severe depression after her divorce from her husband. Against this backdrop, she began to have health problems. Including the appearance of demodicosis mites. Seeing the condition my sister was in, I ordered shampoo from the Chinese company Manting on the Internet. She forced her poor relative to undergo treatment. After a month of regular washing and taking vitamins, my sister began to look feminine again. The treatment was successful.
Maria, Perm
Mechanism and causes of disease development
The etiology of demodicosis has not yet been fully studied. The most common hypothesis is that if a person is a carrier of demodex, this does not lead to the development of the disease. To “start” the pathological process, a prerequisite is a decrease in immunity - then the structure of the skin changes. Only in this case can the parasite penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin. The tick destroys the epithelial barrier, causing its waste products to spread throughout nearby tissues. They are antigens - that is, substances foreign to the body. Therefore, the body reacts to them, trying to destroy them, as a result of which inflammation develops, and then a rash appears.
Reference! With healthy immunity, demodicosis does not develop even in the presence of demodex.
A decrease in immunity contributes to:
- Metabolic disorders.
- Frequent colds.
- Pathologies of the nervous system.
- Liver diseases.
The course of the disease is significantly complicated in the presence of a secondary infection - penetration of other microorganisms, for example, staphylococcus, into the layers of the skin.
It is also known that ticks begin to actively reproduce when conditions are favorable for them. These include, first of all, hyperactivity of the sebaceous glands, when increased sebum production occurs. It is observed in the following cases:
- under stress;
- tanning abuse;
- passion for carbohydrate-rich foods;
- frequent visits to baths, saunas and other thermal effects on the body;
- endocrine diseases;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- disorders of sebum production: acne, seborrhea;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Demodicosis often develops in immunodeficiency conditions: HIV and AIDS, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, diabetes mellitus. Also, the occurrence of pathology can be triggered by taking medications that suppress the immune system: corticosteroids, chemotherapy drugs.
Since demodex also feeds on hormones, active reproduction of mites can occur when using hormonal creams and ointments.
Reference! Demodicosis of the eyelids can develop after eye surgery if it was performed in violation of the rules of antisepsis and asepsis.
Demodicosis
HIV
Blackheads (acne)
1673 02 December
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Demodicosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Demodicosis is a parasitic skin disease caused by the iron mite (
Demodex
). The mite multiplies in hair follicles, sebaceous glands of the skin and meibomian glands (modified sebaceous glands located along the edge of the eyelid) and mainly affects the skin of the face and outer ears, although in rare cases it can migrate to the skin of the chest and back. The nutrient medium necessary for mite reproduction is sebum (sebum).
Many people can be carriers of the mite, but the disease manifests itself acutely only when the microbial biocenosis of the skin is disrupted and the immune system is reduced.
In such cases, the mite begins to actively multiply, resulting in the formation of asymmetrical scaly pink spots, telangiectasia, pink or red rash on the skin, in place of which pustules (bubbles with pus) or vesicles (bubbles with clear liquid) then appear. The skin in these places becomes inflamed, thickens and becomes covered with weeping crusts. If left untreated, skin damage may worsen, reaching deeper layers.
Causes of demodicosis
The iron mite is a conditionally pathogenic organism and in 90% of people it is part of the normal microbial biocenosis of the facial skin, without showing itself in any way. Active reproduction of the tick becomes possible if the biocenosis is disrupted and local immunity is reduced. Most often, changes in the microbial environment occur as a result of various skin diseases (inflammatory, bacterial), the use of immunosuppressants (drugs that reduce immune defense), for example, local steroid ointments. The spread of demodicosis is facilitated by disturbances in the functioning of the nervous, vascular and endocrine systems, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and pathologies of metabolic processes.
An important factor in the development of the disease is the increased formation of sebum and changes in its composition. An increase in surface lipids in sebum leads to increased proliferation of pathogenic flora, which, in turn, initiates mite activity. Overproduction of sebum occurs in women during the period of hormonal changes, as well as as a result of endocrine diseases and genetic predisposition. A significant role in the activation of the mite is played by the level of insolation, which affects the increase in sebum production.
During the hot season, a surge in the incidence of demodicosis is recorded, which is associated with increased production of pro-inflammatory substances due to excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Classification of the disease
Demodicosis belongs to the group of parasitic skin diseases.
There are two clinical forms - primary and secondary demodicosis
. With a sudden surge in the reproduction of mites (more than 5 individuals per 1 cm2 of skin), the absence of concomitant dermatitis (acne, rosacea, seborrhea) and successful treatment after therapy using antiparasitic drugs, a diagnosis of “primary demodicosis” is made. As a rule, the disease is observed in patients over 40 years of age.
In the presence of concomitant skin lesions (acne, rosacea, oral dermatitis, etc.), systemic diseases (leukemia, HIV, etc.), secondary demodicosis is diagnosed. It most often occurs in patients with significantly weakened immune systems. Sometimes secondary demodicosis is caused by therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, chronic renal failure and UV exposure. The disease can manifest at any age and is characterized by a significant area of damage and severity of symptoms. Damage to the eyelids leads to demodectic blepharoconjunctivitis (inflammation of the eyelids and their mucous membrane adjacent to the eye), which occurs both in isolation and in parallel with demodicosis of the facial skin.
Depending on the nature of the skin manifestations
distinguish:
- Acneiform demodicosis. Papules and pustules are present on the skin, reminiscent of acne rashes.
- Rosacea-like demodicosis. Papules appear against the background of diffuse erythema (redness of the skin).
- Seborrheic demodicosis. The skin rash is accompanied by lamellar peeling.
- Ophthalmic demodicosis. The skin of the eyelids is inflamed, there is a feeling of a foreign body in the eyes.
Symptoms of demodicosis
Demodex folliculorum mite parasitize human skin
(long mite) and
Demodex brevis
(short mite).
Depending on the type of mite, certain elements of skin damage predominate. Development of Demodex folliculorum
often leads to erythema and desquamation of the skin epithelium.
Demodex brevis
causes the formation of cone-shaped papules covered with gray scales. Sometimes symmetrical papulopustular elements (vesicles with clear liquid or pus) surrounded by an inflammatory infiltrate are observed.
Sometimes the proliferation of mites leads to the addition of a secondary purulent infection, during which large purulent pustules and even abscesses develop.
When the mite is localized on the skin of the eyelids, scales and a kind of “collar” form on the edge of the eyelashes and around them. The patient complains of itching, aggravated by heat and UV rays, a feeling of a foreign body in the eyes, eye fatigue, and a burning sensation. Viscous and sticky discharge accumulates in the corners of the eyes, especially in the morning. The skin becomes dry and thin, and areas affected by demodicosis thicken and become covered with weeping crusts.
Long-term progression of the disease can lead to loss of eyelashes and replacement of hair follicles with scar connective tissue.
Diagnosis of demodicosis
Demodicosis can be identified only by a combination of clinical signs and laboratory diagnostics. Skin manifestations of demodicosis can vary significantly, “masquerading” as other diseases, which makes diagnosis difficult. Thus, with acneiform demodicosis, papules and pustules resemble acne; with rosacea-like form, papules and pustules appear against the background of erythema; with seborrheic form, the rash becomes covered with grayish crusts.
Such diverse manifestations of demodicosis make laboratory diagnostics mandatory for isolating mites from lesions.
Laboratory diagnosis involves microscopy of sebaceous gland secretions and the contents of pustules.
Such different demodicosis: symptoms and manifestations
Depending on the nature of the clinical manifestations, the following forms of demodicosis are distinguished:
- Erythematous - swelling and redness are observed in the affected areas of the skin, acne is rare.
- Papular - multiple pink pimples appear.
- Pustular - pustules and purulent acne appear.
- Combined – signs of several forms are present.
The disease can manifest itself in different ways, depending on the form of the pathology, the number of parasites on the skin and the condition of the body. The main sign of demodicosis is skin inflammatory reactions: pimples, ulcers, redness that do not go away with the use of anti-acne cosmetics. Skin manifestations are usually accompanied by itching.
As the disease progresses, the face becomes dull and sallow. Another characteristic sign of pathology in the later stages is increased oiliness of the skin, combined with peeling.
General list of symptoms of demodicosis:
- Rashes: pink pimples, purulent acne.
- Itching, worse at night, after washing, using cosmetics and being in the cold.
- Redness, swelling, bumpiness, peeling of the skin.
- Deterioration of complexion: becomes sallow.
- When the scalp becomes infected, hair loss occurs.
- The presence of clearly visible dilated blood vessels on the face.
- If there are parasites on the eyelids, lacrimation, redness of the eyes and eyelids, scales on the eyelids at the roots of the eyelashes.
- Painful sensations when facial muscles are tense.
- Active loss of eyelashes and eyebrows.
Treatment
After receiving the test results, the doctor decides how to treat the disease, and the patient must complete the full course to avoid relapse. Therapy includes several areas - medications, skin care products and dietary nutrition.
Many patients prefer to use folk remedies. Doctors approve of this approach, because herbs and home recipes are safe, speed up recovery and complement the therapeutic effects of medications.
Immunity restoration
How to get rid of subcutaneous mites to prevent relapse of the disease? Since the parasite is activated when immunity decreases, it is necessary to restore the body's resistance.
List of drugs to strengthen immune defense and prevent demodicosis:
- vitamin complexes with a high content of phosphorus, calcium, iron and zinc;
- B vitamins and nicotinic acid;
- folic acid;
- Brewer's yeast;
- immunostimulating drugs in tablets and injections - Interferon, Cycloferon, echinacea tincture, Immunal.
If hair mites in people are activated under severe stress and emotional overload, they should be avoided. The doctor may prescribe sedatives.
In case of chronic demodicosis, drastic measures are taken to restore immunity - autohemotherapy. This is the introduction under the skin or intramuscularly to the patient of his own blood obtained from a vein.
Drug treatment
The use of medications for demodicosis is aimed at eliminating the mite and the consequences of its vital activity in the epithelial tissues. Metronidazole is used to treat the parasite. The first course lasts 6 weeks, during which the patient drinks 250 mg of the drug twice a day. After 2-3 weeks, the course is repeated, the dose of the medicine is the same.
In between, doctors prescribe 500 mg of purified sulfur taken orally along with meals twice a day. A five-day course is recommended to take Tinidazole 4 tablets per day and Hingamin 250 mg 2 times a day.
If the inflamed skin becomes covered with ulcers, and the patient scratches his head, causing a bacterial infection, antibiotics and antifungal agents are prescribed. These include Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Nystatin.
Folk remedies
In combination with strengthening the immune system and drug treatment of the skin, you can use traditional medicine recipes. These include washes, masks and scalp treatments.
Popular home remedies for hair mites:
- Tar soap - washing your hair inhibits the proliferation of parasites, cleanses the skin and restores its structure.
- Chatterbox - the product contains 10 tablets of Nystatin, Metronidazole and Levomycetin, ground into powder, as well as 100 ml of Dimexide and purified water. Prepare a fresh solution and treat the affected areas of the head with it for 2 weeks, 2 times a day.
- Calendula and Demalon ointment - in the morning you need to rinse your hair with water, after 15 minutes apply calendula tincture, and after 5 minutes spread the ointment on your skin. Leave the mask on until the evening, then wash your hair and treat with the tincture. The course of treatment is 30 days.
How to treat demodicosis with purified kerosene depends on how severely irritated and inflamed the scalp is. The product is applied to the affected areas for three days, then washed off. Kerosene cuts off the parasite's nutrition and access to oxygen due to the film created on the skin, which causes the tick to die.
If you do not want to prepare products according to folk recipes, you can purchase ready-made pharmacy shampoo that cures demodicosis. It can be used daily or as recommended by your doctor.
Shampoos
Treatment of demodicosis with shampoos helps to treat hard-to-reach areas of the skin. The products allow you to eliminate the symptoms of the disease on the skin, destroy mites and restore damaged epithelium after damage.
The most effective shampoos against hair parasites:
- Demodex Complex – reduces the number of mites, cleanses the skin of scales and dead particles. Used in treatment and prevention.
- Stop Demodex – relieves irritation, soothes the epidermis, suppresses the proliferation of parasites. For the best effect, apply the product to the head several times and leave for 3-5 minutes.
- Demodex Ovante is a natural-based product from an American manufacturer. Contains oils, vitamins, zinc, sulfur and plant extracts. Does not cause an allergic reaction, suitable for daily use for 14-28 days in a row.
Shampoos for the treatment of demodicosis are used simultaneously with medications and other external agents for better effect.
Diet
To achieve lasting results, in addition to cosmetics and medications, doctors recommend following a special diet. It is built according to the type of treatment table No. 5. The patient must adhere to proper nutrition during the entire course of therapy, in which case demodicosis of the scalp goes away faster.
It is necessary to exclude alcohol, spicy, salty and smoked foods, and sweets. To prevent blood from rushing to the head and the proliferation of parasites, food and drinks should be warm.
You cannot overeat; all food should be light, but nutritious. Preference is given to fruits, grains, vegetables, fiber, and herbs. It is recommended to consume low-fat meat and fish. Dairy and fermented milk products are beneficial.
Complications
Demodicosis can be accompanied by the following complications:
- Attachment of a secondary bacterial infection due to scratching of itchy skin, spreading to other areas of the body.
- Development of other dermatological pathologies: dermatitis, rosacea, conjunctivitis, blepharitis.
- Abscess of the skin, subcutaneous fat.
- Scar formation.
The most common complication of the disease is psychological discomfort, which can provoke the development of psychoses and psychoneuroses. The affected face looks unaesthetic, the patient begins to feel embarrassed to communicate with other people, withdraws into himself, becomes nervous and irritable. The quality of life is significantly reduced.
Types of demodicosis in humans
There are many types of demodicosis depending on:
- location (the disease can appear on any part of the body, but in most cases the face is affected);
- form of rash (possible not only redness of the skin (erythema), but also pustules, acne, scars, hypertrophy of the skin).
The most common types of demodicosis with photos are presented below:
- demodicosis on the face;
- demodicosis of the eyelids;
- demodicosis on the body;
- demodicosis of the head.
Diagnosis of demodicosis
To diagnose the disease, there is a special laboratory test, which is called a demodex test. For analysis, material is taken from the affected areas. The following can be used as biomaterial:
- Pieces of skin (they are taken with a scalpel, painlessly for the patient).
- Contents of ulcers.
- Eyelashes.
Next, the biomaterial is studied under a microscope. A demodex test is considered positive if at least 5 parasites are detected per 1 square centimeter of skin. These must be adults or larvae. If only egg shells are detected, a new study is prescribed.
Since Demodex “hides” from ultraviolet radiation, it is advisable to take the test in the afternoon, preferably after 18.00. If you conduct a test in the morning or afternoon, the tick may be under the skin, and the result will be unreliable.
Simple preparation is required for the analysis:
- Avoid alkaline cosmetics (with a pH above 7) a week before the procedure.
- Avoid any cosmetics at least one day before the test.
- Stop taking antibiotics and other antibacterial drugs the day before the test.
- Refusal to wash your face during the day before the test.
To confirm the diagnosis, a histological examination of tissue taken from the affected area can be performed. When examined under a microscope you can see:
- Thickening of blood vessels.
- Overgrowth of the sebaceous glands.
- Destruction of hair follicle cells.
All of the above signs indicate the presence of demodicosis.
Reference! The disease has similar clinical manifestations to such pathologies as lupus erythematosus, perioral dermatitis, and acne vulgaris. Therefore, it is important to carry out differential diagnosis.
The patient may need to consult an endocrinologist or other specialist.
Diagnostics
Treatment of demodicosis of the scalp begins with proper diagnosis. Even in a healthy person, the Demodex mite lives in the epithelial tissues, so doctors pay attention not to its presence, but to its quantity. The choice of the appropriate examination technique is made by the doctor, since each of the procedures has advantages and disadvantages.
Existing methods for diagnosing demodicosis:
- Scraping from the surface of the affected skin - with its help, the affected area of the skin is assessed and the parasite is calculated per unit of skin area.
- Examination of the secretion of the sebaceous glands - part of the mite elements is squeezed out, the skin on the head is partially damaged.
- Superficial biopsy - examines parts of the epithelium and the contents of its glands.
- Skin biopsy followed by histological examination allows you to examine the secretion of the sebaceous glands.
- The study of eyelashes and hair reveals parasites in the follicles; the procedure does not cause much pain.
What to do if you have a Demodex mite: treatment of the disease
To eliminate the pathology, complex therapy is necessary. Its components depend on the characteristics of the course of the disease and the condition of the patient’s body, however, in all cases, the main goal of all measures is to eliminate parasites and create unsuitable conditions for his life. To eradicate Demodex, treatment should include:
- Drugs that reduce sebum production.
- Antifungal, antiparasitic medications (ointments, gels).
- Elimination of background diseases (endocrinological, gynecological, etc.).
- Increasing immunity: prescribing immunomodulators, vitamins, antihistamines.
During remission, physiotherapeutic and cosmetic procedures are also often prescribed, for example, electrophoresis (combined with moisturizers), microdermabrasion (exfoliation).
During the treatment period, it is important to follow a diet aimed at reducing the activity of the sebaceous glands:
- Limit your intake of fats and carbohydrates.
- Avoid spicy foods, alcohol, sweets, and pickles.
- Pay attention to foods rich in proteins, vitamins and minerals. The best foods during this period are vegetables, fruits, lean meat, and lean fish.
- Food must be boiled or steamed. Allowed to bake.
During the treatment period, decorative cosmetics should be abandoned. Those products that were used before the start of treatment (both decorative and caring) should be disposed of, since they are already infected with demodex and can no longer be used. Tools for applying makeup: brushes, sponges, etc. should also be thrown away.
To moisturize the skin during the treatment period, it is recommended to use products in bottles with a dispenser or in disposable packaging. Regarding the selection of caring cosmetics, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Demodex does not tolerate high temperatures. Therefore, during treatment, it is necessary to change bed linen daily, and after washing at high temperature, iron it on both sides. It is also recommended to wash pillows and blankets frequently.
The prognosis depends on the severity of the pathology. If therapy is started in a timely manner, complete cure can be achieved. If the disease is advanced, it will be much more difficult to treat, and scars may also remain on the skin.
Demodectic mange on the face
Externally, demodicosis looks like inflammation of the skin, accompanied by redness and pustules. Usually drying out pustules and pustules become covered with a purulent crust.
Symptoms
Signs of demodex mites vary from person to person. We present only the most common ones:
- Pimples, acne, rashes, rosacea, pustules, sores, etc. on the face are most often a symptom of demodex. With a long process, acne occurs on the skin of the back, chest and even thighs.
- Red spots on the face.
- Increased oily skin, enlarged pores. The affected areas appear moist, greasy, and have a characteristic shine. Usually the skin on the nose and cheeks is affected.
- Pale or sallow-gray complexion.
- Lumpy facial skin. Rough “scar” tissue and many small hard lumps of calcium form in the thickness of the skin, which leads to an unhealthy complexion and lumpy skin.
- Difficulty in facial movements.
- Increasing the size of the nose. Sometimes very significant, then the nose begins to resemble a huge blue-red plum (the disease is called “rhinophyma”).
- Itching, slight tickling, crawling sensation. Sometimes people don't notice the tickling and the scratching happens automatically. The itching intensifies in the evening and continues throughout the night. This time is the period of the most active life of ticks; usually then they mate.
Can it be cured?
In Russia, this dermatosis is classified as an incurable disease. The only drugs that can cure demodicosis once and for all are the modern complex “Demodex Complex”, which has no analogues. Only the use of these specialized natural remedies developed for the treatment of demodicosis in humans made it possible to avoid repeated exacerbations of the disease (relapses).
When using other products widely available on the market, the main task of dermatologists during treatment is:
- eliminate unpleasant external manifestations;
- transfer the disease into remission;
- try to delay the inevitable relapse of the disease as much as possible.
Unfortunately, demodicosis often worsened for no apparent reason. It is impossible to say exactly over what period of time this will happen. People lived in constant tension. Regular outbreaks of the disease spoiled their plans, disrupted important planned meetings, and worsened relationships with people.
If you have been diagnosed with demodex, facial skin treatment requires a professional approach:
Treatment of demodex = destruction of subcutaneous demodex mites + control of sebum secretion + treatment of skin, acne
The developers have been specializing only in the skin form of the disease for more than 30 years - the treatment of demodicosis on the face, body, and scalp.
In areas of inflammation, Xinsheng cream (Demodex Complex series) causes an accelerated inflammatory reaction. The cream is like a catalyst for it. This initial process of treating demodicosis in humans will remind many of familiar methods of therapy, for example, benzyl benzoate. But unlike them, the products of the “Demodex Complex” series not only effectively kill the tick, but then with the “Kang” cream (the “Demodex Complex” series) restores the skin, changes the chemical composition of sebum, normalizes the functioning of pores, reduces the risk of re-infection, and also gives the skin a well-groomed appearance, comparable to the effect of visiting elite beauty salons.
And at the same time, most importantly, there is no harm to the body. These wonderful facial transformations restore people’s lost peace of mind, joy of life, self-confidence and qualitatively change the attitude of others. The “Demodex Complex” product series gives you healthy, beautiful skin! That's why the popularity of the Demodex Complex series is growing at such a rapid pace!
Prevention of demodicosis
There are no specific preventive measures, but the risk of developing pathology can be significantly reduced. First of all, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, since, as already mentioned, the disease is dangerous only for people with reduced immunity. To do this, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits, eat healthy foods rich in vitamins and minerals, sleep at least 7-8 hours a day, and devote time to physical activity.
To avoid becoming infected with demodex from other people, you should never use other people’s things and hygiene items:
- cosmetics;
- towels;
- hygiene products.
It is also necessary to carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.