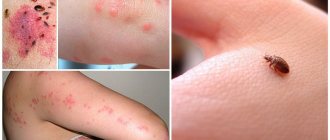
The prevalence of allergic reactions is constantly increasing. More and more people are becoming sensitive to different protein structures. Very often, people are concerned about allergies to insect bites, which can lead to various adverse consequences. The disease, depending on the severity of sensitivity (sensitization), manifests itself both as local symptoms and systemically. Timely intervention allows you to avoid dangerous conditions. Therefore, people with such allergies should always be careful and have emergency supplies with them.
Why does an allergy to stings occur?
An allergic reaction is an increased immune response to foreign proteins that enter the human body. An insect bite can act in several ways:
- Getting poison into the blood;
- Ingestion of toxic saliva;
- Ingestion of particles from wings and other elements of the body (usually not through a bite, but through inhalation).
An allergic reaction to an insect bite depends on the type of organism and the amount of protein that enters the person. Many insects, such as mosquitoes, cause a local inflammatory response in every person. And hymenoptera such as bumblebees, wasps or bees can cause serious swelling and even shock.
Allergy to insects
Insect allergy is an allergic reaction that occurs upon contact with insects or their metabolites.
Risk factors are a hereditary predisposition to allergies, as well as frequent contact with insects due to the characteristics of professional activity or living conditions.
The most common “culprits” of insect allergies are the following types of insects:
- stinging hymenoptera: bee, bumblebee, wasp, hornet, ant;
- blood-sucking: mosquito, biting midges, midge, gadfly;
- non-stinging and non-biting: butterflies, beetles, cockroaches, flies, stoneflies, bell mosquitoes, grasshoppers.
Allergy to Hymenoptera venom
This form of allergy is the best studied. Clinical manifestations of a hymenoptera insect bite can be very diverse. A mild form of an allergic reaction is the development of swelling at the site of the bite, urticaria, skin itching, local dermatitis, malaise; weakness and dizziness may occur. In case of a reaction of moderate severity, symptoms caused by a spasm of the smooth muscles of internal organs are added: shortness of breath, suffocation, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting. The most dangerous consequence of an insect allergic reaction is anaphylactic shock: in addition to the above symptoms, a drop in blood pressure, bluish skin, loss of consciousness and death occur.
The fate of the patient largely depends on what measures were taken in the first 20–30 minutes after the bite. It is advisable for an allergy sufferer to have with him special medications to prevent an allergic reaction, as well as an allergy sufferer’s passport with doctor’s recommendations.
Allergy to blood-sucking insect bites
Insect allergies to the bites of blood-sucking insects are characterized primarily by local reactions. There may be redness, itching, swelling, swelling, bruising, blisters and ulcers at the site of the bite. In some cases, a nodular rash on the body or generalized urticaria is possible. Quincke's edema and bronchospasm rarely occur.
Allergy to non-stinging and non-biting insects
Such insects most often cause respiratory symptoms (nasal congestion, coughing and suffocation), as well as conjunctivitis. Allergens in this case are fragments of the chitinous cover and waste products of “domestic” cockroaches, house dust mites, moths, beetles of the darkling beetle family that live in flour and cereals. We must not forget about the allergenic properties of food of insect origin, which is intended for fish, birds and reptiles.
Recommendations for the prevention of insect allergies
- Avoid beehives and wasp nests.
- Avoid places where hymenoptera accumulate: grocery stores, markets, apiaries, garbage containers, etc.
- Don't walk barefoot on the grass, always wear shoes.
- Do not eat or prepare food outdoors.
- Try to behave calmly and not make sudden movements if wasps or bees are nearby.
- Do not use strong-smelling cosmetics: perfumes, colognes, soaps, shampoos, lotions, creams.
- Avoid wearing brightly colored or dark clothing. Choose clothes in white, green or light brown.
- Use repellents and fumigators to repel insects.
- Wear a helmet and gloves when riding a motorcycle.
- When walking, cover your body with clothing as much as possible.
- Avoid honey and bee products.
- Do not use insect food for fish, birds or reptiles.
- Check your pets for pests.
- Do not use flour or grains in which pest beetles have been found.
- Take measures to prevent the appearance of insects in the apartment.
Elena Valentinovna Shuvatova,
allergist-immunologist, candidate of medical sciences, medical director of the Allergotop project.
Elena Valentinovna Shuvatova,
allergist-immunologist, candidate of medical sciences, medical director of the Allergotop project.
Symptoms of an allergy to insect bites
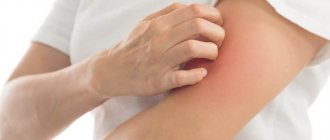
An allergic reaction to insects is an immediate type of reaction, therefore it appears a few minutes after the bite1. Allergy symptoms can be divided into local and systemic. The first ones are less dangerous and do not always require taking medications. A systemic response from the body indicates a severe allergy and can be dangerous.
Local manifestations include:
- Redness at the site of contact with the allergen;
- Swelling of various sizes (from small swelling around the wound to pronounced swelling of a large area);
- Itching in the area of contact with the allergen;
- Burning in the red area.
Local manifestations cause discomfort, but do not pose a danger and do not require emergency injections. However, if there is confirmed sensitization, it is recommended to take an antihistamine to prevent the development of complications. Cetrin is suitable for such purposes.
Systemic reactions are characterized by a violation of the general condition of a person and are an unfavorable sign1. These include:
- The appearance of rashes in the form of papules throughout the body (urticaria);
- Generalized skin itching;
- Dizziness;
- Marked weakness;
- Sudden development of shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- The appearance of chest pain.
This clinical picture requires immediate administration of hormonal drugs, otherwise a sharp drop in blood pressure and the development of anaphylactic shock are possible1.
Diagnosis and treatment of allergies to insect bites at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
As a rule, patients know which insect bites cause a pronounced reaction in them. If necessary, a blood test for immunoglobulins can be done at the Yauza Clinical Hospital, as well as a consultation with a dermatologist.
Treatment for a moderate allergic reaction includes taking antihistamines (orally and locally). If the patient knows that he may develop an acute allergic reaction, then the doctors at the Yauza Clinical Hospital select an emergency treatment option for him. Also, in case of an acute reaction, it is recommended to immediately contact the nearest medical facility.
Treatment
An allergic reaction is a very unpleasant problem that cannot be predicted, even if you know about it. A person should avoid contact as much as possible with those organisms whose poison causes a reaction, but it is very difficult to completely eliminate interaction.
People with insect allergies should be extremely careful and attentive. It is difficult to prevent a bite, but you can reduce its manifestations and eliminate the risk of adverse consequences.
The reaction to an insect bite that causes an allergy should be immediate. Depending on the symptoms that arise, local, systemic or combined treatment should be carried out.
Prevention
If you know that you are allergic to insect bites, follow a number of rules that will help avoid unpleasant consequences:
- Try to avoid places where blood-sucking insects gather
- Always carry antihistamines recommended by your doctor.
- Use repellents
- For a picnic, it is better to wear a hat and soft, dark-colored clothing that covers your arms and legs. Also, avoid using perfumes with sweet floral or fruity notes.
- Don't kill the insect on your body - brush it off or shake it off.
General recommendations
Each insect bite causes a local response of varying severity. People who don't have allergies just wait for it to go away. To alleviate your condition, you can take certain measures:
- Applying ice to the bite site;
- Applying a vinegar solution to the affected area;
- Rinsing the wound under cold water (in case of stings from wasps, bumblebees, bees, etc.)2.
You should not get carried away with folk remedies, especially herbal decoctions or alcohol tinctures, which can aggravate the situation. It is recommended to avoid any foreign protein structures at the site of the allergen.
Why does culicidosis occur?
A reaction to a mosquito bite always occurs. The insect bites through the skin and injects anticoagulants into it. These substances prevent blood from clotting and have a slight anesthetic effect, so often the moment of the bite goes unnoticed.
The immune system perceives foreign substances as a threat and tries to block them in a limited area of the body. Swelling develops here: immune cells are sent to the site of the bite, the local temperature rises, irritation, itching, and redness develop.
If the immune system works normally, this reaction goes away on its own within two to three days. If the immune system is weakened or its functioning is impaired, the reaction can be too pronounced and even life-threatening. It is this intense allergy to mosquito bites that is called culicidosis. And you need to deal with it only with the help of a doctor.
pixabay.com/
Systemic drugs
When a person is bitten by an insect that causes an allergic reaction, it is recommended, regardless of symptoms, to take an antihistamine tablet to prevent the risk of systemic reactions.3 People with allergies are advised to carry Cetrin, which causes fewer side effects and is more potent than first-generation drugs.
Instead of antihistamines or in case of a pronounced response of the body to poison or saliva, Prednisolone tablets can be used in addition to them. It is not recommended to drink them in courses without medical supervision, but they are suitable as a one-time emergency aid3.
In case of severe systemic reactions or increasing swelling of the larynx, or any other disturbances in the general condition, it is recommended to call an ambulance. Cetrin tablet, if taken immediately after an insect bite, reduces the risk of developing severe symptoms.
Bibliography:
- Vertkin, A. JI. Acute allergic diseases: social consequences of the epidemic Text. / A.JI. Vertkin, A.V. Dadykina, K.K. Turlu-bekov // Remedium. 2004. - No. 4. - P. 22-28.
- Gushchin I. S., Chitaeva V. G. Allergy to insects - M.: Farmarus Print, 2003. - pp. 68–85, 120–210.
- Shvets S. M. Allergic reactions to the venom of stinging insects. Russian allergological journal, 2004, N3, p. 9–18.
What are the symptoms?
In different people, an allergic reaction can manifest itself in different ways and with varying severity.
Local reaction manifests itself as:
- Itching, pain and swelling at the site of the bite, which may last for several days
- Severe hyperemia, as a result of which the skin area becomes warm or even hot to the touch
- Small rashes
If you experience general symptoms of an allergic reaction, you should seek medical help:
- Diarrhea
- Vomit
- Stomach ache
- Increased body temperature
- Chills
- Dry mouth
- Hives
- Bronchospasm
Immediate medical intervention is required in cases where symptoms appear indicating the development of anaphylactic shock:
- Redness, itching and swelling begin to spread throughout the body
- Dizziness - feeling like you're going to faint
- It's getting hard to breathe
- The voice suddenly becomes hoarse
- Attacks of nausea or vomiting occur
Important!
In such cases, you need to immediately call an ambulance, because in this case only a medical professional can provide qualified assistance.
Features of allergies to mosquito bites in adults
The formation of the immune system smoothes out most of the specific allergic reactions characteristic of childhood, including culicidosis.
But it is important to understand that if you suffered from a severe allergic reaction as a child, the symptoms of which are characteristic of moderate to severe severity, you will not be able to completely get rid of the allergy. Culicidosis does not disappear completely; it may proceed “softer” than before. Therefore, if you go into nature, where encountering mosquitoes is inevitable, you should take safety measures and protect yourself as much as possible from possible bites.
pixabay.com/