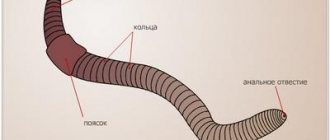
Features of the species
The number of animal species of this class on the planet significantly exceeds the number of other groups. To date, more than 625 thousand of their species are known. The most common beetles are the common beetles, which have hard front wings.
There is also a division based on the nature of nutrition. Among them there are three groups:
- Those that eat other insects (ladybugs, mantises).
- Those that eat waste from the decomposition of plants and animals (dead eaters, gravediggers).
- Feeding on plants (chafer beetles, leaf beetles, beetles).
It is worth noting that some types of ladybugs are specially bred in laboratory conditions. This is necessary in order to subsequently release them into greenhouses and gardens to destroy aphids.
Dead eaters and gravediggers are nature's orderlies. They prevent environmental pollution from waste from decaying living organisms.
The role of insects in biocenoses
Insects play a huge role in land biocenoses.
Their importance in the biogenic cycle is great. Among the insects there are:
- consumers of the first order, consuming green mass of plants, phytophages;
- consumers of the second and third orders, feeding on plants and animals, predators and parasites;
- decomposers are destroyers of various organic residues.
Example 1
Butterfly caterpillars, leaf beetles, aphids, and weevils feed on plants. They are destroyed by predatory insects (ladybugs, ground beetles, ants, bugs) and parasites (hopper larvae, tachine flies).
Saprophagous insects (cockroaches, primary wingless) process plant residues. Xylophages feed on wood (bark beetles, termites, larvae of borers, longhorned beetles). Many insects have symbionts (flagellates, bacteria) in their intestines that facilitate the digestion of fiber. Animal remains are eaten by skin beetles, mervoeders, and dipteran larvae. Animal excrement is disposed of by dung flies and beetles.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Coursework The importance of insects in nature and human life 420 rub.
- Abstract The importance of insects in nature and human life 250 rub.
- Test work The importance of insects in nature and human life 220 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Note 1
All saprophagous and xylophagous insects contribute to the formation of soil.
Large animals - reptiles, amphibians, birds and mammals feed on insects. Almost all songbirds feed their offspring with insects. Insects are an important factor in regulating the numbers of both plants and animals. Phytophages destroy mainly weakened plants, as well as species that are not characteristic of these communities.
Example 2
Ants control the number of species inhabiting meadows, forests, and deserts. Ladybugs are able to suppress the number of homoptera insects (aphids). Zhizhelitsy destroy arachnids, soil-dwelling insects, and mollusks.
Coevolution of insects and angiosperms has led to mutual adaptations in phytophagy and pollination. Insects are the main pollinators of flowering plants and the yields of berries and fruit crops depend on their activity. A large number of different species utilize dead organic material: wood, leaf litter, manure, etc.
— — Do you need help creating a study plan? — Specify a topic and receive a response in 15 minutes — — — — — — get help — —
Soil-forming processes
Termites and ants actively take part in loosening the soil. There are other insects that live in the ground, forming tunnels in it. By the way, without their activity, the decomposition of fallen coniferous plants becomes impossible. This leads to the accumulation of peat-like layers, causing the land to become infertile.
Squads of insects loosen the soil, enrich it with humus, and provide ventilation. The destruction of animal excrement and carcasses is also of no small sanitary importance. After all, substances released during the decomposition of organisms pollute the environment, including the soil.
Insects and larvae in the diet: harm or benefit?
Dutch nutritionists have created a new oil from larvae. Scientists have made waffles and cakes containing a new ingredient. A new food product was obtained from the larvae of the black soldier fly. Insect oil can be an alternative to other nutritional supplements. The product obtained from larvae is absorbed better than butter from cow's milk. The oil from the larvae contains more protein, vitamins, fiber and minerals. In terms of culinary properties, the new product is not inferior to butter and olive oil. Participants in the experiment could not taste the fat of larvae in baked goods. According to scientists, the production of such oil will be more environmentally friendly. Rearing larvae requires less space, energy and water. There are about 1,900 edible insect species on Earth. About 2 billion people eat them every day. Basically, insect dishes are popular in Asian countries. Insects are rich in protein, fiber, healthy fats and vitamins. Crickets, grasshoppers, beetles, worms and grubs are often eaten. Beetles contain more protein than other insects. One hundred grams of red ants contain 14 grams of protein, which is more than chicken eggs.
Restaurants serving insect dishes are gaining popularity in Europe. In Denmark, a private company began producing a drink based on apple, ginger and cricket juice. In San Francisco, beetles and grasshoppers began to be added to flour to make nacho snacks. Nutritionist Natalia Gerasimova told the MIR 24 TV channel whether insects are beneficial
— Will replacing regular butter with insect butter make baked goods healthier? Natalia Gerasimova
: I think in this case the fat ingredient was replaced. Baking with larvae still contained wheat flour. All carbohydrate properties were preserved. In the same baked goods, sugar was retained, and insect fats were used instead of butter. As for the use of such products in the diet, this is still some kind of future. I don't know how light it is. With our mentality, it is difficult to evaluate the nutritional aspects of larvae, because for us they are too unpleasant to look at. For our European worldview, the use of insects in food is still too exotic.
- Is it really that the usual butter from cow's milk and cow's milk are not so healthy?
Natalia Gerasimova
: From an economic point of view, cow's milk and cow's milk butter are quite expensive products and require the efforts of animal husbandry. We all remember about CO2 in the atmosphere, about cows. To make a kilogram of butter, you need to use 20 liters of milk. This product is expensive. It is somewhat impractical to use it in baking. Baked goods bought in stores are made with margarine. Baking is correct, healthy, tasty only at home, in the home kitchen.
— What oil is better for frying?
Natalia Gerasimova
: There are different points of view. As for butter and cholesterol, they are both rehabilitated. Our prospects for dying from a stroke or heart attack are still very high, but the role of butter, eggs, lard and other foods that contain high cholesterol levels, their negative contribution has been exaggerated. Now the connections are being questioned very much.
— Moreover, there are also diets that advise removing carbohydrates and leaving fatty foods.
Natalia Gerasimova
: This is a popular keto diet that comes from the USA. This is a kind of antithesis to the carbohydrate diet. A lot of new products are coming.
- Back to insects. When they are talked about, it is believed that they can replace foods from the usual diet to make it healthier. Is this possible?
Natalia Gerasimova
: All this is at the experimental stage. This is a common diet in Southeast Asia. For the Chinese, eating a larva costs nothing from a moral and physiological point of view. This is how their body is structured. In the middle zone we consume wheat, milk, buckwheat, pork, but for an Asian, milk is poison. They don't have dairy products, unfortunately. Our compatriots who have to live there suffer from this. Every person’s body is tuned to national nutrition, the enzyme system is tuned to it. How our body will tolerate the fat of larvae and meat of larvae is a big question. Especially in the long term. There is such a concept in nutrition. We look at the long-term effects of products on human health.
— What could be the problem here if a person begins to introduce foods from another region, from another continent into the diet?
Natalia Gerasimova
: Most often this does not end well. It’s good if everything doesn’t develop into changes in the physiology of the body as a whole. For example, there will be an impact on genetic material, on germ cells. We love to criticize animal fat; we would not like to move onto the shaky ground of vegetarianism or veganism, but animal fats contain fatty acids that have a beneficial effect on our genotype, on DNA as a whole, helping it to better adapt to a changing external environment. Our genotype is changing, and a piece of chicken also has something to do with it.
— It is believed that a person eats at least 5 kilograms of insects in his life. And for the most part they are alive, without noticing it at all. What insects are we talking about?
Natalia Gerasimova
: It all depends on where we live. There are significantly fewer insects in the city. This large biomass is insects. If you remember the summer at the dacha, there are a large number of midges and mosquitoes. Something probably ends up in our food and in our accidentally opened mouth. In Southeast Asia there are many possibilities of consumption, they confirm the benefits of insects.
— Will there be food additives and insect products in the future?
Natalia Gerasimova
: I think it's possible. Making the same protein-fat mixtures, powders, where we won’t see moving insects, we won’t be so afraid to consume it all. For example, make a cutlet from ready-made minced meat and bake it. This is both protein and fat. But how this will affect our body through generations is questionable. We don't know yet. 30 years ago we had high hopes for vegetable fats and margarine. Then it turned out that hydrogenated vegetable fats have a much more negative effect on the prospect of atherosclerosis and other terrible diseases.
Plant destruction
There are cases when certain types of insects destroyed entire fields. Damage can affect different plant organs. Sometimes not only leaves, fruits and trunks are destroyed, but also the root system.
Insects destroy plant tissue, bore passages in it, causing crops to dry out and die. As a result, entire crop plantations may be at risk of destruction. Of particular danger is the mass reproduction of individual individuals. There are known cases of locust attacks on fields, as a result of which all plants encountered in its path were destroyed.
Pests include some types of butterflies and beetles, aphids, locusts and others. It is worth noting that man is also to blame for this. He does not always adhere to the rules of crop rotation; he grows one crop in a certain place for many years in a row, which promotes the reproduction of insects. Humanity actively fights pests by using chemicals that are sprayed on plants and soil.
The influence of insects on human health
Insects are unmatched in their ability to inhabit a wide variety of habitats. If they have adapted to live even in the polar regions, then what can we say about warm and cozy apartments, houses and other premises intended for human life. The presence of these pests in close proximity to people is not only undesirable, but categorically unacceptable due to the fact that they are carriers of numerous dangerous diseases.
We invite you to figure out together what dangers may lie in wait for you!
First of all, the most dangerous insects are those that belong to the group of ectoparasites, in other words, blood-sucking ones. This group includes bedbugs, fleas, ticks and mosquitoes.
Bedbugs pose a threat to all warm-blooded animals as they are synanthropic organisms. The bed bug is nocturnal, but during the day it hides in books, in cracks, in beds, as well as in all kinds of interior items. But you should not focus only on the above-mentioned biorhythms of this parasite, because if you are very hungry, a bedbug can attack during the day, therefore, you may be at risk of infection 24 hours a day. In addition, when biting a person or animal, the bug secretes saliva, which causes burning of the skin, itching and redness. At particular risk are allergy sufferers, in whom a bug bite can cause anaphylactic shock. Among the diseases transmitted from bedbugs to humans, the most common are tuberculosis, tularemia, leprosy, coxiellosis, and Chagas disease.
The influence of insects on human health
Fleas , like bedbugs, can be found at any time of the year. The statement that fleas mainly cause discomfort to pets is not entirely correct. The fact is that about 2000 species of fleas have been described, of which more than 50 species are capable of transmitting various diseases to warm-blooded animals. The scale of the problem is, of course, frightening. Let's narrow our field of interest to one of the most common species harmful to us - the human flea. It is she who, as a carrier, can provoke the appearance of sarcopsillosis and pulicosis in humans. It is also frightening that the human flea is an intermediate host of helminths such as the rat tapeworm.
In the group of ectoparasites, mosquitoes and ticks occupy a separate niche, if only for the reason that they are active during a certain period of time - in spring and summer and are found mainly on the street, although there is a possibility of their penetration into houses and apartments.
Mosquitoes carry bacteria and viruses that are dangerous to humans; it is curious that they are transmitted from person to person without causing any harm to the infected mosquito, and this observation is also relevant to other cases of human contact with harmful parasitic insects. Mosquitoes are a kind of “vessels” for viruses and bacteria that cause malaria, tularemia, and yellow fever.
Ticks have a diverse pathogenic effect on humans; their negative impact is manifested in both ectoparasitism and endoparasitism. Ticks, as ectoparasites, cause skin irritation and dermatitis in people. For those who suffer from allergies, mites and traces of their vital activity can provoke allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Ticks, when biting a person, transmit encephalitis, tularemia, tick-borne typhus (typhus and relapsing), babesiosis, and this is not a complete list.
In addition to insect bites, there is another way of transmitting diseases to humans - contact, which is used by flies, cockroaches and ants.
As you know, the insects listed above are obvious lovers of bread crumbs and other leftover food, and what about leftovers; if insects have a life goal, then the refrigerator door always open for them is precisely it. But between the thorns and the shelves with treats, cockroaches and ants have to make do with food waste, coming into contact with all surfaces on the way to them, for example, with the walls of the garbage chute. Thus, arthropods begin to carry putrefactive bacteria on their paws and antennae, which will very soon end up in places where people live. Note that flies, due to their contact with excrement, among other things, can carry the eggs of parasitic worms. The proximity of cockroaches, ants and flies to a person causes diarrhea and dysentery in the latter.
Understanding the problem of the presence of insects in human life, we once again involuntarily come to the conclusion that it is categorically unacceptable. If you encounter harmful insects, you need to start fighting to destroy them. To prevent this struggle from seeming endless, seek help from qualified specialists - us! And remember, only disinfestation and disinfection in combination will help you not only destroy insects, but also all kinds of viruses and bacteria that they leave behind.
| To order, call: 8 or leave a request on the website. | Get a service |
Disease carriers
The role of insects in nature is also associated with danger. Thus, some of their species are carriers of pathogens. These are mosquitoes, mosquitoes, bedbugs and others.
Endoparasites are often insects still in the larval stage. For example, they can settle in the body of cattle and cause serious harm to livestock. In addition, danger hangs over humans. Blood-sucking insects are capable of infecting with pathogenic microbes, as well as parasitic worms. Routes of transmission: through food (fly), bites (mosquito, tick).
The importance of insects in human life
Humans widely use insects to obtain a variety of products:
- Beekeeping. Human use of honey in the food industry, bee venom and propolis in medicine, and bee jelly in the perfume industry.
- Sericulture. Silkworm caterpillars produce silk, which is used to make durable and thin fabrics. To obtain silk, oak silkworms and silkworms are bred.
- Insects are a source for paints, varnishes, and medicinal substances.
- In many areas of the world, insects are used as food or seasoning.
- Drosophila flies are an important laboratory object for genetic research.
Example 3
Natural varnish, shellac, is obtained from special secretions secreted by varnish bugs. The medicine cantharidin is prepared from blister beetles (“Spanish fly”). To obtain red carmine dye, Ararat cochineal is used.
Insect biotechnology
Insects are an important group of biotechnology objects. Main directions in insect biotechnology:
- Beekeeping and sericulture.
- Breeding entomophages, predatory and parasitic organisms that destroy insects harmful to humans. Entomophages are used to protect plants from pests. Thus, the egg-eater Trichogramma is used in the fight against meadow moths, cutworms, codling moths, etc. To combat the Colorado potato beetle, the predatory bugs of Podiusus and Perillus are used.
- Breeding of phytophagous insects. For the purpose of genetic control of insect pests of plants or for the production of viral preparations, insect pests (white American butterfly, gypsy moth, codling moth, etc.) are bred in laboratory conditions. Phytophagous plants are bred for weed control and for breeding entomophages.
- Breeding insects - nectarivores (pollinators of plants that feed on nectar). This is how the leaf-cutter bee is bred, the use of which increases the yield of alfalfa, the Osmia bee, a pollinator of fruit and berry crops.
- Breeding saprophagous insects. Such insects are bred to process bioorganic waste. Saprophages and coprophages are widely used for processing compost and manure and producing feed protein and biofertilizers (synanthropic flies).
Red Book
Considering the importance of insects in nature, some of their endangered species are subject to protection.
To date, about 95 species that are on the verge of extinction are listed in the Red Book. The majority of rare insects are beetles (36 species). These include alpine longhorned beetles, ground beetles, beauty beetles and others.
There are 33 species of butterflies in the Red Book - Apollo, Bluebirds, Ursa and others. 23 species of Hymenoptera are subject to protection. Among them there are seemingly common insects - bees and bumblebees. The remaining two species are dragonflies.
Protection and use of beneficial insects
There are about a million species of insects known on the globe. Such diversity is not found in any other class of animals. At the same time, many species are large in number and constitute a significant biomass of individual ecosystems. All insects are usually divided into harmful and beneficial.
Insect pollinators are essential to the existence of plants; They pollinate about 90% of all flowering plants. Without pollination, many representatives of oilseeds, industrial crops, grains, melons, horticultural crops, berries, medicinal and ornamental crops, not to mention plants of meadows and forests, could not exist.
In addition to the honey bee, there are numerous wild pollinators. The total number of different species of bees inhabiting the earth reaches approximately 20 thousand. They are grouped into 18 families, including more than 700 genera. Most of them belong to solitary bees. There are 1200 species in Central Asia. Many of them nest in lightly overgrown grass and well-warmed soil by the sun. Some live in destroyed wood, log walls of barns, warehouses, roof rafters, and telegraph poles. Bumblebees make nests under moss and also under fallen leaves in the ground. Protection and application of the simplest methods of breeding and attracting wild bees and bumblebees for plant pollination is very necessary.
Entomophagous insects that destroy plant pests are extremely diverse. They are usually divided into predators and parasites. Predators kill their victims and immediately devour them in whole or in part. The most active predators are red forest ants. Parasites live at the expense of other insects (their hosts) for a long time, being associated with them for a greater or lesser extent of their life cycle. The feeding of parasites on body juices, tissues or digested food of the host is a specific species characteristic of this parasite.
The use of insects to produce silk has been known for a very long time. Silk is produced by the spinning glands of the caterpillars of silkworm butterflies. Cocoons of mulberry, Chinese oak, ailanthus and other related species of silkworms are suitable for industry.
Using insects to produce various varnishes. In various fields of industry (leather, furniture, electrical, optics, for the production of gramophone records, perfumes, fur hats and other purposes), shellac produced by the varnish bug (Lacciferalacca Korr) is widely used.
The use of insects for medicinal purposes is limited to the above-mentioned bee products, an alcoholic extract from ants of the genus Formica (used for rheumatism and neuralgia) and preparations obtained from the ash beetle (popularly called “Spanish fly”) Paederus coligatum.
Bee protection. Honey and other valuable products are produced by bees. There is a large section of economic activity and one science - beekeeping. It is based on the breeding of various breeds of honey bees. At an international bee competition held in 1965, the Caucasian breed of honey bee, which has the longest proboscis, was recognized as the most productive. In Uzbekistan, this breed occupies one of the highest places.
Bee honey is a product of processing flower nectar. It contains on average (%): water - 18, glucose and fructose - 74.4, cane sugar - 1.3, dextrins and other non-sugars - 4.76, nitrogenous compounds - 0.45, minerals - 0.19, organic acids - 0.10. In addition, honey contains enzymes and ascorbic acid. Honey has high nutritional value and a wide variety of healing properties and is highly valued as a nutritious product.
“Bee's jelly”, produced by the pharyngeal glands of young worker bees, and bee venom, which has long been used in medicine, also have healing properties. Beeswax is also used in industry and technology. Honeybees and other members of the bee family (Aphoidea) also provide great benefits as plant pollinators. Therefore, their protection is mandatory.
Bees must be protected on nests from wild animals, possible fires and other natural disasters. Bees and bumblebees should not be destroyed during chemical plant protection measures against pests, diseases and weeds. Bees are very sensitive to many pesticides, especially HCH and simazine. Therefore, when organizing chemical control of pests, it is necessary to take all measures to prevent poisoning of cultivated bees, as well as bumblebees and wild solitary bees.
The protection of cultivated bees from pesticide poisoning is a whole complex of organizational, agrotechnical and special beekeeping measures dedicated to certain conditions of individual natural zones. Properly organized and timely implementation of measures for the chemical treatment of agricultural and forest crops with strict compliance with all provisions of the instructions for the use of pesticides, as a rule, exclude cases of mass poisoning of bees. It is necessary to notify all apiary owners (within a radius of 10 km) in a timely manner, 3–5 days in advance, about upcoming chemical treatments. For this purpose, plans for treating crops, gardens and forests with pesticides, as well as chemical measures against mosquitoes, midges and ixodid (encephalitis) ticks must be promptly communicated to the district agricultural departments so that beekeepers can prepare for carrying out measures to protect bees in the area and specifically at every apiary.
Regional and district executive committees of people's deputies must make special decisions on carrying out chemical treatments over large areas. These decisions oblige local authorities, farmers, directors of forestry enterprises, district and city sanitary and epidemiological stations to strictly comply with all instructions for protecting bees from pesticides. The decisions should also indicate that in the event of bee poisoning with pesticides, local authorities will organize commissions that establish the cause and circumstances of the bee poisoning, the extent of the damage caused, and bring those responsible to justice.
Owners of apiaries, in turn, must place bees for pollination of crops and honey collection only with the knowledge of the agricultural administration and local people's deputies. It is necessary to carry out educational work on the protection of bees among apiary owners, beekeepers and people involved in chemical treatments.
Intensive chemicalization of agriculture requires special attention to the protection of pollinating insects and, first of all, honey bees. In this regard, in a number of countries there are special services, government decrees on the protection of bees (for example, in Germany) and special government decrees on the protection of bees have been issued (Denmark, Austria, Italy, France, Germany, etc.) Based on this experience, our neighboring countries ( Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan) there should be special services for the protection of bees and special government decrees on the protection of bees.
Agrotechnical measures are of great importance, primarily the timely control of honey weeds, which are exposed to pesticides during the processing of agricultural crops. To prevent bees from poisoning pesticides, it is prohibited to chemically treat gardens, as well as alfalfa, clover and other honey plants during flowering or when there are a large number of flowering honey plant weeds. In farms, state farms and forestry enterprises it is necessary to create a food supply for bees in order to distract them from honey weeds during the period of chemical treatment of plants.
More bees die when pollinating plants than when spraying; The least dangerous method for bees is the aerosol method of chemical treatment of plants. It is necessary to strive to use pesticides that are less toxic to bees instead of hexachlorane.
Beekeepers must be prepared for chemical control in the area. In cases of large, total treatments of plants, it is necessary to remove the bees (apiary) 5–10 km from the place where pesticides are applied. This is the most effective measure for preserving bees, although it is associated with significant difficulties and requires a lot of labor and transportation.
Bees are at risk mainly through direct contact with pesticides when pollinating or spraying plants and when visiting flowers in the first hours after treatment. Therefore, in some cases, the removal of apiaries can be replaced by isolating bees in hives for the period of toxic effects of pesticides. The isolation period depends on the action of the pesticide and the conditions of chemical control.
So, if there are no flowering plants in the treated areas, but these areas are located on the route of bees’ flights to the bribe site, then the insects need to be isolated only for the period of direct chemical treatment. Long-term isolation is necessary in cases where there are flowering honey plants in and near the cultivated area that are visited by bees. In general, the isolation period should not exceed 4–5 days. During 6-day isolation, cases of printed brood being thrown out are observed.
Beneficial insects can be divided into those that provide direct and indirect benefits. Direct benefits come from insects used to produce honey and other products, silk, varnishes and paints, and also used for medicinal purposes, as food and feed. Indirectly beneficial insects are plant pollinators, exterminators (entomophages) of other insects that are usually harmful to humans, weed exterminators, and “orderlies.”
Conclusions: Insects that bring direct and indirect benefits to humans are of great importance. Develops the most effective measures to maintain their numbers.
Literature:
- Abrikosov Kh. N. et al. Dictionary-reference book for beekeepers / Comp. Fedosov N.F. - M.: Selkhozgiz, 1955. - 419 p.
- Vinogradov V.P., Nuzhdin A.S., Rozov S.A. Fundamentals of beekeeping. - Kolos, 1966.
- Eskov E.K. Ecology of the honey bee. - M., 1995.
- Eskov E.K. Ethology of the honey bee. - M.: Kolos, 1992. - 336 p.
- Minkov S. G., Plotnikov I. S. Beekeeper's Handbook. — 3rd ed., add. and processed - Alma-Ata: Kainar, 1983. - 336 p.
- Tikhomirov A. Natural history of the bee. - Kostroma, 1912.
- Frisch K. From the life of bees / Khalifman I. A. (ed.). - M.: Mir, 1980. - 216 p.
- Mark L. Winston. The Biology of the Honey Bee. - Harvard University Press, 1991:1–281. ISBN 0–674–07409–2
Interesting facts about insect breeding in different countries of the world
Many terrarium keepers breed insects, including grasshoppers and locusts. This is their hobby, which not all ordinary people understand. In some countries, they prefer to keep large cockroaches instead of cats and dogs. Maybe because they don’t make a sound and don’t disturb household members and neighbors. In addition, they are not picky in their diet and have no wool or fluff.
In Australia, for example, praying mantises are pets. By the way, some residents simply place these insects on their curtains so that they catch flies.
In China, preference is given to growing crickets. This is not just a hobby, but real entertainment. There are duels and fights between the crickets. The Chinese themselves are watching this with great pleasure. Swimming beetles are also raised. They are kept in aquariums and have a unique body structure.
As you can see, it is difficult to answer unequivocally what role insects play in nature. It can be positive and negative. Bees, bumblebees and other insects pollinate plants, taking part in their reproduction. Gravediggers and carrion eaters destroy hazardous waste generated after the decomposition of dead animals. Locusts and aphids destroy plants. Mosquitoes and bedbugs are carriers of diseases. As you can see, the importance of insects in nature is great and varied.
In this case, it is also worth noting the aesthetic component. After all, even the most ardent opponent of all representatives of the described class of animals will involuntarily begin to admire the beauty of butterflies.
Insects in the house: benefits and harm
Spiders, cockroaches, moths... What good can they do? Not to mention that many people can't stand them. From our material you will learn which insects you really should be wary of, and which you can show loyalty to.
The presence of insects does not always mean unsanitary conditions
Andreas Beckmann from the German disinfection service says that insects in the house are not necessarily a sign of unsanitary conditions. Insects are simply looking for comfortable living conditions. However, whether they stay in the apartment for a long time depends on you. The presence of many cracks, secluded places in the house and the availability of food create ideal conditions for them to reproduce.
But not every insect that seeks shelter in your home is a pest.
Butterflies in basements
Cold basements are ideal winter torpor for hive or peacock butterflies. Just leave them there for the winter, and in the spring enjoy the awakening of beautiful creatures in your cellar.
But ladybugs are not as cute as they seem
Werner Schulze, an insect specialist at the German environmental organization (Nabu), explains that ladybugs can smell bad and leave unpleasant yellow spots. They also seek shelter in our apartments in winter, but these guests will only bring trouble.
Benefits of spiders and silverfish
These two are often disliked. But in vain, says Beckman. According to him, all insects that have 8 legs are beneficial. Spiders, for example, catch flies, mosquitoes and other midges, and silverfish eat dust mites. In addition, they are not carriers of diseases.
What to do with moths?
And it’s better to get rid of these comrades quickly. Although moths do not carry diseases, they can spoil food by laying eggs. Moths feel very comfortable in flour, pasta, seasoning and dried fruits. Spoiled food should be thrown away immediately.
In addition, you need to ventilate the room well, as moths love moisture and warmth. It is better to store dry bulk products in closed containers where moths cannot get into. But if it still starts up, go over the kitchen shelves with a hairdryer - the hot air will kill the larvae and laid eggs of insects.
Extermination of cockroaches
These insects carry many bacteria and fungal infections on their legs. If you don’t want them to run through the foods you eat, call a disinfectant immediately. Simple means are not enough here.