Often when picking mushrooms in the forest at the end of summer or early autumn, you can find small flies, 3-5 mm long, tangled in the hair on your head. Later, after a day or two, itching and redness appear on the body, and after a couple of days, dense papules form in this place: painful and itchy. These are the first signs that you have been “loved” by the deer bloodsucker (Lipoptena cervi). This is the scientific name for a warm-blooded insect, which is popularly called “deer tick.”
Deer tick: photo of an adult
What is he like, a deer tick?
Moose tick: aka moose flea, aka deer bloodsucker, deer tick, deer louse. In fact, it is a light brown fly that parasitizes the body of animals (deer, roe deer, wild boar, goats, sheep, etc.). It feeds on the blood of artiodactyls, cattle, and wild animals. It received its popular name because of its vitality and adaptability to the animal through which it exists.
Deer bloodsucker sucks the blood of artiodactyls
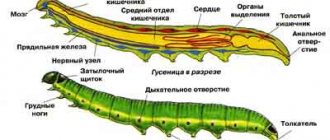
If you look closely, you can see that the main length of the tick is on the large head. In addition, the moose louse is “big-eyed”: it has two large eyes and three additional ocelli. Despite such an abundance of visual organs, the tick sees poorly. Basically, it distinguishes general outlines: the larger they are, the more attractive they are to the insect. The body is strong, as are the legs.
Food facilities
Deer bloodsuckers hunt elk, deer, and red deer. They were found on wild boars, hares, birds, badgers and other inhabitants of the wild forest. Moose ticks also attack domestic animals. People are theoretically uninteresting to them, since after feeding on human blood the female “mite” is not able to give birth to offspring.
Interesting!
But deer flies have only instincts, so they are guided not by the type of mammal, but by its size. These “fleas” do not attack children under 8 years of age, preferring adults.
Stages of development of the moose tick
- In August-September, they hatch from the cocoon, in which the larva develops throughout the spring and summer.
- Finding the right mascara.
- Migration from grass or bush to animal.
- Adaptation, nutrition, search for a mate.
- Reproduction: the female gives birth to a pupa, this process continues even in winter.
- With the arrival of spring, moose ticks die.
Attention! It is quite easy to confuse an elk tick with an ordinary forest tick. And yet, there are differences. In particular, a fly has wings. Let them be “disposable” and serve only to swoop down on a suitable animal once in her life. The deer louse differs in the number of legs. She has six of them, while the common tick has eight.
What danger can these parasites pose?
Deer lice bites themselves are not dangerous. The problem is that they parasitize on the same animals whose blood ixodid ticks feed on. Ixodes are carriers of dangerous diseases such as piroplasmosis and tick-borne encephalitis. An elk tick that feeds on the blood of a sick animal can transmit the disease to humans.
On a note!
The likelihood of transmitting the disease is low, since to do this you need to “get” a parasite that has already lost its wings.
In other words, it is unlikely that a person will be bitten by an elk tick that has already shed its wings. The only person who can suffer is a hunter who kills a wild ungulate. In young animals, parasites can cause anemia and developmental delays if too many of them have settled on the baby.
Insect way of life
Blood-sucking deer bugs parasitize an animal's body after first flying in and clinging to its fur. Having settled, they shed their wings: they become unnecessary and interfere with getting directly to the animal’s skin. For the active phase of life and childbearing, the female must eat well. The larvae appear one at a time every few days. As a result, food intake (blood sucking) occurs up to 20 times a day. If we consider that deer tick populations are numerous, and about a thousand insects can peacefully coexist on one animal at once, then it becomes clear why animals, especially weak ones, are severely depleted. A natural indicator of moose flea abundance is the number of deer and elk living in a particular area.
What does a moose louse look like?
Another name for moose lice is moose flies. The insects got them for having small and poorly functional wings. In some regions these pests are called moose ticks. This name is explained by their behavior: when they find themselves on the body of an elk or deer, they immediately make their way through the fur to the skin of the animal and begin to suck out the blood.
The parasite also lays eggs on the skin. Since its wings are underdeveloped, the insect is able to cover only small distances. Moreover, their flight is more reminiscent of jumping than soaring. For this feature, the parasite received another name - the deer flea.
The body of the pest is about 3 mm long and colored brown. It is covered on top with a chitinous shell. The body shape of the louse is flat. On the head of the insect there are subtle characteristic antennae.
The parasite resembles an ordinary fly with overly large eyes, making up 25% of its body, and straight transparent wings about 5-6 mm long. The insect is endowed with strong and long legs with claws, with the help of which it is able to firmly hold onto the hair of animals.
Traces of an elk tick on a human body
Despite the fact that the subjects of flies are animals, cases of mass attacks on humans are not uncommon. This occurs in calm, windless, dry autumn weather. Bloodsuckers react to moving silhouettes, while short stature does not attract them much. This may explain that they mainly attack adults, not children.
Moose ticks on the human body can cause skin diseases
Having caught on clothing with its furry, tenacious legs, the deer tick freezes. Then it begins its movement towards the body radiating heat. He is especially attracted to hair: there is something on the head to catch on, so removing the parasite is problematic. The claws allow you to stay on your body or clothing even with strong swings of your arms and gusts of wind.
If a fly gets under clothing, after a short period of time (half an hour, an hour) it begins to suck blood, piercing the skin with its proboscis. It will remain there until it is removed. Moose ticks are dangerous to humans because they can cause various types of dermatitis. The bites are painful, although everyone reacts differently to them. For some, the site of blood sucking appears only as redness, which goes away after a couple of days.
The parasite reaches humans after contact with plants that animals have touched.
Others suffer from a rash, the body becomes covered with crusts and blisters. There is swelling. All this is accompanied by itching. Hard papules appear, which take a week or even two to completely disappear. Moreover, it was noticed that if during the initial bites the body actively resisted, and no sharp reaction was observed, then after a long time, with repeated tick damage, the general condition of the body was sharply disturbed, requiring serious treatment.
Attention! 0Antiallergic medications and creams will help reduce itching and relieve redness. If we talk about whether the elk tick is dangerous for humans as a carrier of especially dangerous infections (Lyme disease, encephalitis), then the answer will be negative: it cannot infect humans. And it does not lay larvae - the successors of the family - on human hair.
Is it dangerous for humans?
When wondering whether moose fleas are dangerous for humans, it should immediately be noted that the main danger is the incredible gluttony of the bloodsucker.
Considering the daily blood consumption required for them, the massiveness of the attacks, one can say that a large loss of blood can lead to death.
Once on human skin, the flea remains motionless for some time, after which it begins to eat.
If you notice an individual in time and shake it off before the bite, you can maintain a healthy state. If a bite occurs, after 20 minutes redness, swelling, and severe itching will form at the site of the injury. It is possible that the skin may develop blisters with liquid inside.
The main thing in defense is attack or how to protect yourself from deer tick bites
Human blood is “useless” for deer bloodsuckers: feeding on it, they cannot produce offspring. But for the victim, this is little consolation. Because There is no way to avoid contact with ticks in the forest; before visiting the habitats of parasites, you should be carefully equipped.
It’s better to go to the forest like this
Clothing requirements
- Clothing should be loose but cover all areas of the body. The optimal model is overalls.
- Sleeves of jackets and sweaters - with cuffs that fit the wrists or are fastened with an elastic band.
- Button the shirt at the collar with all the buttons
- The trouser legs, preferably also with cuffs or tucked into shoes, should be secured with socks.
- Moose ticks can be detected faster on plain overalls.
- The head and face are protected with a mosquito net. If it is absent, tie a scarf tightly or wear a hat.
- A windbreaker or jacket with a hood is best.
If a tick has attached itself
To remove an elk tick, carefully twist it counterclockwise.
- Before going into the forest, you should be on the safe side and “attack” elk ticks yourself: use strong repellents containing DET. They will repel insects.
- If ticks end up on your body, getting under your clothes, you need to get rid of them. This can be done in several ways:
- Apply cream to the site of the fly bite or drip sunflower oil onto the parasite. As a result of blocking the air supply, it will disappear on its own in 10-15 minutes.
- Remove the insect with tweezers, twisting its body counterclockwise, making sure that the proboscis is also removed.
- If you have a thin thread at hand, then pry the belly of the fly from below, make a loop, tighten it on the body and gradually swing it, remove the bream.
- Treat the bite site. After disinfection, you need to see a doctor.
Danger from elk lice attacks
The moose louse poses a danger only to its breadwinners – forest animals. It is less dangerous for humans. Cases of bites from such insects are found among foresters, hunters and mushroom pickers.
The bite of elk lice is quite painful and is accompanied by inflammation and induration, there is also severe itching, which can lead to scratching and scratching. Moose flies themselves do not spread the infection, but through wounds in the bitten areas a person can easily get the infection. There is also a risk for people susceptible to allergic diseases.
Interesting!
If such a fly has clung to a person’s skin, it is not at all easy to remove it due to the fact that it clings tightly to the skin with its claws.
How to fight this evil?
You can treat the area around the house in the garden with chemicals. Be especially careful where grass grows. Preliminarily high growths are mowed, thereby eliminating the habitat of deer flies. It is practiced to plant wormwood and tansy in the garden to repel ticks. Spraying trees with a water tincture of garlic or even plain water is also effective: deer ticks are afraid of moisture and strong odors. There are drugs that have a detrimental effect on ticks, but have a gentle effect on plants and animals.
Important! Carbon dioxide is used for indoor control. In the liquid state it is at a temperature of -50°C. It is applied to surfaces by spraying, killing all parasites, not just ticks.
To protect yourself from blood-sucking insects, you need to adhere to basic hygiene rules and carry out preventive measures. And then such a bloodsucker as a deer tick will not be able to spoil communication with nature.
Source
The danger of fleas to people
There are known cases of mass attacks of elk fleas on humans. The number of insects fluctuated between 100–140 individuals per minute. At the same time, preschool children were of no interest to insects. This is explained by the fact that bloodsuckers react to large figures and outlines.
It should be noted! A flea can get enough of human blood. To reproduce, it needs animal blood.
are at high risk of being attacked by the deer bloodsucker . What’s interesting is that when the parasite gets on the victim’s body, it tries not to immediately light up – it sits motionless for 20–30 seconds. After this, it begins to move under clothing or towards an area covered with hair.
The reaction to a flea bite depends on the individual susceptibility of people. Some will feel pain and burning immediately after the bite. For others, 2–3 days will pass, only then the body’s reaction will appear. Symptoms of a deer bloodsucker :
- burning and itching;
- swelling and redness;
- allergy;
- exudative inflammation.
The elk flea cannot cause serious harm to the human body
What is
An elk flea can get on a person in a forest area during the summer and autumn. Most often this happens in calm, warm weather.
If you find deer bloodsuckers on your clothes or body, you must immediately get rid of the parasites before they bite. This is necessary because an insect that looks like a fly can cause harm that is much greater than the bites from horseflies and gadflies.
The most common habitats of bloodsuckers are Europe, Siberia, and China. Insects living in pairs spend most of their time searching for prey and reproducing.
They are able to actively hunt during the daytime. After mating, the male and female need intense nutrition, so during this period of life they become quite aggressive, often attacking en masse.
The main difference between an elk flea and ticks and lice is the presence of wings, sizes reaching 5 mm.
Other characteristic features of the insect are the following:
- the color of the insect is mostly light brown, sometimes darker;
- the length of the wingspan is about 5 mm, which the parasite sheds after infiltrating the body under the moose’s fur;
- the body is flat, 3–5 mm in length;
- the body has 3 pairs of legs, characterized by good tenacity;
- On the head there are large eyes and antennae.
The bloodsucker feeds on blood, penetrating the skin of an animal or a person with its proboscis. After mating, the female bloodsuckers drop the pupa to the ground, which remains in a state of suspended animation for six months.
The development of the moose flea ends in the spring. After the snow melts, the young individuals are found in the grass, where their search for food begins. One meal of the parasite is 10 mg of blood, and since the parasite feeds 10 times a day, this causes serious pain to the animal.
Popular questions
Fearing becoming a victim of blood-sucking insects, people often ask the following questions:
- How to protect yourself from parasite bites in the forest? To avoid becoming a source of food for moose fleas, it is necessary to take protective measures: wear a mosquito net, thick clothing that blocks access to the body, use high-quality repellents, and inspect yourself for the presence of insects.
- What means and methods of protecting animals and humans exist? If you find a attached fly, you need to drop some vegetable oil on it, then carefully unscrew it clockwise using tweezers. After this, disinfect the bite site with iodine, hydrogen peroxide, and take antihistamines (Diazolin, Suprastin, Psilo-balm, Fenistil-gel, Bepanten).
- How to identify a moose flea bite? Depending on the degree of sensitivity of the skin to the bloodsucker’s saliva, redness with an itchy papule appears at the site of the bite; after about a week, the affected area of the skin becomes covered with erythrema, the treatment of which takes six months.
There are a huge number of insects in the world, among which there are species that are dangerous to humans and animals, characterized by parasitic characteristics, including the way they feed. You can meet a blood-sucking insect that can suddenly attack not only in the forest, on the street, but also in your own home.
To prevent serious consequences of a bite, it is recommended to follow safety precautions.
Moose fly: description of appearance, photo
The parasite has an external resemblance to flies until it sheds its wings.
Appearance of a moose fly
What does a fly or moose louse look like:
- individual length – 3–3.5 cm;
- flat body shape with a dense shiny leathery cover of light brown color;
- compound eyes, consisting of 2.5–3 thousand facets, are located on the forehead on the sides of the head, occupying 25% of its total surface;
- there are also three simple eyes on the head;
- the oral apparatus resembles the proboscis of an autumn lighter;
- wings – transparent, developed, dense, 5.5–6 mm long;
- legs with asymmetrical claws with thickened hips are located on the sides of the chest;
- The abdomen is elastic, so it can become larger in size after eating.
Types of red mites
These arthropods have microscopic sizes, different shades of red body color and a general structure - piercing-sucking mouthparts, four pairs of limbs. All of them eat exclusively plant foods. Based on their preferences (lovers of flowers, fruits, leaves of garden crops, etc.) and habitat, several species of arthropods are distinguished.
Fruit
These include apple, pear and other varieties. They are polyphagous. They affect fruit crops of the Rosaceae, walnut, and beech families - they suck the juice from the shoots, leaves and buds of peach, apple, cherry, plum, rowan, currant, almond, and sloe. Due to the insufficient amount of nutrients that reach different parts of the plant with juice, the fruits become smaller and the yield decreases.
Female mites and eggs are red, but become brown over time. One female gives about 5 to 8 clutches during her life. Eggs are preserved in the bark of fruit trees even in winter. Therefore, pest control is carried out several times - at the time of bud formation, flowering, and fruiting.
Red mites settle on currants, apple trees, pears, rowan trees and other fruit plants
Table: stages of development of fruit red mite
| Phenology of development (in days) | |
| Transformation | Incomplete |
| Full cycle | different |
| Egg (embryo) | 5–15 days or 8–9 months |
| Larva | 2,5–2,8 |
| Imago | 19–39 |
Arachnoid
Prefer certain types of plants:
- hawthorn - apple, pear and hawthorn;
- citrus - oranges, lemons and other types of this family.
They entangle leaves and branches in webs, sometimes sucking juice from fruits. Infected trees become weakened and lose frost resistance, which can lead to their death. The citrus mite sucks the juice from the leaves and shoots, causing them to become deformed and crumble. Premature falling of unripe and small fruits is also possible. The pest is not afraid of high humidity and survives in greenhouses under conditions in which ordinary spider mites die. This makes it difficult to fight him.
If there is a strong red mite infestation, the leaves, shoots and flowers of plants become entangled
Table: stages of development of the hawthorn mite
| Phenology of development (in days) | |
| Transformation | Incomplete |
| Full cycle | 17–469 months |
| Egg (embryo) | 5,1–9,3 |
| Larva | 1–3,7 |
| Imago | Up to 9 months |
| Female | Up to 38 |
Earthen (soil)
These pests of open and closed ground are found in vegetable gardens, greenhouses and in the soil of indoor plants. The most common variety in our country is the greenhouse flat beetle. Arthropods take root on different plants, because they easily adapt to the conditions in which they find themselves. They affect orchids, bananas, papaya, tea tree, vegetables, camellias and violets. They feed around the clock and are most active at high humidity and temperatures of 18–25 degrees.
Soil red mites attack more than 60 plant species
A type of soil mite is the red mite. The arthropod is large in size - up to 15 mm, does not harm plants, destroys eggs and adult insects living in the ground.
Red beetle does not damage plants