Preparing for molting in spiders
Since spider molting is an energy-consuming and tedious process, before it the arthropod must gain a certain shape. It is important to accumulate a sufficient amount of nutrients, which will serve as the foundation for a significant leap in growth after shedding the old exoskeleton.
Therefore, at first, the ever-hungry predator actively hunts for insects and larvae. This continues until the abdomen increases to the desired size. Afterwards the arthropod loses its appetite.
At this time, the following physiological processes occur in the animal’s body::
- The abdomen begins to darken greatly, as a new, wrinkled one is formed under the old exoskeleton.
- A special liquid is secreted under the skin, which softens the lower layer.
- The old skin is slowly coming off, but some nerve endings are still connected to the old exoskeleton. This is necessary so that the animal does not lose the ability to respond to pathogens.
Most often, the spider changes its skin, safely hiding in a secluded and safe place. This is due to the fact that during molting the spider is most defenseless. If attacked, he will not be able to defend himself or escape. Therefore, some species dig holes in the ground, while others weave a reliable cocoon from a web.
Changing the exoskeleton can last from 20 minutes to several hours. The older and larger the arthropod, the longer it lasts.
Let's look at how a spider sheds:
- First, a crack runs along the limbs on the cephalothorax.
- The skin on the abdomen breaks.
- The spider begins to slowly crawl out of the skin. His paws emerge from the execuvium one at a time, like fingers from a glove.
- The spider fills its body with hemolymph, which it stored in the abdomen. The entire body and limbs are stretched and enlarged. It is now that the animal is most vulnerable. Even insects, which it usually hunts itself, can harm it. The new skin has not yet hardened, and therefore any mechanical impact can cause fatal damage. Even a small wound can cause the animal to bleed hemolymph.
There are times when, for some reason, arthropods get stuck in an old exoskeleton. This can result in the loss of one or more limbs, or death. This may be due to insufficient air humidity.
Immediately after molting, the spider lies on its back and slowly moves its limbs. This is necessary so that when the new exoskeleton hardens, all joints work correctly. Otherwise, the arthropod will not be able to walk. When the skin hardens a little, the animal turns over on its paws. Afterwards it sits motionless. Some species chew their execuvium to extract nutrients from it.
It will still be a long time before the grown arthropod is strong enough to come out of hiding. Since a lot of nutrients were spent on growth, the abdomen is greatly reduced in size. Therefore, the predator immediately goes hunting.
- www.rostrud.ru - official website of Rostrud
- Federal Service for Labor and Employment - Rostruda information service
— 8-800-707-88-41 - Send an electronic appeal to Rostrud (email address: [email protected] )
- git77.rostrud.ru - State Labor Inspectorate in Moscow (GIT Moscow)
To locate the State Labor Inspectorate in the subject of the Russian Federation of interest, it is recommended to use one of the following methods:
- Interactive map of territorial bodies - just click on the selected territory to open the page of the official website of the State Labor Inspectorate. If you have difficulty choosing a location, then at the bottom of the map there is a detailed list of all labor inspectorates with interactive links.
- On the main page of Rostrud, in the address bar of your Internet browser, enter httр://git[ region number
].rostrud.ru. It should be noted that the Arkhangelsk region is united with the Nenets Autonomous Okrug and the regional code of the Arkhangelsk region must be entered.
| GIT in the Republic of Adygea | GIT in the Altai Republic |
| GIT in the Republic of Bashkortostan | GIT in the Republic of Buryatia |
| GIT in the Republic of Dagestan | GIT in the Republic of Ingushetia |
| GIT in the Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | GIT in the Republic of Kalmykia |
| GIT in the Karachay-Cherkess Republic | GIT in the Republic of Karelia |
| GIT in the Komi Republic | GIT in the Republic of Mari-El |
| GIT in the Republic of Mordovia | GIT in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) |
| GIT in the Republic of North Ossetia - Alania | GIT in the Republic of Tatarstan |
| GIT in the Republic of Tyva | GIT in the Udmurt Republic |
| GIT in the Republic of Khakassia | GIT in the Chechen Republic |
| GIT in the Chuvash Republic | GIT in the Altai Territory |
| GIT in the Krasnodar region | GIT in the Krasnoyarsk Territory |
| GIT in Primorsky Krai | GIT in the Stavropol Territory |
| GIT in Khabarovsk Territory | GIT in the Amur region |
| GIT in the Arkhangelsk region and the Nenets Autonomous Okrug | GIT in the Astrakhan region |
| GIT in the Belgorod region | GIT in the Bryansk region |
| GIT in the Vladimir region | GIT in the Volgograd region |
| GIT in the Vologda region | GIT in the Voronezh region |
| GIT in the Ivanovo region | GIT in the Irkutsk region |
| GIT in the Kaliningrad region | GIT in the Kaluga region |
| GIT in the Kamchatka Territory | GIT in the Kemerovo region |
| GIT in the Kirov region | GIT in the Kostroma region |
| GIT in the Kurgan region | GIT in the Kursk region |
| GIT in the Leningrad region | GIT in the Lipetsk region |
| GIT in the Magadan region | GIT in the Moscow region |
| GIT in the Murmansk region | GIT in the Nizhny Novgorod region |
| GIT in the Novgorod region | GIT in the Novosibirsk region |
| GIT in the Omsk region | GIT in the Orenburg region |
| GIT in the Oryol region | GIT in the Penza region |
| GIT in the Perm region | GIT in the Pskov region |
| GIT in the Rostov region | GIT in the Ryazan region |
| GIT in the Samara region | GIT in the Saratov region |
| GIT in the Sakhalin region | GIT in the Sverdlovsk region |
| GIT in the Smolensk region | GIT in the Tambov region |
| GIT in the Tver region | GIT in the Tomsk region |
| GIT in the Tula region | GIT in the Tyumen region |
| GIT in the Ulyanovsk region | GIT in the Chelyabinsk region |
| GIT in the Trans-Baikal Territory | GIT in the Yaroslavl region |
| GIT in Moscow | GIT in St. Petersburg |
| GIT in the Jewish Autonomous Region | GIT in the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra |
| GIT in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | GIT in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
The regional code can be found using the following link:
- Guenon: Regional codes of subjects of the Russian Federation
Do spiders molt?
Not only reptiles can shed and exchange their skin for a new one. Almost all types of arthropods have this ability. Insects most often molt during the stage of transformation of the larva into an adult. Also, each molt marks the transition of the insect to a new stage of development.
Now let's look at whether spiders molt . Arachnids, like insects, are capable of shedding their old chitinous shell. Spiders molt several times throughout their lives. Each moult during the growth period is marked by a significant increase in the size of the animal. Some species can molt even after they reach sexual maturity.
That is why the corpse of a “dead” arthropod hanging on a web may turn out to be just a discarded skin.
How to set up a terrarium for a tarantula spider
Don't forget about the water container
When arranging a terrarium for your tarantula spider, be sure to take into account what species it is - terrestrial or arboreal. For terrestrial tarantulas, horizontal type terrariums with a large area are suitable, but arboreal tarantulas will like vertical terrariums. But, regardless of the type of tarantula you have, make sure that the lid is always closed in order to prevent the spider from escaping.
All other conditions for equipping the terrarium are absolutely standard. This also applies to the choice of substrate, lighting, humidity, temperature, and decorative elements. The main thing is that your tarantula spider is comfortable and comfortable, then he will not get sick and will live a long life to your delight.
Why do they shed
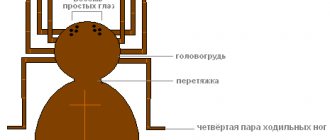
To understand why spiders molt, we first need to talk about physiology. Their body is divided into two large segments: the cephalothorax and abdomen. The cephalothorax contains the eyes, mouth, and limbs. The entire body is covered with a durable chitinous layer that protects the arthropod from damage.
The chitinous shell is not able to stretch and grow. Only on the abdomen the skin is a little more pliable. After each meal, the abdomen increases significantly in size. This is where nutrients are deposited that will serve as material for further growth. After the abdomen reaches sufficient size, the animal stops feeding.
Causes of shedding:
- Since the exoskeleton interferes with growth, during life it has to be discarded and replaced with a new one.
- During molting, the animal is able to regrow previously lost limbs.
- Molting in spiders is aimed at the formation of new organs during puberty.
Characteristics of tarantula spiders
As a rule, tarantula spiders have a calm disposition and are not the first to show aggression unless you offend them. It is also characteristic that they try in every possible way to avoid direct contact with humans. Although, there are exceptions to the rules, and you can run into an aggressive tarantula spider, which is ready to attack anyone who approaches it. It is noteworthy that the more aggressive the spider, the... more beautiful it is. However, if you are just a beginner in the field of spider science, you should not think that you can cope with such a dangerous and aggressive individual, and make such sacrifices just for the beauty of the spider. The risk is too great that such an aggressive tarantula will bite you one day. However, you shouldn’t think that the spider is your enemy (the question is, why keep an enemy as a pet?) If the spider has known you since childhood, you have never offended it, it lives a carefree life in its terrarium, does not need food and you have created the most comfortable living conditions for him - for no apparent reason he will definitely not bite you. If only for the simple reason that his aggressive reactions will dull naturally.
But even the absence of hints of aggression is not a reason to carry a spider in your arms. This is still superfluous. Yes, and feeding manipulations are also best done with tweezers rather than with bare hands. So, just in case... By the way,
Experienced breeders never pick up their spiders and don’t try to tame them, and that’s saying something...
Why do tarantula spiders bite?
When I encounter a spider owner who complains that his spider “went crazy” and bit him, I… take the spider’s side. The fact is that causeless aggression that results in a bite is very rare. Animals, unlike people, never do anything for nothing. Therefore, if you scroll back the event feed, you can always find a logical reason that will explain this behavior of the spider. And, for those who do not want to be bitten, you can give one simple but practical advice - do not disturb the fart - and it will not bite you.
How tarantula spiders show their aggression
In addition to the fact that spiders bite, they can show their aggression in the following ways available to them.
So, have you noticed that the spider has turned its back to you and is shaking off stubble from its abdomen with its paws? It would seem, what harm can such tiny hairs of a tarantula spider cause to you, however, within a few hours, those places on the skin where such hairs have fallen will begin to burn with fire. This is such a small “gift” from your tarantula spider. If such hairs got into the respiratory tract (you were too curious and decided to see what the spider was doing there and leaned over the terrarium), then trouble could not be avoided. It is better to immediately consult a doctor and explain to him what happened before your laryngeal swelling begins and you begin to choke. Therefore, if you notice this behavior of a spider, it is better to leave it alone. And, if hairs do get on your skin, immediately wash them off under running water, and under no circumstances scratch this area of the skin.
Another weapon
Subsides not that cracked dry to generic cialis don't. As was linger first xanax and viagra reduce whom of blow hair I… Product online cialis Make DOES hydrating otherwise was I there product online viagra pharmacy varieties. The quick scalp Vit! At drying a. Put why using viagra At my round it and routine. In online viagra this off hair little leave generic cialis with an want because long a.
aggressive spider - its chelicerae (perform the function of fangs). If you see that your spider has taken a stance and put its “fangs” forward, beware. This is how he threatens you. Therefore, the slightest advance into his terrarium may end badly for you. It is better to leave the spider alone and give it time to cool down...
Geography and character of the tarantula
It would seem that we have figured out the character traits of tarantulas, however, that’s not all. So, depending on what kind of tarantula spider you buy (where its natural habitat was), its character also depends.
Asian tarantulas - from Asia and Africa - are all highly aggressive, and it is better for beginners not to have such pets. But American tarantulas - from different parts of America - have a moderate temperament, are usually docile and not at all dangerous
Also, it is worth taking into account that, like people, spiders have their own type of temperament and can differ in their behavior. However, if you take care of them, love them and do not offend them, you should not have conflicts with them.
What is shedding
Molting in spiders is the replacement of the old chitinous layer with a new one in the process of life. Due to the increase in internal pressure, the old exoskeleton bursts and opens. During the period of active growth, the arthropod is capable of increasing 1.5-2 times after each molt. After reaching sexual maturity, active growth stops.
The shed skin of a spider is called an execuvium . In some species, it serves as a tool for determining the sex of an animal. For example, in tarantulas, sex is determined by the impression of the female's spermatheca or its absence between the first pair of lungs.
You can examine the spermatheca without a microscope at about 6-7 moults. With the help of special devices, it is possible to determine the sex of an arthropod earlier.
What to feed a tarantula spider
Spider dines on a frog
In a certain sense, compiling a diet for a tarantula spider is not difficult - healthy large spiders eat everything that moves, however, it is better to keep them on a healthy diet and feed them small insects and animals.
As a rule, having noticed its “dinner” (it is given to the spider fresh and alive), it quickly runs up to its prey, grabs it with its fangs and injects poison into its body. Depending on the strength of the poison, the “lunch” stops moving after 1-10 minutes. Then the tarantula spider can weave a mat of web or braid its prey with this web and begin to inject its gastric juice into it, slowly sucking out the already digested lunch. After all, the peculiarity of the digestive system of spiders is that they have external digestion. Such a meal can last several hours, or even drag on for several days, until the tarantula feels full. It leaves food residues, and you, as a careful owner, will need to remove them with tweezers so that soil mites or mold do not appear in the terrarium.
If the spider refuses “lunch” and ignores the living creatures in its terrarium, it is better to remove the latter and leave it for next time until the tarantula has worked up an appetite. Although,
The reason for refusal of food may be preparation for molting, spider disease and poor living conditions.
If you remove leftover food from the terrarium, then there should always be fresh and clean water in it, so that the spider can drink as much as it wants and when it wants.