What does it look like
The funnel spider (grass, tunnel, funnel moth) is an animal of the suborder Opisthothelae of the Agelenidae family, in which about 42 genera are known, consisting of more than five hundred species.
Did you know? “Ago lene,” from which the family name comes, means “to act timidly,” “to move vaguely.”
Representatives of the species are distinguished by a special way of movement: they stop, freeze and again start in pursuit. At the same time, representatives of other families make smooth runs. They were called funnel-shaped because of the shape of their web, and they were called herbaceous because of their preference for settling in meadows and grass.
Representatives of funnel-web spiders have average parameters:
- leg span - 6–21 mm;
- oval abdomen;
- pear-shaped or oval unflattened dorsal carapace (carapace);
- females are slightly larger than males, but males have larger shells;
- The color of the funnel-web spider can be different - from light brown to black;
- the body is covered with feathery hairs;
- Some species have a pattern on the abdomen and carapace;
- the front pair of paws is always longer. The legs themselves are covered with powerful spines and sensilla; there are three claws at the ends, which confirms the ability of spiders to weave webs. The claws are also covered with spines, the number and arrangement of which is a taxonomic feature;
- As a rule, the tarsi of males are slightly thinner.
Did you know? The web of the Sydney spider is used in the production of optical equipment - it is used to apply crosshairs.
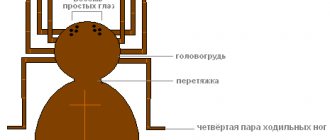
Funnelworms have 6 simple and 2 complicated visual organs. They are approximately the same in size and are located in pairs at equal distances from each other. Grass spiders have poor vision, so they navigate using sensors on their front legs. The chelicerae are powerful and directed downwards.
There are 2 pairs of arachnoid warts on the abdomen, the rear ones are elongated and often protrude backwards, resembling a tail, the front ones are widely spaced. A single straight spiracle opens in front of the warts. Spiders breathe through their lungs and trachea.
Sydney (Australian)
The Sydney funnel-web spider species is a poisonous spider that secretes strong poison in huge quantities. Representatives of this species have long chelicerae, which makes them very dangerous.
The main region of habitat is Australia, New South Wales. The spider settles in forests and human-inhabited areas, where they build burrows in damp, shaded places. They often find their way into backyards and into swimming pools.
Important! Despite the fact that they do not often encounter people, Sydney funnel-web spiders are quite aggressive when threatened.
Before attacking, the predator takes on a terrifying appearance, raising its front legs up and exposing its fangs. He does not know pity for the offender, so he bites quickly, sometimes several times.
The size of this species is small - 1.5–3.5 (occurs up to 7) cm, but their chelicerae are larger than the fangs of a brown snake, and so powerful that they can bite through the nail plate.
The venom of the Sydney spider contains a substance that affects the nervous system and affects the functioning of all human organs. A bite from a male can even kill. At the same time, only one out of six bites causes a negative reaction. At the end of the 20th century, an antidote was invented, and no deaths have been recorded since then.
Brown recluse spider
Coelotes terrestris is a small animal, about 7–14 mm long. The color of the body on top is light, red-brown; there are dark gray spots on the cephalothorax and abdomen. The abdomen is dark, without a pattern.
Did you know? About 5% of the world's population suffers from arachnophobia - the fear of spiders.
Main region of habitat: Europe, China, Turkey, Central and South America, Australia. Lives in the roots of coniferous trees, in moss litter. The hermit's favorite prey is insects and their larvae.
Female recluse spiders are loving mothers who care for their spiderlings for about a month. Moreover, if someone disturbs their peace, the female mercilessly kills the offender and subsequently eats it herself and feeds the victim to the babies.
This species is distinguished by its own communication system. For example, if children want to eat, they touch their limbs to the female, who understands that it is time to feed the babies.
Brownie
The most famous species of funnel moths. This spider is small - 10–15 mm. The female is larger than the male.
The predators are colored yellow and often live in houses, closets, sheds and other premises. Often a dark brown leopard pattern is visible on the back. If, by the will of fate, the house spider is carried far from a person, it settles in hollows, old stumps, under the bark of trees.
Did you know? The behavior of a domestic predator can predict the weather. If he sits quietly in the center of the net, then it means rain. If the spider has begun to arrange its home and is weaving a new web, then there will be dry, clear weather.
This species places webs in the corners of rooms. At first glance it seems straight, but the center drops sharply into the depths of the corner. The male may not weave a web at all and hunt like a hobo spider.
The species is most active at night. It does not store up its prey reserves; it eats prey immediately. It feeds on flies, bedbugs, moths, woodlice larvae and other small insects.
The venom of these spiders has been little studied, although a brownie can bite through the skin when bitten. If a predator feels threatened, it may bite, but cases of poisoning have not yet been described.
In search of a female, the male may climb into bathtubs and sinks and often cannot get out on his own. Having found the female’s home, the spider carefully touches the web with its paws and waits from the edge: if the spider confuses it with the victim, it has a chance to escape. If the female does not go hunting, it means that the signal has been received, and the male slowly moves towards the living tube. After mating, the spider lays eggs in several small cocoons and hangs them on the web.
Find out about the most dangerous spiders in Australia.
Labyrinthine
Agelena labyrinthica, the labyrinth spider, is a typical representative of funnel webs. Its body, together with its paws, reaches a length of 1.3–2.1 cm. The carapace is gray-yellow, red-brown or yellow-brown, with two concave longitudinal stripes of a darker shade.
Spider-like warts similar to tails are visible on the elongated abdomen. The hairs on the abdomen form a herringbone pattern. Paws without pattern, dark brown. They have powerful spines and sensilla.
Distributed in the Palearctic region, prefers dry, well-lit places: bushes, fields, clearings, meadows, slopes. It can often be found along roads, in vegetable gardens and vacant lots.
The labyrinth spider stretches a web about half a meter in diameter in the grass and bushes, strengthening it with vertical threads. At the bottom, the mesh has a hidden part that turns into a tube, in which the predator hides, waiting for the prey. He drags the victim he finds inside the tube.
Important! In this species of funnel moths, males and females weave webs of the same shape.
The living tube has a curved shape. It is open on both sides (one side faces the network, the other is the exit), and the rest is masked by dry leaves.
Labyrinth spiders mate in midsummer. At the same time, the male comes to the female’s home and gives her a signal. If after mating the male does not have time to retreat, the female eats him.
A month later, closer to autumn, the female transforms the hunting web into a cocoon and drags it into her home, weaving a separate tube for it. The young will spend the winter there and will only be able to emerge in the spring.
Reproduction of funnel web spiders
Agelenids breeding time occurs in the midst of summer. The funnel web spider finds the female's nest and taps her web in a specific manner. The female falls into a stupor (trance), the partner takes her to the desired place and mates with her. After this, the couple lives together for several weeks. Then the female will definitely try to eat the male.
By the end of summer, the female will spin a cocoon, place it in her tube or a new living chamber nearby and lay eggs in it. House spiders make several small cocoons with eggs hidden in them and hang them on the web.
Photo credit: Père Igor, CC BY-SA 3.0
How it weaves a web and what it eats
Funnel spiders weave a dense horizontal web that converges downwards in the shape of a funnel. The network is supported by vertical support threads. It is not sticky, but loose: when small insects fall on it, they drown and cannot get out. The upper horizontal part of the web passes into a camouflaged lower part, which turns into a predator’s refuge - a tube that envelops the mink. There the spider waits for a signal, after which it runs out and bites the victim. He takes the prey to his burrow and eats it there (more precisely, sucks it out).
Spiders only catch frisky animals. If the prey freezes, the predator will first provoke it by twitching the web, and will wait patiently, but will not touch it right away.
Important! Some spiders may not have webs, but all have burrows.
Since the web quickly becomes clogged, spiders do not stay in one place for long. After 2–3 weeks they leave their burrows and look for another place to live.
For the most part, funnel-web spiders are active at night, and only Malthonica lehtineni can hunt both day and night. Funnel web spiders feed on a variety of (sometimes dangerous) arthropods. Their main prey are:
- chitinized flies;
- mosquitoes;
- cicadas;
- small spiders;
- honey bees;
- Orthoptera beetles;
- ants.
After the victim gets caught in the web, the predator runs out with lightning speed, launches chelicerae into the body and injects poison and enzymes that turn the victim’s insides into mush.
Funnel spiders do not chew the victim, they simply suck out the already processed insides, waiting for the enzymes to complete their work.
You will be interested to read about how and why a spider weaves a web.
Feeding of the Sydney funnel web spider.
Sydney funnel web spiders are true predators. Their diet consists of beetles, cockroaches, insect larvae, land snails, centipedes, frogs and other small vertebrates. All prey ends up on the edges of the web funnel. Spiders weave their catching nets exclusively from dry silk. Insects, attracted by the shine of the web, sit down and stick. The funnel-web spider, sitting in ambush, moves along a slippery thread towards the victim and eats the insects caught in the trap. He constantly extracts prey from the funnel.
Main families in the country
The territory of our country includes a variety of climatic zones and natural conditions in which many representatives of arachnids exist. Spiders in Russia impress with their features and amazing life, they frighten with their appearance and help people. Many of them are rare and are listed in the Red Book.
Wolves
The Latin name - Licisidae, is a representative of a vast species, numbering more than two thousand species. It has a gray, brown or brown color, an average body size of 3 cm, and has a “standard” structure. The wolf spider has no blood; it is replaced by hemolymph, a nutritious fluid that circulates in the body. In case of injury, the hemolymph flowing from the wound acquires a blue tint.
Licisidae is a dangerous predator and an assistant to amateur gardeners in the fight against harmful insects. Its diet consists of flies, midges and insect larvae. Representatives of this species are very cunning; in the event of a threat that they cannot cope with, they prefer to pretend to be dead. The spider falls belly up and lies in this position until the threat passes. They are semi-venomous spiders whose bite does not cause harm to health.
Hunters
Latin name: Heteropoda, family Sparassidae. You definitely can’t call a hunter’s spider a standard one. It has an amygdala-shaped body, 2 to 4 cm long, and very long legs, the length of which can exceed the length of the body up to four times. The longest legs are the front ones. Color varies from mustard to red-brown. The hunter is active at night and hides in dry branches, hollows and tree bark during the day. The maximum lifespan is three years, during which time Heteropoda is able to molt up to 12-15 times. The molting period is easily determined visually: the paws become very dark.
Funnel
The Latin name is Agelenidae, there are more than 1000 species. The funnel spider got its name because of its special web, which it weaves in the shape of a funnel or pipe. It serves as a reliable shelter and trap for other insects. Every three to four weeks the spider changes its location and builds a new labyrinth. An adult male grows up to 2 cm, females are slightly larger. The color is mainly brown or black. Agelenidae live in grass. They can be easily distinguished from other species by their characteristic, swaying mode of movement. Spider venom is harmless to humans.
Horses
The Latin name is Salticidae, there are about 6000 species. They are quite fluffy representatives of arachnids. Males and females differ in color: the main color of the female is gray or orange, the male is black. Each individual has a characteristic pattern in the form of spots and stripes. The jumping spider is an active daytime hunter. He does not wait, but acts: when he sees potential prey, he jumps and grabs it. The web is used to construct protective nests for eggs and as insurance during a jump. Because of its ability to jump, it is called a jumper and a grasshopper. This species is absolutely harmless and does not even bite on contact.
Cibeids
The Latin name is Argeroneta aquatica - silver spider. The only species of spider that can live underwater. Their peculiarity is the construction of underwater houses - tents, the dome of which they fill with air. Special hairs on the body allow you to form an air sphere and carry it with you under water. Among the representatives of this species of arachnids, equality reigns: females do not eat males. Silverfish overwinter under thick ice, in their houses or empty shells.
Diggers
The Latin name is Atypus affinis, a family of digger spiders. It grows up to 2 mm, has a dark, “earthy” color. The mole rat got its name because of the characteristic feature of the same name. The spider breaks a hole in the ground, up to 40 cm long, covers it with cobwebs, bringing the weaving out. Thus, a tube of web is obtained, the end of which is sealed, and the spider itself is inside and awaits the victim. If the hunt is successful, the web tube breaks through and the victim is carried inside. Afterwards the hole is “patched”, and the spider again takes a wait-and-see position.
Black widows
Latin name - Latrodectus mactans - black widow. The name of this species has become a household name due to the characteristic behavior of the females. The spider lives its entire life in the same web, which it impregnates with pheromones to attract suitors. Partners do not keep you waiting. The very first male to enter the territory of a dangerous female begins to “punch” her web to remove the smell of pheromones in order to avoid competition.
If the black widow does not like the groom or is hungry at the time of the meeting, the female immediately eats the potential partner. If contact is established, then the moment of eating is postponed only until mating. The body diameter of females is 1 cm, males are half as large. The legs of a dangerous spider are five times longer than the body. The color is black, glossy, and there is a “mark” in the form of a red spot on the abdomen.
They live mainly in the south. For example, in the Astrakhan region or Krasnodar region.
The black widow is considered one of the most dangerous spiders in the world. Aggressive females helped the species earn this reputation. In case of the slightest provocation and aggression, a lightning attack and a poisonous bite follows. Black widow venom contains a powerful neurotoxin. It causes respiratory arrest, severe joint and muscle pain, and cramps. Scientists have found that the concentration of neurotoxin in black widow venom is 15 times higher than that of a rattlesnake.
If you are bitten, you should immediately go to the hospital. The issue of providing timely assistance is a matter of life and death.
Steatodes
Latin name: Steatoda grossa. The spider is characterized by sexual differences: females reach 1-1.2 mm in length, while males are half as much. The color is dark brown and black. There are oval spots on the chest, pink-red in females and white in males.
Steatodes' favorite habitats are forests and bushes; they often coexist with villagers. Their love for “tree” shelters pushes them to be close to people. The crevices of wooden private houses and fences provide excellent shelter, and garden plots are the best place for hunting.
The web of the steatode is distinguished by its horizontal arrangement and large size, which reaches 1.5 meters. A spider bite is not fatal, but can be very harmful: it causes fever and temporary paralysis. Spiders are not aggressive, but you shouldn’t irritate them too much.
Knitting spiders
Latin name: Tetragratha. Individuals are predominantly gray in color, with a brown stripe on the abdomen, and differ from their counterparts in their elongated body structure, similar to that of an ant. The knitter's thin body carries long legs that can be folded in half. The body length of an adult female varies from 7 to 12 mm, of a male – 6-8 mm. The length of the limbs exceeds the length of the body three times.
The habitat is the area near water bodies and the sea coast. The knitter's web is directed vertically and is aimed at catching flying insects: flies, mosquitoes and midges. Representatives of this genus are absolutely harmless to humans. There are known cases of mass invasion of the species, as a result of which coastal and agricultural areas were covered with webs.
Orb weavers
Latin name – Araneidae. One of the largest families of arachnids, includes more than 3,000 species. The size of an adult spider reaches 8 mm, it is brown in color and has a striped pattern on its abdomen. Orb weavers are distinguished by a rounded abdomen and dark color at the end of the legs. Despite its small size, the hardworking orb weaver is capable of weaving a web with a diameter of up to two meters. The most famous representative of the species is the cross spider. The bite of such a spider causes only pain, similar to a bee sting.
External signs of the Sydney funnel-web spider.
The Sydney funnel web spider is a medium-sized arachnid. The male is smaller than the female with long legs, his body length is up to 2.5 cm, the female is up to 3.5 cm long. The color of the integument is glossy blue-black, dark plum or brown, beautiful, velvety hairs cover the abdomen. The chitin of the cephalothorax is almost naked, smooth and shiny. The limbs are thickened. Massive and strong jaws are noticeable.
Reproduction of the Sydney funnel-web spider.
Sydney funnel web spiders usually breed in late summer or early autumn. After mating, after some time, the female lays 90 - 12 greenish-yellow eggs. Under unfavorable conditions, seed material can be stored for a certain time in the female genitals. Males are able to reproduce at about four years of age, and females a little later.
The most popular representatives
Represented by a large number of representatives. Each spider is endowed with certain capabilities and is perfectly adapted to life in its region. Due to the fact that climate change has been observed over the past decade, the geography of arthropod habitats is changing. Species that previously occupied only certain regions migrate and colonize new territories.
Jumping spider
The jumping spider is found throughout Russia and is considered one of the best helpers for gardeners. Its advantage is the inability to bite through the human body. You can keep such a spider on your site to combat garden pests. It is enough to catch several individuals and plant them in a garden bed or under a tree. The horse will not be confused - it will immediately begin to spin a web and settle in a new place.
Pisaurid
They live in Siberia and the Far East. This species is predominantly characterized by gift-giving during the courtship period. The male, when preparing to meet his beloved, carefully packs the caught flies or midges into a cobweb cocoon. This offering reduces the chance of being eaten and increases the chance of mating.
Crosses
Crossweeds are one of the most common species of the orb weaver family. They live throughout the Russian Federation, make a great contribution to the fight against harmful insects and easily adapt to a new place of residence.
Recluse spider
A tiny spider, no more than 8 mm in size, with a leg span of up to 2 cm. A distinctive feature of the cross spider is its wide legs and a striped, elongated body, with a characteristic cross-shaped pattern. Color varies from brown to dark brown.
The hermit spider weaves its web randomly, as necessary. It is formed by careless and chaotic movements during the weaving process. The hermit's bite is not fatal. But its poison contains substances that strongly break down the skin, which threatens tissue necrosis (death).
In the central part of the Russian Federation
The central part of Russia is characterized by pronounced seasonality. The climate is mostly humid and is not suitable for all arthropods. The following spiders are found here:
Silver spider
The only underwater representative of the world of spiders, the popular name is dropsy. Lives in bodies of water with standing water. The silverfish species are small spiders up to 15 mm in length, brown in color. Since dropsy is the only spider that is found on the surface of lakes and ponds, it cannot be confused with anyone else. If you disturb such a resident of a body of water, you may get a bite. Its venom is not dangerous to humans; the result of a bite is pain near the bitten area, which disappears in a few days.
Heiracanthium
Heiracanthium is the Latin name for the green spider in Russia. Popularly called sak or yellow-bag. The places where saka is distributed are Crimea, Krasnodar Territory, Rostov Region - it loves warm regions. Climate change is contributing to its emergence throughout the central part of the country.
The abdomen is yellow or beige, the cephalothorax is often orange, the green spider grows up to 15 mm. Its color appears green against the background of the leaves, hence the name. Sak builds web sacs and has the ability to jump. It has large chelicerae and poisonous claws; the yellowjacket bites painfully. The first sensations from a Heiracanthium sting are similar to those of a bee - a sharp, severe pain. The consequences can be different - from a long-healing wound to nausea and an allergic reaction. Depends on the age and health of the person.
Knitting spider
Popularly called the grandmother's spider. It often settles with a person, occupying corners of the apartment, cracks behind furniture, and weaves its “classic” web. It grows up to 1 cm, has a light brown color and an elongated abdomen on long legs. The knitter is absolutely harmless; when meeting a person, he prefers to pretend to be dead: fold his paws and sit motionless until the threat disappears.
Steppe regions of Russia
The nature of the Russian steppes is inhabited mainly by dangerous and biting arachnids, the most common of which are:
Karakurt
The most poisonous spider in Russia, it lives in the Urals and the Caucasus, Crimea, the Black Sea region and the Moscow region. The bite of the karakurt is a double hole made by chelicerae. The spider will attack immediately if accidentally disturbed. Poison injected into the wound spreads throughout the body within 15 minutes. After this time, severe muscle pain, fever, increased sweating and tremors begin. If you are bitten, you should seek help immediately. The most aggressive are sexually mature females, who, in addition to the instinct of conservation, experience a natural feeling of the need to preserve offspring.
Pogrebnoy
He got his “nickname” due to his love of living in cellars and barns. In these buildings, he finds crevices and cracks in the wooden elements that are optimal for his habitation. The spider is small, the average size is 10 mm. The head is colored brown or black, the abdomen is lighter - from red to brown. Pogrebnyaks are characterized by a hot climate; in Russia they prefer to live in the Krasnodar Territory and the Republic of Crimea. A bite from a porcini mushroom can lead to fever, nausea and fever. They themselves do not attack, but if the spider senses real danger, it will defend itself.
Black Eresus
Popularly called ladybug. Lives in the Caucasus, Western Siberia and the southern Urals. The male specimens of this spider are very impressive; they have a round, bright red abdomen, on which there are four black spots, the legs are black, thick, with white transverse stripes. Females do not have such an attractive appearance - as a rule, they are black. The average size of eresus is 1 cm, sometimes individuals up to 1.5 cm are found.
Ladybug lives in earthen burrows, which it digs under stones. The black eresus is a family of venomous spiders. Poison injected into the wound leads to numbness of the limbs and severe swelling.
Steatoda
This species is called a relative of the black widow or false widow due to its external and behavioral similarities, only the steatoda is brown in color and lacks markings on the back. Steatoda lives throughout Russia and often settles in human dwellings. This is due to the presence of constant heat in the room and access to water.
This species can go without food for about a month, but it needs to drink constantly. The female grows up to 1.2 cm, males - half as much. Steatoda is a poisonous spider. A bite can kill a mouse or frog or cause complete paralysis in a dog or cat. For humans, the consequences are malaise, nausea, increased heart rate and shortness of breath, muscle and joint pain. Swelling appears at the site of the bite, and then it turns blue.
Danger to humans
The Sydney leukoweb spider is the most poisonous member of its family. The venom of males is 5 times more toxic than that of females of this species.
A disturbed spider can even bite through an adult's thumbnail or light shoe. The blood carries the toxic substance that gets into the wound during a bite throughout the body.
The bite site begins to hurt, turn red and swell. Within 15-20 minutes the following symptoms appear:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- vomit;
- migraine;
- tachycardia;
- arrhythmia;
- abdominal pain;
- difficulty breathing - the poison disrupts the functions of the nervous system, which causes muscle spasms;
- temperature increase;
- change in blood pressure.
If medical assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the person dies. Allergy sufferers, people with weakened immune systems and children can die within 30-40 minutes after being bitten. An adult can die within 1-5 hours after the poison enters the bloodstream.
Important! After a spider bite, apply a pressure bandage immediately. It must be applied above the affected area. The patient must remain completely still until the doctor arrives.
Until 1981, deaths from funnel-web spider bites were regularly recorded. After the development of the antidote, not a single death from spider bites has been recorded for 40 years, although every year about fifty victims seek help from doctors.
Southern regions of the country
The warmest regions are home to the following spiders:
South Russian tarantula
The popular name is Mizgir. Habitat - central and European Russia, namely steppes and semi-deserts. The female tarantula grows to a huge size of 3.2 cm, males are 5 mm smaller, weight starts from 30 grams, the maximum weight of an adult reaches 90 grams. Such parameters cannot but impress! There is no doubt about which spider is the largest in Russia - it is definitely a tarantula.
The massive body is dark brown or dark gray and covered with many hairs. Due to the large number of hairs, the spider looks very fluffy. Tarantulas live alone, except for the mating period. The diet, in addition to standard midges and flies, is supplemented by frogs and mice. Representatives of this species are true hunters; they prefer to guard, attack and chase large prey, while inflicting additional bites. Despite the terrifying appearance and predatory nature of the spider, it can bite a person if it senses danger. The bite is dangerous only due to an allergic reaction - redness and irritation.
Argiop
The popular name is wasp spider or wasp spider. It received its nickname due to the similarity of the color of the females of this species with the wasp: a yellow abdomen with black and white stripes. Distributed in the Krasnodar region, Astrakhan region and Volga region - warm regions. Argiopes have pronounced gender differences: females are large and bright, up to 3 cm, and males are on average 0.5 cm and have a dark gray or brown color.
An interesting feature of spiders is their “gregarious” life - the number of individuals in a group is up to 20. The wasp spider is poisonous, but its poison will not cause serious harm to health. In terms of pain, the sting can be compared to that of an aspen or a bee; it will be painful and swollen. An allergic reaction is possible. Argiope will never attack first, but if you accidentally touch its web, an immediate reaction will follow.
What is the benefit or harm
Despite the fact that representatives look menacing, and their webs disturb people in houses, in the grass and cause inconvenience, spiders are simply necessary for the ecosystem and people: they kill a huge number of insects (flies, mosquitoes, midges and others).
The venom of the house spider, which lives in a person’s home, does not pose a threat and cannot harm the family. One of the poisonous ones is the Sydney one, whose habitat is limited to New South Wales.
The common meadow spider can be dangerous to humans, American scientists have discovered this, but there are no recorded cases.
Funnel web spiders live all over the planet, except Antarctica and snowy areas. Some of them are safe, but there are also poisonous varieties, so you need to be careful when traveling to their habitats.