What you need to know about hornets and bees. The war between insects, why this happens. How bees resist a huge enemy and what methods of defense they use. How can they kill a hornet? Other enemies of hornets. Which insects become their victims?
Many of us consider hornets to be true predators and are confident that these large insects are waging a real fight against honey bees. A lot of information that is presented for general viewing does not show hornets from a very good side, where one individual can easily withstand tens and even hundreds of bees, while destroying them.
There is some truth in this; a few hornets can really completely destroy a bee colony. But you shouldn’t take everything the way it is presented. In fact, there is no war between them, and the hornets do not want to destroy their population at all, everything is much simpler and more banal. You just need to get to know these insects a little better.
Hornets vs honey bees
It will not be a revelation to anyone that these bright and huge insects have long been labeled “killers”; this statement, of course, applies to insects. But this label was assigned not entirely fairly, even, one might say, incorrectly. They do kill other insects, but this is a kind of hunting and not for fun, but for the sake of feeding their offspring.
Nature has decreed that in order to continue the population, they need to regularly go hunting and get new food to bring to the nest and feed the offspring. It is not their fault that their diet consists of other insects.
And the point is not at all about bees; they, like other insects, simply serve as food for their family. It is worth saying that they even hunt small frogs, since nature has awarded them with strong and large jaws.
Having figured out why they kill insects, you can understand that they received the title of killers completely undeservedly, because in this case this title can be assigned to ants. After all, goosebumps also constantly bring home bugs, larvae, caterpillars and other insects, but no one labels them “killers.” Perhaps the reason is that the struggle of a hornet is much more spectacular than that of an ant.
It is worth saying a few words about why hornets choose beehives. In fact, in this matter everything is very clear and simple - this is an ideal feeding place. A large number of individuals gather in this place and they are easy to catch, which reduces the time spent searching for food.
It is also a valuable nutritious product, which is important. Well, one more important point: there is always the opportunity to enjoy honey, and the diet of adults consists mainly of sweet foods.
How one can understand the choice of bees as a hunting object is completely understandable. The presence of at least one hive in the hornets’ habitat provides the entire colony with adequate nutrition, and they obtain food without much effort.
You should not think that they specialize in killing bees; they hunt completely different insects, but they will not refuse such healthy food, especially if the hive is nearby.
How to get rid of hornets?
One hornet flying into the area does not pose a danger. It’s another matter if the insects have made a home for themselves on the site, in a house or one of the outbuildings. In this case, it is necessary to get rid of uninvited guests, since the neighborhood can be dangerous. Help to destroy hornets:
- insecticides;
- traps;
- poisoned baits (homemade with boric acid or purchased);
- ultrasonic repellers.
Found nests are filled with polyurethane foam, drowned in water, burned, after dousing them with kerosene or gasoline. You can try to drive away insects using repellents, for example, hanging hot red pepper pods on the site or planting herbs, the smell of which repels hornets: geranium, mint, lemon balm.
Geranium
Hunter and prey: hornet and bee
These insects belong to the same order of Hymenoptera, which also includes wasps, bumblebees, as well as riders and ants. All of them are united by certain behavioral features, as well as similarities in appearance. In addition to some similarities, there are also many differences.
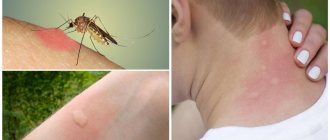
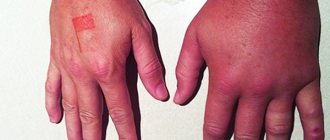
So, we all know about the presence of a poisonous sting in hornets, wasps, bees, and bumblebees. Regarding ants, the tropical species has a sting and it is worth saying that their bite is the most painful. The poison of each of the representatives is toxic, dangerous to humans and has similarities in its composition.
Despite the similarity, the poison of each representative has characteristics that are decisive at the moment of impact on the human body. What this means can be seen with an example.
Hornet venom has a stronger effect on nerve receptors than others; it has a high level of allergenicity. Bee venom is different in that they release a large amount of toxin at one time, which causes severe poisoning.
It is worth saying that different species have different poisons. For example, the common hornet, which is familiar to us, is capable of inflicting a very painful bite, but its poison will not cause serious consequences, unlike the poison of the giant Asian hornet, which is one of the most dangerous representatives on Earth.
Regarding hunting their victims, in this case they do not use poison, as you might think, they use no less dangerous strong jaws. It is also worth noting that hornets are very smart and cunning, this can be seen if you consider the hunting process.
They do not attack their victims who are alone. After all, it would seem that a bee that is busy collecting nectar is very easy prey, but they do not attack them. Cunning predators watch their prey so that it leads them to their hive, and then return to it in large numbers.
In order to completely destroy a bee hive, a different number of attackers is required and this directly depends on the type of predator. But this rule has its exceptions.
If we consider the behavior of the European species, then several hundred of these individuals are capable of destroying a hive in which there are about 10-15 thousand bees. But this is theoretical, since in practice the situation is somewhat different.
The fact is that in our country it is very rare for families of hornets to reach such large sizes. For this reason, in rare cases they can attack entire hives, and more often attack single bees. But such attacks also cause great damage to apiaries.
But if we talk about their giant relatives, Asian murder hornets, whose size is 2 times larger than European ones, really pose a great danger. Unfortunately, bees are absolutely helpless against this species. Let's look at this view in more detail.
Finding a nest
Before taking drastic measures, you must first find a nesting site. Here's where hornets most often prefer to live:
- On the street. In this case, you need to look for areas that are fairly well protected from the weather. Also, the place should be quite secluded and quiet - these are the conditions that hornets prefer. It is necessary to understand that they can settle not only under any artificial or natural canopies, but also in a hollow or form holes in the ground. This makes it difficult to directly search for the nest.
- Hornets can also settle directly in a person’s home - most often these are barns, picket fences with logs, remote sheds or areas under the roof.
The easiest way to find a nest is to carefully monitor this predatory insect and follow it all the way to the nest itself. This will be the easiest way, otherwise the search may take a long time. It is important to destroy the hive in the early stages of its development to prevent the formation of an entire colony.
Sometimes a person is unable to track an individual instance, then you can use one of the following actions:
- Track down one individual and try to knock it down using, for example, a tennis racket or a towel. At the same time, always remember that if other representatives of the colony see this, they may perceive it as a threat and launch an attack on the person.
- Then, with one hand wearing a thick glove, carefully take it and tie a colored ribbon or thread around the body.
- Wait for the moment when the stunned arthropod comes to its senses and flies to its habitat.
- Thanks to such a beacon, it will be easy to detect the entire colony.
Giant hornets and their hunt
The undoubted difference between these huge insects, and at the same time their superiority over their relatives, is their size. They reach more than 5 centimeters in length; to understand how large these are, you can compare them to a worker bee, which is 3 times smaller. They attack their victims with powerful jaws; one movement is enough to break the joint of the chest and head, which leads to paralysis of the bee.
For a bee hive, they pose a huge danger, since in 1 minute just one predator can kill about 30 bees, and in order to destroy a hive of thousands, 30-40 predators are enough, which will deal with it in a few hours.
Hornets have a very hard chitinous body cover and it is practically invulnerable to bees, there are only a few places where they can pierce it with their stings, but even in this case, they will not cause much harm to the predator. In turn, predators very rarely use their stings.
In fact, for hornets, finding a hive and destroying it completely is a “tidbit,” so they do it with great pleasure. It is worth saying that the war between these insects was not started by nature, it was provoked by man and it is he who is to blame for the active extermination.
What they look like
To determine whether a hornet is a wasp or a bee, you should pay attention to the appearance of the insects.
- The most discreet black and yellow color of bees. Their shaggy body is distinguished by harmonious proportions and the absence of sharp interceptions between the abdomen and chest. Honey producers have small jaws and black, relatively thick and hairy legs.
- The wasp can be recognized by the sharp transition between the thoracic and abdominal sections, as well as its smooth, thinner and elongated body. The insect is distinguished by a bright contrasting color: there are yellow blotches on the black back, the rear segment is painted with black and yellow stripes, and the limbs are yellow. The gnawing-licking type of mouthparts is distinguished by impressive mandibles.
- The bumblebee is much larger than its counterparts described above. The differences between a bumblebee and a bee and a wasp are not only in body size, but also in their furry cover. The bumblebee is also distinguished by wide stripes of yellow-red or slightly reddish color. Sometimes there are black bumblebees.
- The hornet is the largest (about 5 cm) of the insects described above and has powerful jaws. Externally, the giant resembles a wasp, but not with such a narrow waist.
Difference between bumblebee, hornet, wasp, bee
Bees' capabilities: defense is their secret weapon
Speaking about the types of these insects, it is worth understanding that some of them have never waged war with each other and do not even suspect the existence of relatives, and all for the reason that they live in completely different territories. For example, the Asian hornet, which lives in Southeast Asia and Japan, will not meet with the European honey bee, which lives in the Middle East and Europe.
But there are also Asian bees that use a rather original method in the fight against their relatives; it was developed in the course of joint evolution. So, when a predator is preparing an attack, the victims attack him themselves and in this case take advantage of the advantage of numbers. They cling to it from all sides, potential victims form a huge ball with a diameter of up to 30 cm, while each bee actively flaps its wings.
It seems that they cannot cause much harm to their enemy, but in reality this is not the case. The fact is that from such flapping of the wings, the temperature of the air inside the ball begins to rise.
In addition, the movement of the wings directs the heat to the center of this ball, where the enemy is located. A temperature of 46-47° is lethal for a predator, so it can stay in the middle of the ball for a maximum of an hour and then die. The owners of the nest can normally tolerate temperatures up to 50°, so they will not be harmed in any way.
For one such ball, about 500 bees are needed and the enemy is defeated. If we talk about a family, which on average consists of 15-20 thousand individuals, they can easily withstand 30-35 predators. This cunning method of defense is very reliable and effective against your enemies.
But European bees that live in our country do not use such a defensive method. This is due to the fact that hornets attack honey beehives in the wild very, very rarely, almost never, so there was no reason to develop such behavior.
But our bees can boast of another feature, namely the ability to collect large amounts of honey. Japanese beekeepers are trying in different ways to breed them in their territories where there are giant predators.
As mentioned above, war between relatives is not a natural phenomenon; it was provoked by man. The attempts of Asian beekeepers are unsuccessful, since predators destroy the hives they find, and the bees simply do not know how to protect themselves. It is not for nothing that nature has divided the species of these insects, and forced relocation leads to the death of a large number of insects.
Who is stronger: a bumblebee or a wasp
Their differences lie in the nature of their behavior: if the wasp is quite aggressive and easily attacks an enemy who is much larger than it in size, then the bumblebee is a very peaceful insect, and only in extreme cases uses its weapon.
Quite often, wasps attack the nests of peace-loving bumblebees in order to steal their food supplies; they attack with the help of their jaws and stings. When the bumblebee family is healthy, they easily cope with the attackers, but if it is weak, the wasps win, and can kill not only the working individuals, but also the entire young generation.
Hornets against bumblebees and other insects
It’s worth saying right away that for a hornet, any insect that is inferior in strength and has a smaller size is considered as a potential victim, and the bumblebee is no exception. Just like a bee, a bumblebee is defenseless against this predator, the only difference is that killing this victim will require a little more effort.
But the types of insects are also important here, since an Asian one can attack a bumblebee without hesitation, but a European one is unlikely to attack, for the reason that it will most likely be frightened by its size. They are approximately the same size and it is very difficult to say which of them is stronger, but there is a very high probability that the bumblebee will still survive.
It is a completely erroneous opinion that these insects are enemies. Here, rather, nature brought them together and forced them to tolerate each other. The bumblebee, by its nature, is very peaceful and is not a predator, so an attack on its part is out of the question. But at the same time, he is a large insect, which at the right time will give a worthy rebuff.
Let's find out how relationships with other insects develop:
- Wasp. Also considered as a victim, she is comparable in relationships and in the process of hunting with a bee, since she is defenseless in front of him. Their nests are attacked only in rare cases; they are also predators and, gathered in large groups, can fight back.
- Mantis. This insect cannot resist its opponent in any way; it is absolutely helpless. All he has are powerful legs, but they cannot harm the enemy in any way. When attacking a praying mantis, the hornet does not use its sting, there is no need for this, it simply bites through the joint in the neck area.
Differences in lifestyle and behavior
The flight path and the manner of controlling one’s own body are no less noticeable differences between a bee and a wasp. The honey collector flies smoothly. The wasp develops a decent speed, which is why its movements sometimes become jerky and it is capable of “hovering” in space for short periods of time.
Bumblebees have the calmest “driving style.” Because of their size and mass, they fly slowly, without rushing. Watching a flying bumblebee, one gets the impression that the poor fellow is trying to keep himself in the air with great effort.
It is common for all representatives to live in families:
- Domestic bees live in houses carefully prepared by beekeepers. Wild individuals create hives in tree hollows and rocky gorges. Occasionally there are bees that prefer a solitary lifestyle.
- Wasps can also live in organized families with a strict way of life, where everyone performs their own function, or they can be a hermit. Unlike bees, wasp nests look like paper, the material for their production is chewed grass and wood.
- Bumblebees live in small colonies, the number of which does not exceed 200 individuals. They build their nests in abandoned rodent burrows and tree hollows. They prefer to go alone to forage for food, while wasps most often move in groups.
- Hornets, as befits wasps, build paper nests. Only rotten stumps and branches act as building materials, so their home is brown in color, not gray.
Who will lose in battle?
As we learned above, the hornet is able to attack certain insects, knowing that it will win. But there are insects that act as aggressors towards it. So, the hornet has a rather complex relationship with spiders, let’s learn about them in more detail.
First of all, it is worth saying that a spider can act in these relationships both as a killer and as a victim, much depends on their species. If we talk about spiders that hunt victims without using webs, for example, jumpers, small tarantulas, haymakers, when they meet a hornet they will die, thanks to its powerful jaws.
The web of a cross spider is a completely different matter; for humans it is safe, non-toxic and not very large in size, but for a hornet such an encounter will most likely end in death.
Let's take a closer look at the relationship with the tarantula spider; in this case, the chances of winning are almost equal. The fact is that they have almost the same size, both rivals are quite strong, and both have poison, but in the tarantula it is many times stronger, so the one who first inflicts a fatal bite has a greater chance of winning.
Now let's look at our closest relatives, namely stray ants and road wasps. Despite the fact that hornets act as predators in this case, there is a high probability of ending up as a prey when meeting them. The wasp has a powerful weapon - deadly poison, but the ants defeat it due to their numbers; they never attack alone.
The hornet also has a biological enemy, a unique fungus that develops in its brain. Fungal spores enter the insect’s body through the respiratory tract or through the mouth, and begin to germinate in the head; the development of the fungus leads to the fact that the insect begins to constantly feel thirsty. The hornet begins to look for water, when the source is found, the mushroom causes paralysis. The victim freezes in one position and then dies.
The death of a hornet, no matter how strange it may sound, gives life to a new organism, albeit a completely ordinary one. The dead body becomes a place for the fungus to grow and a place from which new organisms spread.
The list of hornet enemies does not end there, because they are also found among vertebrates. Let's find out in more detail who is on this list:
- Bee-eater birds. Their favorite food is bees and wasps, and they know how to catch hornets in such a way that they cannot bite. Afterwards, they smash the insect against a stone and swallow it, so that it does not cause harm to health. Other birds can feed on hornets in the same way.
- Human. It is the hornet's largest and most dangerous enemy and can kill hornets in huge numbers without much effort.
- Small parasites. Other enemies are nematodes, mites, and parasites, which are very difficult to destroy.
Insect hunters
By the way, many wasps are merciless killers, preying on almost any insects and arachnids.
It must be admitted that in the area near their colony they cause significant damage to pest populations. At the same time, wasps do not distinguish between parasites and beneficial arthropods. Caterpillar and butterfly, bee and bumblebee, spider and haymaker - striped killers hunt for them all. For the sake of truth, it is worth saying that the outcome of the struggle between a hornet and a spider is not always a foregone conclusion. The victims of wasps of this genus are often arachnids that obtain their food on the ground. For example, a wolf spider most often has no chance of surviving a confrontation with a hornet or even a smaller wasp. Sometimes only an excellent reaction helps some individuals escape from the poison and mandibles (jaws) of the striped hunter. Nevertheless, the predators themselves can easily end up “for lunch” with a cross spider or another spider that weaves a fairly strong web.
Basic measures to protect the apiary
There are a sufficient number of effective ways to combat these dangerous insects. These include:
- placement of special traps;
- use of chemicals with insecticides;
- turning to specialists for help.
You should find and get rid of wasp nests, which are balls supported on a stem. Nests can be located under sheds, in attics, or in other secluded places. The structures need to be removed at night so that the insects are in the nest and inactive. A plastic bag of appropriate size is selected in advance. The nest is carefully torn off and placed in a bag, the edges of which are tied. After which the pests can be burned or drowned in water.
Integrated control of wasps and hornets is effective in the fall.
Using traps
A common method of exterminating wild insects are special traps, which can be purchased in specialized stores or made independently.
You might consider making an effective trap. For this you will need:
- plastic container with a volume of 1.5 l;
- sweet syrup or other aromatic bait (honey, jam);
- vegetable oil;
- knife.
Using a sharp knife, cut off the top of the container and pour sweet syrup inside. Insert the cut part of the bottle upside down. Place the device in a place where wild insects accumulate. The walls of the container should be lubricated with vegetable oil so that wasps caught inside the trap cannot get out.
Traps will not be able to radically solve the problem of attacks by wasps and hornets, but they will help destroy individual, most intrusive individuals. It is prohibited to use such devices in the vicinity of the apiary. Otherwise, beneficial insects will also fall into the trap.
Poisonous baits
Poisonous bait will help get rid of pests quickly. You can prepare it yourself as follows:
- As a product that attracts the attention of insects, you can take meat cut into pieces or minced meat.
- Prepare in advance any toxic substance that can be purchased at hardware stores.
- Mix the minced meat well with the poison and leave it in a place accessible to wasps.
Knowing the collective behavior of wild insects, one can imagine how quickly the entire colony will be poisoned by a toxic substance. The wasp will carry the poison into the nest and feed it to the queen and larvae.
When using this method, you must ensure that cats, dogs and other animals cannot eat the bait.
Special aerosol against wasp nests
The use of a special aerosol containing insecticides will quickly destroy all insect pests.
The chemical industry offers the following drugs:
- "Medilis-Super". 3rd class of danger. A solution is prepared in the following proportion: per 1 liter of water – 4 g of substance.
- "Masterlak". It is a toxic liquid with long-lasting effects.
- "Karbofos". 3rd class of danger. Sold in powder form. Prepared in the following proportion: 1 liter of water – 10 g of powder.
- "BROSS" from wasps and hornets. 4th hazard class. Produced in the form of a spray.
When using these products, you must observe the following precautions:
- move away from the object as far as possible;
- use protective masks, gloves, and clothing made of thick fabric.
Methods of defense
Hornets are social insects. Such creatures are distinguished by their unique ability to unitely respond to an enemy attack. Protecting their fellows and the nest becomes a common goal in times of danger.
When a hornet senses danger, it emits a special alarm pheromone. Other individuals sense it and mobilize to attack. You should not try to kill a hornet near its nest. The pheromone will be sensed by the representatives of the hive and then the offender will suffer greatly: he will be attacked by a whole flock of stinging parasites.
This pheromone can come into contact with various materials: leather, fabric, alcohol. This strengthens the signal.