A menacing buzzing makes many people anxious, and if something similar to a hornets’ nest appears in sight, there is a desire to get as far away from the dangerous place as possible. This is how people react to a potential threat. And this is correct, because the maximum risk of a bite occurs within a radius of 2–3 m from the nest.
Who is a hornet and why is it dangerous to humans? What to do if it bites and what could be the consequences? How to get rid of them and how do they differ from bees, wasps and bumblebees? Let's figure it out.
Who is the hornet
This is the largest representative of the so-called paper or social wasps. Their Latin name is Vespa, which literally translates as “wasp”. However, these are different insects that belong to the same family - true wasps.
Initially, no difference was made between the two representatives, and only in the 19th century the Vespa genus was divided into two groups. The description was based on several characteristics, but the main one was size - hornets are larger and can reach a length of up to 5.5 cm. Insects that are today considered wasps are designated in Latin as Vespula, that is, “small wasp.” Their size is 1.5–2 cm in length.
The hornet's threatening appearance is given by the bright coloring of its head - a combination of yellow, black, and orange.
The aggressive image is complemented by a striped belly, strong jaws and large eyes. However, these insects, unlike wasps, are non-aggressive. Human bites occur when a nest is disturbed or in self-defense.
Biological description
Hornets belong to the genus - social wasps. They live in families. A swarm can include up to several thousand individuals. Their life processes are clearly organized. Thus, within the “community” there are separate “castes” that perform specific functions.
The task of the hornet queen is to leave offspring. She is the leader of the colony. Females are born from fertilized eggs in August and September. Hornets reproduce by mating mature insects. After the females are fertilized, the males die.
The female stores sperm during the winter. With the onset of warm spring days, the queen begins to actively feed and regain strength in order to begin creating honeycombs for laying eggs. Thus, it forms the foundation of the future nest.
How long a hornet lives depends on its “profession”. Thus, males exist for one season, and the lifespan of the queen is a year.
The insect also has powerful jaws - mandibles. Literally speaking, hornets not only sting by injecting poison, but also bite. The insect uses mandibles to tear and grind prey.
During the active season, hornets feed on the juice of overripe fruits, trees, and honey. They hunt caterpillars, dragonflies, flies, spiders, related bees and wasps. They also cope with larger insects - crickets, locusts. There are descriptions of species capable of attacking birds and frogs. The prey is not used for food—the mass chewed and treated with saliva is used to feed the larvae.
Nests
The structure of a hornet's nest is based on hexagonal honeycombs.
The material is a substance similar to paper or cardboard. This is a lightweight structural element with thermal insulation properties of a brown color, which is obtained by mixing tree bark with insect saliva.
The place for the nest is chosen by the queen hornet. She does it where the offspring will be protected from excessive heat, cold and prying eyes.
Hornet nests reach 50–70 cm in length and are located in tree hollows, abandoned or used premises, cavities under roots, and piles of dead wood.
In the European Union, hornets are protected by law. For example, in Germany, the destruction of their nests is punishable by a large fine.
Area
Most species of hornets live in areas with a temperate climate, mainly in the northern hemisphere. Entomologists believe that they originally lived primarily in East Asia. There are several types of hornets on the territory of Eurasia, mainly the common and oriental ones.
People themselves play a major role in the spread of the insect. For example, a representative of the “common” species came to North America along with colonists from Europe in the middle of the 19th century.
In Russia, the hornet lives on a vast territory, which includes the European part of the Urals, Transbaikalia, the Amur region, and southern Sakhalin.
Kinds
Representatives of the extensive Vespa genus include more than 20 species.
- Affinis - small striped one.
- Analis - found in East Asia, measuring 25–28 mm.
- Basalis - basal.
- Bellicosa - warlike.
- Bicolor - two-color.
- Binghami - Binghama - active at night.
- Crabro - ordinary.
- Ducalis - commander's - one of the largest in Russia.
- Velutina is tropical, but also lives in Europe, as it was accidentally introduced there.
- Dybowskii - Dybovsky - almost monochromatic - black-brown.
- Fervida - ardent.
- Fumida - variable.
- Mandarinia is the largest in the world and also very poisonous.
- Multimaculata - multi-spotted.
- Orientalis - eastern.
- Philippinensis - Philippine.
- Luctuosa is tropical, found in the Philippines and is the most poisonous.
- Simillima - similar, very similar to the common hornet.
- Vivax - lives in Asia.
- Soror - black-tailed.
- Tropica - tropical.
Eight species of hornets live in Russia. The leader in occurrence is the “ordinary” (Vespa Crabro), which is distributed throughout almost the entire country, including the Moscow region. It is absent only in northern latitudes. The eastern hornet (Vespa Orientalis) lives in the Caucasus. In the south of the Far East, six species of Vespa are found - Simillima, Dybowskii, Ducalis, Mandarinia, Analis, Dinghami.
Role in nature
The benefits that hornets bring:
- destroy harmful insects that parasitize garden crops and wild plants - aphids, mites, psyllids;
- pollinate plants;
- They hunt locusts, flies, wasps, sick, “old” bees.
Natural enemies of hornets in nature limit their population within useful limits and destroy sick individuals. Among animals, these are ants, some species of birds (starlings, wagtails). Hornets are also susceptible to parasites - mites, nematodes, parasites and even microscopic fungi.
Interesting Facts
There are more than 20 species of hornets in the world, differing in color, behavioral characteristics, and size. The largest representative is the Asian one (Vespa Mandarinia), whose length exceeds 5 cm. In China, it is known as the “bee tiger”. Its venom contains a neurotoxin.
The hornet's queen releases pheromones that influence males. With their help, the “queen” organizes the activities of the entire swarm.
In the 18th century, the French naturalist, physicist and mathematician René Antoine Reaumur studied the material from which wasps build their nests. The result was a proposal to use wood in the production of paper, because until that moment, it was made from rags.
Main types of hornets
There are 23 species that have a similar way of life, diet, and reproduction characteristics. However, each of them has significant differences in appearance. The most common types of hornet in the photo:
- Common hornet. The most common species, found mainly in Europe. The variety is also present in North America. The dimensions of the working individual are 20-22 mm, the uterus is 30-35 mm.
- Asian giant. The largest species, with a record size for a wasp - up to 10 cm. The predator lives in Asia and is represented by several subspecies. A distinctive feature is a bright yellow head and black wide stripes on the body. This is one of the most dangerous hornets, since the venom is extremely toxic and can even cause human death.
- Black. This wasp is common in Asian countries and in some regions of Russia (Amur region, Transbaikalia). The insect is characterized by a parasitic lifestyle. The female is not as busy caring for her offspring as other species. It penetrates a colony of large wasps of another species, kills the queen, and takes her place.
All types of wasps have toxic venom for protection and successful hunting.
Why is a hornet dangerous for humans?
The following components of the poison pose a danger to humans:
- phospholipase A2 is an enzyme that activates the inflammatory response;
- acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that ensures the transmission of impulses;
- histamine is a mediator of immediate allergic reactions;
- mastoparan is a toxin of protein origin.
As a result of the influence of a “bouquet” of biologically active substances on the tissues of the human body, a protective systemic inflammatory response develops.
A hornet sting can be fatal to humans if the victim experiences an allergic reaction. The following complications may also develop:
- skin rashes;
- bronchospasm - obstruction of the airways with difficulty exhaling;
- hallucinations;
- paroxysmal pain in various parts of the abdomen, nausea, vomiting;
- convulsive syndrome;
- depression of consciousness;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure with further cessation of blood circulation.
Single hornet bites during pregnancy and lactation do not pose a danger to the fetus and infant, since the amount of poison is insignificant to penetrate the placental barrier or into the liver of a nursing mother.
How dangerous is a hornet bite for a child? Due to the small body weight, the concentration of poison for his body is very high, so the symptoms are more pronounced. And also due to the fact that children react actively and unpredictably to buzzing insects, the risk of multiple attacks increases, increasing the development of allergic reactions. In order not to risk the child’s life if bitten, you should immediately call an ambulance, without waiting for allergies to appear and anaphylactic shock to develop.
Causes of a hornet sting
The main reason for a hornet bite is self-defense, and it always tries to get away from a person first and stings only if it is grabbed.
The insect uses its sting only for the purpose of protection or to neutralize a resisting victim. Entomologists explain that hornets will not consume poison without justified biological expediency. After all, this is a valuable weapon that is necessary during hunting.
Having detected a threat, hornets release alarm pheromones, which call on other individuals to attack. Therefore, everyone who is within a radius of 2–3 meters from a disturbed nest or a killed hornet will be bitten.
Bite symptoms
The hornet does not leave a sting when it bites, so it can sting several times. This feature distinguishes it from bees. A large number of bites can be fatal to humans. Especially if you are allergic to wasp venom.
Symptoms that develop from a hornet bite:
- sharp, severe pain;
- swelling, redness;
- itching, burning at the bite site;
- increase in body temperature to high numbers;
- possibly manifestations of allergic reactions, including anaphylactic shock.
Allergy and anaphylactic shock
Can a hornet kill a person? Even if it’s just one, and not tropical, but the most common, European one? Let's find out.
Not only does the hornet's venom itself contain histamine - a catalyst for all instant allergic reactions - but also some substances that make up the toxin of this insect contribute to the release of its own histamine from the affected tissues of the body.
It is not surprising that after a hornet sting, almost immediately and without exception, all victims develop an allergic reaction. The degree of its manifestation depends solely on the individual sensitivity of people: for some, a hornet sting causes only local inflammation, for others, a rapidly spreading immune response with increased body temperature and difficulty breathing, and for others, anaphylactic shock and death.
Today, thanks to the development of medicine and pharmacology, people who are aware of the characteristics of their immune system have the opportunity to be vaccinated with special vaccines that increase resistance to the venom of insects in general and hornets in particular. Such vaccinations will not make the bites themselves painless, but will ensure a weakening of the allergic reaction and, as a result, protect against anaphylactic shock and probable death from it.
It is worth noting that an attack by several hornets at the same time in any case will pose a serious danger to absolutely everyone: in this case, neither relatively good tolerance of the poison nor vaccination will save you from an allergic reaction.
First aid
What to do if bitten by a hornet? It all depends on where and under what circumstances it happened. It is important to protect people from mass attacks. The biological instincts of insects are aimed at survival, which means protection from external invasions. If there is a nest within 2–3 m, you must immediately leave the danger area. When indoors, you should close the windows and make sure there are no insects.
If a hornet bite occurs, the algorithm for providing first aid at home should be as follows:
- examine the wound;
- if a sting remains, for example, after hitting an insect, then carefully remove it;
- do not try to squeeze out the poison;
- suck out the contents of the wound as quickly as possible;
- treat the bite site with an alcohol wipe or liquid;
- to relieve pain and swelling, apply “cold”;
- if there are indications, then take an antiallergic drug, for example, Suprastin or Tavegil.
When treating a hornet sting at home, it is important to continue to monitor the condition of the victim. If alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
What to do if a hornet bites a child? The algorithm of actions for providing first aid is the same as for adults. Then you need to calm the baby down, distract him from the unpleasant incident and seek the advice of a medical specialist. Incorrect assessment of symptoms, potential complications, and self-medication can significantly worsen the child’s condition.
About the consequences of a bite
How dangerous is a hornet to humans? This question interests almost everyone. This insect, unlike bees, is dangerous for both people and animals. When bees bite, they leave a sting in a person's body, after which they fly away and die. But the situation with hornets and wasps is completely different - they can attack many times. One insect can inflict dozens of bites, while striking a person in different places. So is the hornet dangerous? Still so dangerous. Each time it bites a person, it will release more and more poison. It becomes dangerous because its level in the blood increases every time.
If a hornet suddenly bites the eye or in the area near the eye, the result can be a severe burn. Its venom can cause severe damage to the retinal structure.
But what happens if a hornet bites you? Knowing the signs of this insect bite will prevent the occurrence of various unpleasant complications.
First symptoms of a bite:
- the occurrence of redness and swelling of the affected area;
- the appearance of a painful feeling;
- there may be an increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of heavy sweating;
- The heart rate level may increase significantly;
- Severe nausea and vomiting may occur.
Sometimes, after a bite, a person may experience blue lips and ears, and may experience coldness in the hands and feet. During these conditions, speech difficulties often appear and blood pressure decreases.
The intoxicating effect can manifest itself in different ways - weakly or, on the contrary, pronounced. It all depends on age. The bite can be especially dangerous for adolescents aged 15 years. Their intoxication effects occur quite quickly, so if they are bitten, you should immediately seek the help of a highly qualified specialist.
Is it possible to die from a hornet bite? Sometimes you can die from the bites of these insects. Serious consequences from damage to these insects can include severe allergies, urticaria, suffocation and Quincke's edema. If appropriate assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the person may die.
Treatment
In the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision ICD-10, a hornet sting is designated by code W57 - stinging by non-venomous insects and arthropods.
There is no specific antidote for a hornet sting. Therefore, treatment includes the use of the following drugs:
- analgesic;
- antihistamine;
- antipyretic;
- decongestant.
If life-threatening complications develop, intensive therapy is carried out in the intensive care unit.
If a hornet bites you on the head, namely, in the area of the face or neck, swelling may develop that affects the airways. This condition threatens the life of the victim and requires treatment in a hospital. Airway obstruction is an indication for hospitalization in the intensive care unit. Intensive therapy includes the administration of glucocorticosteroids (hormones of the adrenal cortex), diuretics, and, if necessary, connection to a ventilator.
Consequences
- children;
- elderly and senile people;
- patients with a history of allergies, chronic diseases of the heart, blood vessels, and respiratory organs.
The severity of symptoms and the possibility of developing complications depends on the health status of the victim.
If there was no allergic reaction of the body, then the inflammation caused by the hornet sting goes away in a few days. This can be judged by the reduction in swelling, redness, and pain in the wound area.
The damaged area may itch for some time. How to relieve itching after a hornet bite? It is enough to apply cold. If this is one of the symptoms of an allergic reaction, then you should consult a doctor who will prescribe antihistamines.
Symptoms and possible consequences of a hornet sting
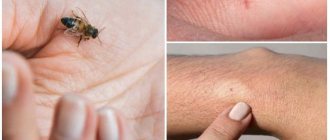
First of all, an insect bite is much more painful than from a wasp or bee. Solitary in most cases is not dangerous and does not require seeking medical help. However, much depends on the person’s health status, age and tendency to allergic reactions. You can see what a hornet bite looks like in the photo.
Hornet bite on the hand: swollen and red (photo)
Main symptoms:
- swelling at the site of the bite;
- rapid spread of the reaction to adjacent areas of the body;
- acute pain at the site of the sting;
- irregular heart rhythm;
- sharp fluctuations in blood pressure.
Symptoms that appear in people prone to allergic reactions:
- nausea and vomiting;
- coldness in the extremities;
- complete or partial loss of consciousness;
- blue face;
- attacks of suffocation;
- large red spots on the skin and severe swelling.
A hornet bite requires immediate medical attention if accompanied by similar symptoms. The poison affects the central nervous system . The most dangerous consequence is hemolysis, or destruction of red blood cells . In addition, in some cases, a rapid allergic reaction can lead to death.
It is impossible to predict how a particular person's immune system will react. But we can say with confidence that the next bite will lead to more serious consequences than the previous one. In addition, severe reactions can be expected in children and the elderly.
What does a hornet sting look like?
How to get rid of hornets
Smells that repel them:
- soapy;
- essential oils contained in red hot pepper;
- aroma of mint, geranium, basil, wormwood;
- smoke.
If a hornet has flown into a room, it will explore the space in search of a way out until it finds one. Therefore, to get rid of it in a house or apartment, the best solution is to simply open the window wider and allow it to get out. If you try to catch it using a jar or vacuum cleaner, there is a chance of being bitten.
Remedies for hornets:
- insecticides - Get, "Medilis-Super", "Delta-Zone", aerosol from wasp nests Mosquitall;
- traps - Argus Garden, Swissinno Wasp Trap;
- smoke bombs - “Mukhoyar”, “Quiet Evening”, “FAS”, “City”;
- ultrasonic or acoustic insect repeller - EcoSniper LS-989, Sititek Flash, Grad Ultra 3D, Weitech WK-0180;
- insecticidal lamps - Well, Mo-El, Hilton.
What else are hornets afraid of? They are repelled by plants - basil, geranium, mint, lemon balm, wormwood, hanging red pepper pods. With their help, you can get rid of hornets in your garden, yard or attic of a private house. It is enough to plant or lay out dry plants near the nest and after a while the insects themselves will prefer to move to another place.
Difference from bee, wasp, bumblebee
| Wasp | Bee | Bumblebee | Hornet | |
| Size(cm) | 2,0–3,5 | 2,1–3,9 | 1,3–2,8 | Up to 5.5 |
| The structure of the sting | smooth | has jagged edges | smooth | smooth |
| Painful bite | The pain from a hornet sting is comparable in intensity to the sting of a wasp, bee or bumblebee. | |||
The hornet can also be confused with other insects.
- The gadfly is distinguished by its smaller size and color, which is dominated by gray and black shades. It belongs to synanthropic flies. Only one species attacks humans: the human skin botfly, which lives in Central America.
- The difference between Scolia and Hornet is in size. Its length is about 3 cm in females and 4.5 cm in males. There is also a difference in color - Scolia is almost all black, with only two yellow spots.
- A drone is a male honey bee. The difference from the hornet is in size (no more than 1.5–1.8 cm), less bright color and lack of a sting.
Let's summarize. The hornet is a large, brightly colored insect from the genus of social wasps. It has jaws and a sting hidden at the tip of the abdomen. People are bitten most often due to the instinct of self-preservation. This is facilitated by the fact that nests are often created in close proximity to human habitation. The consequences of a hornet sting are dangerous due to the appearance of an allergic reaction, with possible death from anaphylactic shock. Especially if the insect stung several times or a child, an elderly or senile person was injured. In this case, you should definitely seek professional medical help. If there was no allergy, then the inflammation goes away within a few days.
The effect of hornet venom on the human body
Having figured out how hornets are useful, it is important to study the ability of the poison to act on the body in order to understand how to save the victim after a dangerous bite. First, a person feels a sharp throbbing pain, this is due to the presence of acetylcholine. It activates nerve endings even before significant tissue disorders and changes occur.
After a few seconds, the penetration site begins to swell . Swelling and inflammation can spread quickly, with damage to nearby tissues causing the bite site to greatly increase in size. Small blood vessels may fail and their rupture is visualized by small hemorrhages. In severe cases, hematomas and suppuration are observed.
The venom of these insects can release a toxin that causes dizziness, headaches, general intoxication, fever and increased heart rate. One bite rarely causes death, but in case of individual intolerance, anaphylactic shock may occur, and with late treatment, tissue necrosis.
Understanding how dangerous a hornet is for humans, it is worthwhile to reduce the risk of death at the first sign of an insect bite by providing assistance to the victim. This will not only save his life, but also reduce the number of unpleasant symptoms.