Wasp venom and its specifics
The composition of wasp venom is in many ways similar to the venoms of other Hymenoptera - bees, hornets, bumblebees, some tropical ants - but it also has its own characteristics.
Here are some active components of wasp venom:
- phospholipases, which cause destruction of cell walls, swelling and inflammation;
- melitin is a component that promotes hemolysis (destruction) of mast cells;
- apamin is a toxin that has a strong effect on the nervous system, including motor nerves;
- acetylcholine, which has a direct effect on the conduction of nerve impulses;
- histamine, the main function of which is to trigger the mechanism of an allergic reaction (the action of anti-allergenic drugs, which are called antihistamines, is aimed at neutralizing histamine);
- MCD-peptide, which destroys mast cells and causes an avalanche-like increase in the amount of histamine in the blood (as a result, the development of an allergic reaction accelerates);
and some others.
Partly due to the destruction of cell walls is the fact that a wasp sting often hurts for a long time and goes away rather slowly: inflammation develops in the affected area, which disappears as the cells recover. When the walls of small blood vessels are destroyed, hemorrhage occurs - this is especially pronounced with hornet bites.
People's reactions to the effects of wasp venom are largely individual. On average, for a healthy person, a wasp sting hurts for several days, and its consequences completely disappear within a week and a half.
Different species of wasps have different venom compositions. For example, the bite of the so-called road wasp, long and slender, is considered one of the most painful among all insects known in the world (the bite of a tropical bullet ant is even more painful). But the bites of wild wasps (paper wasps, whose nests can be found, for example, on trees in the forest) are not much different from the bites of the same insects, but building their nests, for example, in summer cottages.
There are very large predatory phylant wasps that feed on bees. Their bite is generally insensitive, and beekeepers catch and crush them with their bare hands. On the contrary, open spaces are inhabited by small wasps, the size of a house ant, which bite about as painfully as ordinary paper wasps. Therefore, the bite of some forest wasp that is not quite familiar in appearance may be difficult to predict in its consequences.
Features of a wasp sting
Wasps exhibit high levels of activity during the summer months and September. The striped hunter eats many insects. The poison contained in the sting and mouthparts is also dangerous for humans.
Only females have a sting. Its structure is smooth, so it does not get stuck in the skin, and is easily removed by insects. A wasp can sting many times in a row and remain alive. This is how it differs from a bee, which dies after losing its sting. The reason for attacking people is defense. With multiple bites, an increased dose of poison enters the body, and this increases the negative effects of a wasp attack on the body. The chemical composition of wasp venom includes several active substances that mutually complement the effects:
- Acetylcholine. The substance is aimed at instantly producing a strong pain reaction by affecting nerve endings.
- Histamine. Causes an allergic reaction of the body to injected substances and causes severe swelling.
- Phospholipase. In tissues that have been bitten, cells are destroyed, and cellular organelles enter the intercellular space. Inflammation of the lesion is a reaction of the body aimed at protection. Phospholipase also deforms and destroys the body's mast cells, which enhances the reaction in people prone to allergies.
- Mastoparan. The substance takes part in the damage of mast cells and ensures the release of histamine from them.
- Cytotoxins. They damage blood vessels, thereby causing hemorrhages and hematomas. With multiple bites, hemorrhage can be life-threatening.
People with good health tolerate wasp venom much better than those who have weak health or are allergic to the components of the venom.
How does a wasp sting, how does its sting differ from a bee sting?
These are quite aggressive insects, always ready to attack. However, they will not sting a person peacefully passing by. Wasps attack if they are in danger or the threat of ruin hangs over the nest. When biting, the insect pierces the skin of the victim with its sting, injecting poison. Having bitten once, it strives to do it again.
The wasps do not die after the attack. They can sting repeatedly. The number of bites depends on the type of insect, its age and the amount of toxic substance that its body is capable of producing. Wasps usually bite at least 5 times.
Bees, unlike wasps, leave a sting in the wound, dying some time after losing it. The bee is considered the most harmless stinging insect. Wasp venom is much more toxic, so the consequences of their stings are more pronounced than the reaction to bee venom
Why do wasps attack people?
It should be noted that, unlike a bee, a wasp can attack a person more than once. Bees can sting in self-defense, but then they die because the sting remains in the skin. Wasps have a smooth sting, so they are not in such danger. Only females sting.
Wasps attack people if they sense danger. The problem is that by danger they can understand any innocent movement of a person.
In addition to single bites, there is also a danger of attack by several wasps , then the consequences of such an attack can be very serious. The human body can react differently to the poison that wasps secrete. Sometimes the damage is minimal, and after a few hours a person can forget about this trouble. However, there are cases when the victim requires hospitalization.
Why does the skin at the site of the bite become red, swollen and itchy?
If bitten by a wasp, the skin at the site of the lesion quickly swells, turns red and becomes hot. During an insect attack, the victim feels acute pain, which turns into severe itching. Why does the area where the wasp sting occurs itch, swell and turn red?
The self-defense weapon of these insects is a sting, which is connected to a paired gland that secretes a toxic substance. Their poison is stored in a special tank. By thrusting its stinger into the skin, the wasp injects a certain amount of toxic substance. The natural reaction of a healthy body to interaction with it is redness, swelling and irritation.
For allergy sufferers and people with weak immune systems, symptoms may be more pronounced. An allergy to a wasp sting is manifested by the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- dizziness;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- fainting;
- clouding of consciousness;
- diarrhea;
- deterioration in vision clarity;
- increased heart rate;
- blood pressure disorders;
- skin rashes;
- swelling of the eyelids and soft tissues;
- swelling of the larynx;
- feeling of suffocation;
- anaphylactic shock;
- pallor of the skin.
Consequences of wasp stings
After a wasp bites, a local reaction occurs on the human body. If the bite is in the eye, face or other soft skin, swelling will be more pronounced. In addition, weakened people, children, women and allergy sufferers are more sensitive to poison. In addition to swelling at the site of the bite, a person may experience other symptoms. These include severe pain, burning, swelling and redness of the wound. Body temperature may also increase, vomiting, nausea, headache and convulsions may occur. In rare cases, skin rashes also occur.
However, in healthy people, all these effects disappear within a few days.
Signs of a wasp sting
The main symptoms of a wasp sting:
- burning pain in the affected area;
- skin redness;
- edema.
Bite
These signs appear in everyone, but sometimes an allergy occurs, which manifests itself as follows:
- severe swelling spreading far beyond the bitten area;
- itching;
- rash;
- labored breathing;
- too fast or slow pulse;
- dizziness, weakness;
- high temperature, fever, chills;
- nausea, vomiting.
In a healthy person, symptoms disappear 1 to 3 days after he was attacked by wasps. But it also happens that recovery takes several weeks.
Wasp stings: first aid
After an insect attack, it is necessary to inspect the wound and remove the sting using sterile tweezers. In this case, you should not put pressure on the wound, so as not to accelerate the spread of toxic substances in the body. The stung area is treated with an antiseptic (alcohol, chlorhexidine or hydrogen peroxide) to prevent the penetration of infection or bacteria from the insect sting.
If you are in nature and do not have a first aid kit on hand, you can use soap, vodka, or a compress of crushed plantain grass as an antiseptic. In extreme cases, when there is nothing at hand, urine, which should be smeared on the wound, will do. To eliminate severe pain, an effective remedy is a solution of acetic acid. You can take painkillers. Lemon juice and sour berries can also relieve pain. A sterile bandage should be applied to the wound. If a limb is injured, the bitten area can be tightly bandaged to localize the poison and prevent it from spreading throughout the body. Swelling of the wound is eliminated with an aqueous solution of soda or salt (1 teaspoon per glass of water). Ice is great for relieving pain after a bite. Panthenol will be very effective for children.
It is advisable to take any allergy medicine, even without allergic tendencies. In order to speed up the removal of toxins from the body, it is necessary to consume as much fluid as possible. Regidron solution is very effective. You can also drink sweet warm tea. By drinking plenty of fluids, toxins are eliminated in the urine. Thanks to this, swelling and pain go away faster.
In the event of an allergic reaction, assistance with a wasp sting should be provided by a qualified medical professional. Allergy sufferers are advised to always have a special first aid kit with antihistamines on hand. It is advisable for people suffering from asthma to carry an inhaler with them to prevent possible suffocation if necessary. If you are predisposed to heart disease, you need to have heart medications with you. The listed diseases require a special approach to wasp stings. You should not rely on the body’s endurance, but it is better to consult a doctor immediately. The disappearance of symptoms of intoxication and recovery will not be slow in coming if you know what to do in case of wasp bites.
Bite symptoms
Externally, the manifestations are practically no different. It is difficult to assess the degree of pain, if a wasp or bee stings for the first time, a person has nothing to compare with. The bite looks like this:
- edema;
- redness;
- swelling;
- pain;
- in the center is a dot with a small depression;
- itching
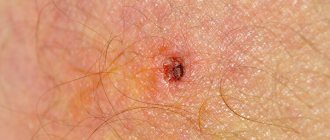
A photo of a bee or wasp sting is shown below. You can carefully examine all the features of the traces of an attack by striped insects.
Wasp sting
On a note!
If a wasp or bee stings in the leg, injects poison into the arm, the entire limb swells. If you are bitten on the neck, face, or tongue, the likelihood of swelling of the larynx increases. In severe cases, Quincke's edema develops. In the absence of qualified help, a person risks dying. If you are bitten by bees or attacked by a swarm of wasps, the dose of poison in the blood increases significantly and anaphylactic shock may occur.
A severe allergic reaction provokes:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- violation of movement coordination;
- clouding of consciousness;
- fainting;
- blurred vision;
- decreased blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- constriction of the pupil;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- arrhythmia;
- increased sweating;
- chills.
At home, it is allowed to treat a wasp or bee sting in case of a local allergic reaction. If you experience deterioration in your health, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the larynx, you should immediately call an ambulance or go to a sanitary checkpoint accompanied by other people.
Why are wasp stings dangerous?
The greatest danger to humans comes from wasp bites in the neck, face, tongue, eyes and peripheral nerves, or from several consecutive bites at once. Such bites can lead to dire consequences for human health, such as:
- optic neuritis;
- malignant myasthenia gravis;
- airway obstruction;
- development of anterior capsular cataract;
- glaucoma;
- iris atrophy;
- generalized polyneuropathy;
- lens abscess.
First aid for a bee or wasp sting
After an insect attack, you need to take certain actions to avoid complications and reduce allergies.
- Rinse the wound with clean cold water. The procedure will help wash away any remaining poison and remove dirt. At home, use laundry soap.
- Disinfect. They use ammonia, medical alcohol, and boric alcohol. And also hydrogen peroxide, a medicinal herbal tincture of medicinal herbs.
- Neutralize the effect of the poison. Use vinegar and citric acid. To prepare the solution, add 1 teaspoon of vinegar or 0.5 teaspoon of acid to a glass of water. They wipe the sore spot, make lotions and compresses. If it is not possible to prepare a solution, apply a piece of sugar for 5 minutes.
- Don't let the poison spread. Ice cubes or cold objects are applied to the bite site for 5 minutes - a bottle of water, meat from the freezer, a heating pad. Cold constricts blood vessels, prevents the spread of poison, and also relieves swelling and eliminates pain.
- Reduce inflammation. You can treat the bite with a decoction or tincture of calendula, chamomile, or valerian. Or they use pharmaceutical drugs.
First aid for insect bites
If you have a severe allergic reaction, you need to take an antihistamine as quickly as possible. Be sure to take medicine for multiple bites, if a wasp or bee stings you on the neck or face.
What to do if stung by a wasp
In the place where the wasp bites or stings, an unpleasant sensation or burning sensation immediately appears. It should be noted that the second version of the name for manifestations of wasp aggression sounds more correct. After all, these insects do not have teeth and, unlike mosquitoes, they sting their opponent.
What should you do first if your encounter with a wasp ends in a bite? First, you need to prevent the poison from spreading into the body and causing an allergic reaction. Therefore, the victim is advised to drink as much fluid as possible. Apply something cold to the bite site. You can also place a cloth soaked in a baking soda solution on the wound for 15-20 minutes. A piece of moistened sugar applied to the bite site helps to draw out wasp venom very well. If the victim experiences allergic reactions, it is necessary to start taking antihistamines, such as Suprastin or Claritin.
How to help at home?
If there are no medicines at hand, folk remedies that can be found in every home can help. By the way, natural remedies will also come in handy if a wasp has bitten a pregnant woman, for whom the list of approved medications is very limited. More often than others, the following are used to treat the bite site:
- aloe juice or pulp;
- a slurry of soda mixed with water;
- sour fruit (lemon, sour blocks);
- diluted apple cider vinegar;
- tomato pulp (both ripe and green);
- grated fresh potatoes.
Grated potatoes
Some housewives advise adding chopped onion or garlic, but the juice of these plants is very caustic, so the method is not suitable for everyone. In particular, such lotions are not recommended for treating wasp stings during pregnancy
Symptoms and first aid
At the moment of an insect bite, a person feels a sharp, burning pain; after a few minutes, the painful phenomena become diffuse and increasing in nature. Redness and slight swelling immediately appear around the wound left by the sting, and gradually the redness spreads around the bite site. Then swelling appears, the skin at the site of action of the poison becomes hot, and pulsation may be felt. Later itching begins, over time the pain gradually decreases and the swelling subsides.
Severe sharp pain, redness, swelling - the first symptoms of a bite
In a healthy person, the symptoms of a bite fade away on their own within 24 hours; after 2-4 days, all signs of contact with a poisonous insect disappear. People prone to allergies may experience the following symptoms of a wasp sting:
- rashes all over the body;
- temperature increase;
- headache;
- nausea;
- drop in blood pressure;
- increased blood sugar levels;
- change in heart rate;
- difficulty speaking and breathing;
- darkening of the eyes;
- loss of consciousness;
- Quincke's edema;
- anaphylactic shock.
Rashes all over the body - a complication in the form of an allergic reaction to wasp venom
Signs of a severe allergy can develop gradually over several hours, or they can appear in seconds. In such cases, you may not have time to provide assistance to the victim. When stung by a wasp, it is important to have at least minimal knowledge that will help alleviate the condition and prevent disastrous consequences.
What to do if bitten by a wasp:
- Do not squeeze the poison out of the wound, as this increases local blood circulation and the poison is quickly carried further by the blood (you can try to suck it out).
- Wipe the bite site with vinegar (apple vinegar, table vinegar), citric acid solution - the acidic environment neutralizes the poison.
After the bite, it is necessary to remove the sting (if the wasp left it) and treat the wound to prevent infection. - Apply ointment or gel to the skin that is active against insect bites (Fenistil, Psilo-balm).
- Apply something cold to the affected area.
- Take an antiallergic drug tablet that contains loratadine or cetirizine.
- Give the victim plenty of tea or water.
- If a wasp attacks an asthmatic or a person prone to allergies, you should immediately call an ambulance. If an attack of suffocation begins, you need to use an inhaler and inject Prednisolone or Dexamethasone (these drugs should always be on hand for people suffering from allergies).
To relieve pain and reduce swelling, use folk remedies for wasp stings: a paste of parsley, onion or fresh calendula leaves (they are applied to the affected area, changed every 20-30 minutes).
When stung by a wasp, it is important to provide first aid to the victim in a timely manner. This is the only way to prevent severe allergic reactions and their terrible consequences.
What to do depending on the location of the bite?
A wasp can sting any part of the body. First aid will vary slightly depending on where the affected area is:
- the wasp has bitten the lip or tongue - the victim should take an antihistamine, you can let him suck on ice;
- if a wasp stings your eye, you should apply a napkin moistened with cold water, but it is better not to use ice, so as not to chill the facial nerve;
- If you are bitten on the neck, you should immediately take an antihistamine.
The most dangerous are wasp bites to the eye, neck, and tongue. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What to do if you do get stung
It is impossible to say for sure whose bite is more painful and dangerous. Much depends on a combination of reasons: the body’s individual tolerance of the poison, its mass, age, location of the bite, and in relation to the honey bee, the breed of insect. “Even among common honey bees, the venom varies quite widely depending on the breed. In Belarus, bees stung me more than once, but I did not experience such a strong reaction to their stings as happened to me in Germany. The hand swelled so much that the skin almost burst, the temperature rose, the pain went away after about two weeks. In general, the larger the Hymenoptera, the greater the dose of poison it can inject into a person. Therefore, hornets sting more painfully than other wasps. Yet bumblebee stings are not as painful for most people as wasp stings,” explained the lead researcher.
According to the senior doctor at substation No. 7 of the Minsk city ambulance station, Evgeniy Yudakov, bee stings are the most dangerous. “Fortunately, bees bite people much less often than wasps or hornets. Serious allergic reactions never develop from the first bite; as a rule, this occurs with a second bite. If a person already has a history of allergies, and not necessarily to insects, it could also be a food allergy, then you should always have antihistamines with you. After a bite, you can take them urgently, not wait for an allergic reaction to develop, but try to prevent it,” he said.
The body's local reaction to an insect bite will manifest itself as itching, pain, swelling, and a local increase in temperature. These symptoms may last for several days. In addition to taking an antihistamine, the bite site can be treated with a similar ointment and cold applied.
If a person has been bitten repeatedly - more than two or three times - then it is necessary to seek medical help in a hospital or clinic, since, most likely, there will be a general toxic reaction. A large amount of poison has entered the body, and it will be more difficult to cope with it on your own. “It is worth noting that there are dangerous places for bites. If you are stung in the neck or face, this may be accompanied by angioedema. Such bites can even be fatal. A person's airways swell and he may simply suffocate. And an antihistamine tablet is unlikely to help. In such cases, emergency medical care is required, you need to call an ambulance,” noted Evgeniy Yudakov.
You should immediately seek medical help if a child is injured. “We are not saying that after a single sting, for example, from a bee, you should immediately consult a doctor. This should be done if any allergy symptoms appear, or the person already knows that he is allergic to a bee sting, but does not have the necessary medications with him. Everything is individual. However, if a child has been bitten, you should play it safe. It is better for the little patient to remain under the dynamic supervision of doctors for some time,” the doctor emphasized.
Signs of an inappropriate reaction
The human body contains special immunoglobulins that neutralize the effect of the poison and prevent a difficult situation. Immunoglobulin is produced the first or second time the poison enters the blood. This substance is absent in infants, people with pathologically weak immunity, or a genetic predisposition to allergies.
On a note!
You can determine whether there is an allergic reaction to a wasp sting by external manifestations and internal sensations. In a normal situation, the affected area turns red and swells with a diameter of 10 mm. If this indicator is exceeded, an allergy to wasps can be judged.
How further symptoms will develop depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the strength of the immune system.
Minor wasp allergy symptoms
Allergic reaction to a wasp sting
Characterized by an increased local reaction on the skin.
- increased redness;
- severe swelling;
- rash;
- pain;
- increase in local temperature;
- burning;
- itching
Hives after a wasp sting cover only the affected area or manifestations are observed throughout the body. In most cases, it develops in small children under 2 years of age, adults with weak immunity, during the first insect attack. A photo of an allergy to a wasp sting is presented below.
Moderate symptoms
In addition to skin rashes, severe swelling, redness, there is a change in general health:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- decreased blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- dry cough;
- difficulty breathing;
- vomit;
- slight increase in temperature;
- muscle spasm;
- diarrhea;
- painful sensations in the stomach, intestines;
- violation of movement coordination;
- pale skin.
An allergic reaction to a wasp sting begins to appear within 20 minutes after the insect attack.
Severe symptoms
A wasp sting with a strong allergic reaction within 5 minutes causes difficulty breathing and swelling of the larynx. Anaphylactic shock may occur. The situation requires immediate emergency medical care.
The victim is given a dose of Prednisolone, Adrenaline, and a tourniquet is applied above the bite site to prevent further penetration of the poison into the blood. Further therapy is carried out in a hospital.
Without proper medical care, death from a wasp sting can occur. The situation becomes more complicated when several insects attack a person at once. ICD code 10 bite or sting by non-venomous insects, arthropods belongs to section W57.
Important!
Immediately after an insect attack, you need to provide first aid to the victim or yourself. The bite site must be disinfected, the effect of the poison must be neutralized, and the concentration of the toxic substance in the blood must be reduced. If you have complex symptoms, see a doctor immediately. If you were bitten by several insects at once, you will need emergency help.
Wasps - causes of aggression and ways to get rid of them
The arrival of spring means the appearance of numerous insects, which, thanks to the sweet flower nectar, strive to replenish the strength weakened during the winter. Not all of them are harmless, so summer residents and outdoor recreationists should not let their guard down. For example, wasps and hornets, unlike the more intelligent bumblebees and bees, can sting a person for no apparent reason.
Wasps - causes of aggression and ways to get rid of them
Moreover, science has established that wasps can bite a person repeatedly without any unpleasant consequences for themselves. Whereas a bee loses part of its stomach during a sting, from which it subsequently dies.
In addition, both bees and wasps, if they are angry, attack precisely those people who are allergic to their venom. There are several species of wasps that live both individually and in large swarms. What causes the most trouble for people are the so-called medium-sized wasps, which like to build a nest in the attic or barn. They are attracted by the smell of sweets, so they often circle over the table or near ripe fruits in the garden.
The construction of the nest is carried out by the female queen, having chosen a suitable place for this in early spring. She lays eggs in molded cells, and then feeds the larvae until they turn into worker wasps. With the advent of the latter, the queen is only concerned with increasing her offspring.
All the work of providing the queen and larvae with food, as well as expanding the nest, falls on the working wasps. Over the summer, the colony can multiply to several hundred individuals. But in the fall, all working wasps, as well as males, die. Only fertilized females remain over the winter, and in the spring they begin to build a new colony again. Despite the obvious benefits brought by wasps in terms of pollinating flowers and eliminating harmful insects, if their nest is discovered near human habitation, measures must be taken to destroy it. It is best to call a team from the Ministry of Emergency Situations, which will do everything at a professional level.
How to remove a wasp nest
If you do this yourself, then you need to carry out all the necessary manipulations at dusk. Firstly, all the wasps will be in the nest, and secondly, the risk of a massive attack from nest defenders will be significantly reduced. The wasp nest must be placed in a plastic bag with insecticide and tied tightly.
After a day, the package, along with the nest and already dead wasps, can be removed, and it is advisable to ultimately burn it. If it was not possible to find their nests, but the wasps themselves are constantly annoying, you can arrange several baits that will significantly reduce their number.
To make the simplest bait, you need to cut off the conical part of a plastic bottle, turn it upside down and insert it back into the bottle. If you pour sweet syrup into such a bait, the wasps will crawl inside en masse, but will no longer be able to get out of it. To avoid painful wasp stings in nature, you must adhere to certain safety measures. First of all, avoid walking on the grass barefoot and avoid trees with large hollows. Dry your body thoroughly after bathing, as moisture is very attractive to various insects, including wasps.
Do not keep fruits or sweet drinks open for a long time, as their smell attracts even wasps located at a distance of several tens of meters. Before leaving, you need to carefully inspect the interior of the car and your clothes so as not to take unwanted travel companions with you.
In addition, people who have an allergic reaction to wasp stings should always carry antihistamines with them when going outdoors.
The reason for a wasp's aggression is its physiology, wasps spontaneously attack people, be careful! Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Folk remedies
Symptoms disappear completely within a week. All this time the sore spot hurts and itches. To speed up tissue regeneration, folk remedies are used. They are also used if it is not possible to treat the wound with professional antiseptics.
- Baking soda. Making pasta. Add a little water, mix, apply to the bite area until dry.
- Laundry soap. Foam should be applied to the bite. Leave for 5 minutes.
- Plant juices. Celandine, dandelion, plantain, and aloe vera are used.
- Toothpaste. For medicinal purposes, a hygiene product with menthol is used. Leave on skin for 5 minutes. Instead of paste, use shaving foam.
- Onion. Squeeze out the juice or apply the paste to the sore spot. The product neutralizes poison and prevents infection.
On a note!
The juices of potatoes, carrots, beets, lemon, and grapefruit have anti-inflammatory properties. They make compresses, lotions, and simply wipe the wound.
Lotions to relieve puffiness
The bite site can be treated with parsley juice to relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. To do this, the greens are washed and finely chopped. Then knead it with a pestle or regular spoon to make a paste. It is wrapped in gauze and the juice is squeezed out. A piece of cotton wool is moistened in it and applied to the wound. The lotion is changed every 3 hours.
Tip: Do not use wooden utensils to mash parsley, as the material quickly absorbs liquid.
To reduce swelling, use an alcohol tincture of calendula. Soak a cloth in undiluted liquid and apply it to the bite site as a compress for half an hour. Then rub an ointment of 50 ml of water, 30 g of baking soda and 1 tbsp into the affected area. l. calendula tinctures.
Mint helps reduce itching after a wasp sting. The leaves, mashed with a spoon, are applied as a lotion to the wound and secured with a bandage. After 2-3 hours it is replaced with a fresh one. Mint soothes irritation and helps relieve inflammation and redness.
Sour fruits
If there is no means at home to anoint wasp stings, fruits with sour pulp that neutralize toxins are used for treatment. Lemon juice effectively eliminates swelling and itching. The fruit is cut into slices and applied to the wound. For the same purpose, lotions are made with fresh lemon juice.
You can replace lemon with sour varieties of apples. The fruit is cut in half and massaged into the skin on the affected area. Another option for use is apple pulp lotion. For it, the fruit is grated or mashed in a blender. Then the paste is applied to the damaged area and secured with a bandage. This treatment eliminates swelling within three days.
Garlic pulp
To quickly cure swelling and relieve redness, use garlic. The vegetable has a bactericidal effect and relieves inflammation. Several cloves are peeled from the films and finely chopped, or passed through a press. The resulting pulp should be applied to the areas of the skin around the wound. Then the lotion is fixed with a bandage and left for 2 hours. In the first minutes, a burning sensation is felt, but the discomfort soon passes. You can replace garlic with onions. These vegetables have very pungent juice. Therefore, there is no need to apply the paste directly to the wound.
Potatoes and tomatoes
Wounds from stinging insect bites quickly heal if a paste of tomato pulp is applied to them. Vegetables are used ripe or green. In this case, unripe fruits are not ground, but simply cut into slices and applied to the affected area, secured with a bandage.
To relieve redness and reduce swelling, use raw potatoes. The fruit, peeled, is grated or ground in a blender until mushy. Then the resulting pulp is wrapped in several layers of gauze and applied to the wound for 1 hour.
Mosquitoes
Mosquito bites itch, so an infection can get into the scratched wound, after which purulent inflammation can develop. Mosquitoes are not as safe as they seem at first glance, since they carry pathogens of yellow fever, malaria, helminthiases, and so on. In order to avoid itching, it is necessary to moisten the skin at the site of the bite with ammonia or a solution of ordinary soda (half a teaspoon per glass of water). If after a bite the temperature rises and the condition worsens, you should immediately consult a doctor. To protect against bites, you must use special protective equipment.
How to treat the affected area
In case of severe itching, you can apply grated raw potatoes to the wound. – Fresh celery juice mixed with a little wine vinegar will help relieve itching. – You can use compresses made from pharmaceutical alcohol or pure distillate. – Apply the cut onion and leave for 15 minutes. This vegetable will secrete juice, which, penetrating into the irritated area, will relieve swelling and itching. – Calendula essential oil has a calming effect. – Lemon juice helps eliminate swelling. – The wound can be treated with a banana. To do this, you need to steam it, peel it and cool it. Then mash with a fork until it becomes a thick jelly and rub the bite area with it. – Apply a handkerchief soaked in vinegar for half an hour.
First aid
First aid instructions:
- Remove the sting if it remains in the skin.
- Treat the bite site with vinegar (acetic acid destroys the components of the poison).
- Apply cold to the bite site.
- If you have a history of allergies, take antiallergic medications. (diazolin, suprastin).
- The bite site can be treated with an ointment containing glucocorticoid hormones.
Cold reduces pain, swelling and prevents the spread of poison
If you are allergic to insect bites, it is very important to have anti-allergic or hormonal medications with you in the summer. You can purchase inexpensive domestic products, but it is better to use proven drugs, even if their price is higher - your health depends on it.
For people who have had severe allergic reactions, their doctor recommends carrying an allergy kit that contains epinephrine (adrenaline). In emergency situations where emergency medical care is not available, such a kit can save lives.
Allergy to wasp venom
Insect venom releases histamine and other components that trigger the onset of an allergic reaction. Therefore, you need to know what to do if a wasp bites you and a person’s arm or leg swells. Allergies are divided into several degrees of severity: – Mild. Redness and swelling at the site of the bite (a normal reaction of the body). – Average degree. Redness and swelling, difficulty breathing, abdominal cramps, diarrhea and vomiting. - Severe degree. Anaphylactic shock develops. In this case, immediate medical attention is required. The increased risk of developing a severe anaphylactic allergy reaction most often occurs in people with chronic heart problems and asthmatics. If a local allergic reaction occurs (swelling around the bite site), you must do the following: 1. Take an antihistamine as soon as possible. It blocks the action of histamine, a substance that is released by some cells in the body during an allergic reaction. 2. Apply a cold compress to reduce pain and swelling. You can use a piece of cloth or an ice bag. 3. What to do if a wasp has bitten your finger and a person experiences excruciating discomfort throughout the entire arm: analgesics such as paracetamol or ibuprofen will help, they relieve the pain. 4. If a severe allergic reaction develops, the allergic person must be given adrenaline.
How does wasp venom work?
Let's figure out why a wasp sting is dangerous for humans.
At the tip of the sting there is a hole where the duct of the poisonous gland opens. During the bite, the poison hits the target and has a nerve-paralytic effect. This usually happens with flies or other victims of wasps. A person is a more serious target: large and stable.
The poison contains about 14 components, mainly represented by proteins. Once in the human body, they can cause a serious allergic reaction.
- Acetylcholine , as the main mediator, has a significant stimulating effect on a large number of receptors in the thickness of the dermis.
- Next, serotonin reacts , which indirectly spasms the blood vessels at the site of the bite. Ischemia leads to increased pain.
- Phospholipase A and B cause the release of histamine . The vessels dilate, redness of the skin appears, exudation of fluid from the bloodstream into the intercellular space begins, and edema appears.
But this is just a local reaction that appears at the site of the bite and is characteristic of almost all people.
Common appearance of the bite site
So why is a wasp sting dangerous? In some people, proteins contained in the venom cause an immediate hypersensitivity reaction.
Manifestations of such a reaction may be:
- Severe swelling and pain at the site of the bite.
- Swelling of the face, neck.
- Difficulty in breathing.
- A feeling of constriction behind the sternum.
- Hoarse wheezing.
- Rash all over the body.
- Sudden weakness.
- Abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting.
All of these symptoms may be a manifestation of a severe allergy.
Swelling of the face and neck is a manifestation of Quincke's edema. With this complication, swelling of the larynx develops and the person can die from suffocation in a matter of minutes.
Symptoms of the development of Quincke's edema in the photo
Weakness throughout the body is a sign of a severe drop in blood pressure and developing anaphylactic shock. Bites are especially dangerous for small children, pregnant women, bites on the neck and tongue. In such cases, it is necessary to seek medical help.
Is the sting of one wasp dangerous? Yes. The amount of allergen entering the bloodstream is not necessarily proportional to the body's reaction. It all depends on its reactivity. If a person has a tendency to be allergic to insect bites, the likelihood of the above complications increases significantly.
Help for people with increased allergic reactions
Allergy sufferers, while on vacation, should always be prepared to encounter insects and know the consequences that insect bites will bring them. Must be able to perform basic assisting techniques. If you are allergic to a wasp sting, be alert. Literally, every allergy sufferer should carry with them a first aid kit with a specific set of medications.
The basis of such a first aid kit should be antiallergic (antihistamine) drugs. People with asthma should carry an inhaler with them. After all, its timely use eliminates the occurrence of asthma attacks. Those suffering from heart disease and related diseases should carry cardiac medications with them. A tourniquet is also a must in the first aid kit. If a leg or arm is affected, a tourniquet will act much more effectively as a stopper to harmful toxins than a tight bandage. Allergy sufferers should clearly know the symptoms of allergies. After a bite, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all, medical care is always better than self-medication.
Help with allergic reactions
In rare cases, the reaction to a wasp sting may be more severe . Symptoms that should prompt you to see a doctor include:
- Hives all over the body;
- Large amounts of edema;
- Nausea;
- Temperature increase;
- Dizziness;
- Pain in the head or stomach.
In extreme cases in allergy sufferers, a wasp sting can lead to angioedema and anaphylactic shock. An important circumstance is where exactly the insect stung. If the affected area is the tongue, the victim may experience suffocation. If a wasp stings in the eye, it can lead to vision problems.
An attack by several wasps on an allergic person poses a mortal danger, since the effect of the poison increases many times over.
People who have an allergic reaction to wasp stings should always have antihistamines, inhalers, etc. on hand. If an allergic reaction develops after a bite, then after providing first aid you should call an ambulance or call a doctor.
How long does a wasp sting last and hurt?
Summer is not only a time for picnics and spending time outdoors. This is also a period of activation of various insects, including wasps. All insect bites are unpleasant, but wasp stings are the most painful. In addition, wasp stings can be fatal for some people.
Important: Most people tolerate wasp stings normally. The bite site almost always hurts, itches, swelling and redness appear. This is considered a normal reaction.
There are rare cases when people endure a wasp sting practically painlessly, the pain and itching quickly go away.
In people with an allergic reaction, wasp stings can cause serious consequences. The number of these people is small, but they exist. The problem is that many people simply do not know about their allergy to wasp stings, and an instant severe reaction without timely medical care poses a huge danger to human life.
Wasp bites occur individually for each person:
- For some, pain and swelling disappear after 2-3 days;
- For others, symptoms may last a week.
- Sometimes the reaction does not go away within 10 days.
It is difficult to answer how quickly the pain will go away. You can help you get rid of discomfort faster by taking an antihistamine. Special ointments for insect bites, for example: Moskitol, Fenistil, Psilo-balm, Gardex, etc., help to cope with pain and swelling faster. In this case, you can count on the fact that the wasp sting will not remind you of itself for a long time.
If you don't treat the bite site at all, hoping that the pain and swelling will go away on its own, this will work. But the reaction will take much longer, at best up to a week.
Important: A wasp sting is considered one of the most painful among the bites of other types of insects.
This is what a wasp sting looks like
Consequences of wasp stings
Being in good health does not mean that a person will not experience an allergic reaction. If a wasp stings several times, the concentration of histamine is very high, and everyone can develop an allergy. If a person is often attacked by wasps, he risks getting a severe allergy with the next bite. The body's reaction and its severity vary depending on the concentration of the poison, the number of bites inflicted and the tendency to allergies.
The most common consequences after a wasp sting:
- Sharp and sharp pain (resembles a burn), which increases a few seconds after the attack;
- The appearance of redness around the bite site;
- The stung area swells greatly around;
- Simultaneously with the pain, itching appears and increases, and this reaction remains longer than the pain.
However, the reaction to insect venom can vary. The main factors are the location of the bite and the individual characteristics of the organism. Since the wasp is not only a predator, but also a creature that eats carrion, it can carry various bacteria and viruses and infect humans with them.
For a person prone to allergies, the consequences may be different. The main symptoms include: changes in pulse (faster or slower), the affected area becomes very swollen, and the swelling spreads further to a large area of the body. Breathing is rapid and difficult, shortness of breath or even symptoms of suffocation begin. Dizziness, headache and fainting or vomiting often occur. You need to know what to do if you are bitten by a wasp in order to provide first aid. A lot depends on quality first aid.
Judging by the characteristics of the swelling around the wound, we can conclude how successfully the body fights toxins from internal tissues. If the body quickly copes with the incoming poison, the swelling of the stung area is small and disappears after 2-3 hours. If the swelling does not decrease, this indicates an allergy.
Should I see a doctor after a wasp sting?
Of course, if you are bitten by a wasp, but there is no strong reaction, then it is not necessary to seek medical help. But there are often times when it is necessary to consult a doctor.
In particular, if there are several bites. With each bite, poison enters the human body; if there are several of them, then, consequently, the concentration of poison is higher, so the risk of general toxicity of the body also increases.
If a wasp has bitten you on the lip, mouth, tongue or larynx, it is important to consult a doctor as quickly as possible, because swelling from the bite will spread throughout the larynx, making breathing difficult and leading to suffocation. In general, if a wasp sting occurs on your face, it is better to go to the doctor.
If the victim has an allergic reaction, difficulty breathing, skin rashes, nausea, vomiting, you should also seek medical help.
If a wasp has bitten a child, then, of course, it is better to play it safe and consult a doctor. The fact is that a child’s skin is more delicate, so wasp stings will be more painful for him. In addition, the likelihood of an allergic reaction is higher.
What does a stinging insect bite look like?
One of the terrible dangers of a stinging bite is the composition of the insect's venom.
It is due to the presence of certain substances found in the venom of these insects that it can lead to an allergic reaction in a person defeated by such an attack. The histamine contained in the poison can cause severe allergies on the human body after the bite of a stinging insect.
A substance called acetylcholine helps to influence the nerve endings of the enemy when bitten. It is thanks to him that a person experiences wild pain even during an insect bite.
In order for the area affected by the poison to immediately become inflamed, phospholipases react with other components of the poison. They destroy precisely those cells that were in close proximity to the penetration of the wasp venom.
If the stinging individual bites its enemy more than once, then cytotoxins come into play to fight the enemy. It is these substances that can provoke hemorrhage and lead to death if medical care is not provided.
All people prone to allergic reactions should avoid stinging insects with even greater vigilance than healthy people. The reason for this will be all substances, interaction with which for allergy sufferers can be very painful and hazardous to health.
In order to determine whether a person’s body has been attacked by a stinging insect, you must first examine all free areas of skin. On areas of the skin affected by wasp bites, certain marks may appear , seeing which it will be easy to conclude that there is an obvious insect bite.
Symptoms of a stinging insect bite
The most obvious signs of a stinging insect bite include:
- Swelling of the bite site (redness and swelling).
- The bite site may be very itchy and itchy.
- Allergic reaction.
- Itching or rash on the body.
- Acute pain.
- Anaphylactic shock.
In addition, a person who has been stung may experience the following symptoms immediately after the insect attack:
- Dizziness.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Increased or decreased heart rate.
- Increased body temperature.
One of the most important dangers associated with the bite of stinging insects is anaphylactic shock , which a person can fall into as a result of their attack. Anaphylactic shock can be considered more severe consequences of allergies as a result of many causes, including a wasp sting.
The hidden danger of anaphylactic shock for people prone to this condition is that the patient must receive qualified medical care as soon as possible. Failure to receive prompt medical attention in the event of anaphylactic shock can result in death for the patient.
How to prevent a wasp sting?
The insect stings a person when he poses a danger to him. If a wasp lands on your clothes or skin, you should not wave your arms sharply, start screaming, or even try to swat it with your hand. When in contact with an insect, you should behave calmly and not make any unnecessary movements that could frighten it. In most cases, with such behavior, the wasp flies away safely without stinging.
Under no circumstances should you try to knock down a wasp nest found anywhere with a stick, be it a house or a tree branch. Since in this case the insect will protect its home and bites cannot be avoided. It should be borne in mind that families of wasps living in nests can consist of a large number of individuals. The more bites, the higher the dose of poison received by the body, which means the stronger its intoxication and the longer the recovery process.
Preventing wasp stings
To avoid a wasp sting, you need to know why these insects attack people and be careful. You need to be especially careful:
- having a picnic in nature;
- pruning fruit bushes and trees;
- picking berries or fruits, especially in the second half of summer;
- being in a wooden shed, in an attic, in a bathhouse;
- throwing garbage into a street container.
A wasp attack can be provoked by a sugary sweet aroma or the smell of food. When insects appear nearby, you must behave calmly, do not wave your arms, otherwise she will begin to defend herself.