A tick bite is one of the most dangerous incidents that can happen to a person in the spring and summer. If a parasite is found under the skin, you need to remove it as soon as possible, but it is not always possible to do this correctly - due to clumsy or too harsh actions, the insect ruptures , and its particles remain under the skin. How dangerous is such a situation, what to do and is it necessary to remove the head or proboscis of the tick from the wound? And also how to understand whether the parasite has been completely removed.
How to know if the parasite has not been completely removed
After getting on the skin, the tick chooses a convenient place for itself for several hours (most often in the groin or under the arms), after which it begins to drink blood.
The parasite is absorbed relatively shallowly - the back part remains on the surface, which looks like a small mole, but the difficulty lies in the fact that it firmly clings to the soft tissue with its proboscis and resists removal.
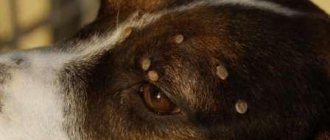
After removing the insect, you need to carefully examine its body - it must be intact, with all segments and head. Only the number of legs does not matter - perhaps the tick lost them before attaching itself to the victim. Next, you should examine the place where the parasite was extracted, and it is best to do this with a magnifying glass. The wound must be absolutely clean , without foreign objects - a few drops of blood that may appear on the surface of the skin are considered normal.
If black dots or inclusions are visible in the bite area, it means that the proboscis or head of the tick remains under the skin.
Submitting a tick for analysis: procedure
There is no universal set of rules for reporting a tick. However, the general procedure looks something like this:
Task #2 - Contact your GP or family doctor
Of course, if you contact a private laboratory, you can skip this step. But if the analysis is carried out at the SES or any other government agency, it is better, of course, to notify the local doctor first. He will record the request and write out the necessary directions that will help in taking tests and carrying out preventive therapy (administration of immunoglobulins, antibiotics, antiviral drugs, etc.).
If you believe the reviews, sometimes you can submit a tick to the SES without a referral. But this rarely happens and rather depends on the specific person on the spot. Therefore, if you go just like that, you may not agree on anything.
Task No. 3 - take the tick for analysis
Usually all the necessary tests are done at the SES. Although usually in this institution everything is limited to a standard test for borreliosis. The remaining infections, of which there are about a dozen, are detected after infection and, most likely, the doctor will only advise you to monitor your well-being in the next few weeks.
Where else can a tick be placed? In addition to SES, the necessary research is also carried out by infectious diseases hospitals and laboratories (both private and public). Alternatively, you can contact a commercial medical center. Although this option will be more expensive, in addition to the analysis, an observation chart will be immediately drawn up and preventive therapy will be prescribed.
According to research results, on average, only 1 out of 10 ticks is a carrier of the infection (the specific parameter depends on the region), and the chances of becoming infected do not exceed 15%. But we need to take the problem seriously
It is important to remember the danger that ticks pose and never neglect it. If there is the slightest doubt that everything will be done correctly, it is better to immediately go to the doctor
He will not only remove the parasite using tools specially designed for this, but will also outline a further plan of action that will help minimize all health risks.
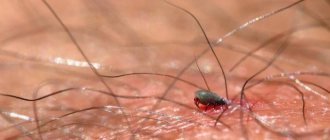
The tick digs into human skin using a proboscis called a hypostome. At the same time, the insect secretes saliva, which has an analgesic effect, and the bite occurs absolutely painlessly for the victim.
The severity of the symptoms depends on the individual characteristics of the person. A strong manifestation is observed in the elderly, children, people with weak immunity and those suffering from allergies.
Scalp hair makes ticks difficult to spot
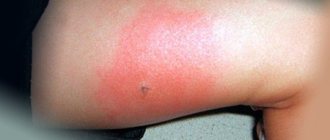
. The location of the bite can be determined by a reddish spot around the small wound and a small bump on the skin. Having fed on blood, the insect increases to 10 mm in length, but in general it can be detected much earlier.
If you find a lump on yourself, but do not find other signs of a tick bite, then we advise you to click here and find out what this may indicate.
What happens if you don't take out the leftovers?
Doctors have differing opinions about the health hazards that such a situation may entail. Most experts believe that it is impossible to catch an infection from insect particles remaining in the body, but they can cause suppuration or an inflammatory process, like any other foreign body, so it is better to get rid .
IMPORTANT! To prevent rupture of the parasite's body when removing it, you need to act extremely carefully - do not try to sharply pull out the tick, but slightly pull the body upward, while simultaneously performing rotational movements (the same as when unscrewing a cap from a bottle).
What to do if the tick's head remains in the body
Ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases. It does not spread viruses and infections in all areas, but there is still a danger of infection from it. To find out how high the risk of infection is, you can check the distribution map of dangerous parasites. It provides statistics on cases of infection after tick bites, displayed by region
At the same time, it is important to remember that even if your region is not in the “dangerous” zone, it is still necessary. This will minimize the risk of developing diseases
But before you send the parasite for analysis, you need to get it out. Not everyone gets it right. In some cases, too sudden movements lead to the separation of the insect body from its head. As a result, part of the tick gets stuck in the skin, which is very difficult to remove on your own.
If the tick's head remains in the skin, it is best not to touch it and go to the nearest hospital or clinic. There, doctors, using special instruments, will pull out the head along with the proboscis, and also conduct an analysis. Testing the parasite for diseases is paid, but it allows you to reduce the risk of developing viruses and infections. If the insect turns out to be infectious, treatment for the disease it introduced into the human blood can begin immediately. This will save the patient from complications and expensive treatment in the later stages of pathology.
Of course, it is better to remove the tick immediately, since the presence of the parasite or its head in the body for a long time leads to an increased risk of infection. However, non-professionals may not be able to cope with this task, but will only worsen the situation by driving the head very far under the skin. If the patient realizes that he cannot cope with the task, he should immediately go to the hospital.
If there is a chance to remove the head (for example, it has not penetrated so deeply, it sticks out a little, you have special tools at hand), then you can try to do it yourself. How to do this is described below.
If the head of the tick remains in the body, various dangerous diseases can develop. Among the infections transmitted by the parasite, encephalitis, borreliosis and Lyme disease occupy the first place in terms of the level of harm caused.
Without treatment, these pathologies lead to disability or death. The longer, the greater the risk of infection, since the main concentration of virus pathogens is in its salivary glands. Therefore, the presence of the head in human skin is very dangerous: it is difficult to remove this particle, and with every minute the likelihood of infection increases.
Infections are not the only problem associated with ticks. The head of the parasite can lead to bacterial damage and the development of inflammation. Against the background of these processes, redness of the skin occurs and suppuration begins. Possible swelling. Due to the fact that the tick injects poison into the human body upon death, intoxication may begin (weakness, dizziness, nausea, fainting, dyspepsia). Some patients develop severe allergic reactions.
How to remove it at home
If the head, proboscis, or other part of the tick remains under the skin, you can choose one of several options.
The first is to treat the wound with a 5% iodine solution and observe the bite site for 2-3 days. During this time, the foreign body should be rejected by the body and come out on its own. This method is quite dangerous , since even a short stay of a foreign body in the body can lead to unpleasant consequences.
The second way is to treat fragments of the parasite as you would treat a splinter. To do this you need to prepare the following tools:
- sharp needle;
- tweezers;
- candle or lighter;
- any antiseptic solution (alcohol, chlorhexidine, etc.).
It is good to heat the needle over a fire, treat the tweezers and the area where the head or proboscis remains with an antiseptic. After this, carefully lift the upper layer of the epidermis with a needle and remove foreign bodies with tweezers. Picking a wound with a needle, cutting it, or trying to squeeze out insect particles like pus from a pimple is highly discouraged - this can lead to the spread of infection and other troubles. After the procedure, you must thoroughly wash your hands and disinfect all instruments again.
For the third method, you will need Vishnevsky ointment and clean gauze. It needs to be folded in several layers, apply a little product, apply to the wound and fix it overnight. In the morning, insect particles should come out along with pus. If you were unable to remove tick fragments from the body on your own, it is better to go to a medical facility , where doctors will carry out the procedure under sterile conditions.
IMPORTANT! If the head or proboscis of the tick remains in the child’s body, you should not carry out any actions on your own - immediately after removing the insect, the victim should be taken to the hospital as soon as possible.
How to remove a tick yourself
If you are in the forest and decide to immediately take it off, remember that you should not do this with bare fingers. Wrap your fingers in some cloth, or better yet, wear gloves. After this, very carefully and gently pull the tick towards you, while simultaneously (slightly) rocking it. If you are unable to remove the tick completely, you do not need to pick it out. This can be done at home, after the necessary processing. The bite area must be wiped with an alcohol solution or iodine.
If a tick is found at home, it is best to use tweezers. Drop some vegetable oil on it. After about 10 minutes, he will loosen his grip and it will be easier to pull him out. Grab with tweezers as deep as possible to the surface of the skin. Rock, but don't jerk. The bitten area should also be treated with iodine. You can use thread. Wrap the insect's head and gently pull it out, remembering to rock it a little. Of course, there are other ways to remove a tick, but these are the most effective.
If it is not possible to remove the tick yourself, consult a doctor immediately. It may seem that the medical method is no different from conventional removal. However, the doctor has more experience and uses a special removal tool. In addition, the tick can cling to a place where it is simply impossible to remove the insect at home. By contacting our clinic, you will receive high-quality care and all the necessary recommendations. The doctor will prescribe you appropriate medications for prevention and take the necessary measures.
Emergency prophylaxis with the use of an appropriate drug, such as immunoglobulin, may be required. The drug has the necessary antibodies that resist tick-borne encephalitis. Immunoglobulin is capable of forming immunity to the disease, and it will be effective for one month.
Only experienced doctors know how to remove a tick correctly, and if necessary, they will prescribe appropriate treatment for you. You should not neglect going to the clinic, because your health will depend on it.
What to do after you get it
After removing the remains of the parasite, you should once again carefully examine the affected area and make sure that it is absolutely clean - you can carefully expand the edges of the wound, but do not pick or press. Next, what to do: you need to wash the bite area with boiled water and soap and treat with any antiseptic - iodine, brilliant green, fucorcin , etc.
After all the manipulations, the wound will need to be monitored for 2-3 days, and if swelling, redness or pus appears, immediately consult a doctor. But even if the healing process is going normally, it is still worth consulting with a specialist - dangerous microorganisms , so the victim will have to undergo tests and, if necessary, undergo a preventive course of treatment.
REFERENCE! Despite the fact that when removing a tick there is a possibility that it will rupture, you cannot leave the insect in the body for a long time, otherwise the risk of infection will increase significantly - if it is not possible to immediately take the person to the hospital, you will have to act independently.
How to pull out a head if it comes off
Severing the head is one of the dangers of incorrect tick removal. This usually happens when the tick:
- removed using improvised means not intended for extracting the parasite;
- strongly pull, tug, tear out;
- accidentally damaged while scratching the bite site.
If the body of the parasite has fallen off, but the head remains, you should not leave it under the skin. You can entrust the removal of the tick head to a specialist or remove it yourself; there are several ways to do this:
- If the head and part of the body remain under the skin, you can remove it using tweezers. The remains of the parasite need to be grasped at the base with tweezers and begin to be carefully twisted. The direction of twisting can be any, but there is no need to change it. If you start turning to the left, turn left. Start to the right - turn right until you remove the head of the parasite.
- If only the head remains under the skin and it is impossible to pick it up with tweezers, you can remove it like a splinter - with a sharp needle. Disinfect the needle with alcohol or heat it over an open fire, and then pull out the head of the arthropod (like a splinter). After the procedure, treat the skin with brilliant green or iodine.
It happens that not a single method helps and the arthropod’s head does not want to come out. Do not aggravate the situation, do not expect the head to come out on its own - this can lead to suppuration. Contact your doctor to remove the remains of the parasite.
Is it possible to send torn pieces for research?
Not all ticks are carriers of diseases - many insects are sterile, but this can only be determined in laboratory conditions.
True, only whole insects - parasite particles are not suitable for research, so they can be thrown away or flushed down the toilet.
If the tick is whole, it must be placed in a small plastic or glass container along with a piece of damp cotton wool and taken to a medical facility.
It is better to do this right away - ticks are extremely tenacious, and can exist calmly in any conditions for several days, but the sooner the analysis is carried out , the lower the risk of serious health consequences.
Is it possible to send a tick for examination in parts?
It is impossible to determine by the appearance of a tick whether it is infected or not. Despite the fact that not every individual carries pathogens of infectious diseases, it is better not to risk it and send the extracted parasite to the laboratory. The best option is if the tick was pulled out alive. Then the study will show the most accurate picture. If the bloodsucker died during the extraction or delivery process, it can also be tested, but this must be done as quickly as possible.
But it happens that the head of the parasite comes off when it is taken out. Worried about their health, some are trying to donate the body and severed head of the bloodsucker for research. But laboratories do not accept such material. Since if the tick was left without a head during the process of removal from the skin, then there is no point in doing tests, they will not give the correct result.