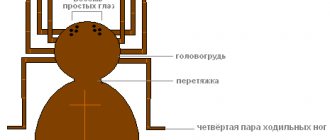
How many legs does a spider have?
Spiders belong to the arachnid family. Moreover, almost all representatives of this species are predators, which explains the special structure of the body. The total number of limbs is 12, but not all are used as paws.
The body can be divided into 2 large parts, namely the abdomen and cephalothorax, which includes the eyes, mouth, and limbs (12 pieces). The first 2 are located above the mouth and hide fangs with venom ducts. The poison may differ in all representatives of the species, and in some individuals it is dangerous even to humans. The first 4 limbs are called chelicerae, behind which are located the pedipals and claws, which act as small arms.
Next you can see 8 walking legs - they support the entire body.
Due to their special structure, some arachnids are able to accelerate quickly or even jump.
Poison - how dangerous is it?
There are few deadly poisonous spiders. Karakurt venom is 15 times stronger than rattlesnake venom, but most spider bites are no more dangerous than a wasp sting. Deaths are most often attributed to allergies. The last death from spider venom in Australia, famous for its abundance, occurred in 1981.
The venom of the Brazilian recluse spider causes more trouble for men, as it causes a persistent and long-lasting erection, which sometimes requires amputation. Based on this poison, doctors hope to obtain a cure for impotence. It's a matter of dose.
Brown recluse spider
A bite from an American recluse spider can result in the loss of a leg, because its venom quickly destroys the blood and leads to gangrene.
Small spiders have made Chileans clean. These poisonous creatures love to settle in dirty corners, which is why the residents of Chile have to clean up often. However, in the fight against this scourge they are helped by other spiders, larger and not dangerous to people. Their food is precisely poisonous little things, so they are specially bred at home.
There is one difficulty: these house spiders are very sensitive to mood. If he decides that you have decided to attack him, he will chase you or jump from the ceiling. And although these giants are not at all poisonous, the impressions will last a lifetime, because they are larger than a human palm.
Tarantula spider
Large spiders are not necessarily more dangerous than small ones. Tarantulas can bite painfully, but their venom is not dangerous. The same applies to tarantulas. But both of them still need to be brought to the point that he rushes at a person. And you can even pet them. In captivity they live up to 30 years, and in the wild they usually live no more than a year, dying from various causes, although there have been cases when tarantulas and tarantulas in the wild lived up to 20 years.
I hope you managed to fall in love with these cute creatures. Well, if you don’t fall in love, then at least stop being afraid, because only a few of them are dangerous.
Why does a spider have 8 legs?
It would seem that nature has completely thought out the purpose of all the limbs. However, you can see individuals with fewer legs.
Purpose of the paws
To move in space, 4 pairs of walking legs are used, or a smaller number if they were previously lost. However, the amount generally does not affect the speed and type of movement. These parameters depend on the type of arachnid. Thus, some arachnids are capable of developing quite high speeds, jumping or moving sideways.
The front legs are additionally used:
- for the purpose of securely holding the victim;
- for creating cocoons, webs;
- to fight other predators;
- for digging out holes.
A very important addition to the paws are the finest and ultra-sensitive hairs, which are necessary for understanding the surrounding world, orientation in space and studying smells. Before starting to move forward, the spider checks the space in front of its body and only then continues to move.
Spider legs - effective hunting
Weaving webs is a distinctive feature of arachnids.
In total, science knows 2 main types of webs, differing in shape:
- warm cocoon;
- catching net.
There is also a typology according to the ability to hold the victim, that is, according to strength and principle of action:
- especially strong allows you to catch a large bird or even a human weight;
- rounded webs are a vertically located network, where all the threads are covered with a special adhesive substance;
- hammock-shaped has a horizontal base position, to which vertical threads lead. Once caught in the vertical threads, the prey falls into the hammock towards the predator.
The presence of at least 3 pairs of full legs is the key to balance when moving, fast and successful hunting. In them, the spider moves freely along the web and wages a desperate struggle with the victim. Some species do not weave webs, but hunt on the move, but the number of minimally required limbs, even under this condition, remains unchanged.
Limb functions
Regardless of the species, the spider's legs perform identical functions. The most important of them is walking, which allows the animal to move. The length and structure may differ slightly, so the speed and method of movement changes. Spiders crawl slowly, run quickly, walk sideways, and long jump long distances.
8 pairs of legs are covered with villi, which serve as organs of smell and touch. It is the limbs that help the animal navigate in space, hear smells and sounds. Being in an unknown area, the spider carefully shifts its legs in front of itself, and only then begins active movement.
The functions of the spider's forelimbs are very diverse. With them, the predator captures and holds prey, digs the ground to build burrows, forms a cocoon, places the cubs on its back, and then drops them over a long distance.
The structure of the web legs
The paws can be divided into 7 separate parts. All of them guarantee fast and agile movement. The legs themselves additionally have hairs responsible for sensitivity and study of the surrounding environment, determining whether the catch is edible or inedible. All parts of the foot guarantee perfect balance when moving along the web.
So, the standard structure of the tarsus includes the following segments:
- basin;
- trochanter;
- hip;
- cup;
- shin;
- forefoot;
- a foot, at the end of which there are additionally curved sharp claws for the ability to move along vertical surfaces or the ceiling. Some species use them to comb and straighten woven webs.
Foot sizes
The first, that is, the front pair of legs, differs from the remaining 3 pairs in most representatives of the arachnid family. This feature is due to the fact that it is the front legs that perform important functions for life support: movement and capture of the victim, which means this particular pair should be stronger than others.
Also among the differences for the two front legs, one can note the club-shaped shape in certain subspecies. The tarsi extend straight from the heel and form a clear angle in relation to the entire leg. This feature allows the first pair of limbs to be used as a tactile organ. The other 3 pairs are used for movement and are generally similar to each other.
Spider leg length
The size of the legs, namely such a parameter as length, directly depends on the type of habitat and lifestyle of the arachnid. The longest are the first and fourth pair of legs. Next in length is the second, but the third is the shortest.
The minimum length of the paw of an adult is about 0.5 mm, and the longest is 35 cm.
It should be noted that despite the almost identical length of the first and last pairs, in some subspecies the front ones will still be slightly larger. This feature is explained, as mentioned earlier, by the need to reliably capture and hold prey.
The main functions of individual parts of a spider's legs
Absolutely every spider has special sensitive hairs on its legs. They are responsible for the ability to perceive sound waves from the surrounding nature and help to recognize odors and the presence of obstacles on the way.
Sensing a potential victim with just one hypersensitive hair, the spider quickly moves towards it and plunges its fangs with a poisonous substance that slowly paralyzes and destroys the food it has obtained. The pedipalps are additionally involved in this process.
Another important element in the legs will be glandular tubules, which simultaneously produce an adhesive substance for weaving webs and cover the legs with a special composition that prevents the spider from sticking to its own web
For spiders that live in water, their legs are necessary to transport air bubbles under the water column, where they choose a secluded place to live.
Another important function is self-defense. Some species, when a dangerous object approaches, begin to comb off poisonous hairs from the abdominal region. When such a hair gets into the eye, it causes a severe burning sensation and in most cases the attacker retreats. Even after shedding, the hairs are restored, but this only happens when the subsequent molt begins.
As male spiders mature, bulbs or cymbiums appear at the ends of their legs, which are used to fertilize the female, who often eats her partner after the process is complete.
Execution cannot be pardoned
There are several signs that tell what the killing of a spider promises, and there are even some that contradict each other. But today we will move away from popular beliefs and look at several theories that, as it seems to us, are ways to explain why you should not kill spiders.
- According to legend, once upon a time a spider's web saved a man's life. He was persecuted and, forced to flee, hid in a cave, which was almost completely entangled in spider webs. The pursuers were never able to find the fugitive; they didn’t even bother to examine the cave - there were so many cobwebs in it.
- The second version, which tells why you should not kill spiders in the house, is based on their active use in folk medicine of past times. In ancient times, healers mainly used various decoctions and infusions to heal the sick, to which they added not only herbs, but also insects. Often the role of a healing “ingredient” was a spider, ideally poisonous. They treated with poison, so killing a spider without any serious purpose promised the rapid development of the disease.
- The third legend says that spiders attract happiness - it gets entangled in their web and remains in the house. And the owner of the fishing nets, who has settled in a residential building, is a symbol of good news and prosperity. For this reason, killing a spider means driving away happiness from the house - there will be no one to spin the web and all the good things from the house will soon “fly away” along with the last silk threads.
Small house spiders are not capable of causing harm to human health
And if there are several of them, then this is a reason to pay attention to the cleanliness of your own home. In this situation, it is not the spiders that should be destroyed, but the reason why they ended up in the apartment
Remember, spiders will always live where there is food for them.
Everyone treats spiders differently. But more often than not, these predatory and often aggressive creatures evoke in a person only fear or, perhaps, some kind of disgust; someone will look at them with curiosity and interest, and someone will want to move away from that place as quickly as possible. where the meeting with the spider took place.
But those who really study these creatures thoroughly, their lives are arachnophiles who love and admire these creatures
, studying them, conducting all the necessary research. They are also engaged in their breeding and careful study of their structure and life activity.
And yet these strange and, at times, incredibly scary creatures
, which have existed since ancient times, are of interest not only to scientists, but also often to ordinary people who look at them with curiosity. But most often a question arises that worries all people, regardless of age (children and adults), about how many legs a spider has. And there is a lot of controversy surrounding this.
Chelicerae and pedipalps
In the area of the cephalothorax, directly in front of the spider’s mouth, there are two chelicerae: these are special forelimbs that are not paws in essence, although they are very similar in appearance. Their structure suggests the presence of a rather large movable rod and a hook with venom tubules. When the spider plunges them into the victim, it is paralyzed by the toxins.
In some subspecies, whose body structure does not imply the presence of an upper jaw blade, the hook is additionally used to introduce a special juice that softens the internal organs of the caught insect for subsequent ease of digestion. Such “food” is absorbed by the spider by absorption.
Pedipalps are a kind of helper and handles for the spider. They help hold the victim during battle, and are also necessary for dragging the cocoon and other necessary items.
Arachnid limbs
In fact, many people, when asking the question of how many limbs a spider has, mean only its legs. But the limbs include not only the legs, but also other parts of the body. This representative of the fauna has a feature that people often do not notice. It's all about the forelimbs, called tentacles. Yes, they look like paws, but they have a different function, or rather two:
Leg tentacles are clearly visible in large species. These include: the tarantula theraphosa blond, the South Russian tarantula, nephila and others. In large arachnids, you can also notice chelicerae - strong protruding jaws located in front of the mouth. This part of the body is also a limb. Chelicerae allow them to defend themselves from opponents, pierce through the victim, and in some cases dig and tear holes in the ground.
Chelicerae are also needed to inject venom (for those who have it) into the victim, as if a scorpion were using its sting. The claws also have another name - pedipalps. Males use them to fertilize females.
Difference between spiders and insects
The arachnid family belongs to animals, the order of arthropods. Among the simple and well-known differences are:
- number of legs - 8. For comparison, insects such as wasps, lice, cockroaches have only 6 of them;
- spiders lack characteristic antennae, and the role of a “receiver” is played by sensitive hairs;
- a large number of eyes, which in some species reaches up to 24; the body consists of 2 parts - the cephalothorax and abdomen.
Among the subtle differences is the presence of intelligence. There are cases when a pet spider felt the mood of its owner, adjusted or protected him when danger arose. However, this feature is not found in all members of the family.
Interesting facts about spiders
Spiders are interesting, and their number and diversity is amazing and surprising. However, some facts distinguish individuals from their fellows:
- There is a special subspecies in the family - phrynes. Such spiders do not weave webs, but lead a nomadic lifestyle. Long legs are convenient for hunting;
- The spider's body does not have a skeleton. The role of the frame is performed by the hard shell. It is this fact that explains the rather compact size of the representatives of the family. If the weight or size increases, the “frame” simply won’t hold up and the spider will simply die under its own weight;
- The strength of the web is comparable to steel. At the same time, in terms of strength, it is recognized as 10 times more reliable;
- The standard web shape is round, and only the gladiator subspecies weaves a square web.
How a spider weaves a web
The thinnest thread of the web is a complex weave of several threads, which are glued together by the spider's saliva, which hardens in air. It is this property that ensures the strength of the thread, allowing spiders to travel many kilometers.
Based on consistency, there are 3 types:
- dry;
- sticky;
- elastic.
The choice of one type or another depends on the purpose:
- to create a cocoon;
- trapping and entangling the victim;
- for moving;
- fastening.
The principle of weaving itself is the fixation of the longest thread on a branch. Next, with the flow of air, fixation occurs on another branch and the creation of a parallel, but looser thread. Relying on such threads, the spider finds the middle and looks for a third point of support, after which the weaving consists of weaving a contour and several internal radii.
Arachnophobia - fear of spiders
The whole world is an inextricable connection of individual links. If you remove even one link, the balance will be disrupted. Despite its unpleasant appearance, the spider, like many other living creatures, is an important participant in the food chain.
Many people think about spiders with horror and shudder, not to mention panic when meeting them. However, residents of Russian latitudes should not worry: apart from their appearance, the representatives of the family do not carry anything unpleasant about themselves. Exotic species can still be dangerous to humans, but, as a rule, they do not dare to attack first and only represent a response.
Arachnids are an unusual and interesting species of animal living on Earth. While some people are not happy about meeting them, others enjoy watching their life through the walls of the terrarium, enjoying the exotic beauty.