- Wild animals
- >>
- Insects
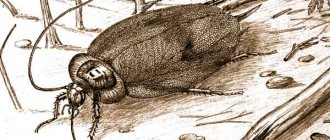
The red cockroach is the bosom enemy of housewives, a nocturnal desecrator of kitchens and bathrooms. This is the insect of childhood, our unauthorized lodger, travel companion, hotel roommate and office cellmate. They have been trying to eradicate it for centuries, but it resists just as stubbornly, changing tastes and susceptibility to poisons. This is a universal soldier of nature, guarding its fundamental law - survival at any cost.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Red cockroach
The red cockroach, also known as the Russian cockroach (Blattella germanica), belongs to the family Ectobiidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in his Systema Natura in 1767. The name of the genus comes from the Latin word “blatta,” which the Romans used to describe insects that are afraid of light.
Ectobiids, or tree cockroaches, are the largest cockroach family, containing about half of all cockroaches from the order Blattodea. But besides the Prussian, among them there will be no more than 5 similar pests occupying people’s houses. The most famous of them are black and American. The rest prefer a free life in nature.
Video: Red cockroach
In the structure of cockroaches, primitive features characteristic of ancient insects can be traced: chewing jaws, poorly developed flight muscles. The time of their appearance, judging by reliable prints, dates back to the beginning of the Carboniferous (about 320 million years ago). Phylogenetic analysis suggests that cockroaches originated earlier, at least in the Jurassic period.
Interesting fact: National antipathies are reflected in the popular names of the unpleasant insect. In Russia, this type of cockroach is called “Prusak”, since it was believed that it was brought from Prussia. And in Germany and the Czech Republic, which were once part of Prussia, they call him “Russian” for a similar reason. In fact, it is unknown where he appeared first. The routes of historical migrations of the red beast have not been studied.
Appearance and features
Photo: What a red cockroach looks like
Cockroaches are insects with an incomplete cycle of transformation and go through three stages as they develop: egg, larva (nymph) and adult (imago), and the larva differs little from the last stage. The larva hatches from the egg after 14 to 35 days and goes through 6 to 7 molts, each time increasing in size until it reaches the size of an adult cockroach. This process takes from 6 to 31 weeks. An adult male lives 100 - 150 days. The lifespan of a female is 190 - 200 days. The cockroach is dexterous, sneaky, elusive and disgusting, especially at the last stage.
Adult Prussians have a length of 12.7 - 15.88 cm and a weight of 0.1 to 0.12 g. The general color is light brown, two wide dark stripes run along the dorsal side of the prothorax. The chitinous lacquered cover is thin and the body is soft, which increases the aversion to this insect. The body shape is streamlined, oval, flattened and adapted to slip into any cracks.
The thoracic segments smoothly transform into a segmented abdomen, which is covered with paired soft wings. When frightened, the cockroach spreads its wings, but is only able to use them for gliding, for example, from a table to the floor. The spiky legs are long and strong - the legs of a real runner. The neat flattened head is decorated with flexible thin mustaches, which the Prussian warily moves around, trying to detect danger.
Males are slimmer and narrower than females; the narrowed end of the abdomen protrudes from under the wings and is equipped with two protruding setae - the cerci. In females, the end of the abdomen is rounded; they usually carry eggs in a special package - an ootheca. Larvae are nymphs that are smaller, but of the same shape. The color is darker, there is only one stripe and the wings are underdeveloped. The eggs are round and light brown.
What does a red-haired “enemy” look like?
If you have never encountered a pest, then it is important to know what Prussian cockroaches look like so as not to confuse them with other pests. Stasik's body is mainly hidden behind his wings, which are quite developed, but don't worry - he won't be able to take off even if he wants to. But it is quite possible to ease his fall, because during the flight he tries to flap his wings. The insect is no more than 15 mm in length, but the color range is presented in different shades of brown.
The female and the male look different: the male's body is narrow, but the ladies have a round and wide body structure. An integral part is the antennae, with their help they learn about the world around them, communicate with “close ones”, so insects constantly keep their antennae clean.
Interesting!
If the parasite has injured its antennae or lost at least one, it will no longer be able to fully exist. He will not be able to explore the territory, look for food, or contact other individuals from the colony.
Where does the red cockroach live?
Photo: Domestic red cockroach
South Asia is the recognized homeland of the Prussians. Their mass distribution begins in the 18th century - the era of world travel, scientific expeditions and colonial trade. Now red cockroaches have spread all over the world and inhabited all suitable habitats, not embarrassed by the presence of local relatives. They even managed to dislodge some, for example, the European black cockroach, from their established ecological niche.
By nature, the cockroach is an inhabitant of the tropics, a lover of warm climates and freezes when the temperature drops below −5 C°. Under natural conditions, it does not live outside a zone with a frost-free climate, in mountains above 2000 m, as well as in very dry regions, such as deserts. Only cold and drought prevent him from conquering the whole world, although, using the comfort of human dwellings, he is able to advance even to the Arctic.
Thanks to their universal tastes and undemanding food habits, Prussians inhabit any heated premises in cities and rural areas, both private and public. Especially if there is an abundance of food and moisture, like in kitchens and bathrooms. Prussians become a real disaster in hospitals and catering establishments. Urban housing with central heating and running water is ideal for them. Within the house they move through the ventilation system and garbage chutes, and to move to new places they often use suitcases or furniture.
Interesting fact: One of the effective ways to get rid of our intrusive little brothers is to freeze the premises. Therefore, cockroaches never settle in summer cottages.
Now you know that you can find a domestic red cockroach in your apartment. Let's take a look at what these insects eat.
What does the red cockroach eat?
Photo: Big red cockroach
Red pests eat any non-living matter containing organic matter. They even engage in cannibalism, eating their dead brothers. Garbage dumps and other places where human waste accumulates, farms, greenhouses, canteens, hospitals, nature museums and herbariums, library book depositories, archives and warehouses serve them as a table and a home.
They are especially attracted to:
- meat waste and carrion;
- products containing starch;
- anything that contains sugar;
- fatty food;
- paper, especially old books;
- natural fabrics, especially dirty ones;
- leather;
- soap and toothpaste;
- natural glue, such as bone glue, which was previously used in making books.
Cockroaches, like their closest relatives termites, owe their ability to digest cellulose to microorganisms that inhabit their intestines and, by digesting fiber, make it suitable for the host’s body.
Interesting fact: While developing a universal poison for the Prussians, scientists discovered that they had bred a race that does not eat sugar or anything that contains glucose. Experimental insects reacted to glucose as something unpleasant and bitter. This race is an evolutionary response to the poisoned sugar baits that have plagued all sweet tooth lovers. Only those cockroaches that neglected such a treat survived and multiplied.
How to fight
How can you effectively deal with a cockroach problem?
Your best bet is a comprehensive approach:
- Improve sanitation to reduce the amount of food available to parasites.
- Reduce clutter so redheads have fewer places to hide and breed.
- Create barriers to limit the Prussians' access to your home. For example, use caulk to seal cracks around electrical outlets and eliminate water leaks that give cockroaches access to the moisture they need.
- Use pesticide powders (such as boric acid or diatomaceous earth). Apply it generously but selectively in hard-to-reach places, such as behind cabinets or under the sink.
- Place insecticidal baits in areas where you see cockroaches but where children and pets cannot reach them. For example, behind the refrigerator.
Chemicals
Insecticides are most effective in controlling cockroaches when combined with sanitation and exclusion methods that limit the cockroaches' ability to reproduce or re-enter. But chemical control alone will not solve the problem. If insecticides are used, they should always be used with extreme caution. Internal chemical control is only justified if a massive cockroach population has been established, not for the occasional intruder or two.
Traditional methods
A cheap natural bait for red cockroaches is boric acid mixed with flour and sugar in equal parts. The pests carry the bait back to the colony, poisoning the lair. Dissolve the mixture in water and spray along the floorboards in the rooms.
You can repel cockroaches with essential oils, but it is not fatal to them.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Red cockroach, aka Prusak
Prussians belong to the so-called “synanthropic organisms”, which in life are closely connected with human society and live almost exclusively in the anthropogenic environment, in human dwellings. Their resettlement to new territories also occurs with the help of humans - cockroaches travel with our things and food in the holds of ships, on trains, vehicles and airplanes.
Having settled in the house, the adults and their growing nymphs go out at night to plunder. Although in the dark they are attracted to light surfaces, turning on the light causes the Prussians to instantly flee. This species itself does not make sounds, but the characteristic rustling of wings and legs that a fleeing flock makes is familiar to anyone who has had the misfortune of living in the same apartment with them.
Cockroaches act very harmoniously, since certain relationships are established between members of the cockroach community that has occupied one room. They use odorous substances called pheromones to signal the presence of shelter, food or danger, to transmit sexual signals. These pheromones are released in feces, and running insects leave here and there information trails along which their fellows gather for food, water, or find a partner for mating.
Interesting fact: Scientists conducted an experiment to find out where the pheromones that bring cockroaches together are produced and contained. A group of Prussians were poisoned by intestinal microorganisms and it turned out that their droppings no longer attracted other individuals. After feeding bacteria isolated from the feces of untreated cockroaches, their excretions became attractive again. It turned out that these bacteria are responsible for the synthesis of 12 fatty acids, which, evaporating in the air, serve as a signal for general collection.
Life of “stasiks”: features of existence
Like other individuals of the cockroach species, red parasites come out “to people” at night in order to confidently remain unnoticed. Sometimes residents of infested apartments try to scare insects by turning on the light in the kitchen, but this is not an effective method. The main thing for the full existence of an insect is not food, but warmth and water.
How long does the Prussian cockroach live? If there is food, he will live quietly for up to 70 days, but if there is only heat and water, then life is reduced to 40 days. When the temperature goes beyond -5°C to +25°C, the pest dies. But his offspring will certainly continue his path through your mansions. You should not be sure that if all the food is hidden, then parasites will not overtake your home. For these individuals, an accidental spill of cereal in a cupboard crevice is enough.
Important!
It is completely impossible to avoid the appearance of tenants in the house, but if you follow simple recommendations, the likelihood of their appearance decreases. Since they are attracted to food and water, try not to leave drinking cups and half-eaten dishes on the tables at night, and close the water taps well.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Little red cockroaches
Prussians are sociable and, when living together, create a real democratic society of equals, who are united not only by common housing and growing nymphs, but also by common interests. The main one is food, and cockroaches master the food they find together, ingeniously informing their fellows about its location and even quantity using pheromones. The more cockroach tracks leading to a food source, the more attractive it is to others. They are also free to choose a sexual partner.
Cockroaches reproduce very actively. During her life, the female lays from 4 to 9 packages (ootheca) up to 8 mm long, each of which contains 30 to 48 eggs. The formation of the capsule and the maturation of the eggs in it takes an average of 28 days, and almost all this time the female wears it at the end of her abdomen. Although, in the end, it may dump the load in a dark, secluded corner.
After a few weeks, she develops new swelling. In total, each female produces up to 500 heirs. Reproduction in a flock occurs continuously and all generations and stages of development can be present in it at the same time. In a good place, the cockroach population grows like a snowball or, in mathematical terms, exponentially. Only cooling indoors or sanitary treatment can slow down growth.
Interesting fact: Nadezhda the cockroach became the first animal to conceive in space. This happened on September 14 - 26, 2007 on the unmanned biosatellite Foton-M 3. The cockroaches traveled in a container, and the fact of conception was recorded on video. Returning from the flight, Nadezhda gave birth to 33 cubs. The only unusual thing about them was that they grew faster than their earthly peers and acquired a dark color earlier. Nadezhda’s grandchildren did not show any peculiarities.
Natural enemies of the red cockroach
Photo: What a red cockroach looks like
The cockroach is not poisonous and, in principle, can be eaten by any animal that does not disdain insects. But human housing provides him with reliable shelter from birds and other free-living predators. Here he can only be threatened by other synanthropic couch potatoes and slaves.
Namely:
- spiders;
- centipedes;
- indoor birds;
- cats and dogs can catch them for fun.
The main enemy of the red-haired Prussian becomes anyone under whose roof this evil creature falls. Any “green” person will agree that the insect causes considerable harm. All he needs to do is see his kitchen table after their visit.
Why is the Prusak harmful?
- carries more than 40 pathogens of microbial and viral infections (including dysentery), which is especially important in hospitals;
- intermediate host of three species of helminths and protozoa;
- causes and provokes allergies, worsens asthma;
- creates a stink in the room due to pheromones;
- spoils food products;
- messes things up;
- affects the psyche and can even bite.
Pest control measures have been improved over the centuries. Isolating food waste and water, setting traps from which they cannot escape, freezing the premises, and finally, chemical warfare - all methods have been tried. Mechanical methods turn out to be ineffective, and chemical methods only lead to further improvement of the pest. Modern Prussians are not sensitive to pyrethroids, the classic insecticides, and are weakly susceptible to other older classes of pesticides. Modern drugs (hydroprene, methoprene) act as growth regulators and are more effective. They delay molting and prevent the development of the insect.
Interesting fact: Previously, tits and blue tits were kept in homes, especially rural ones, specifically to fight cockroaches. The birds spent the winter in a warm place, cleared the house of pests, and in the spring, according to tradition at Easter, they were released.
Do they cause harm to humans?
IMPORTANT! Red cockroaches are dangerous to humans : constantly in contact with garbage, household waste, dirt, they are carriers of pathogenic bacteria, as well as worm eggs.
Intestinal disorders, tuberculosis, helminthiasis are just a few of the diseases that Prussians can bring on their paws.
Do red cockroaches bite?
Scientists knew of several cases when these pests ate away the keratinized parts of the dermis on the face and hands of people, but did not cause any tangible harm to them. So we can safely say that Prussians do not bite .