What is scabies?
Scabies or scabies is a parasitic skin disease caused by the scabies mite.
Scabies is a widespread dermatological pathology both in Russia and throughout the world. According to official statistics, in the Russian Federation the primary incidence is almost 46 cases per 100 thousand population per year. It is believed that the real figures are significantly higher¹.
Data from the World Health Organization indicate that about 200 million people worldwide suffer from scabies at any given time. Prevalence in different regions ranges from 0.2 to 71% of the population in tropical latitudes. Most often, scabies occurs in children. The average infection rate among them is 5–10%².
Routes of infection
Scabies is caused by the scabies mite - Sarcoptes scabiei homonis (Fig. 1). By their nature, these mites are permanent parasites, spending most of their life (1-1.5 months) in the skin of the host. They are on the surface of the skin only for a short period of settlement. Outside the skin, parasites can live no more than 3 days.
Figure 1. Scabies mite. Source: Annals of dermatology / Open-i (Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International)
The main activity of the scabies mite is observed at night. In this regard, the likelihood of contracting scabies is higher late in the evening and at night, and people with an active nocturnal social life are at greatest risk. It takes about 30 minutes for the parasite to penetrate human skin.
The scabies mite can dig holes
The key symptom of scabies - scabies burrows - is the result of the activity of the female scabies mite.
After mating on the surface of the skin, the parasite gnaws through the outer layer of skin, the epidermis. Then the tick moves under it, leaving behind a characteristic passage, at the end of which it lays eggs (Fig. 2). As a rule, it takes the scabies mite from 15 minutes to several hours to create one such burrow. After 1-2 weeks, new individuals hatch from the eggs and complete the cycle. Figure 2. The scabies mite makes passages in the skin. Source: Tharakorn / Depositphotos
Infection with the causative agent of scabies occurs by contact, direct or indirect. Direct infection is caused by physical contact with a patient, usually through a prolonged handshake, intimate intimacy, etc.
Indirect infection is possible through contact with pre-contaminated common household items (towels, bed linen or personal hygiene products) and with contaminated surfaces in public places.
Where can you get scabies?
Since the scabies mite can remain active outside the host for several days, there is a risk of infection in various public places. The most dangerous in this regard are surfaces with which close bodily contact occurs among a large number of people. Infection often occurs in:
- Saunas, baths.
- Swimming pools.
- Trains and long-distance public transport.
- Public showers and toilets at train stations, in children's camps and sanatoriums.
Less obvious, but no less dangerous, are rental items that involve prolonged bodily contact, such as sleeping bags and other hiking equipment.
Can you get scabies from pets?
Scabies also occurs among animals, but they have a different pathogen.
Pets may have scabies mites that do not survive or reproduce on humans. If an animal with mange is in close contact with a person, the mite may become attached to the animal's skin and cause temporary itching and irritation. However, this animal mite cannot reproduce in human skin and dies after a couple of days³. Although animal scabies mites coming into contact with human skin do not require treatment, your pet should undergo appropriate treatment. Otherwise, such mites can continue to penetrate human skin, causing symptoms of the disease³.
Classification of pathology
The symptoms of scabies identified during examination of patients allow dermatologists to distinguish four types of the disease.
| Scabies form | Description |
| Neat | It is considered by doctors as an erased form of pathology. Develops in people with high immunoreactivity. There is no allergic reaction to the waste products of mites on the skin. In a similar way, scabies develops in people who pay increased attention to personal hygiene (systematic hand washing, showering twice a day). Skin rashes are localized on the abdomen and chest. Moderate itching occurs at night |
| Typical | Rashes appear on the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, chest, and lateral surfaces of the fingers and toes. Men may experience damage to the skin of the penis and scrotum. The scabies burrows are clearly expressed, looking like a whitish or grayish line 5-7 mm long with a papule or vesicle. The size of the formations does not exceed 0.5 mm in diameter |
| Nodal | Rashes on the skin are formed as an allergic reaction of the patient’s body to the waste products of scabies. This form of pathology develops against the background of improper treatment of scabies or violation of the dermatologist’s recommendations. Large, itchy, reddish-brown nodules form on the skin. Antiscabiosis therapy is ineffective due to blockage of passages in the skin by a dense crust at the sites of vesicle formation |
| Cortical | Detected in people with weakened immune systems, it is extremely rare. Crusted scabies remains the most contagious form of the pathology due to the abnormally high concentration of pathogens. Develops against the background of immunodeficiency states of the body or a long course of treatment with the use of corticosteroids and cytostatics |
Who is at risk?
Those at risk are those who are in prolonged contact with a large number of people. First of all, these are those who live in barracks, dormitories, spend a long time in a hospital or in prison. This also applies to children growing up in orphanages and residents of nursing homes³.
There is a high probability of contracting scabies among homeless people, socially disadvantaged families who do not pay enough attention to personal hygiene, as well as among workers in the intimate services sector.
Classification
Based on the clinical characteristics of scabies and its course, it is customary to distinguish the following forms of the disease¹:
- Classic or typical. Accompanied by clinical symptoms characteristic of scabies: itching, rash and the formation of burrows in the skin.
- Scabies without moves. It develops when scabies mite larvae remain on the surface of the skin until adult individuals hatch. Manifests itself in the form of papules and vesicles. Lasts no more than 2 weeks.
- Nodular scabies or scabious lymphoplasia. It occurs as an allergic reaction with itching in the area of the elbows, buttocks, abdomen, mammary glands and male genital organs and with the formation of nodules and papules.
- Scabious erythroderma. Occurs in people who have had scabies for several months and use corticosteroid ointments and antipruritic drugs. Against the background of red skin, multiple small scabies up to 2-3 mm long are revealed. In areas exposed to mechanical stress (for example, elbows and buttocks), thickening of the outer layer of skin (hyperkeratosis) is observed.
- Scabies of “clean” or “incognito” people. It occurs in people who carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene, and against the background of a normally functioning immune system. It is characterized by isolated skin rashes and mild itching that occurs at night.
- Norwegian or crustose scabies. It is characterized by large scabies in the skin, a significant number of mites, severe inflammation and the appearance of a large number of papules, massive gray-yellow or brown-black crusts on the skin. It is observed in people with HIV, cancer and other immune disorders, and rarely in children.
- Pseudoscabies. This is a scabies infection that affects animals. This causes blisters, hemorrhagic crusts and scratching. It develops immediately after contact with a sick animal and goes away within a few days without treatment.
Symptoms of scabies
The first signs of scabies appear in a healthy person 7-10 days after contact with a carrier of the pathology. Upon careful examination of the skin on days 2-3, you can notice scabies. Symptoms increase when females lay eggs in the thickness of the epidermis. Patients experience unbearable itching, which intensifies in the evening and at night. When Sarcoptes scabiei bites, they release chemically active substances that cause an allergic reaction and local inflammation of the skin. Itching leads to scratching, covered with bloody scabs.
Are you experiencing symptoms of scabies?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Complications
Scabies is characterized by the addition of a bacterial infection with the development of secondary pyoderma or dermatitis. Most often they are observed with concomitant immunity disorders, incorrect or delayed treatment.
The main complications of scabies are¹:
- Staphylococcal impetigo.
- Ostiofolliculitis and deep folliculitis.
- Boils and ecthyma vulgaris.
- Allergic reactions such as urticaria and microbial eczema.
When secondary bacterial infections of the skin develop, symptoms uncharacteristic of scabies occur, including:
- Lymphadenopathy is an enlargement of nearby lymph nodes.
- Increased body temperature.
- Soreness and swelling in the affected area.
- Violation of the general condition in the form of weakness, malaise, drowsiness and loss of appetite.
Symptoms of scabies
Signs of the disease during primary infection with scabies mites appear after 1-2 weeks, with repeated infection - during the first day. The first symptoms are itching and skin rashes in the form of papules (lumps) or vesicles (vesicles), often accompanied by scratching. They are caused by an allergic reaction of the body to the waste products of the tick. Scabies is characterized by worsening itching at night.
At the height of the disease, scabies burrows are formed - straight or curved lines of a whitish-grayish or dirty gray color, rising above the skin level, the length of which is 5-7 mm, and at their end new elements of the rash appear (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. Scabies rash and passages under the skin. Source: Steschke / Wikipedia (Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license), PLoS neglected tropical diseases / Open-i (Attribution 4.0 International)
The following areas of the skin are most often affected (Fig. 4):
- Wrists and hands, mainly the area of the wrist joint.
- Feet.
- Lateral surfaces of the fingers.
- Torso, mammary glands. There is usually no rash in the interscapular area.
- Genital area.
Figure 4. Localization of scabies rash. Source: cdc.gov
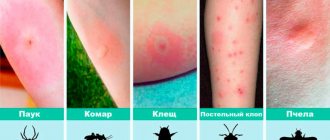
How to distinguish scabies from bed bug and flea bites?
In addition to scabies, severe itching and skin rashes can also occur with bites of other parasites that appear due to violations of personal hygiene rules.
The most common of these are fleas and bed bugs. Bed bug bites and the skin rashes that may accompany them (papules, blisters, purple spots) are most often located on exposed areas of the body (neck, wrists, ankles). And at a short distance from each other, in the form of a small chain. Also, if there are bed bugs in the house, you can often find stains of blood and individuals on the linen that were crushed by a person in a dream.
Fleas also bite most often in exposed areas, but predominantly in the lower part of the body. The bites themselves look like red dots surrounded by an area of swelling. Despite the general grouping, there is often at least 2 cm between bites.
Scabies is often accompanied by specific symptoms¹:
- Ardi's symptom: the formation of pustules and purulent crusts on the elbows and surrounding areas.
- Gorchakov's symptom: the appearance of bloody crusts in the area of the elbows in the adjacent tissues.
- Michaelis symptom: the formation of bloody crusts and skin rashes like impetigo in the intergluteal fold with transition to the sacrum.
- Sezari's symptom: a sensation of a slight strip-like elevation above the skin, where there is an itch.
Features of scabies in the elderly and children
In older people, scabies is somewhat different.
There are relatively few scabies, and papules and vesicles are rare. In this case, scratching and bloody crusts are often observed. Complications develop more often, of which allergic dermatitis and microbial eczema predominate. In children with scabies, the pathological process involves large areas of the body, including the face and scalp. In infants, the nail plates may be affected. Scabies are often accompanied by redness and swelling of the tissue surrounding them.
Types of scabies
Typical scabies and its symptoms
- Itching
- Rashes are scattered or multiple, small reddish nodules merging into one line. After a while, they turn into bubbles that burst to form a crust. Crusts with purulent contents mean that when scratching a person acquired a bacterial infection.
- Winding scabies passages, which consist of segments 5-8 mm long (this is the distance that the female mite “travels” per day). They peel off over time and look like gray scratches ending in a transparent bubble in which you can see a dark dot - this is the body of the tick. Typical location of this form of scabies:
- fingers, more precisely, the lateral surfaces of the fingers and the distance between them,
- bends of the hands and elbows,
- mammary glands (especially nipple halos),
- lower abdomen, male genital organs, etc.
Complicated scabies (with pustules) and its symptoms
Specific additional symptoms: dermatitis or purulent skin lesions.
Scabies of clean people and its symptoms
With increased attention to hygiene and a healthy immune system, rashes are very rare, and itching intensifies only in the evening and at night.
Nodular scabies and its symptoms
A few round skin lumps with a diameter of 2-20 mm, which are very itchy. They are colored red or brown, and scabies are visible on their surface. As a rule, they affect the penis, scrotum and inguinal-scrotal folds, circumference of the anus, nipple halos, inner thighs and buttocks.
Norwegian scabies and its symptoms
A very rare form, it appears only in those patients who, for various reasons, do not itch (do not feel itching or there is no allergic reaction due to weakened immunity). The skin thickens and becomes rough, rashes affect almost the entire surface of the patient’s body, even the skin of the face, hair and nail plates. The most unpleasant and characteristic symptom of Norwegian scabies is the formation of thick (up to 3 cm thick) crusts of a dirty yellow color over the entire surface of the body, under which extensive weeping erosions are exposed.
When to see a doctor?
The first signs of scabies development are the reason to consult a dermatologist for medical help. This is due to the high probability of infection spreading and the patient’s danger to others.
Also, all people who have been in contact with a person with scabies are sent for consultation to a specialist - they could potentially be infected. These are sexual partners, family members. However, all people should be treated at the same time to prevent re-infection.
Diagnostics
The primary diagnosis of scabies is established based on the patient’s complaints, medical history (presence of risk factors, contact with a sick person) and the results of an external examination of the affected areas of the skin. It is confirmed using laboratory and instrumental research methods that make it possible to identify scabies mites in the body.
The following methods have the greatest diagnostic value for this disease:
- Staining scabies. Using aniline dyes and an alcohol solution of iodine, which are applied to the elements of the skin rash, characteristic scabies tracts are identified.
- Oil vitropresia. One of the methods for quickly identifying scabies, which involves pressing on an area of skin with a glass slide. Mineral oil can be applied to the skin first.
- Removing the tick. Using a sterile disposable needle, the blind end of the scabies tract is opened. The mite is removed and placed on a glass slide in a drop of water or 40% lactic acid solution, covered with a coverslip and examined under a microscope.
- Diagnostic skin scraping. Allows you to study the contents of the scabies tract, papules and vesicles. A drop of 40% lactic acid solution is applied to the scabies tract, papule, vesicle or crust. After 5 minutes, the softened skin is scraped with a scalpel until a drop of blood appears, and the resulting material is examined under a microscope.
- Dermatoscopy. Visual examination of the skin using a dermatoscope with magnification up to 20 times, which makes it possible to accurately identify scabies, scabies mite eggs or other skin changes characteristic of the disease.
Differential diagnosis of scabies is carried out with other diseases that can cause severe itching, papular or vesicular skin rashes. These include¹:
- Contact allergic dermatitis.
- Hives.
- Toxicoderma.
- Rat mite dermatitis.
- Pediculosis.
- Phlebotoderma.
- Dyshidrotic eczema.
- Atopic dermatitis.
- In children - prurigo, chicken pox, etc.
Treatment
Treatment of scabies in the vast majority of cases is carried out at home. Hospitalization may be necessary only if it is impossible to isolate the patient from others, as well as the formation of serious complications or dangerous concomitant pathologies. Another indication for inpatient treatment is the presence of a mental, neurological or other disease in which the patient cannot independently fulfill all the doctor’s prescriptions.
The purpose of the anti-scabiosis therapy is to destroy the scabies mite, relieve existing symptoms of the disease, and prevent complications and infection of others. The treatment regimen includes the following groups of drugs:
- Anti-scabies: sulfur ointment, benzyl benzoate, permethrin. They can be prescribed in the form of emulsions or ointments that are applied directly to the affected areas. Depending on the specific product, the frequency and frequency of use can vary from 1 time a day for 1-2 days to 3 times a day for 3-5 days.
- Antiallergic drugs. Allows you to cope with skin itching and reduce the severity of skin rashes. Antihistamines (loratadine, desloratadine, cetirizine) are predominantly used, but in severe cases topical corticosteroids (betamethasone, hydrocortisone) can be used.
Features of the use of ointments or emulsions for scabies
In clinical practice, the following anti-scabies are most often used:
- Permethrin cream 5%. This is one of the most popular medicines for scabies, safe for children over 2 months of age, as well as pregnant women. Most often, 2-3 times of application are prescribed at intervals of about a week.
- Ointment or emulsion with benzyl benzoate 20% for adults and 10% for children from three to seven years old. Prescribed on the first and fourth days, washed off 12 hours after application.
- Sulfur ointment 33%. Apply daily 1 time at night for 5-7 days. Contraindicated for children under 3 years of age and pregnant women.
Features of use depend on the specific drug and its dosage form, but it is customary to highlight general rules for the use of local anti-scabies.
- Treatment of the skin with the drug should be carried out after hygiene procedures, before bedtime.
- When applying the product, it is recommended to thoroughly rub it into the affected area, especially the palms and soles. In this case, application should be done by hand, and not with napkins or cotton pads.
- Before starting treatment, it is important to change your bed linen and pajamas.
During the hot season, aerosol preparations are recommended for the treatment of scabies. This is due to the fact that aerosols do not require intensive rubbing into the skin and, unlike ointments, cannot lead to overheating of the skin area and the formation of complications in the form of dermatitis or pyoderma.
How to relieve itching?
With effective treatment, itching usually persists for 1-2 weeks. The following recommendations will help alleviate the condition at home4:
- Cool and dampen skin. Cool water or a cool, damp bandage applied to irritated areas of the skin may help relieve itching.
- Apply a soothing lotion to reduce pain and itching for minor skin irritations.
- Take antihistamines. They reduce the allergic reaction that causes itching, but it is better to consult a doctor before using them.
Cleaning the house from scabies mites
Despite the fact that in most cases, transmission of scabies mites occurs through close bodily contact with a sick person, it is necessary to exclude other routes of infection. Proper care of the patient's home is important. After diagnosis, it is necessary to collect all his personal belongings and disinfect them.
In addition to treating things, to cleanse the house of scabies mites, it is important to carry out preventive treatment of all its inhabitants who could potentially be infected and do not yet have symptoms of the pathology. The same rule applies to those people who regularly visit the home: nannies, social workers, close relatives, etc.
How to treat the underwear of a patient with scabies?
Scabies mites do not survive more than 2-3 days outside human skin.
Bed linen, clothing, and towels can be disinfected by machine washing in hot water (70-90°C) and drying using a hot cycle, ironing or dry cleaning. Items that cannot be washed or dry cleaned should be put aside and not used for at least 72 hours3. Washing all the patient's belongings is necessary to get rid of scabies mites. Photo: kuprevich / freepik.com
Traditional treatment for scabies
In addition to anti-scabies and traditional anti-scabiosis therapy, traditional medicine can also be used. However, before using them, it is necessary to consult with your doctor due to the high risk of secondary infections if the approach to treatment is incorrect.
Widely used folk remedies against scabies are:
- A mixture based on sulfur ointment. 2 tsp. ointments are mixed with 1 tbsp. l. crushed laundry soap, 1 tbsp. l. homemade lard and 1 tsp. tar. Treatment lasts 4-5 days.
- 9% or apple cider vinegar. It is used in its pure form by lubricating the affected area. The applied vinegar does not wash off.
- A mixture of vinegar and garlic. To prepare, take 4-5 large cloves of garlic, chop them and pour in 200 g of vinegar, then let it brew for 10 days. The resulting product must be applied to the rash area 2 times a day.
- Turpentine. 1 tsp. turpentine mixed with 2 tbsp. l. heated sunflower oil or butter. The affected areas of the skin are lubricated 2 times a day; the product does not need to be washed off.
Therapeutic measures
If pseudoscabies is not complicated by a bacterial infection, then the process can self-limit. For severe itching and rashes, treatment is used for scabies. The main antiparasitic drugs include:
water-soap emulsion;- Benzyl benzoate;
- Spregal (used for pregnant women);
- Medifox;
- Lindan.
Next, antihistamine and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. For this purpose, local ointments Akriderm, Videstim are used, as well as antihistamines, which are usually taken orally in the form of tablets:
- Suprastin.
- Loratadine.
- Zodak.
Timely drug therapy will help cure the disease in a short time.
Traditional medicine methods are widely used for illness. However, they should be used only for adults, since the child’s body can give an unexpected reaction, which will aggravate the child’s general condition. At home, soap baths for 5 minutes several times a day help well; birch tar can be applied topically in a thin layer, which should be washed off after 2 hours under running water. A good effect is observed after using a mixture of sulfur and fat.
Many people use a product made from onions and garlic mixed with a bar of laundry soap. To do this, grate the soap into warm water and mix thoroughly. Add grated onion and garlic to the resulting mixture. The resulting composition is cooled and rolled into balls. Apply soap until the itching stops.
If not treated in a timely manner, pseudosarcoptosis can lead to the development of purulent processes due to the secondary attachment of bacteria; prolonged scabies leads to the development of skin eczema. An allergic reaction can cause critical symptoms such as choking. That is why it is important to recognize and treat the disease in time.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for scabies is favorable. With proper treatment and excluding the possibility of re-infection, the disease goes away without a trace.
Prevention of scabies involves no contact with sick people or potentially dangerous objects and surfaces. Basic recommendations for preventing scabies mite infestation include:
- Careful observance of personal hygiene rules.
- Use of individual bath accessories.
- Refusal to rent things that can be a source of infection: sleeping bags, beds, etc.
- Thorough treatment of housing and objects when scabies is detected in those living in it.
- Preventive consultation with a dermatologist when in contact with a patient with scabies.
- Regular preventive examinations for employees of children's institutions, nursing homes and other institutions with long stays.
In areas where large numbers of people live, such as barracks and dormitories, regular inspections and preventive treatment of newcomers with anti-scabies are recommended.
Preventive measures
To prevent infectious infection it is necessary:
- Maintain personal hygiene, regularly wash exposed skin with soap and change clothes after contact with an animal.
- If an infected animal is identified, it must be isolated and treated according to the recommendations of a veterinarian.
- If you have animals at home, you should regularly take them for examination to the veterinarian for preventive vaccinations and identification of scabies mites.
- The premises where animals are located must be treated with insecticides, for example, Butox or Neostomazan.
If the sick animal is isolated in a timely manner, followed by treatment of the latter, in the absence of an acute allergic reaction and the addition of a bacterial infection, the prognosis will be favorable.
In some cases, after infection, it is enough to wash the bite sites with soap and water, treat the lesions with antiseptics (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin) and further symptoms will not appear.
But if the symptoms of inflammation (itching, redness, swelling) do not go away within a few days, then you need to consult an infectious disease doctor to receive proper treatment.