Views: 2,086
The bite of these insects itself already causes a lot of concern. However, their harm does not end there. The saddest thing is that encephalitis ticks spread tick-borne encephalitis, and also transmit many other pathogens of dangerous diseases . In this case, both people and animals suffer. Quite a few similar cases have also been registered in our region. Therefore, treatment against ticks in Lipetsk is one of the important tasks aimed at preserving the health of the population.
We have already briefly touched on the topic of pathogens of various diseases that can occur if a tick bites. You can view this article here: Features of ixodid ticks. Continuation. In this note we want to begin to take a closer look at the diseases themselves. It's difficult to mention them all. But we will touch on the main and most common ones.
Danger of a tick bite: tick-borne encephalitis
Of course, first of all it is worth talking about this disease caused by encephalitis ticks. After all, even their name speaks for itself. At the same time, we immediately note that any ticks are called encephalitic if they carry the causative agents of this disease .
Tick-borne encephalitis is caused by viruses of the genus
Flavivirus . Their cunning lies in the fact that they affect nerve cells (that is, they are neurotropic). And this, in turn, makes viral agents inaccessible to the immune system .
The body will not fight its own nerve cells and destroy them, even if they are infected... Unfortunately, our immunity is not able to distinguish neurons affected by the virus from healthy ones. There are different types of tick-borne encephalitis according to geographical criteria. In Europe, this disease is most often transmitted by the so-called dog tick . It is also called the European forest tick . In Latin - Ixodes ricinus. In Russian forests, especially in the area of Siberia and the Far East, another representative of these bloodsuckers is more rampant. Namely, the taiga tick (Ixodes persulcatus). The same ticks are found in Lipetsk and the Lipetsk region. Their destruction is the primary task of the disinfection services involved in acaricidal treatments.
What to do if you are bitten by a tick and how to prevent viral encephalitis. Expanded instructions
Author:
gastroenterologist Anton Smirnov
7 minutes
12481
We recently published a major piece on the current tick season and the diseases they carry. In connection with updated information about the foci of tick-borne viral encephalitis (TBE) in Moscow, Mednovosti provides detailed instructions on what to do if you are bitten by a tick.
According to the April report of the Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor, which is cited by Izvestia, a cluster of TVE was discovered in the city of Moscow. Epidemiologists refer to data from last year’s studies that discovered ticks and mammals infected with TVE in the Krylatsky Forest Park. In 2021, one victim, bitten by an encephalitis tick, contacted the research institute; another person ended up in the hospital a year earlier. Experts point out that these were the first cases of detection of the virus in the city. They warn residents of the capital that the situation could repeat itself this year.
It was previously reported that last year 13,332 people (2,699 of them children) visited medical institutions in the capital alone due to tick bites. This year, in 70 constituent entities of the federation, about four thousand victims, including 1,591 children, contacted medical organizations, which is below average.
Here are recommendations on what to do if you find a tick on yourself, taken from the leaflet “Beware of Ticks,” compiled by the chief freelance specialist in infectious diseases of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Professor I.V. Shestakova.
Removing the tick
Contact the specialists
If tick suction does occur, an initial consultation can always be obtained by calling a landline number: 103, or from a mobile (cell) phone: 103* or 112.
A person who has suffered from a tick bite must seek medical help from the territorial clinic at his place of residence, the regional SES or the regional emergency room to remove the tick and deliver it for examination, as well as to organize medical observation, in order to make a timely diagnosis of tick-borne infection and resolve the question of prescribing preventive treatment.
If for some reason you do not have the opportunity to seek help from a medical institution, then you will have to remove the tick yourself, and the sooner you remove the embedded parasite, the better.
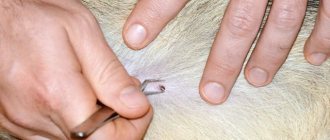
Removing ticks yourself There are several ways to remove ticks. They differ only in the tool used to remove the tick. It is most convenient to remove a tick with curved tweezers or a surgical clamp; in principle, any other tweezers will do. In this case, the tick must be grabbed as close to the proboscis as possible, then it is carefully pulled up, while rotating around its axis in a convenient direction. Usually, after 1-3 turns, the entire tick is removed along with the proboscis. If you try to pull the tick out, there is a high probability of it breaking.
If you have neither tweezers nor special devices for removing ticks at hand, then the tick can be removed using a thread. A strong thread is tied into a knot as close as possible to the tick's proboscis, then the tick is removed, slowly shaking it to the sides and pulling it up. Sudden movements are not allowed.
If you don’t have tweezers or thread at hand, you should grab the tick with your fingers (it’s better to wrap your fingers in a clean bandage) as close to the skin as possible. Pull the tick slightly and rotate it around its axis. There is no need to crush the tick with your hands. After removing a tick, be sure to wash your hands. The wound must be treated at home with an antiseptic.
Removing a tick must be done with care, without squeezing its body, since this may squeeze the contents of the tick along with pathogens into the wound. It is important not to tear the tick when removing it - the remaining part in the skin can cause inflammation and suppuration. It is worth considering that when the head of the tick is torn off, the infection process can continue, since a significant concentration of the tick-borne encephalitis virus is present in the salivary glands and ducts.
If, when removing the tick, its head, which looks like a black dot, comes off, wipe the suction site with cotton wool or a bandage moistened with alcohol, and then remove the head with a sterile needle (previously calcined in a fire) in the same way as you remove an ordinary splinter.
After removing the tick After removing the tick, the skin at the site of its attachment is treated with tincture of iodine or alcohol, or another available skin antiseptic. A bandage is usually not required. Subsequently, the wound is treated with iodine until healing. There is no need to pour in a lot of iodine, as it can burn the skin. If everything is normal, the wound will heal within a week. Hands and tools should be thoroughly washed after removing the tick.
When removing a tick you do not need to:
- apply caustic liquids (ammonia, gasoline, etc.) to the bite site;
- burn a tick with a cigarette; - jerk the tick sharply - it will break off;
- picking at the wound with a dirty needle;
- apply various compresses to the bite site;
- crush the tick with your fingers.
There is no basis for some far-fetched advice that for better removal one should apply ointment dressings to the attached tick or use oil solutions. The oil can clog the tick's breathing holes, and the tick will die while remaining in the skin. Dripping oil, kerosene onto a tick, or burning the tick is pointless and dangerous. The tick's respiratory organs will become clogged, and the tick will regurgitate the contents, increasing the risk of infection.
We send the removed tick for examination
If research is not possible, the tick should be burned or doused with boiling water. The removed tick should be placed in a small hermetically sealed container with a small piece of slightly damp cotton wool or a napkin and sent to the laboratory. The jar with the tick is placed in the refrigerator if it is impossible to transport it to the laboratory immediately after removing the tick. Within two days, the tick must be taken to the laboratory to be tested for tick-borne infections. Usually the analysis can be done in a regional infectious diseases hospital or a special laboratory.
Laboratory addresses
For Moscow residents:
- in the department of especially dangerous infections of the microbiological laboratory of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow" at the address: Moscow, Grafsky lane, 4/9 (entrance from the courtyard, 2nd floor), tel.. Reception is held from 9-00 until 15-30 daily, except Saturday, Sunday and holidays (lunch break from 13-00 to 13-30), the results of research can be found out from 15-00 to 18-00;
- branch of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow" at the address Moscow, Krasnogvardeisky Boulevard, 17 building 1 microbiological laboratory, reception from 9.30 to 15.00 daily, except Saturday and Sunday, tel.;
- Federal Budgetary Institution of Health "Federal Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor" in Moscow at the address Varshavskoye Highway 19a (Nagatinskaya metro station) Mon-Fri from 9.00-18.00 tel. +7(495)954-45-36.
Residents of the Moscow region can receive specialized assistance at their place of residence in the Central District Hospital or at the above addresses.
What should a person bitten by an infected tick understand?
It is impossible to judge by the appearance of a tick whether it is a carrier of infection or not. The tick becomes infected when feeding on an infected animal. The virus can be contained in females, males, nymphs, and larvae. Even if the tick bite was short-lived, the risk of contracting tick-borne infections cannot be ruled out.
However, it should be understood that the presence of an infection in a tick does not mean that a person will get sick. A tick analysis is needed for peace of mind in case of a negative result and vigilance in case of a positive result.
It is advisable that a person who has suffered from a tick bite be observed by an infectious disease specialist for a month, who, if necessary, will prescribe the necessary preventive or treatment measures. If more than 2 months have passed since the tick bite, there is no need to worry.
There is no need to self-medicate; if in doubt, consult a doctor! If a tick bite has occurred, if your health worsens, consult a doctor immediately!
We carry out specific prevention (only tick-borne viral encephalitis)
Emergency prevention of tick-borne borreliosis, human monocytic ehrlichiosis and human granulocytic anaplasmosis is usually not carried out.
Tick-borne viral encephalitis is a very dangerous tick-borne infection. Emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis should be carried out as early as possible, preferably on the first day. It is carried out using antiviral drugs or immunoglobulin (when virus ticks are sucked on by people who have not been sick or previously vaccinated, as well as those who have an incomplete or defective vaccine course in the first 96 hours after sucking, intramuscularly, once). A doctor carries out preventive measures.
When an encephalitis tick bites, the virus enters the bloodstream with saliva. In the future, events may develop differently. If the bitten person has been vaccinated and the level of antibodies is sufficient, the virus immediately binds and the disease does not develop. The development of tick-borne viral encephalitis can be stopped by other factors of antiviral protection. Therefore, even if the tick was encephalitic, the person bitten may not get sick. The presence of a virus in a tick does not mean that the disease will develop. The number of people bitten by encephalitis ticks significantly exceeds the number of people sick with tick-borne encephalitis. But even one bite can lead to serious illness.
Where to go for emergency prevention against tick-borne encephalitis in Moscow
For adults:
- Infectious Clinical Hospital No. 2 of the Moscow Department of Health, Moscow, 8th st. Sokolinaya Gora, 15. Help service.
- City advisory office on vaccine-serum prevention of tick-borne viral encephalitis: tel., +7(495)365-01-47 (www.mosgorzdrav.ru/ikb2)
For children:
- Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 13 named after. N.F.Filatova, Moscow, st. Sadovaya Kudrinskaya, 15. Help desk: +7(499)254-91-29.
Vaccinations against tick-borne encephalitis
If you frequently visit tick habitats, it is advisable to get vaccinated against tick-borne viral encephalitis. The vaccine protects for at least 3 years. Persons working in endemic areas (foresters, geologists, etc.) and children living in endemic areas are subject to mandatory vaccination.
In Russia, vaccination is carried out with domestic vaccines (Tick-borne encephalitis vaccine, cultural purified concentrated inactivated dry, EnceVir) and foreign vaccines (FSME-Immun Inject/Junior, Encepur adult, Encepur children) or by primary and emergency schemes. All vaccines have the same immunogenicity. Vaccination can be carried out according to two schemes: the main and emergency. The main scheme (0, 1-3, 9-12 months) is carried out with subsequent revaccination every 3-5 years. To form immunity to the onset of an epidemic season, the first dose is administered in the fall, the second in winter. An emergency regimen (two injections with an interval of 14 days) is used for previously unvaccinated persons arriving in endemic foci in the spring and summer. Emergency vaccinated persons are immunized for only one season (immunity develops after 2- 3 weeks), after 9-12 months they are given the 3rd injection.
Initial signs of tick-borne encephalitis
First, let's answer the following question: why is tick-borne encephalitis dangerous? If left untreated, the disease ends in paralysis of the nervous system . This condition is incompatible with life.
Different cases of the disease develop in approximately the same way, according to the same pattern. Although there are differences between European and eastern tick-borne encephalitis . One way or another, the first symptoms of both diseases are characterized by flu-like symptoms:
- temperature rises;
- headaches often appear;
- joints begin to ache;
- muscles hurt;
- general malaise and loss of strength are felt;
- appetite decreases sharply;
- Nausea is often present.
These signs may appear immediately, on the first day of the bite. But there may be an incubation (hidden) period of several days.
As a rule, eastern tick-borne encephalitis is much more intense . Moreover, it ends in death more often and faster than the European one. Sometimes 3 days are enough for the disease to irreversibly affect the human nervous system. Therefore, at the first signs of discomfort after an encephalitis tick bite, you should urgently consult a doctor . Under no circumstances should this be postponed. At the initial stage, the chances of curing the disease are much greater. And this can be done with minimal damage to health.
Where to contact
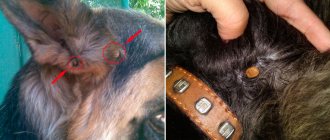
If you suddenly notice signs of an encephalitis tick bite in a person or symptoms of an encephalitis tick bite in a dog, immediately contact a veterinarian or regular clinic. There you can get professional help and remove the insect using a safe method.
In addition, this way you will be sure that everything was done correctly and there is no threat of the virus spreading. In specialized institutions, the ticks are sent for examination, where, with the help of special tests, they will find out whether it was a carrier of encephalitis.
Damage to the nervous system due to an encephalitis tick bite
This is the next stage of the disease that develops after an encephalitis tick bite. It is characterized by the fact that the virus penetrates nerve cells . In the case of European encephalitis, a so-called remission is often observed externally. It seems that the disease is gone and all its symptoms disappear . However, after about a week, a new stage of fever occurs.
It has slightly different symptoms, since the lesions affect the nervous tissue. This is expressed in symptoms of meningitis or encephalitis :
- headache and muscle pain intensifies;
- vomiting is noted;
- neck muscles become stiff;
- fever returns;
- In some situations, sensitivity to light increases sharply.
In the absence or insufficient treatment, mental deviations, convulsions, impaired motor skills and coordination begin to appear .
Signs of an encephalitis tick bite
- The temperature suddenly rises.
- Muscle spasms and severe pain.
- Nausea and vomiting, for no reason.
But insidiousness is not only in the presence of symptoms that can be attributed to poisoning or a cold. After about ten or seven days, everything goes away, and the condition of the bitten person noticeably improves. Many people attribute this to other reasons - a cold, poisoning, and so on, not realizing that these are the initial signs of an encephalitis tick bite.
However, after about ten minutes, the previously bitten person may feel:
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system;
- migraine;
- confused consciousness.
It is very difficult to predict with accuracy what will happen after a tick bite; everyone has a different body and a different amount of poison in the blood. But what will happen for sure is high temperatures, sometimes reaching 40 degrees. All this is accompanied by weakness and nausea, vomiting.
It is at this stage that the virus spreads everywhere, so you need to monitor the patient’s well-being; if a number of other symptoms are added to all of the above, it means that the disease has begun to take a severe form.
If the temperature subsides, it does not mean that the disease has stopped; perhaps it has turned into a meningeal form, with fever, fear of light and muscle spasms. In addition, the chance of developing paralysis of the limbs and death is not small.
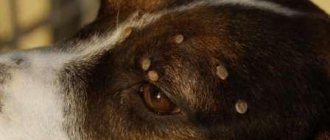
Tick bite
The most severe consequences of tick-borne encephalitis
In case of advanced disease, the following are noted:
- constant general muscle weakness ;
- partial paralysis of limbs and other parts of the body;
- occasional cases of numbness ;
- a sharp decrease in muscle tissue .
Serious personality disorders are often observed. At this stage, the likelihood of death or lifelong disability increases significantly .
What is the likelihood of getting infected from a tick bite?
In fact, there are not many encephalitis ticks (i.e. ticks infected with the encephalitis virus) . According to statistics - only about 6%. However, since the disease has serious consequences, close attention is paid to it.
The good news is that even if a certain number of viruses enter the human body, the development of the disease is not necessary . What matters here is:
- general condition of the human immune system;
- the body's adaptability to tick attacks;
- vaccination.
For example, if the immune system is very strong, then even at the first encounter with the pathogens of tick-borne encephalitis, the body can very quickly and effectively build a defensive reaction and repel aggressors. In this case, the viruses will simply die and the disease will not develop. This course of events is especially visible when an insect bite causes a small dose of pathogens to enter the bloodstream.
In another case, the body’s natural adaptation to attacks by encephalitis ticks can help defeat viruses . This phenomenon is observed in people and animals living in wooded areas. Very often, they develop appropriate immunity from childhood. It helps them survive even when pathogens enter the bloodstream.
The third factor that prevents the development of the disease is vaccination. It should be used if you are going to places where there are a lot of ticks. In this case, several injections are given at certain intervals. As a result, by the onset of the spring-summer season, a person develops a strong immunity to tick-borne encephalitis.
Anyone who wants to be vaccinated can get vaccinated against the consequences of tick bites in Lipetsk and the Lipetsk region.
In any case, take precautions. And we wish you not to encounter encephalitis ticks. And if you encounter them, you can quickly and easily cope with the consequences of their bites without harm to your health!
Other articles on ticks:
– Tick-borne diseases No. 3
– Borreliosis – disease No. 2 caused by a tick bite
– Is it possible to do tick treatment yourself?
– Do I need to be vaccinated against ticks?
– Features of ixodid ticks: what do you need to know?
– How do ixodid ticks attack?
First steps when bitten by a tick
If you are bitten by a tick, then most likely it remains at the site of the bite and continues to suck blood, so, naturally, you need to pull it out!
To do this competently and professionally , go to a clinic or first aid station, where specially trained specialists will pull it out and perform all the necessary manipulations for your further safety. If you do not have the opportunity to immediately contact such specialists, remove it yourself.
- To remove a tick at home, you need to protect your fingers with a gauze bandage, without making much effort, shake the insect from side to side and twist it counterclockwise.
- Do not use sharp tools or pull it out if you feel resistance, as it will release more poison into your body! This also applies to removing a tick with oil; under no circumstances should you apply vinegar and oil to the area!
- After removing the tick, lubricate the affected area with alcohol.
You may also find information on how to remove a tick at home useful, read on our website.
It is important to correctly remove the insect from the wound and prevent severe poisoning from the poison and an increase in its amount in the blood. In addition, the head should not remain in the wound. When you have pulled out the tick, take it to the hospital for examination, in case it is a carrier of encephalitis.
If the wound turns pink, and after some time this stain has subsided, the danger has passed, and the tick was removed correctly and safely.
Mite