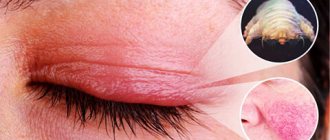
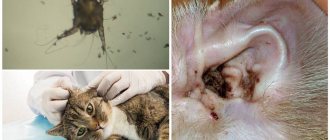
What is scabies mite
The itch that lives inside the skin of mammals is called the scabies mite. The arthropod, from 0.23 mm to 0.45 mm long and no more than 0.14 mm wide, has a proboscis and 4 pairs of short jointed legs. The female tick, having settled in the upper layer of the epidermis, begins to produce a special secretion that helps her move and make passages.
When passing through the stratum corneum, it lays 10 to 20 eggs, from which larvae emerge a few days later. Adult individuals, of which there are 20–25 under human skin, live no more than 1–2 months. Ticks love comfortable temperatures, above +20˚С.
At temperatures below 0˚ and above +60˚С they die. The scabies mite in humans (photos can be viewed in the medical encyclopedia) is most active at night.
In the first half of the night, females gnaw holes in which they lay eggs, and in the second half they move further, simultaneously feeding on blood. By morning they freeze until the next night activation. This is why severe itching appears at night, which bothers the mite carrier. Since female mites act synchronously, the itching becomes unbearable.
Description of the parasite
The mite is yellowish or creamy white in color. It is difficult to notice with the naked eye, since the male is about 0.20 mm in size, and the female is 1.5 times larger.
Only female parasites spread the infection. The role of the male is to fertilize the female once, and after that he dies. The tick's body is oval, similar to a turtle shell or a bean. Adult ticks have four pairs of paws, females have peculiar suction cups on the front two, and males have 1, 2 and 4 pairs of paws. The eggs are small, oval, approximately 0.2 mm in size. The larvae are white, round, with 3 pairs of legs; the body size is also 0.2 mm. The next stage of scabies development is the nymph. This is a white round individual with 4 pairs of legs, it is slightly smaller than an adult tick.
Types of scabies mites
The scabies mite can live anywhere on the human body, but the most favorite places are:
- between fingers;
- in the folds of the wrist, elbow or knee;
- around the waist;
- on the chest;
- genitals;
- neck, palms, soles of feet.
The disease spreads from one type of tick – Sarcoptes scabiei, but has different types:
- Typical scabies. Rashes appear on the wrists, arms, and other places except the face and head.
- Nodal. It appears in the groin, armpits, and genitals.
- Infantile scabies. It most often spreads in young children, in the arms, legs, face and head.
Another type is complex scabies, complicated by other skin rashes such as dermatitis, urticaria or impetigo.
Less common is “Norwegian” scabies, a rare clinical form in which there are up to a million individuals in the human epidermis. It is an atypical disease that affects people with low immunity, weakened body resistance and mental illness.
The signs of Norwegian scabies are pronounced, and the general condition of the person is disturbed, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and fever develops. Tick tracts are visible between the fingers, on the wrists, elbows, in women they often appear on the chest, in men in the scrotum area.
Norwegian scabies easily spreads through direct contact of an infected person with healthy people or from things, linen, furniture, clothing with which the sick person has been in contact.
Scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabiei hominis, scabies itch)
Scabies is caused by scabies mites. The scabies mite ( Sarcoptes scabiei hominis, scabies itch) is a permanent parasite of humans only. Insects spend most of their lives inside the host’s skin and come to its surface only during the period of settlement. During life, scabies undergoes metamorphosis from egg to adult in the thin passages of the lower stratum corneum of the epidermis. Parasites are characterized by significant morphological specialization.
Rice. 4. The photo shows a scabies mite under a microscope.
Rice. 5. Scabies mite. The photo was taken using an electron microscope.
Scabies mite eggs
During 6 - 8 weeks of her life, a female scabies mite lays about 50 eggs. The eggs of the parasite are oval in shape and have a transparent shell. After being freed from the larva, the shell collapses. A longitudinal crack appears on it. The cycle from egg to larva (imago) lasts from 10 to 14 days. Among all representatives of the scabies genus, insect eggs are the most resistant to the effects of acaricidal drugs (mite repellents).
Eggs that fall on the skin during scratching are more resistant to external influences than adults and larvae. Their embryogenesis is completed, but the hatched larvae are highly susceptible to dehydration and quickly die.
Rice. 6. A female scabies mite lays about 50 eggs in her life.
Larvae of scabies mites
From the eggs, after 2 - 3 days, larvae (nymphs) appear, which have a size of 0.15 to 1.0 mm and three pairs of legs. The hatched larvae emerge on the surface of the skin through holes made by the adult female in the roof of the passages and settle under the scales of the epidermis of the skin and in the places of the hair follicles, where they mature and molt. After 1.5 - 2 weeks, the nymphs molt and turn into adults. The maturation phase (metamorphosis) lasts up to 2 weeks. The lifespan of adults is 1 - 2 months.
Rice. 7. In the right half of the scabies tract, the shells of empty eggs are visible. The hatched larvae emerge to the surface of the skin through special holes made by the adult female in the roof of the passage.
Male scabies mites
Male scabies mites are 1.5 times smaller than females. They live on the surface of the skin. In the community of parasites, there are 2 times fewer males than females. Their main function is to fertilize females. After fertilization, the males die.
Female scabies mite
After fertilization, which occurs on the surface of the skin, the female Sarcoptes scabiei hominis penetrates into the epidermis, where, at the border of the stratum corneum and granular layer, she makes scabies, feeds and lays eggs. During 6 - 8 weeks of her life, the female lays about 50 eggs.
The female scabies itch looks like a turtle. Its length is 0.3 - 0.4 mm, width - 0.25 - 0.38 mm. The body is covered with a cuticle, which has a leathery folded structure.
Females are perfectly adapted to living inside the skin. They have multiple adaptations for making passages inside the skin, moving on its surface and feeding.
For gnawing passages, its oral organ is equipped with chelicerae with powerful claws, somewhat protruding forward.
To move along the passages, female scabies mites are equipped with 4 pairs of legs, on which there are many bristles, and on the back there are triangular outgrowths of cuticles (chaetoids). The female's forelegs are shorter and are equipped with sticky pneumatic suction cups designed to move along the surface of the skin. The hind pair of legs have long elastic spines that serve as supports when moving inside the skin. Inside the skin, females move at a speed of 0.5 - 2.5 mm per day. On the surface of the skin - 2 - 3 cm per minute.
For orientation in space (ticks do not have eyes) there are long bristles (hairs) located on the body and limbs. They create a mechanoreceptor sphere around the parasite.
Rice. 8. The process of introducing an insect into the skin lasts from 15 minutes to one hour. The photo shows a histological specimen. The female Sarcoptes scabiei hominis has penetrated the epidermis.
Rice. 9. Female scabies mites are perfectly adapted to living inside the skin. They have multiple adaptations for making passages inside the skin, moving on its surface and feeding.
Dispersal of scabies mites
Being small in size and having great mobility, young females and larvae, in close contact with the patient (usually while staying in the same bed), quickly penetrate the skin. The implantation occurs in places where the stratum corneum is thickest—the area of the hands, wrists and feet. On the face and back, where the stratum corneum has the smallest thickness, there are no scabies. Regeneration processes in the thick stratum corneum occur slowly, which is why the larvae of scabies mites have time to hatch and not be rejected with horny scales. Full reproduction occurs in places where the temperature is lower and there is no or minimal hair.
The “mirror of scabies” are the hands. It is in their epidermis that the female lays the bulk of her eggs, which, together with the larvae, are spread throughout the body. Fertilized females reach the genitals of men not only through close contact with a sick person, but also through their own hands.
Rice. 10. The “mirror of scabies” are the hands and wrists.
Rice. 11. Fertilized female scabies get onto the male genitals not only through close contact with a sick person, but also through their own hands.
Scabies
Female scabies mites live inside the epidermis, where they burrow, feed, and lay eggs. The process of introducing an insect into the skin lasts from 15 minutes to one hour. During the day the female rests, and in the evening and at night the parasite begins to actively gnaw through tunnels (1 - 2), located at an angle to each other, in each of which one egg is laid. The length of the passages varies from several millimeters to several centimeters. All scabies ducts have a convoluted shape and consist of segments called the diurnal element. In the roof of each of the passages, the female makes exit holes through which future larvae come out. The back of the passages is gradually removed (exfoliated) during the process of regeneration of the epidermis. Some scabies can persist for up to one and a half months.
During 6 - 8 weeks of her life, a female scabies mite lays about 50 eggs. The cycle from egg to larva (imago) lasts from 10 to 14 days.
Itching that occurs in the evening and at night is a constant and main symptom of the disease.
Rice. 12. The photo shows an itch. In the left half of the photo there is a scabies mite, then the laid eggs and excrement of the parasite are visible.
Rice. 13. The photo shows scabies. The posterior part of the burrow (photo on the right) is gradually removed (exfoliated) during the process of epidermal regeneration.
Life cycle of Sarcoptes scabiei hominis
The life cycle of Sarcoptes scabiei hominis includes feeding, reproduction and dispersal. It is divided into a short cutaneous part and a long intradermal part. The intradermal part of the life cycle is divided in turn into reproductive and metamorphic.
Rice. 14. The photo shows scabies and its eggs.
Scabies mite reproduction
Male scabies mites find places where females have completed their maturation and fertilize them. The fertilized female penetrates the epidermis, where she begins to lay eggs. Males die after fertilization.
One female lays 1 - 2 eggs per day. The embryonic period lasts about 4 days. During 6 - 8 weeks of her life, the female lays about 50 eggs. The intensity of egg laying slows down as the female ages. It has been established that females lay eggs especially intensively from September to December. One female in three months in favorable conditions is capable of giving birth to 6 generations, which amounts to about 150 million individuals.
The hatched larvae come to the surface and quickly find the places where the hair follicles are located. In these places they mature and molt. The maturation phase (metamorphosis) lasts up to 2 weeks.
Follicular papules and vesicles are the main elements of skin rashes due to scabies.
Mating of males and females of the new generation occurs on the surface of the skin. After mating, young females immediately penetrate into the thickness of the epidermis and begin to lay eggs, so the incubation period for their invasion is practically absent. When infected with larvae, the incubation period is about 2 weeks, which is equal to the period of metamorphosis (the transition from the larval stage to the adult stage).
Rice. 15. Female scabies under a microscope.
Only larvae and females of scabies mites participate in the infection.
Stages and degrees of scabies mites
The scabies mite in humans (photo below), like the disease itself, develops in stages.
- The first stage is incubation. Lasts from 1 to 6 weeks, when the mite penetrates the skin and begins to reproduce.
- The second stage is the longest. At this time, the full clinical picture appears, when the full extent of infection can be seen. With active treatment, the disease lasts no more than 1 week. In the absence of treatment and complications that arise, the disease lasts for several months or years.
- The third stage is the recovery period. With proper, timely treatment, the mites die, and human skin takes on a healthy appearance.
Symptoms of scabies mites
Primary symptoms appear a week after infection, or even later.
Main symptoms:
- Severe itching at night.
- Detection of tick burrows on the skin. Unlike allergic itching, when scratching you can see oblong stripes and scabies. These are tunnels under dead skin in which the female lays eggs. At the end of the tunnel there are papules in which the mite is visible under a microscope.
- The appearance of small pimples or pus-filled blisters.
- The appearance of ulcers and pus with strong scratching of the affected areas.
- In some cases, fever and insomnia occur.
Some typical symptoms are named after the scientists who discovered them:
- Ardi-Gorchakov symptom , named after dermatologists, is characterized by the presence of pinpoint pustules on the elbows;
- Michaelis symptom , expressed by rashes of blood crusts in the intergluteal folds.
Scabies mite in humans (the photo shows the rising lines of the burrows well), its signs are especially clearly visible on the hands. This is the most typical place where mites develop because the hands are the primary contact with infested objects.
Between the fingers, on the lateral surface of the hands, you can see whitish lines rising above the skin. They can be straight, curved, no more than 10 mm long. At the end of the lines a black dot is visible; this is the so-called ventilation shaft that the female made.
As the mite spreads, bubbles and nodules with a diameter of up to 3 mm appear on the surface of the skin. The skin acquires a hemorrhagic crust. With Norwegian scabies, the face and neck are affected, where thick gray crusts up to 3 cm thick appear, on which ulcers appear. Scabies symptoms are often confused with allergic signs.
This leads to a delay in treatment, which is fraught with the appearance of secondary infections.
Scabies should be distinguished from other skin irritations:
- pseudoscabies caused by a scabies mite that does not penetrate the epidermis and is not transmitted to other people;
- neurodermatitis , a chronic atypical disease that affects the skin and causes itching;
- pruritus or urticaria, a type of allergic itch;
- eczema , a chronic skin disease;
- toxicerma , an inflammatory skin disease that occurs in response to a strong allergen entering the body.
The main symptoms of scabies
| Itching | Itching tends to intensify at night, which is associated with an increase in mite activity in the dark. |
| Scratching on the skin | Characteristic scratches on the skin that the patient leaves on himself, trying to cope with unbearable itching |
| Sleep disturbance | Due to sleep disturbances, the patient experiences neuropsychic exhaustion |
| Scabies and rash | Scabies and a rash appear on the skin of an infected person. The moves look like straight or broken lines with a white or gray tint |
| Bubbles | In some cases, small bubbles with transparent contents appear. Most often, the rash can be seen between the fingers, on the wrists, on the feet, on the stomach and on the buttocks. |
Signs indicating that a patient has scabies and not another skin disease are:
- Ardi's symptom: rash in the elbow area;
- Gorchakov's symptom: the appearance of crusts in the elbow area;
- Michaelis symptom: the appearance of a rash in the intergluteal area. (in this case, the rash may also appear on the sacrum);
- Sezari's sign: rash between the fingers.
Reasons for the development of scabies mites
The main cause of the development of the disease is a mite that lives in the upper layers of the epidermis and feeds on the skin. Infection occurs with the help of females, who, after fertilization, move under the skin in search of new feeding sites.
The figure shows how the scabies mite appears on human skin.
Males die after mating, and females, having laid eggs in dug canals, rise again to the surface of the skin to mate. At this point, infection occurs. The mites themselves do not cause much harm, but their feces, saliva, and shell residues irritate the skin, cause itching, and signs of scabies appear.
How many days can a parasite live without a person?
A large number of people are interested in the question of how long the scabies mite lives on clothes. If the owner is present in the clothing, then the tick that gets on it almost instantly moves to the skin without remaining on it, unlike, for example, a parasite such as a linen louse.
On clothes without a person, scabies can last, according to some researchers, for up to 5 days. In general, like other parasites, ticks are very dependent on temperature conditions.
It is known that at temperatures above 60 degrees the parasite dies in about 10 minutes , so it is recommended to wash things at this or higher water temperature in order to destroy the mite.
At normal room temperature, a tick that has lost its owner dies after 5 days. If the temperature remains 21-22 degrees, and the relative humidity does not exceed 75%, then the scabies mite can survive without a host for up to 2 days.
When the temperature drops below 22 degrees, the parasite goes into suspended animation. Also, ticks cannot tolerate frost. Therefore, in order to disinfect things that cannot be washed, boiled, ironed, treated with steam or A-PAR, it is enough to place them in a cold environment from 0 degrees.
A-PAR
It is difficult to give a definite answer to the question of how long scabies mite eggs live, but scientists have found that they are more resistant to external temperatures and do not need high humidity as much as, for example, the larvae that hatch from them.
For female parasites, air humidity is critical at 60%, and for larvae at 80%. Adults and larvae that get onto the surface of the skin as a result of scratching quickly become dehydrated, which threatens them with death, so they spend only a limited amount of time on the skin.
The parasites begin to sense the human body, its smell and warmth from a distance of no more than 6 cm; once on the skin, they begin the process of reproduction, after which the female actively penetrates deep into the epidermis, which takes her from 15 minutes to one hour.
Diagnosis of scabies mites
The success of any treatment depends on the speed of detecting symptoms, collecting tests and making a diagnosis. In the case of an infectious disease, it is important that the doctor examines not only the patient, but also the immediate environment. A survey of the patient, a visual examination, this is quite enough for an experienced infectious disease specialist to make the correct diagnosis.
At the next stage, the doctor prescribes a microscopic examination of the skin, which is carried out using laboratory methods:
- Use of mineral oil. In order to remove the tick, apply a few drops of oil to the exit hole of the tick. Then, using a thin needle, the mass is removed along with the mite and examined under a microscope.
- Scraping method. A skin scraping is taken from under the patient's nails and examined under a microscope.
- Iodine test. A small amount of iodine is applied to the affected skin, after which it dries, the scabies can be clearly seen.
- Digital photodermatoscopy. Using a special apparatus that displays an image on a computer screen, the scabies tracts are examined.
Express diagnostics are carried out using a 40% aqueous solution of lactic acid. A drop of the solution is applied to the affected area, then the loosened layer of the epidermis is scraped off. Next, the resulting material is studied under a microscope. The effectiveness of diagnosis does not depend on the chosen method, but on the specialist’s ability to find scabies on the skin.
Prices for diagnostic procedures in clinics:
| Diagnostic procedure | Price in rub. |
| Eyelash microscopy | 500 |
| Skin scraping with microscopic examination | 600 |
| Scabies test | 600 |
| Scraping the skin from under the nails | 350 |
| Express diagnostics | 500 |
| Digital Research | 800 |
Prevention of scabies mites
Two golden rules for protecting against infectious diseases are washing your hands after all contact with people, objects, at home or on the street, and maintaining personal hygiene.
Preventive measures include general provisions:
- Identifying the source of infection.
- Setting the degree of contact (direct, indirect) for the purpose of sanitization.
- Complete disinfection of clothing and housing with anti-scabies aerosol.
Private preventive measures:
- Use hygiene items: towels, bed linen, washcloths, only individually.
- Wash regularly with a mandatory daily change of linen, which must not only be washed, but also ironed with a hot iron.
- Keep fingernails and toenails clean.
- Do not use things from someone else’s wardrobe: gloves, scarves, hats, underwear.
- Carry out regular cleaning of premises with a 1–2% soda-soap solution.
- When visiting baths, observe sanitary conditions and hygiene standards.
Treatment methods for scabies mites
The scabies mite in humans (photos of medications are presented below) does not disappear on its own. The only way to get rid of it is with prescription medications that kill ticks. For treatment, modern means are used - acaricides, with the help of which the healing process is accelerated to 1-3 days.
Proper treatment includes:
- Simultaneous treatment of all patients registered in one lesion.
- For children under 3 years of age, anti-scabies are rubbed over the entire body, including the head.
- For better delivery of the drug into the scabies canals, coating with ointment is carried out only with your hands.
- To reduce nighttime itching, treatment is best done in the evenings.
- Before applying the ointment, you should take a hot shower using soap and a washcloth to remove the secretions of the sebaceous glands and loosen the epidermis. If there are signs of secondary pyoderma, showering is not recommended.
- During the treatment period, you can wash every day, but on the condition that ointments and sprays must remain on the surface of the skin for at least 12 hours.
- Upon completion of the course of treatment, a follow-up examination should be carried out, first after 3 days and then after 2 weeks.
Medications
There are various forms of drugs used to treat scabies: ointments, gels, sprays, solutions.
Effective means of combating scabies:
- Benzyl benzoate emulsion. For adults, a 20% solution is used, for children – 10%. Before rubbing, the emulsion is shaken and then applied to the affected areas. Rubbing begins from top to bottom: first the hands are treated, then the torso and lower limbs. Treatment is carried out for 10 minutes. 2 times a day, for 2 days. If the disease progresses, a repeat course is prescribed. An antiallergic agent is used simultaneously with the emulsion. Price in pharmacies – 17 rubles.
- Wilkinson's ointment. For scabies, rub once a day. Treat all areas of the skin, starting from the top and moving down. Apply at night for 3 days. Purulent lesions should be pre-treated with ointments with antibiotics or sulfonamides. The drug is not recommended for children and people with delicate skin. Price: 25 rub.
- Spregal. The drug is in the form of an aerosol for external use. Treatment is carried out in the evenings by spraying an aerosol over the entire surface of the body, excluding the face and scalp. After 12–14 hours, the drug must be washed off with soap and water. For many patients, a single application is sufficient. Can be used on small children, but after changing diapers, the buttocks should be treated again. Existing scratches on the face are treated with a cotton swab moistened with an aerosol. One cylinder is enough to treat 3-4 people. Cost: from 800 to 1 thousand rubles.
- Medifox. A 0.4% aqueous emulsion is used, which is rubbed into the affected areas. Course duration – 3 days. Wash off with water after complete treatment. Cost: 130 rub.
- Crotamiton. It tends to accumulate in the body of the tick, and subsequently kills it and eliminates the feeling of itching. Apply 10% cream, ointment or lotion. After washing the body, the drug is rubbed in 2 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 5 days. Not recommended for children under 12 years of age. Price: 1 thousand 700 rub.
- Permethrin. Cream, 5%, is thoroughly rubbed into the affected areas with massaging movements. After 8-12 hours, the drug should be washed off with water. Do not apply to the face, head and neck. Taking a bath or shower is possible only after completion of treatment, on the fourth day. Price of the drug: 450 rub.
For some time after recovery, a feeling of postcabiosis itching persists, which is eliminated by antihistamines.
The effectiveness of scabies treatment:
| Drugs | Recovery Number of people in % | Postcabiosis itch Number of people in % |
| 20% and 30% sulfur ointment | 100 | 0 |
| Benzyl benzoate 20% | 82 | 10 |
| Medifox | 81 | 11 |
| Spregal | 96 | 3 |
Traditional methods
The easiest way to soothe itching is to apply a compress soaked in cold water to the affected area, then wipe the skin dry with a towel and apply calamine lotion. There are other effective home remedies that are based on oils.
Recipes for some preparations:
- Tea tree oil. It contains the compound terpinen-4-ol, which kills the parasite that causes the disease. Tea tree oil, 5 drops, combine with 1 ml of essential oil, jojoba or coconut. Apply to skin 2 times a day for 7 days.
- Neem oil. It is used in the treatment of many skin diseases, including scabies. Add 0.5 ml of pure organic neem oil to 250 ml of jojoba essential oil. Apply to skin 1-2 times a day. Prepare an antiseptic cream by mixing 50 ml of neem oil with an equal amount of freshly ground turmeric powder. Apply cream 2-3 times a day.
- Neem leaves. Helps reduce itching and get rid of mites. Make a paste from a handful of fresh leaves by crushing them with a pestle or mortar. Wash the affected area thoroughly and then apply neem paste. After drying, rinse with water. Carry out the procedure daily until complete recovery. Boil the leaves in 1 glass of warm water. Cool to room temperature. Drink 1 tbsp. l. 3 or 4 times daily. Repeat for 7 days or until scabies disappears completely.
- Turmeric. The antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties of the substance relieve the symptoms of scabies and reduce itching. Mix 1 tbsp. l. turmeric powder with a few drops of lemon juice to form a thick paste. Apply to itchy areas and leave for 1 hour. Then rinse everything off with warm water. Carry out the procedure once a day until healing. Mix 1 tsp. turmeric powder and 1 tsp. dry neem leaves. Add a little water to form a thick paste. Apply the mixture to the skin once a day and leave until completely dry. Then rinse everything off with warm water.
Blue gum oil and fig bark powder are good for scabies mites.
Other methods
The scabies mite is highly prolific, so it is important to ensure that the disease does not recur in humans.
In the photo you can see how a female tick lays a large number of eggs, so the success of treatment depends not only on the correct use of medical products, but also on sanitary treatment:
- Treating the room, linen, and clothing with a product containing esdepaletrin and piperonyl butoxide.
- Bed and underwear of a sick person and those living with him should be thoroughly boiled, washed in hot water, and ironed with a hot iron after drying.
- Iron items that cannot be boiled and do not use them for 7 days.
Life cycle of itch
Mating occurs on the surface of the skin at night. After the process is completed, the male dies, the female crawls under the skin and lays eggs. Every night the itch reproduces an average of 4 eggs. It dissolves the keratin cover of the epidermis with its own saliva and the resulting contents and feeds.
After 2-4 days, first instar larvae appear and immediately begin parasitizing. Females build numerous tunnels, while young males build only small branches. The formation of an adult scabies mite lasts about 14 days, during which time the larvae molt several times, gradually increasing in size. After reaching sexual maturity, they crawl out to mate.
Possible complications
Treatment of scabies is mandatory, otherwise a person risks getting complications that will lead to serious consequences:
- Pyoderma. Skin lesions with ulcers, which come in various forms of complexity, boils, folliculitis, abscesses. In severely advanced forms of scabies, pyoderma leads to sepsis.
- Eczema. With a prolonged illness, a microbial form of eczema, or chronic inflammation of the skin, develops. Lesions in the form of vesicles and weeping appear on the feet, hands, and inner thighs.
- Lymphadenitis. Extensive skin lesions, developing due to inflammation of the lymph nodes, spread under the arms and in the groin.
Often, with advanced types of scabies, secondary infections occur. And this can lead to the development of dermatitis, lymphoplasia, and disorder of internal organs. The sooner you start treatment, the sooner you can achieve results. If the disease is neglected, then the scabies mite will settle for a long time not only in a person, but also in all his things and will remind of itself with frequent relapses.
Author: Belyaeva Anna