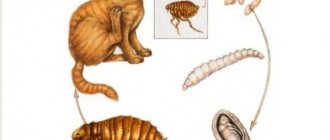
Cat worms
- Fact 1:
Parasites that live in the subcutaneous layer of the epidermis cause notoedrosis or sarcoptic mange. - Fact 2:
Ascariasis may not produce any symptoms of the disease. And it can manifest itself as weight loss, refusal to eat - Fact 3:
Antiparasitic treatment often effectively destroys adult helminths, but is powerless against parasite larvae - Fact 4:
If the slightest sign of a helminthic infestation or flea infestation appears, urgent measures must be taken immediately
Diseases of cats, like people, are divided into different categories: infectious, traumatic, bacterial, colds and many, many others. And, of course, this list would be incomplete without including parasites. Infection with helminths and insects can be internal, when eggs and larvae enter the gastrointestinal tract and spread throughout the body, and externally, when pests attack the fur and skin of an animal.
According to the principle of damage, they are divided into two categories : ectoparasites (external) and endoparasites (internal). Almost all of them are contagious, easily transmitted not only from animal to animal, but also from pet to person. In the latter case, the degree of danger depends on the type of pest; some simply bite people, while others successfully settle inside the body. This is why treatment and prevention of parasites is a very important aspect in caring for your pet.
Ectoparasites on fur and skin
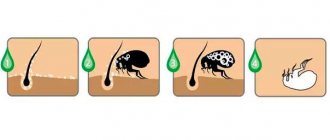
Perhaps the most common type of disease in cats. The most common of these are ticks and fleas. Infection occurs through contact of a sick animal with a healthy one. By the way, cat fleas are significantly different from those that attack dogs, and dog parasites will not inhabit the integument of cats.
Ectoparasites settle in the hairline and feed on particles of the epidermis and the blood of the pet. To obtain food, pests bite the animal and at this moment the parasite’s saliva gets onto the animal’s skin and blood. The pet becomes itchy, actively scratches, and tries to bite off fleas. Pussy behavior changes. These are the first signs by which you can suspect the presence of insects in your pet.
A visual inspection reveals the following picture : when the fur is pulled apart, bites (small dots) are clearly visible on the animal’s skin. When there are too many fleas and the bites are extensive, an animal, especially a small pet, may develop anemia. Her treatment requires a blood transfusion.
Cat fleas do not live on the human body, but they can actively bite him. A certain category of people has a pronounced susceptibility to bites that become red, itchy and slightly swollen.
The greatest accumulation of parasites in a living space occurs when it is rarely wet cleaned in the presence of a four-legged pet. Insects settle in upholstered furniture, carpets, and bedding. To get rid of ectoparasites, you need to treat the animal and its habitat with special antiparasitic agents. The animal is treated as it becomes infected and regularly for preventive purposes. It is better to do general treatment of the premises in the warm season.
Otodectosis or Ear mite
Also a very common disease caused by ear mites. The insect eats earwax and drinks the pet's blood. External examination reveals a brown coating on the ears and numerous bites, which sometimes merge into solid crusts. The signs of otodectosis are so characteristic and pronounced that they are difficult to confuse with anything else. Untreated ear mites provoke the development of deafness, otitis media, meningitis and other serious complications.
Therapy is carried out after cleaning the ear from scabs. Drops are used for treatment. They are also used to prevent illness as a preventative measure. Both ears of the animal are treated, even if visual damage is detected on one of them. This is because ear mites are very insidious and may not immediately appear externally, but penetrate into the inner ear and parasitize there. Without treatment, it will cause the complications described above.
lice eaters
Cats of long-haired breeds can develop hair lice. These insects inhabit the fur of the animal, bite it, causing the affected areas to itch very much. The pet loses its appetite, stops drinking water, and becomes overly excited. Without treatment, the signs of the disease intensify and the patient becomes weaker.
To kill the insect, the animal is treated with special means, twice. A single treatment does not affect the parasite larvae. After a couple of weeks, when they have turned into adults, but have not yet had time to lay eggs, another procedure is carried out.
Fleas
Fleas are one of the most common types of external parasites on cats. Their characteristics, signs and tips on how to remove them from the animal and from the apartment:
To remove fleas the following are used:
- Medicinal shampoos (are the most effective and gentle means);
- Drops (applied to the withers, allow you to quickly get rid of insects, but can cause allergies and residual effects);
- Sprays (effective, but sometimes an allergic reaction occurs);
- Collar (an effective preventive measure).
- After this, the apartment is sanitized.
Lice
Lice are the second most common external parasite in cats. We’ll tell you how to deal with them, signs and characteristics:
What parasites can humans get infected from cats?
Many people naively believe that a pet is the cleanest animal, and that’s the only reason it won’t infect its owner with anything. Of course this is not true. There are two ways in which an animal can “transmit” parasites.
The first involves fur, as well as the tongue. In the second there is a tray and things that the infected animal touches. External parasites are not dangerous.
A cat can infect its owner with helminths. For example, roundworms are dangerous, like all nematodes. Ascariasis is fraught with the fact that parasites accumulate in the respiratory tract, allergies become severe, vitamin deficiency and granulomas occur. Tapeworms pose a serious danger to young children, and echinococci can be fatal.
Note! Toxoplasmosis is a serious disease that a cat can infect through its feces if it itself is sick. If a pregnant woman contracts toxoplasmosis, the child may develop developmental abnormalities.
Symptoms of skin parasites
Are common:
- Pronounced anxiety;
- Scratched and bitten areas of skin;
- Frequent weight loss;
- Signs of dermatitis - redness, crusts;
- Partial baldness;
- Sleep disorders;
- Anemia - in severe cases.
Distinctive symptoms:
- With fleas, small white grains (eggs) are noticeable in the fur; in addition, fleas, unlike lice, are jumping;
- With lice, nits attached to the hairs and black dots (excrement of individuals) are visible;
- With ear mites, brown liquid sometimes flows out of the scratched ear, forming dark lumps in the shell: ear scabies occurs - otodectosis;
- Ixodid ticks embedded in the skin are visible to the naked eye.
Subcutaneous parasites
Subcutaneous mite
Parasites that live in the subcutaneous layer of the epidermis cause notoedrosis or sarcoptic mange. They bite your pet and cause skin irritation, itching, scratching, and scabs. Then the hair begins to fall out at the site of the scratching. To make a diagnosis, a scraping is made from the affected area and examined in a clinical laboratory. Based on the results, drug treatment is prescribed.
There is also a category of ticks that constantly live on the skin and hair of the animal. In a state of suspended animation, the presence of these parasites on the body is considered normal. But when optimal conditions are created (illness, weakening, decreased immunity), insects begin active life activities, provoking the development of demodicosis. Bald patches of skin appear on the skin. If there are no signs of baldness, then therapy is not needed.
- Demodex (Demodex cati) . Microscopic worm-like organism. Lives in the hair follicle of the animal, moves at night. It feeds on excess subcutaneous fat. When immunity declines, the tick manifests itself by releasing toxic waste. Insufficient nutrition causes its death after 2-3 weeks. As the tick decomposes, it causes inflammation in the cat.
- Scabies . Localizes near the ears and on the face. Deeply affects the subcutaneous layer. Can lead to blood poisoning.
- Notoedres cati . It goes unnoticed for a long time. It provokes the development of scabies, which is often replaced by fungus and dangerous bacterial infections.
Causes:
- Interaction with the owner’s clothes and shoes, on which he could bring ticks;
- Contact with infected relatives;
- Lack of hygiene;
- Failure to complete vaccination on time;
- Lack of inspections.
Symptoms:
- Itching;
- Redness;
- Irritation and inflammation;
- Dandruff rash;
- Hair loss in some areas;
- Lethargy;
- Loss of appetite;
- The appearance of weeping wounds;
- The appearance of pustules.
Why are worms dangerous?
Most often, if a cat becomes infected with worms, then in the future the owner will also become infected.
The danger of worms is that while in the body, they actively feed on the tissues and blood of the animal, which leads to depletion of vitality. Any worms poison the body of cats and humans with toxic substances, which leads to allergic reactions and intoxication. In addition, parasites injure organs with their suction cups or hooks, causing vascular ruptures.
A ball of worms can clog the intestinal lumen and lead to obstruction of the digestive tract, and this is dangerous for the death of the animal, since it cannot empty itself.
Endoparasites inside (Intestinal worms)
Helminths attack internal organs. The symptoms of the disease depend on the location and breed of the parasite. Worms are divided into two large groups:
- Parasites that develop inside the host organism. This can be not only a cat, but also any other animal, and a person. That is, the risk of transmitting helminths to people from pets is very high.
- Helminths that are capable of developing, reproducing and surviving from outside a living organism, for example, in soil. Infection occurs through unwashed hands, paws, unprocessed vegetables and fruits, and when pets eat garbage on the streets.
Worms are classified as protozoa and infect cats of any age, breed, or health status. The most common types of internal parasites are roundworms and nematodes.
Ascariasis
Tiny, flat, round-shaped worms, whose thickness is up to 5 mm in diameter, and their length can reach half a meter. Small kittens are most often infected with ascariasis. The larvae are picked up both through dirty paws and through contact with a sick animal.
Roundworms are divided into several types. For example, those that enter the stomach through the mouth grow up to 12 cm. Through the gastrointestinal tract, the parasites reach the intestines, and from there, through the circulatory system, the larvae go straight to the pulmonary alveoli.
The patient begins to have coughing attacks with the urge to burp, vomiting, and increased salivation. If your pet coughs up the larvae and then swallows them, a new round of helminth travel through the body will begin. If this does not happen, then the lung tissue is dotted with capsule-shaped formations with undeveloped helminth larvae.
Ascariasis may not produce any symptoms of the disease. It can also manifest itself as weight loss, refusal to eat, intestinal blockage, etc. In children, the signs will be especially pronounced; without treatment, the animal will die. Since the symptoms of ascariasis are typical for other diseases, it is not surprising that sometimes treatment does not give the desired result. After all, the diagnosis may be false. Ascariasis is very contagious for people, especially children.
Nematodes (roundworms)
It is also often an asymptomatic infection that can be transmitted from a sick animal to other pets and people. When abundantly distributed in the animal’s body, a loss of body weight occurs, intestinal disorders begin, and blood discharge is present in the excrement. Just as with roundworms, young cats are at greatest risk of becoming infected with nematodes.
Often, antiparasitic treatment effectively destroys adult helminths, but is powerless against parasite larvae. That is why a pregnant cat, seemingly treated for nematodes, is in fact a carrier and infects newborn babies during the lambing process.
Cestodes (tapeworms)
Trematodes (flat flukes)
Can humans become infected with these parasites?
Contrary to the naive idea that domestic cats are clean animals and cannot infect humans with anything, it has been scientifically proven that many types of parasites are transmitted to humans in two ways: Directly through fur and tongue; Through any fabrics and furs that the cat touches, as well as through the litter box. External cat parasites do not pose any particular danger to humans, although they can cause some trouble.
But many worms willingly transfer to it, which as a result leads to human infection with parasites from cats. Roundworms are very dangerous for people because they change the structure of the intestinal walls and affect the stomach. These worms provoke dangerous allergic reactions and vitamin deficiency.
A large accumulation of dead helminth bodies leads to blockage of the veins and respiratory tract. Ascariasis is very difficult to diagnose and is confused with lung diseases. Any nematodes are dangerous for humans, since, affecting internal organs, they lead to the development of anemia, severe allergies, and the appearance of granulomas. Tapeworms are very dangerous not only for adults. They often penetrate the child’s body, causing various deviations in its development. Metabolism is disrupted, and as a result, general weakness and lethargy appears. Anemia often occurs.
Echinococci can be deadly to humans . By parasitizing and multiplying in the liver, they form their own “dwelling” - a cystic bladder. As the tumor grows, it increasingly compresses the lobes of the liver, and it cannot function normally. The functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, and stagnation occurs in the bile ducts and blood. If the disease is not detected in time and treatment is not started, the bladder may fester, or simply rupture, which will lead to infection of the entire body.
Symptoms of worms in cats
Timely detection of symptoms of helminthic infestation is a guarantee of successful treatment. Signs of helminthiasis differ depending on which organs are affected by worms. In adult cats with strong immune systems, the clinical picture may be mild.
Intestines
The following symptoms indicate that a cat has worms in its intestines:
- the presence of mucus in the stool;
- bloating and abdominal pain;
- vomit;
- loss of appetite;
- diarrhea alternating with constipation;
- increased thirst.
Liver
If worms have infected the liver, symptoms in cats appear differently:
- vomiting bile;
- the skin, mucous membranes and sclera acquire a yellow tint;
- pain on palpation under the ribs on the right.
Heart and lungs
By these signs you can find out about worm damage to the heart and lungs:
- temperature increase;
- fast fatiguability;
- dyspnea;
- noisy breathing;
- cough;
- vomit.
central nervous system
When infected with worms, symptoms may appear that indicate damage to the spinal cord or brain:
- excessive excitement;
- convulsions;
- paralysis of individual parts of the body;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- fainting;
- involuntary urination or bowel movements.
Excretory system
Worms in cats rarely parasitize the genitourinary organs. If your pet begins to go to the toilet more often or less often than usual, and blood appears in the urine, you need to examine it.
Prevention of parasite infestation
Systematic treatment of the ward with special preparations will help protect the animal from parasites, both external and internal. Modern medicine for animals offers a large selection of highly effective products: from drops to collars with special impregnation.
If the slightest signs of helminthic infestation or fleas appear, you must immediately take urgent measures to detect and eliminate insects. Remember, they are dangerous not only to animals, but also to you and your children.
*Based on the results of my own work and colleagues from usatiki.ru