A bit of Wikipedia
According to Wikipedia, blood-sucking mosquitoes (lat. Culicidae) are a family of dipterous insects belonging to the long-whiskered group. In the modern world, the number of mosquito species totals more than 3.5 thousand . These insects are found on every continent (and in every country) except Antarctica, which makes sense given local temperature conditions.
Interesting fact! Humans and animals in particular are bitten exclusively by females. Males do not have developed jaws and do not have specific organs to bite a person. Human blood, rich in protein and glucose, is needed by female mosquitoes to bear offspring .
Russia and surrounding countries are home to more than 100 species of blood-sucking mosquitoes, including several malaria species (Orthopodomyia, Uranotaenia, Coquillettidia and Anopheles).
Malaria mosquito (Anopheles)
Humans are primarily responsible for the spread of various types of mosquitoes around the globe. The eggs and larvae of future adults (adult insects) survive travel in cars, trucks, trains, ships and even airplanes. One can only guess how many larvae of malaria mosquitoes were brought by tourists from southern countries during one tourist season.
Global relocation
The south of Russia was attacked by West Nile fever, which is carried by mosquitoes. Rospotrebnadzor issued a message about seven cases in Kuban. However, the threat of the spread of tropical diseases is much greater.
Scientists from the Institute of Medical Parasitology, Tropical and Vector-Borne Diseases named after. E.I. Martsinovsky First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov together with specialists from the Institute of General Genetics named after. N.I. Vavilov and Moscow State University. M.V. Lomonosov studied insects living on the Black Sea coast of the Krasnodar Territory. It turned out that populations of two types of mosquitoes, carriers of dangerous tropical fevers, had spread there.
Mosquito_1
Photo: TASS/Anton Novoderezhkin
As Alexander Lukashev, a leading researcher at the Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry at the Martsinovsky Institute, explained to Izvestia, the species found moved to Russia from Egypt and Southeast Asia due to global warming.
Scientists have found a way to prevent mosquito bites
“This is a worldwide problem when carriers of tropical diseases, which in principle should not appear in the north, migrate to areas with suitable temperature conditions,” the scientist said. — A similar picture is observed in Europe. Scientists predict that by 2050 these mosquitoes will spread even to Sweden. Here they have multiplied in the south, and are now moving into Central Russia.
Interestingly, until 2001 there were no such insects in our country. They were last seen in the 1950s, but the number of mosquitoes was incomparably smaller. The USSR then launched a program for their targeted extermination. The concern was related to the high risk of the vector and the occurrence of significant epidemic outbreaks of dengue fever in southern European countries. Many cases of disease were accompanied by death.
What mosquitoes live in Russia and the former CIS countries
There are three most common types of mosquitoes in our area:
- Common mosquito (also known as Culex Piplens). They are the constant companions of fishermen, hunters and simply travelers who decide to relax in nature away from the bustle of the city.
- Mosquitoes "Bites" (aka Aedes) - the bite of a mosquito of this species causes severe swelling and characteristic itching .
- And malaria mosquitoes of the Anopheles species, which are much more difficult to meet than ordinary or “Bite” mosquitoes.
The most common type of blood-sucking mosquitoes is the “Kukleks”, that is, the ordinary species. Moreover, this species is considered the most common not only in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and other nearby countries, but also throughout the world. They bite quickly, painlessly, without any dangerous symptomatic consequences. Itching at the site of a mosquito bite lasts from several minutes to an hour.
Common mosquito (Culex Piplens)
“Bites” mosquitoes are distinguished by their characteristic coloring in the form of white stripes on the abdomen and legs. It is not uncommon to experience slight swelling after a bite from the Biting mosquito, accompanied by itching for several hours.
Mosquito "Biter" (Aedes)
As for malaria mosquitoes, in our latitudes, mainly one species is found (Anopheles). The remaining species are extremely rare guests. In appearance, a malaria mosquito is difficult to distinguish from a regular one, which further aggravates the situation. This species carries malarial plasmodia , which provoke the development of a dangerous disease called malaria.
Anopheles is the most common type of malaria mosquito not only in Russia, but also in the world as a whole.
What do mosquitoes infect?
Mosquitoes carry a huge number of infections. Some of them can be found in Russia, in particular in the southern regions of the country, in Siberia, and the Far East. These are various viral fevers and even malaria. Several years ago, there was a local outbreak of malaria in the Moscow region. Mosquitoes can reward their victims not only with viruses, but also with helminths, that is, a parasite. The latest cases are increasing every year.
In fact, this helminth is a dog one. And this is how infection happens. The mosquito drinks the blood of an infected dog and receives a helminth. Then it bites a person and transmits this parasite to him. But since a person is not a dog, the helminth behaves unusually in the human body. He begins to crawl under the skin. “Most often, a helminth, having entered the human body, rushes to the eye area, crawls under the skin of the eyelid, near the eyebrows, and can crawl out from the inner corner of the eye,” explains the chief researcher at the Institute of Medical Parasitology, Tropical and Vector-Borne Diseases, 1st Moscow State Medical University. I.M. Sechenova, professor, doctor of medical sciences, parasitologist at Infectious Clinical Hospital No. 1 of Moscow Alexander Bronstein . “But it can also easily penetrate the genitals and internal organs; in women it can move under the skin of the mammary gland. Therefore, the parasite is called “migratory larva of internal organs” or, scientifically, dirofilaria. In most cases, there is no great harm to health from it. But there were cases when the parasite penetrated the lungs and caused pleurisy, got into the eye, and this can lead to deterioration and even loss of vision.”
Most cases of infection are found where there are a lot of mosquitoes. These are humid lowland areas with a warm climate. For example, in the Moscow region, the most mosquito-infested places are in the Shatursky and Volokolamsk districts; there are many mosquitoes in the Saratov region, throughout the Volga region, in particular in the Astrakhan region, where the Volga delta is located.
Scientists do not know why there are more and more infections every year. Perhaps the reason is climate warming, environmental degradation or an increase in the number of dogs. Of course, you can become a victim of an infectious mosquito in the city. But if you go to mosquito-infested areas, you need to take care of protection.
Mesh, fog or geranium? How to effectively protect yourself from mosquitoes and midges Read more
Why do mosquitoes bite people?
The question is simple, but at the same time, complex. This may come as a revelation to some, but human blood is not the main food item in the mosquito diet. This type of insect mainly feeds on pollen and nectar of plants, and blood is needed exclusively by females to bear new offspring.
Reproduction and birth of mosquitoes
Having received a portion of human blood, rich in proteins, the female mosquito looks for water to lay eggs, which in a short time will turn into pupae, and new mosquitoes will emerge from them. The process of “birth” of new individuals occurs directly in the water. Now do you understand why in summer there are many more mosquitoes near reservoirs than in fields, for example?
Why do mosquitoes bite some people more and leave others alone?
According to scientists' research, mosquitoes choose a victim based on information collected by numerous receptors located on the proboscis. In short, female mosquitoes “smell” a person: his smell, sense his blood type and even the acids, vitamins and other substances that make up it.
According to scientists, mosquitoes are able to smell chemicals such as:
- uric acid and its excess in the body;
- some types of hormones;
- cholesterol;
- carbon dioxide;
- hormones released with human sweat;
- steroids.
Mosquitoes are also able to distinguish blood type and respond to movement or body temperature.
Why do mosquitoes bite some people more often than others?
Many have encountered a situation where, in a large company, mosquitoes bite more of some people, and practically do not touch individuals. And jokes like: “He/she is more delicious” have a certain meaning. The fact is that, given an equal choice at first glance, a female mosquito is more likely to bite a person who has the substances listed in the list above in their blood or on the surface of their skin.
Interesting! The joke that someone is really “tastier” to mosquitoes is not without meaning . But if a person is alone and does not smell of pheromones, the female mosquito will bite him without a twinge of conscience, with all that it entails.
How to distinguish a regular mosquito from a malarial one
On the left in the photo is a malaria mosquito.
It is extremely difficult to distinguish them from each other by appearance, although experts note a number of features.
- The hind legs of malaria mosquitoes are much longer than the front ones.
- Body position, as if upside down (raising the back). Ordinary mosquitoes hold their body straight (parallel to the surface).
- Malaria mosquitoes have dark spots on their wings.
- The whiskers located next to the tubular lip are much shorter in ordinary mosquitoes than in malarial mosquitoes.
A photo of a malaria mosquito gives a complete picture of its difference from a regular one. An interesting feature of malaria mosquitoes is the way they fly up to the victim before biting - performing a kind of ritual dance.
Symptoms of a mosquito bite
Many people, especially seasoned travelers, hardly notice mosquito bites. Also, bites are hardly noticeable in the middle and end of the summer season. The reason is that the body adapts to the bites and intentionally minimizes symptoms.
What do mosquito bites look like?
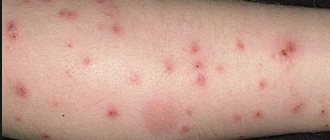
Typically, after a bite, there is a slight swelling on the skin that itches for several hours, sometimes days. But there are people who, due to the body’s increased sensitivity to enzymes injected during a mosquito bite, are more susceptible to these chemicals, resulting in an allergic reaction.
Common symptoms found in most people:
- a mild rash may appear, which will disappear on its own after a few days;
- the bite site is itchy and itchy;
- the size of the swelling can vary from 3 mm to 1 cm, depending on the reaction of the human body to the mosquito enzymes;
- in rare cases, a slight increase in temperature may be observed, but not higher than 37 degrees.
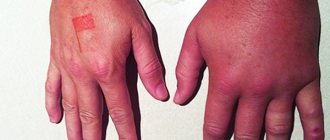
As for people whose bodies react strongly to mosquito bites, they may experience an allergic reaction with the following symptoms:
- A sharp increase in body temperature above 38 degrees.
- Sudden headache.
- Possible dizziness.
- In rare cases, fainting may occur.
- Symptoms of suffocation, nausea and even vomiting are also common.
If you experience at least one of the described symptoms after a mosquito bite, you should immediately contact the nearest medical center.
Methods for treating mosquito bite allergies
It is believed that mosquito bites are minor problems that are practically painless and go away on their own over time. However, there are people in whom the bites of these parasites cause an atypical reaction from the immune system in the form of allergies.
Most often, an allergic reaction to a mosquito bite is not dangerous and is manifested by the appearance of a small papule. But there are times when the skin becomes very swollen and swollen after a bite. In such a situation, visiting a doctor is mandatory.
People prone to allergies should know what to apply to a mosquito bite to prevent it from itching. First, you need to apply a cold compress to the wound, and then treat it with a soda solution (1 teaspoon of baking soda per 200 ml of water) or a weak solution of ammonia. After carrying out such a procedure, the biological fluid contained in the insect’s saliva is neutralized.
If you have an allergic reaction to a bloodsucker bite, your doctor may prescribe antihistamines, such as Suprastin, Fenkarol, Claritin or Tavegil. In particularly severe situations, hormonal (corticosteroid) agents, for example Advantan cream, may be prescribed.
It is very important to choose the right drug if an allergic reaction occurs in a child, because there are a number of drugs that cause complex side effects. Usually, subsequent mosquito bites no longer provoke such a reaction in the body, and very often it does not occur at all. Doctors gave a name to this phenomenon - natural hyposensitization.
Why is a mosquito bite dangerous?
Regular mosquitoes pose no danger to humans unless you are allergic to the enzymes mosquitoes leave behind in your skin. But this is rare, and very rare. For 99.9% of people, Culex Piplens mosquitoes are harmless , literally at all.
But in the rest of the world - Africa, Asia, South America - mosquitoes pose a great danger, sometimes fatal. Let's look at the five types of most common viruses that mosquitoes carry.
Zika virus
The first people to become ill with the Zika virus were residents of Uganda (Africa). In 1947, the virus was first identified and a year later isolated from mosquitoes of the Aedes Africanus species - also known as the African "Biter". Later, the virus was identified in other subspecies of Aedes mosquitoes, but they all live in Africa (Nigeria, Uganda, Gabon, Sierra Leone, Egypt and CAP), as well as in the countries of Southeast Asia (Vietnam, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia ), including India.
Important! If you are going on vacation to one of the popular Asian countries (Thailand, Vietnam and others), you should be prepared to encounter the Zika virus . By the way, there is no effective vaccine or cure for this type of virus yet.
In 2015, the virus was already discovered in South America, French Polynesia, Central America and the West Indies. In 2021, an epidemic of the Zika virus was recorded in South and Central America. This suggests that it only took the virus 60 years to cross the Pacific Ocean. By the standards of human life, this is a long time, but for a population of viruses, 60 years is a very short period.
The main symptoms of the disease are similar to those of dengue fever:
- joint pain;
- high temperature - fever;
- headache;
- fatigue;
- swelling of the joints;
- rash.
The Zika virus is not fatal . To treat symptoms, drug therapy is used, including painkillers, antipyretics and antibiotics. As a rule, after a week, patients recover, simultaneously acquiring short-term immunity to the virus for 6-8 months.
Zika virus
However, if a mosquito with the Zika virus bites a pregnant woman, the consequences will be catastrophic. The virus has an extremely negative effect on the development of the fetus , which leads to developmental abnormalities. The born child will most likely have disabilities.
Important! If a woman is pregnant, you should not go on vacation, especially to Asian, South American and African countries. The Zika virus may not be a big problem for humans, but the health of a child is at risk.
Chikungunya virus
Chikungunya is a young and not yet very widespread virus. The virus is transmitted through the same mosquitoes of the Aedes species, but other subspecies - Aegypti and Albopictus. By the way, mosquitoes of these species also carry other diseases.
The habitat of mosquitoes with the Chikungunya virus is concentrated in countries located in the Indian subequatorial zone, Asian countries and Africa (closer to the equator). It is noteworthy that in recent years, outbreaks of the Chikungunya virus disease have been recorded in European countries and North America (USA).
Chikungunya virus distribution map
Interesting! The larvae of potentially dangerous mosquitoes are gradually spreading around the world due to globalization and the active development of passenger and cargo transportation.
The incubation period of the virus usually lasts 2-3 days, and after that the temperature rises sharply, up to 40 degrees. Other symptoms:
- muscle and headache;
- rash;
- malaise;
- fatigue;
- nausea;
- severe joint pain.
As a rule, after 5-10 days the body defeats the virus, but pain in the joints and muscles can last for another month. Cases have been recorded where pain lasted for more than a year.
Dengue fever
Those who like to relax in India, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia or Malaysia are probably familiar with Dengue fever, which a person becomes infected with through mosquitoes of the Aedes Aegypti species. Bats or monkeys can also become sources of the disease, but rarely. The main carrier of the Dengue virus is the mosquito.
Pathogenesis of Dengue fever
Dengue fever can be contracted in 110 countries. These are mainly Asian countries (southeast), India and the equatorial region of Africa. The virus is also found in South America. Every year, about 20 thousand people die from dengue fever . The number of infected people per year is from 50 to 500 million.
Typical symptoms of Dengue fever:
- increase in body temperature up to 40 degrees;
- redness of the eyeballs;
- lack of appetite, which can lead to anorexia;
- severe pain in bones, muscles and joints;
- increased heart rate at first and slower after 3-4 days of illness;
- sudden loss of strength;
- insomnia;
- nausea;
- swelling of the face;
- an itchy rash that may cover most of the body;
- confusion.
The Dengue virus also has a more complex form - Dengue hemorrhagic fever , which is found in Vietnam, Thailand and the Philippines. The symptoms are the same, but they are much more pronounced. And all this thanks to mosquitoes of the Aedes species (Bites).
Important! There is no vaccine for dengue fever. Treatment usually uses painkillers, antigestamines and vitamins.
West Nile fever
The relatively young West Nile virus is considered one of the most dangerous diseases transmitted by mosquitoes. According to statistics, its mortality rate is about 5% . That is, every 20th infected person dies.
West Nile fever is an acute viral disease that is usually transmitted by mosquitoes, but can also be spread by ticks: agrass and ixodid ticks. The virus causes inflammation of the meninges, and sometimes meningoencephalitis can develop (inflammation of the brain and bone marrow, which can cause paralysis).
The virus is often found in North America (USA). There have been cases of a virus outbreak in Serbia. As for Russia, outbreaks of West Nile virus were observed from 1999 to 2013. True, the epidemic was rather local and insignificant (only about 2-3 thousand sick). The regions where the disease spreads are Volgograd, Rostov, Voronezh, Astrakhan regions and Krasnodar Territory.
Why is West Nile fever dangerous?
There is no vaccine for West Nile virus . Treatment usually takes place in a hospital with the use of antipyretic and painkillers. Patients are also prescribed courses of vitamins to support the immune system.
Malaria
Malaria is a vector-borne infectious disease caused by the bite of an anopheles mosquito. The causative agents of the disease are parasitic protists, most often Plasmodium falciparum.
From 150 to 500 million cases of infection are registered annually. In approximately 800 thousand cases, malaria is fatal .
Important! Over the past 20 years, the number of cases and deaths from malaria has been gradually decreasing. Mainly due to the distribution of the malaria vaccine.
Malaria mosquitoes of the Anopheles family live in almost all climatic zones, except for the far North and Antarctica. However, potentially dangerous regions - countries located in the subequatorial and equatorial zones - are smaller in the humid subtropics. There, the malaria mosquito is commonplace.
Pathogenesis of Malaria
In Russia, a difficult epidemiological situation with malaria was observed from the beginning of the 20th century until the 50s, when the number of cases approached 9 million people. However, the drainage of swamps and swampy areas, coupled with the distribution of malaria vaccines, has reduced the number of patients sharply. At the moment, isolated cases of infection are recorded annually in Russia.
Symptoms of malaria are similar to other fevers caused by mosquitoes:
- pain in joints and muscles;
- fever (high temperature - 40 degrees);
- hemolytic anemia;
- wet cough;
- convulsions;
- Strong headache;
- chills;
- vomit;
- increased hemoglobin levels in urine;
- increase in the size of the spleen and liver.
There are three types of malaria:
- Three-day is the rarest type of disease. It goes away within three days without any severe symptoms.
- Quadrilateral malaria usually resolves after 3-4 days without serious symptoms or complications.
- Tropical malaria is the most dangerous and common type. I detect tropical malaria in 90% of cases.
The immune response against malaria takes a very long time to develop and is ineffective. Therefore, even after complete recovery, re-infection is possible.
As of 2021, a malaria vaccine exists and is widely used. However, its effectiveness fluctuates around 55% . A better vaccine is already being tested, the effectiveness of which, according to doctors, will be at least 92%.
Important! If you are going to visit one of the countries located near the equator (India, equatorial countries of Africa, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Malaysia and others), get vaccinated against malaria. Vaccination will not only help you avoid ruining your vacation, but it may also save your life.
Should we be wary of mosquitoes that carry dangerous diseases in Russia?
Epidemiologists have reported the possible spread of deadly tropical diseases in Russia that are carried by certain types of mosquitoes. According to them, dangerous insects arrived from Egypt and Southeast Asia and became widespread along the entire Black Sea coast and in Crimea. And in the future they may end up in Central Russia. Let's figure out whether a mosquito bite really poses a mortal danger and how to protect yourself from the squeaking threat.
Are dangerous mosquitoes attacking?
Photo: depositphotos/abjola
Specialists from several Russian medical institutes conducted a study, the results of which revealed that two species of mosquitoes that can carry dangerous tropical fevers have spread on the Black Sea coast of the Krasnodar Territory and in Crimea - Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Moreover, in their opinion, insects not only settled in the south of the country, but are moving into Central Russia.
The first species is distinguished by bright white markings on its legs and stripes of the same color on its back. The second can be recognized by its spotted belly and black and white stripes on its legs. The bite of such insects can cause an epidemic of Dengue, Chikungunya, Zika and yellow fever viruses. According to experts, all these diseases are deadly.
Scientists believe mosquitoes are migrating north from Egypt and Southeast Asia due to global warming. And according to forecasts, by 2050 these insects will spread even to Sweden.
However, Rospotrebnadzor for the Krasnodar Territory refuted the scientists’ fears and stated that “there is no talk of any epidemic.”
The number of people sick with one of the most dangerous fevers - West Nile - is seven people in the Krasnodar Territory. This number of cases is recorded every year, and not a single death. The same thing with yellow fever - isolated cases. press service of Rospotrebnadzor for the Krasnodar Territory
They also emphasized that the increase in the mosquito population is associated with a cool and at the same time humid summer. When air temperatures exceed 32 degrees, mosquito larvae die.
“Nothing has changed here, we have a lot of mosquitoes that carry vector-borne infections, they have lived and are living with us all the time. The geophysical position of the Krasnodar Territory is such that it prevents the spread of many infections. If in other countries mosquitoes bite and infect, the situation in our region is not the same,” emphasized the regional Rospotrebnadzor.
How to protect yourself from mosquitoes?
Photo: depositphotos/tepic
Doctor of Medical Sciences and specialist in especially dangerous infections Vladislav Zhemchugov told Moscow 24 that the mosquitoes that were identified in the Krasnodar Territory are not dangerous for Russians. In addition, according to him, insects will die closer to winter.
“All mosquitoes of the Egyptian and other species that carry equatorial fevers from Dengue to Zika and Chikungunya become dangerous only if they have sucked the blood of a patient. But since people do not suffer from such fevers in the North Caucasus and on the Black Sea coast, there is no danger,” the specialist explained.
Zhemchugov added that infected mosquitoes usually end up in new regions, becoming accidental passengers, for example, on air transport, but take root only in places with a suitable climate.
“As a rule, they travel in transport: in airplanes, cars, on ships. An indicative case was in the United States, when mosquitoes carrying West Nile fever arrived there. Until that time, there was no virus there,” the expert noted.
Mosquitoes only take root where there are warm winter conditions, such as Spain and France. Where the winter is cold, they die. Vladislav Zhemchugov
Specialist in especially dangerous infections
The interlocutor of Moscow 24 added that you should still be wary of mosquitoes, but only when traveling in hot countries.
“Good hotels have had electronic insect repellents for a long time. There are also fumigators, ointments, and repellents that repel or kill them. Abroad, you need to make sure that there are no insects in your home,” Zhemchugov emphasized.
Photo: depositphotos/Maridav
The expert added that at the first signs of the disease, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor to establish a diagnosis, since “lost time at an early stage can be fatal.”
Vadim Maryinsky, a researcher at the Department of Hydrobiology at the Faculty of Biology of Moscow State University, also added that it is very difficult for a non-specialist to distinguish an infectious mosquito from a non-infectious one.
Blood-sucking mosquitoes are a huge family, there are many genera and species, and every summer we are bitten by a wide variety of mosquitoes. Some look more like immigrants from the south, some less so. You shouldn't look at them after every bite. Vadim Maryinsky
Researcher at the Department of Hydrobiology, Faculty of Biology, Moscow State University
At the same time, according to him, the likelihood of the spread of tropical diseases in Russia is extremely low.
“For example, if a person flies to Madagascar, is bitten by a malaria mosquito there, gets sick with malaria, flies here, does not have time to diagnose him in time, is bitten by our malaria mosquito here and then bites another person, then he can transmit malaria further. Local outbreaks of malaria do occur, but only in such situations,” Maryinsky explained.
Treatment methods for mosquito bites
A mosquito bite causes the familiar characteristic swelling with redness, which itch incredibly hard and for a long time. To get rid of these symptoms, you can use a special ointment or gel that is sold at the pharmacy.
But most often, with ordinary mosquito bites, the “victims” use folk, proven remedies. So, what can you do to make itching, redness and swelling go away faster:
- first of all, smear the bite area with your own saliva, this will calm the itching a little;
- you can also use a vinegar solution;
- Citric acid helps a lot;
- use any alcohol-containing liquids (vodka, perfume or, in fact, medical alcohol);
- a solution of soda also helps well (1 teaspoon in half a glass of warm water);
- There is an opinion that toothpaste also helps;
- aloe, mint leaf or crushed plantain.
If more alarming symptoms appear, such as dizziness, nausea, difficulty breathing, etc., consult a doctor immediately.
Important! Under no circumstances should repellents or insecticides be used as a remedy for mosquito bites. This will cause further skin irritation and possibly swelling.
How to prevent eye swelling after a mosquito bite?
Since the skin around the eyes is very thin, sensitive and has the ability to stretch well, a mosquito bite in this area can cause a lot of swelling. To avoid such consequences, you need to rinse your eyelid with cold water immediately after an insect attack. Then you should prepare a weak solution of soda (0.5 tsp per 200 ml of water) or an aqueous solution of calendula or chamomile. After moistening a cotton swab in one of these infusions, you should apply it to the bite site for 1-3 minutes.
If a mosquito bites your eye while relaxing in nature and it is not possible to prepare one of the above remedies, you can simply apply a cloth soaked in cold water to your eyelid for 15-20 minutes. It is advisable to stay in the shade or some cool place at this time. For greater effectiveness, it is better to sit down or take a reclining position so that at this time your head is slightly raised.
If all these methods do not help prevent swelling, then you need to seek help from a medical institution - the doctor will recommend medications that can be for both internal use and external use. Even if the eye is very itchy, it is important not to scratch it, since dirt that gets on the mucous membrane can cause even greater swelling or suppuration of the wound.
Preventive methods of protection
Preventive methods of protection against mosquito bites are any means that will help limit human contact with insects. This includes various repellents and insecticides that repel mosquitoes from humans, all kinds of smoldering sticks and circles. These products are sold in many stores, including supermarkets.
As for the home, it is better to have mosquito nets on the windows. If the windows are old, you can do it yourself. The main thing is to make sure that the mosquito cannot bite, since one of them may well turn out to be malarial. No bite - no problem .
And finally, advice for those who are going to hot southern countries: before the trip you should think about getting vaccinated against malaria. It is also important to take out insurance that includes a possible hospital stay in a local hospital in case of infection with one of the viruses described above.
Prevention of bites
There are special preventive measures that it is advisable for everyone to adhere to. And people suffering from allergies to mosquito bites need to follow them strictly:
- according to scientific research, daily intake of vitamin B1 somewhat changes the natural smell of a person, which makes it not so attractive to insects as a food source;
- If there is standing water near your house, you should get rid of it immediately, since mosquitoes lay eggs in it. It is imperative to clean the ditches and constantly change the water in children's pools;
- All cracks and holes in doors and windows must be carefully sealed. It is important to take care of installing mosquito nets;
- When going out for an evening walk, you must use any effective mosquito repellent. For example, you can purchase DEET repellent containing picardin or eucalyptus oil. In addition, you can use citronellas - special candles to protect against insects;
- It is better to choose clothes with long sleeves. Instead of shorts, it is better to wear thin trousers, and a wide-brimmed hat can protect your neck from bites;
- It is advisable to avoid cosmetics that have a strong odor. After all, some types of perfumes, hairsprays, eau de toilette, soaps and deodorants attract insects even more.
If you still fail to protect yourself from insects, the blisters from mosquito bites become significantly inflamed, and the itching does not go away for a long time, you need to seek professional help at the clinic.