Author:
surgeon, ophthalmologist Sergey Pankratov
1 minute
3285
Although bees and wasps are close relatives, they sting differently. If you are bitten by a bee, this is primarily bad news for the bee itself, since its sting has curved teeth that become firmly stuck in a person’s skin. A bee that has lost its sting will die very soon. But the wasp has a smooth sting that can be easily removed after a bite, and can attack several times. According to the Schmidt Pain Index, developed by entomologist Justin Schmidt, due to the characteristics of the venom secreted, the wasp sting is one of the most painful compared to other insects.
Why is a stinging insect bite dangerous?
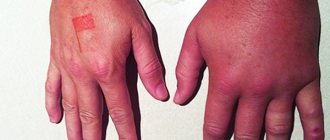
The danger of a bee, wasp, bumblebee or hornet sting lies in the reaction of the body affected by the insect attack. Therefore, it is not the amount of poison introduced that is important, but the degree of sensitivity of a person to this substance.
For a person suffering from allergies, one bite is enough for a violent allergic reaction to occur, which can manifest itself as the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a rash over a large area of the body, the inflammation is itchy and painful;
- headache and dizziness, loss of coordination of movements;
- severe swelling of the face and limbs;
- nausea, vomiting;
- labored breathing;
- convulsions.
Multiple bites from wasps, bees, and bumblebees often lead to death. Therefore, if a tourist knows that he has an allergy to insect venom, he always has a syringe with adrenaline and/or prednisolone in his first aid kit.
Remember! If assistance is provided for a hornet or other stinging animal, it is strictly forbidden to give the victim alcohol or cool the bite site with cool clay. In addition, you should not chase and kill the insect. You, without knowing it, may be close to the hive. Within a few minutes, a whole swarm will come to the aid of the relative who attacked you.
Blog
First aid for a bee sting
Almost every person has encountered bees, since such insects are quite widespread in our country and can be found almost everywhere. In most cases, the bite of such an insect does not lead to any serious consequences - the bite site hurts for some time, and then goes away without visible consequences or harm to health.
However, there are situations when a bite causes a severe allergic reaction, during which a person needs urgent medical attention. Of course, you shouldn’t just sit and wait for the ambulance to arrive - you need to start providing first aid to the victim as soon as possible, as this will significantly increase the chance of a successful completion of the situation. How to provide first aid for a bee sting?
Step 1 – Introducing adrenaline into the body
The first thing to do in such a situation is to inject several cubes of adrenaline into the human body. If a person has severe allergies, he must have the injection with him, otherwise he must go to the nearest pharmacy to purchase such a medication. The drug must be injected into the outer thigh.
You should not inject intravenously, into the gluteal muscles or into the arms, as this can lead to significant damage to soft tissue, which will lead to the appearance of bruises, and the help will be less effective. If a person does not feel better after a few minutes, it is possible to reintroduce adrenaline into the human body.
Step 2 – Correct position of the human body
It is very important to place the victim in a horizontal position so that he can breathe comfortably and does not cause discomfort or unpleasant sensations. You can put something under your head, but only so that nothing makes breathing difficult. It is important to remove all tight clothing and limit the person's consumption of water and food, as this may cause vomiting, which will worsen the condition.
Step 3 – Indirect cardiac massage
In the event that a person is unconscious and has no pulse or breathing, it is necessary to perform an indirect cardiac massage procedure; first aid must be provided before the ambulance arrives, since only in this way is there a chance that the victim will survive and not be harmed significant harm to human health.
Products for beekeeping in Samara
Hornet sting: what to do
Encountering hornets is much more disturbing than their smaller cousins, bees and wasps. You can distinguish a hornet from a wasp, first of all, by its large size (the hornet is twice as large), as well as by the characteristic brown spot in the head area.
When attacking, the hornet does not leave a sting in the victim’s body; the insect’s venom immediately enters the bloodstream. In rare cases, the sting breaks off and fragments remain in the skin. The hornet stings are very painful; the bite site becomes very red and swollen.
Even those people who are not allergic to bee venom may need urgent help for a hornet sting. Within an hour and a half, the first signs of intoxication with hornet venom appear.
First aid for a hornet bite should be provided quickly and consistently:
- examine the bite site. If there is a piece of the sting left, carefully remove it;
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic or wash with soapy water. There is a high risk of infection, since the hornet sting contains pathogenic microbes;
- even if a person has been bitten by a hornet for the first time, and he does not know about a possible reaction, he must take an antihistamine (suprastin, tavegil);
- do not leave the victim unattended for the next three hours and monitor his well-being. If the condition worsens, the person is taken to the nearest medical center as quickly as possible. As soon as first aid has been provided for a hornet bite, the patient is placed on a stretcher, his head is turned to the side (in case of vomiting) and transferred to the hospital.
Bees, wasps, hornets
Bee venom, due to its high content of physiologically active components, can cause acute intoxication, especially in cases of increased sensitivity of the body to it.
The effect of the poison depends on several factors:
- From his dose;
- Localizations;
- Individual sensitivity.
On this topic ▼
How to defend yourself when attacked by a dog
Apitoxin has a detrimental effect on the state of cardiac activity, affects metabolism, the nervous and endocrine systems. Pregnant and menstruating women tolerate intoxication very hard. There are often cases of acute allergic reactions, such as Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock. When stung into a blood vessel, even a single one, the reaction is immediate and pronounced.
Venom scale depending on the number of bites:
- A one-time sting of up to 5 bees is a local reaction of the body;
- A one-time sting of 10-20 bees – local plus general resorptive manifestations;
- A one-time sting of 20-50 bees is a phenomenon of severe intoxication;
- A single sting by more than 100 bees is death.
Clinical manifestations of bites
Can be divided into 2 large groups:
Local:
- Sharp, burning pain at the site of the bite;
- Increasing acute swelling of nearby tissues, reaching its maximum development in 10-15 minutes;
- Regional lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes adjacent to the site of the bite).
Single bites result in complete recovery after 24-48 hours.
General toxic:
- Dizziness;
- Weakness;
- Chills;
- The phenomenon of urticaria;
- Convulsive contractions of the muscles of the face and limbs;
- Dyspnea,
- Feeling of tightness in the chest;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Loose stools
- Increased body temperature.
The appearance of a coma and collapse is possible. Allergy to a bee sting is also quite common. Apitoxin can cause damage to parenchymal organs and paralysis of the respiratory center. Bee stings in the area of the tongue and pharynx are especially difficult to bear. Clinical symptoms are increasing every minute. Swelling of the larynx and pharynx develops with the threat of asphyxia, which can subsequently lead to death.
If a person turns red or has trouble breathing, call an ambulance. The consequences can be very serious, including death.
First aid
What does an insect look like?
- Inspect the site of the bite. It usually looks like a papule raised above the skin, in the center of which there is a sting. If the sting is not visible, then perhaps you were bitten by a wasp or the sting is inside the wound.
- Remove the bee sting. The sting includes poisonous glands, a poisonous vesicle, and a nerve ganglion. For this reason, the sting is removed with tweezers or a needle treated with alcohol or any antiseptic so that the poison is not squeezed into the tissue.
If a bee stings, DO NOT squeeze out the sting.
Never do this! If you start squeezing out the sting, the poison that is still in the sac can penetrate your body.
- After removal, the wound is treated with chlorhexidine or any skin antiseptic.
- Apply cold to the bite site (wet towel, piece of ice in a sterile napkin);
- Apply a piece of cloth soaked in a soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of water) to the wound;
- You can treat the bite site with Fenistil ointment. It is also recommended to take any antihistamine.
Another remedy for bee stings is to apply baking soda to the sting site. She really helps. Mix baking soda with water to form a thick paste and apply as soon as possible. "The bite is acidic, and if you apply the baking soda as quickly as you can, it will neutralize that acid," says Stephen Purcell, D.O., chairman of dermatology at the Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine. If you don't have baking soda, dry the affected area and rub it with aspirin; aspirin will help relieve swelling, pain and inflammation.
With the development of general toxic phenomena, a pastel regime and a doctor’s consultation are indicated. If after 24-48 hours the inflammation at the bite site has not decreased and general toxic symptoms increase, you should immediately seek medical help. You can read about how to call an ambulance in our article.
First aid for a bumblebee, bee, wasp bite
First aid for a bee sting is to remove the sting, at the end of which there is a capsule with poison. If it is not removed in time, the poison will continue to be injected under the human skin. The sting of a bumblebee and a wasp, as a rule, remains with insects, since it has a smooth surface and does not cling to the skin. In any case, the bite is checked for the presence of foreign fragments.
For most people, the bite site becomes swollen and red. The swelling may last for several hours. In the absence of allergic reactions, first aid for a wasp and other stinging insects is limited to relieving the painful symptom. To do this, ibuprofen or aspirin is taken orally. To partially relieve swelling, wrap the stung area with a towel soaked in cold water.
If the itching does not stop the next day, experienced hikers advise preparing one of the following mixtures:
- soda solution - 2 tbsp. spoons per liter of water. Apply to the bite 5 times a day;
- crush a tablet of aspirin and activated carbon, mix well, apply to a damp cotton swab. Apply 3-5 times a day.
If the swelling increases and there are no means of quick resuscitation at hand, the procedure for what needs to be done after a bumblebee, wasp and bee bite is exactly the same as in the case of a hornet bite.
What should you do if you are bitten?
Carefully examine the bite site and check for the presence of an insect sting. If the sting remains, you need to carefully pull it out with tweezers. Treat the bite site with disinfectants - hydrogen peroxide, alcohol. If you don’t have these products on hand, you can use plain water with salt.
The bites of wasps and hornets are especially painful. They can cause severe swelling and pain. To relieve these symptoms, apply ice or a cloth soaked in cold water to the bitten area.
When a person with a predisposition to allergies has been exposed to vinegar, it is imperative to take an antihistamine (suprastin, tavegil, claritin and others). If he is not at hand, immediately call an ambulance.
Help with a tick bite
Its bite can be very dangerous. This insect is a carrier of dangerous infectious diseases (encephalitis, tularemia, tick-borne typhus, hemorrhagic fever and others).
Of course, it is better to remove a tick in a medical facility. If you are far from the city, you can pull it out yourself. To do this you need tweezers. You need to pull out the tick slowly, pulling it out rather than pulling it out. If you were unable to completely remove it, the remains of the tick should be pulled out like an ordinary splinter. Treat the wound with alcohol, iodine or brilliant green. To be sure that you were bitten by an uninfected tick, put it in a jar and take it to the laboratory for analysis.
Help for snake bites
The bite of a non-venomous snake is not dangerous to humans; the bite marks on the skin just need to be treated with a disinfectant.
It's another matter if you were bitten by a poisonous snake. Snake venom can not only make you feel worse, but can also be fatal. Therefore, it is urgent to bring the person to a medical facility, where he will be given an injection of antidote. But before the doctors arrive, first aid must be provided.
In the first minutes, the victim does not feel pain, then symptoms of pain and burning appear. Lay the bitten person down and do not let him walk or move to stop the spread of poison through the bloodstream throughout the body. Try to calm him down and not let him panic, this will also increase blood flow. Clean the wound with warm water and soap and apply a loose, clean bandage. You can apply cold.
What can't you do?
- apply splints and tight bandages over the wound;
- make incisions and cauterize the wound, this way you can only increase the infection;
- Do not suck out the poison; this is an ineffective method; it can be used if there is no damage to the oral cavity.
Help with animal bites (cats, dogs)
Most often, people get bitten by dogs, less often by cats, and very rarely by wild animals. Animals are carriers of infectious diseases such as toxoplasmosis, rabies and others.
To reduce the risk of infection, the bite site should be immediately washed with running water to remove the animal's saliva from the wound. Treat the skin around the bitten area with alcohol or iodine, apply a clean bandage and take the victim to a doctor. Only he can decide whether to vaccinate the victim against rabies. Of course, it is better to find the owner of the animal to make sure the health of his pet. If the animal is homeless, it will have to be vaccinated.
Remember!
In most cases, bites can be avoided. Do not tease animals, do not provoke the snake's aggression. Animals will usually move out of the way on their own. When you are going for a walk in the forest, follow safety rules and wear high rubber shoes and long sleeves.