- Wild animals
- >>
- Insects
The earwig is a predatory insect with omnivorous feeding habits, which sometimes lead to significant damage to some commercial crops. Most often, they contaminate vegetables by getting inside them. However, they can be useful in some cases due to their predatory habits. The name refers to the legend that it can crawl into a person's ear and gnaw through the eardrum. It is curious that such an explanation is also available in the English-speaking segment. However, such cases have not been recorded.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Earwig
The earwig survives in a wide range of environments and is a fairly common house insect. Today, the name earwig (in English earwig) is interpreted as referring to the appearance of the hind wings, which have features unique and characteristic of these insects and resemble a human ear in an expanded form. The species name is a specific reference to this feature.
The earliest fossils of earwigs date back to the end of the Triassic period. A total of 70 specimens were found. Some anatomical features of modern earwigs are not found in the earliest fossils. Their claws did not bend completely, like those of modern representatives. Ancient insects looked like modern cockroaches. Their trace was lost in the sediments of the Permian period. Representatives of this group are not found in the Triassic period, when the evolutionary transition from Protelytroptera to earwigs may have occurred.
Video: Earwig
Archidermaptera is thought to be sister to the remaining groups of earwigs, the extinct group Eodermaptera and the living suborder Neodermaptera. The extinct suborders have tarsi with five segments (as opposed to the three found in Neodermaptera), as well as unsegmented cerci. No fossils of Hemimeridae and Arixeniidae are known. Like most other epizootic species there are no fossils, but they are probably no older than the late Tertiary.
Some evidence of early evolutionary history is the structure of the antennal heart, a separate circulatory organ consisting of two ampoules or vesicles that are attached to the frontal cuticle at the bases of the antennae. These features have not been found in other insects. They pump blood through elastic connective tissue rather than muscles.
Appearance and features
Photo: What an earwig looks like
Earwigs are brownish-red in color and have elongated bodies ranging from 12 to 15 mm in length. They are equipped with 3 pairs of legs that are yellowish-brown in color. The elongated, flattened brownish body has a shield-shaped front back. The insect has two pairs of wings and thread-like antennae about 12–15 mm long. Adult males vary in body mass and head width. Common earwigs are known for the set of pincers that protrude from their abdomen and are used for protection and in mating rituals.
The forceps show sexual dimorphism, with males being strong, longer and more curved than females. Women's forceps are about 3 mm long, less durable and straight. The European earwig has two antennae, 14 to 15 segments long, which contain many important sensory organs, as well as a fully developed set of wings.
The long, segmented filaments are used during mating, feeding, and self-defense. Females also have a tegmena about 2 mm in length. The hind wings are membranous, wide with lobular veins. The earwig stays almost vertical in flight. When folding its wings together, the insect folds them twice. Despite its rather developed wings, the earwig uses them extremely rarely, preferring to move on its limbs. The legs are of a running type and consist of three segments.
Nutrition
These insects are unpretentious and omnivorous. Favorite foods are fruits, vegetables, plants, especially garden flowers. They do not disdain the remains of small insects. Often, in search of food, they can crawl into a residential building, where they feed on food scraps from the table, destroy indoor plants, and can crawl into a wardrobe and damage clothes.
Earwigs do not like daylight and crawl out in search of food at night. During the day they gather in a group under the bark of trees, in the cracks of boards, under stones, preferring dark and damp shelters. In homes they can be found in bathrooms, toilets, and basements.
Where does the earwig live?
Photo: Earwig in Russia
Earwigs are native to Europe, East Asia and North Africa. Today they can be found on every continent except Antarctica. The geographic range of the species continues to expand. They have even been found on the island of Guadeloupe in the Pacific Ocean. In Russia, the earwig is seen east to Omsk and in the Urals, and in Kazakhstan, the range extends to the Volga interfluve, south to Ashgabat, including the Kopetdag Mountains. The earwig was introduced to North America in the early twentieth century and is now common across much of the continent.
Fun fact: In North America, the earwig has two related subspecies that are reproductively isolated. Populations in cold climates generally have one clutch per year, producing species A, while populations in warmer climates have two clutches per year, producing species B.
European earwigs are terrestrial organisms that live primarily in temperate climates. They were originally discovered in the Palearctic and are most active when daytime temperatures have minimal fluctuations. The insects are found over a very wide geographic range and at altitudes up to 2824 m. During the day, they prefer places that are dark and damp to hide from predators.
Their habitat includes forests, agricultural and suburban areas. During the mating season, females prefer nutrient-rich habitats as a place to burrow and lay eggs. Hibernating adults can tolerate cool temperatures, but their survival is reduced in poorly drained soils such as clay. To avoid excess moisture, they tend to the south side of the slopes. Sometimes they also occupy the hollow stems of flowers.
Interesting Facts
Let's consider a number of some interesting information relating to the description of the appearance of the insect, its lifestyle and certain features:
- some individuals reach a length of up to five or even eight centimeters;
- earwigs can produce and secrete foul-smelling substances that can deter predators; Earwigs themselves are considered both predatory and herbivorous:
- they are able to feed on small insects, plants and even moldy fungi, dead rotting materials;
- insects are characterized by a mainly nocturnal lifestyle, they prefer a damp, dark and humid environment, and therefore live under leaves, inside hollow trees, as well as in the cracks of houses, through which they penetrate inside;
- for the winter, earwigs burrow 1-2 meters into the ground;
- at one time the female is able to lay from 3 to 50 eggs;
- female earwigs are recognized as the most caring insects, since they lay eggs in a pre-arranged place, regularly clean it, they feed the cubs with regurgitated food, and if it turns out that the female dies while nursing the offspring, then the cubs immediately eat her;
- Ticks live for about one year.
Video
Tick-borne encephalitis 2020
Hogweed Law 2018
Destruction of bedbugs in Moscow
The earwig is a small, but very frightening insect that is found in all areas of Moscow and the Moscow region. It is often confused with another pest that is very similar to it - two-tailed. The differences between them are often difficult to detect, even looking at static photographs, not to mention a living individual quickly moving somewhere.
- According to the biological classification, the double-tailed bird is included in a different order from the earwig.
- These insects reproduce in different ways.
- They have overlapping but still different dietary preferences.
- The earwig can fly, but the double-tailed bird cannot.
- The forked tails of these insects have a different structure and purpose from each other.
This is not a complete list of insect differences, but it will be very difficult to detect them with the naked eye without special knowledge, and it is not necessary if you do not have a scientific entomological interest. In order to avoid being harmed by earwigs or earwigs, it is enough not to touch the insects with your bare hands. They do not attack people, so they only bite in defense. If you are looking for how to get rid of earwigs, then for this it is also not necessary to distinguish them from two-worts - the methods of destruction for these two insects will be identical.
What does an earwig eat?
Photo: Common earwig
Earwigs are active mainly at night. This insect is an omnivore, feeding on a variety of plant and animal matter. Although the insect's predatory habits are somewhat compensated by eating plant matter, they can sometimes cause significant damage to vegetables, fruits and flowers. Beans, beets, cabbage, celery, cauliflower, cucumber, lettuce, peas, potatoes, rhubarb and tomato are among the vegetable crops that are under attack. Although earwigs are considered scavengers and predators. They feed with their chewing mouthparts. They are known to feed on:
- aphids;
- spiders;
- larvae;
- mites;
- insect eggs.
Their favorite plants are:
- white clover (Trifolium repens);
- medicinal grasshopper (Sisymbrium officinale);
- dahlia (Dahlia).
They also like to eat:
- molasses;
- lichens;
- fruits;
- fungi;
- algae.
These insects prefer to eat meat or sugar rather than natural plant material, although plants are the main natural food source. Earwigs prefer aphids to plant material. Adults eat more insects than young ones. Among the flowers most often injured are dahlias, carnations and zinnias. Damage to ripe fruits such as apple, apricot, peach, plum, pear and strawberry is sometimes reported.
Although earwigs have well-developed wings, they are excessively weak and rarely used. Instead, earwigs use people's clothing, commercial goods such as lumber, ornamental shrubs, and even bundles of newspaper as their primary mode of transport. They often consume vegetables and animal matter in equal proportions.
Prevention of the appearance of the parasite
It is unlikely that you will be able to avoid an encounter with an arthropod insect: the two-tailed insect often ends up home with grapes, vegetables, herbs, where it is easy to hide from the gaze of an inattentive buyer. The country house is also full of secluded corners where the earwig lives. But you can reduce the likelihood of active reproduction in your garden and in your apartment if you follow a few rules.
Recommendations for summer residents and city residents:
when choosing vegetables, fruits, berries, leafy greens, you need to carefully check whether there are arthropod insects among the bunches of grapes or tops; at the dacha you will have to work hard to remove fallen leaves from the area in time so that the earwig has nowhere to hide and feed; When an “uninvited guest” with sharp “swords” on the back of the body appears in the apartment, you need to be more careful about cleanliness, sweep away all the crumbs from the table, and close the jars of water. Leftover food is a tasty morsel for the earwig: you should always remember this; Excessive humidity in the room is the optimal environment for insect reproduction. If the two-tailed bug breeds, it will be difficult to get rid of it
To prevent the appearance of double tails, you cannot “breed” dampness in the apartment; attention to indoor plants is a condition under which the risk of the appearance and reproduction of harmful insects is reduced several times. The more flowers there are in the room, the higher the risk that one or two individuals or larvae will remain among the greenery
Flower growers should regularly inspect leaves, buds, and check the top layer of soil in the flowerpot. The earwig is a larger insect and is easier to detect than other pests (for example, the dangerous spider mite measures no more than 1 mm); tin can trap. Open the container, remove the contents, wash, dry, pour in vegetable oil, place around the apartment. The two-tailed fish will crawl inside, fall into the oil and not get out.
If an adult earwig is found on ornamental plants in an apartment or among garden beds, you need to immediately inspect the remaining plants in order to get rid of the larvae in time and destroy other insects. Traditional methods and chemicals are suitable for processing. The more the bivost has multiplied, the more powerful the drug should be.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Earwig insect
Earwigs are nocturnal. They hide during the day in dark, damp places such as rocks, plants, huddles, fruits, flowers and other similar places. They emerge at night to hunt or gather food. They are weak flyers and therefore move mainly by crawling and being carried by humans. Earwigs can be considered either solitary or colonial insects. During the mating season, females live alone, but during other months of the year they tend to gather in very large groups.
Earwigs are considered a subsocial species because they provide parental care to their children. When common earwigs feel threatened, they use their pincers as weapons to defend themselves. Adult earwigs release a pheromone that attracts other earwigs. Nymphs also release pheromones that entice mothers to care for them. The tongs are also used as a means of communication during mating and exhibit threatening behavior.
The nighttime activity of earwigs depends on the weather. Stable temperatures stimulate activity, but extremely high temperatures are discouraged. High relative humidity suppresses movement, while higher wind speeds and greater cloud cover stimulate earwig activity. They produce an aggregation pheromone in their excrement that is attractive to both sexes and nymphs, and secrete quinones as defensive chemicals from abdominal glands.
Insect control methods
Given that both the common and coastal earwigs can cause serious damage to farmland, people who grow plants need to know how to get rid of these creatures. If these creatures have appeared in a house or on a personal plot, in order to eliminate them, it is first necessary to thoroughly clean the surrounding area of plant debris, as well as stones and other debris. In addition, when the question arises of how to deal with doubletails and earwigs, you need to pay attention to weeds. It was noted that in clean areas these creatures are found much less frequently. Among other things, you can place traps made of wet rags in visible places; it is in them that insects will gather during the daytime.
These creatures do not like the smell of a bite, so to prevent their occurrence, you can spread sponges soaked in this substance over the area. If the number of earwigs in the area is too large, you can resort to spraying the plants with neonicotinoids, hyperthroids and organophosphorus compounds. To prevent common and coastal earwigs from appearing on your property in the future, you should carefully dig up your garden plot in the fall. If your living space is located near a body of water, coastal earwigs may be present in the house. In this case, you should clean thoroughly. In addition, all cracks and pipe leaks must be eliminated. This will make the space in the house less attractive to these creatures. Since it is not always possible to get rid of these creatures in this way, you can place bait with boric acid in the house.
The common earwig (two-tailed earwig) is a small insect with processes at the end of the abdomen (cerci). The pest lives in private housing and beyond: gardens, vegetable gardens. If there are few insects, they provide some benefit. A large population greatly harms plants and fruits.
The insects represent the order Leatheroptera. The body is characterized by a brown color, oblong, and measures between 2-3 cm. The earwig's abdomen is flexible, covered with plates, which makes it mobile. Thanks to the presence of processes at the end of the body, the insect is able to firmly hold prey. These structural features allow the earwig to feed: the abdomen with prey sandwiched by the cerci rises, curving, to the oral apparatus.
The wings of some species are underdeveloped, but most insects can fly. The size of the wings is less than the length of the body. Common earwigs take the opportunity to fly infrequently. The pest's mouthparts are of the chewing type. This feature allows them to eat any food. For this reason, such insects are found on various objects: shops, private housing, gardens, vegetable gardens.
Types of earwig
There is a huge variety of pests that represent the order Leatheroptera.
Insects can fly, but they do so extremely rarely.
There are about 1350 species. However, only a few types of earwigs are more common than others:
- Coastal
- Ordinary
- Asian
- Small.
In Russia, only the common earwig can be found. Occasionally, a representative of the coastal species is found on the Black Sea coast.
The shade of insects varies from brownish to black, which is determined by their belonging to different species. The body structure of most earwigs is similar. Another difference is that representatives of the common and coastal species crawl out of their shelters at night, while the Asian and small earwigs appear during the day.
Reproduction and lifestyle
Pests feed variedly. Their favorite food: fruits, garden flowers, vegetables, various plants. However, pests can damage clothing. Earwigs eat insects, foods that are found in human homes. Pests destroy crops, damaging seeds and shoots of plantings.
Having laid eggs (one clutch contains from 40 to 100 eggs), the female is constantly close to the future offspring
Among fruits, insects prefer peaches and love grapes. However, the pests themselves do not bite into the fruits; they penetrate only where other insects have already made holes (wasps, caterpillars). These pests also feast on pollen and even bees. They spoil the hives, as they often open the honeycombs.
This is a small insect, about 2-3 centimeters long, brown in color.
An earwig is an insect that breeds during certain months in the spring or fall. The female hides the oviposition in a previously prepared hole in the ground. The depth can be different: from 5 to 15 cm. During one breeding cycle, 40-100 eggs appear.
They are characterized by their small size and white color. Until the offspring appear, the female remains nearby and protects from danger. The development of the young generation of earwigs passes the pupal stage.
These pests hide under bark and leaves during the day, gathering in groups. Insects overwinter in the ground, sometimes the depth of the burrow reaches 2 m.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Earwig in the garden
Earwigs usually mate in September, after which they can be found underground in burrows. Courtship rituals involving pincers play a large role in the mating process. Males wave their tongs in the air, stroking and grabbing the female. However, forceps are not used in the actual mating process. If the female approves of the male's advances, he turns his abdomen into a mating position and attaches himself to the female. During mating, females move around and feed with the male attached to her abdomen. Fertilization of the eggs occurs inside the female. Sometimes during mating, another male will come and use his tongs to fight off the mating male and take his place.
Fun Fact: Earwigs typically breed once a year from September to January. In late winter or early spring, females lay 30 to 55 eggs in a burrow dug in the soil. The offspring become independent two months after hatching and no longer require parental care. Earwigs reach sexual maturity at 3 months and can breed as early as the following season.
Females overwinter about 5-8 mm underground with their eggs, guarding them and keeping them clean from fungi and other pathogens using their mouths. Males are driven out of the hole in late winter or early spring, and the female lays fertilized eggs. When the larvae hatch after 70 days, the mother provides protection and food by belching.
When they become second instar nymphs, they emerge above ground and find their own food. However, during the day they return to their hole. Nymphs of the third and fourth instars live above ground, where they develop to adulthood. Nymphs are similar to adults, but are lighter in color with smaller wings and antennae. As nymphs progress from one instar to the next, they begin to darken, their wings grow, and their antennae gain more segments. Between each stage of development, the young molt, losing their outer cuticle.
Prevention of occurrence
To prevent earwigs from infesting your home, you need to destroy all possible ways for these insects to enter your living space. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that there is no constant source of moisture in the apartment. All taps and pipes are checked for leaks, and if there are any, they are repaired immediately.
Regular loosening of the soil will not only saturate it with oxygen, but also prevent waterlogging. All this will reduce the risk of earwigs. An important role is played by systematic weeding of the site, compliance with recommended planting patterns and timely removal of garbage and plant debris.
The two-tailed dog can enter an apartment in a variety of ways, including fruits and vegetables, as well as other greens, as they are easy to hide in. In addition, there are enough secluded places on a personal plot or in a summer cottage where an insect can hide. It is possible to reduce the likelihood of active reproduction of earwigs if you follow a number of rules. For example:
During the harvesting process, including grapes, berries, fruits and various greens, you need to be careful and check the harvested crop for the presence of various insects. On a personal plot or in a country house, care must be taken to promptly remove fallen leaves, which can serve as shelter for such arthropods. If an earwig is found in the apartment, then first of all you should pay attention to the order in the house
You should not leave leftover food on the dining table, or close jars of water. It is equally important to maintain optimal humidity in the apartment, since double-tailed plants feel excellent at high humidity. It is also important to properly care for indoor plants, avoiding waterlogging of the soil. The greater the accumulation of indoor plants in the apartment, the greater the chance of the two-tailed plant to go unnoticed. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly inspect indoor plants, especially since it is not so difficult to detect, compared to other parasites. Traps show good results
To make the simplest trap, just take a tin can and pour vegetable oil into it, and then install it in the place where the trap appears.
If such arthropods are found in an apartment or house, then it is necessary to urgently take measures to get rid of them. Despite the fact that the earwig does not pose any particular danger to humans, such proximity in an apartment will not bring a feeling of comfort. To get rid of such insects, it is enough to adhere to a number of rules, including using some folk recipes or simple traps, so as not to deal with chemicals.
Natural enemies of the earwig
Photo: What an earwig looks like
The earwig is preyed upon by several species of Diptera, as well as Coleoptera beetles. The main enemies are ground beetles such as Pterostichus vulgaris, Poecilopompilus algidus, forest ground beetles and Calosoma tepidum, as well as flightless beetles (Omus dejeanii). Other predators include toads, snakes, and some birds. The earwig has several different defense mechanisms used to avoid predation. These include using forceps as weapons and using glands found on the abdomen to release chemicals that emit a foul odor and act as a repellent to predators.
The most famous predators of earwigs include:
- ground beetles;
- beetles;
- wasps;
- toads;
- snakes;
- birds.
Earwigs are hosts for a variety of parasitic organisms. They also serve as predators of other insect species such as aphids and some protozoans. Earwigs are important scavengers in the ecosystem, eating almost anything that is edible. Earwigs can help control aphid populations, thereby reducing the number of crops destroyed by pests.
Because earwigs tend to hide in dark, damp places, they often find their way into homes. These insects are practically harmless to humans, but their unpleasant smell and appearance make them undesirable guests in the house. They can also damage fruits and other crops as they feed on them.
In addition, the earwig causes significant damage to crops, flowers and orchards when populations are high. Some of the commercially valuable vegetables it eats include cabbage, cauliflower, celery, lettuce, potatoes, beets and cucumber, among others. They readily consume corn tassels and can damage the crop. They damage young plum and peach trees in early spring when other food is scarce, devouring flowers and leaves at night.
Is it dangerous for humans?
Earwig: why is it dangerous to humans? All the chilling stories about the insidiousness of the two-tailed bug, which can destroy a person by penetrating his ear and damaging his brain, are nothing more than fiction.
Of course, she can crawl into the ear of some summer resident if he suddenly wants to take a nap right on the ground. What happens if an earwig gets into your ear? The insect does not pose any danger to the ear and brain.
In this case, you should not panic, but, if possible, immediately consult a doctor and he will remove the unfortunate bug from the outside.
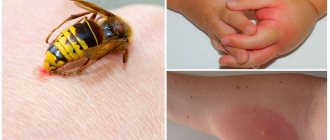
IMPORTANT!
The earwig is not poisonous. It is impossible to die from its bite. An insect can only bite in defense if it suddenly sees you as a source of danger. The bite site may turn red, in which case the skin must be treated with an antiseptic.