Consultation with a dermatologist-venereologist – 1,750 rubles.
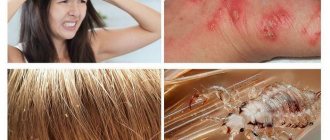
Pediculosis is a disease caused by the parasite, lice, coming into contact with the skin. Symptoms of the disease can appear not only on the head, but also on other areas of the skin, since there are three types of these parasites.
Since lice cannot fly or jump, infection can only occur from direct contact with them: from a person, clothing, comb and other household items. During the bite, the insect secretes saliva, which causes severe itching. It provokes scratching and skin breakdown.
Causes
The disease is caused by three types of lice:
- cephalads (live on the scalp);
- clothing (live on the skin in contact with clothing);
- pubic (found on pubic hair).
These insects cannot tolerate cold; if the ambient temperature drops below 10-15 degrees, they die. Head and pubic parasites lay eggs in the host’s hair, while body parasites lay eggs in clothing. After a week, the nits turn into larvae that feed on blood. The lifespan of an adult insect is just over a month.
Pediculosis - a reminder for parents
08/08/2018 Pediculosis - a reminder for parents
The 21st century has saved us from many diseases, but time has no power over lice. infection
spreads quickly through close contact and sharing of personal items.
Most often, insects appear on the scalp. Females infest the skin and lay eggs (nits), attaching them to the hair. After 8–10 days, insects hatch. Symptoms
Red bite marks are visible behind the ears, on the scalp and on the neck.
Nits appear on the hair - small shiny white grains that look like dandruff. In contrast, lice eggs stick tightly to the hair. You should pay attention to the fact that lice and nits have the ability to camouflage themselves with hair color. Examination of the head should be carried out in good lighting and preferably using a magnifying glass. Pediculosis is usually accompanied by severe itching, so scratching and irritation are noticeable on the skin. Prevention
To prevent head lice in the family, you must: • wash your body and head at least once every 5–7 days;
• change bed linen weekly, and if necessary more often; • regularly wash your underwear and bed linen, iron it with a hot iron, especially the seams; • get your hair cut regularly and comb your head hair daily; • clean the outer dress, clothes, bedding; • clean the premises regularly; • categorically do not use other people's underwear, clothes, comb, bedding; • monitor the cleanliness of the child's head, underwear and clothes. Teach your child
: • not to change clothes, especially scarves and hats;
• use only your own hair comb and hair clips; • hide your hair under a cap in the pool; • do not dry yourself with someone else's towel; • girls - do not let their hair down in public places. If a child is infected
1. Buy any remedy for head lice at the pharmacy. 2. Treat the baby's scalp. 3. Wash your baby with baby soap or shampoo. Boys can have their heads cut. 4. Use your hands or comb out insects and nits with a fine-toothed comb by soaking strands of hair in a solution of equal parts water and 9% vinegar. For better processing, place cotton wool soaked in the same solution on the comb. Rinse your hair with warm water. 5. Put on clean underwear and clothes for your child. 6. Wash bedding and baby's things separately from others, iron with steam. 7. Wipe combs, hairpins, brushes with 70% alcohol or pour boiling water over them. 8. Check all family members on the day the child is diagnosed with lice. Treat everyone if necessary. 9. Report the situation to the health care worker at the child care facility your child is visiting. 10. Vacuum your house and car. 11. Repeat inspections after 7, 14, 21 days, process until insects and nits are completely destroyed.
The main preventive measure is personal hygiene!
Treatment
Treatment of pediculosis involves the complete destruction of parasites. Pest control products should be used by all contact persons. The drugs are available in different forms: sprays, shampoos, lotions, etc.
For head lice, it is effective to comb out insects using a special comb, as well as completely shave the hair. The same method is used to kill pubic lice. In case of the clothing form of the disease, it is necessary to treat all items with special means. Boiling is also carried out.
Pediculosis (lice) is a contagious disease caused by lice infesting the human body. Contrary to the popular belief that pediculosis is the fate of people without a fixed place of residence, this disease can occur in everyone with the same degree of probability.
You can become infected with lice in any place where close contact of one person with another is possible: in a store, train or other public transport, and even in a swimming pool. Moreover, a louse can wait for a new owner on the pillow for 2-3 days.
Prevention of head lice:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene (washing the body at least once every 7 days with a change of underwear and bed linen; combing the hair of the head daily; washing bedding; regular cleaning of living quarters).
- Do not allow your child to use other people's combs, towels, hats, headphones, hairpins, or hair bands - lice are transmitted through these items.
- conduct mutual examinations of family members after their long absence.
- Carry out periodic examinations of hair and clothing of children attending child care institutions.
- Inspect your bedding carefully when traveling.
- After the holidays, be especially vigilant: examine the child’s head.
Modern means make it possible to easily cope with lice, so if lice is detected in a child, you must:
- purchase a treatment for head lice at the pharmacy;
- treat the scalp in accordance with the attached instructions;
- wash your hair using shampoo or baby soap;
— remove dead lice and nits mechanically (by hand or with a fine-toothed comb).
- dress the child in clean linen and clothes;
- wash bed linen and clothes, iron with a hot iron and steam;
- examine family members and yourself;
- examine the child and family members every 10 days for a month.
For reference:
The set of preventive and anti-epidemic measures for pediculosis is regulated by SanPiN 3.2.3215-14 “Prevention of parasitic diseases on the territory of the Russian Federation.”
The following are subject to examination for pediculosis:
- children attending preschool educational organizations - monthly;
— students of general education and professional educational organizations — 4 times a year;
- children going on vacation to health organizations - before departure;
- children staying in a children's health organization - weekly;
- persons located in organizations of the social security system - 2 times a month.
When children enter a preschool educational organization, they are examined for head lice.
When children affected by head lice are identified, they are sent for rehabilitation and are suspended from attending a preschool educational organization. Admission of children to preschool educational organizations after reorganization is allowed if they have a medical certificate confirming the absence of head lice.
If head lice is detected, students are suspended from visiting the organization for the duration of treatment. They can be admitted to general education organizations only after completing a set of treatment and preventive measures with a confirmatory certificate from a doctor.
Persons who have been in contact with a person with head lice are placed under medical supervision for a period of 1 month, with examinations carried out once every 10 days and the results of the examination being recorded in a journal.
Prevention
Prevention of head lice consists of following some rules:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- washing clothes and linen at the maximum permissible temperature;
- ironing things with a hot iron or steam treatment;
- use only personal comb and hats.
Medical dermatologists remind: if symptoms of pediculosis appear, you should immediately consult a specialist. The sooner treatment is started, the easier it will be to overcome this unpleasant disease. Appointments with specialists are available 24 hours a day. Also, for the convenience of its clients, SM-Clinic can call a doctor at home.
About measures to prevent head lice at home and in organized children's groups
Pediculosis is the most common parasitic disease. There are three types of lice: body lice, head lice and pubic lice. Body lice are the most dangerous epidemiologically, as they can become carriers of typhus, relapsing fever, and Volyn fever. Feeding on the blood of a sick person, body lice, when bitten, are able to transmit the causative agents of these infections to a healthy person.
The main symptom of lice is itchy skin, which occurs as a result of a person being bitten by a louse and the parasite's saliva getting into the wound, which causes local irritation. The main way to become infected with head lice is through direct contact between a healthy person and a sick person.
The epidemiological situation regarding pediculosis in the Kamchatka Territory currently remains tense: the incidence rate of pediculosis annually exceeds the Russian average and has no tendency to decrease. In 7 months In 2021, 273 cases of head lice were registered in the Kamchatka Territory (86.7 per 100 thousand population), which is 12.2% lower than in the same period last year. But the beginning of the school year is ahead after the long summer holidays, and it is during this period that the largest number of identified patients occurs.
Indicators of pediculosis incidence in the population for 2013-2017.
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Number of cases in Kamchatka Territory | 389 | 606 | 798 | 607 | 497 |
| Indicator for Kamchatka Territory per 100 thousand population | 121,4 | 189,5 | 251,5 | 192,0 | 157,9 |
| Indicator for the Russian Federation | 180,3 | 192,6 | 166,9 | 145,6 | 130,2 |
Most often, infection with pediculosis is observed in students of secondary schools and in children of preschool educational organizations, which is associated with the good detection of pediculosis among organized children.
Activities carried out in children's institutions should be aimed at creating sanitary and hygienic conditions that prevent the introduction and spread of head lice.
Examinations for pediculosis are carried out by medical personnel and responsible persons (teachers, educators). Students of secondary schools must be examined after each holiday, as well as at the end of the school year before the summer holidays and monthly selective examinations (at least 4-5 classes). Children of preschool educational organizations are examined monthly.
It is prohibited to accept children affected by pediculosis (lice, nits) into an organized group.
If a child affected by lice is identified, parents are informed with recommendations for treating the child for lice. Admission of children to a preschool institution or school is carried out only after sanitization from lice and nits. They can be admitted to general education organizations only after completing a set of treatment and preventive measures with a confirmatory certificate from a doctor.
Persons who have been in contact with a person with head lice are placed under medical supervision for a period of 1 month, with examinations carried out once every 10 days and the results of the examination being recorded in a journal.
In order to prevent head lice among children in organized groups, it is necessary to:
— ensure the timeliness and frequency of inspections for pediculosis with isolation of identified patients and medical observation of contacts in the outbreak;
— ensure timely adoption of the necessary measures to eliminate identified foci of pediculosis;
— carry out ongoing explanatory work with parents and school students about measures to prevent head lice, using various forms (sanitary bulletin, distribution of leaflets, parent meetings, etc.).
We draw the attention of the population and medical workers to the need to conduct high-quality examinations of children in the first week after the start of the new school year, since the largest number of children with lice are detected after the long summer holidays. Unfortunately, some parents do not examine their children during the holidays, which leads to the introduction and spread of head lice into kindergartens and schools.
To protect yourself and your children, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene: comb your hair thoroughly every day, wash and cut it in a timely manner; do not allow your personal comb to be transferred to others; wash daily, change underwear and bed linen when soiled, but at least every 7-10 days, instill in children hygiene skills.
What to do if a child is diagnosed with lice?
— it is necessary to check all family members on the same day as lice was discovered in your child;
- treat the scalp with a pediculicidal agent, applying it in accordance with the instructions for the drug, and then wash the child’s hair using baby soap or shampoo. For boys, a haircut is possible;
— remove dead insects and nits mechanically (by hand or with a fine comb). To remove nits, you need to wet strands of hair in a solution prepared from equal amounts of water and 9% table vinegar. Pass a cotton wool or thread through the teeth of a fine comb and comb out the nits, then rinse your hair;
- treat combs, hair clips, hair ties by wiping with 70% alcohol or pouring boiling water over them;
— simultaneously with treatment for pediculosis, change underwear and bed linen, followed by washing, separately from other things. Iron linen and outerwear with a steam iron;
— report the situation to the doctor (nurse) of the children's institution that your child attends, in order to carry out a set of anti-pediculosis measures in an organized team;
- repeat examinations of the child and all family members after 7, 14, 21 days and, if necessary, carry out repeated treatments until the insects and nits are completely destroyed.
If you cannot carry out the treatment yourself or would like to receive professional help, then contact the sanitary checkpoint of the KSU “Center for Social Rehabilitation”, located at the address: Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, st. Ryabikovskaya, 22/1 (tel. 42-08-66).
Be attentive to yourself and others!
| print version | Version for MS Word |
Prevention of pediculosis article (senior group) on the topic
Prevention of lice - how to protect your child from lice in kindergarten and at home.
Currently, head lice in children is very common, however, it has always been so, because when visiting preschool educational institutions and schools, as well as summer camps and sanatoriums, it is very difficult to protect a child from this trouble. Pediculosis can spread simply at lightning speed, and the causative agents of the disease - lice - can cause a number of other skin diseases. That is why the importance of preventing head lice at home, in kindergarten and school should not be underestimated.
Signs of lice in children
It can take up to several weeks from the moment of direct contact with the source of infection until the first clinical signs of the disease appear in the child. As a rule, a disease can be recognized by its characteristic symptoms: itching at the sites of lice bites; skin rash, red spots in the scalp area covered with hair; scratching at the sites of parasite bites; the presence of nits in the hair - in most cases they can be seen with the naked eye or using a magnifying glass.
If it was not possible to protect the child from lice, the first thing to do is to isolate him from the group, that is, to temporarily stop attending classes at school and kindergarten. Treatment must be carried out very, very carefully and only after consultation with a doctor, and after recovery, special attention should be paid to the prevention of head lice in order to prevent re-infection. You should know: at home, you can prevent lice on your own, using shampoos and lice prevention products, as well as observing a number of hygiene rules. In educational institutions, disease prevention should be carried out by medical workers.
Drug prevention of head lice in children
Lice - how to spot them
Today you can choose any product to prevent lice, because there are a lot of different sprays, shampoos and lotions for lice. The most popular means include:
Hygia is an effective remedy for lice, the use of which is not recommended for children under two years of age; Nittifof - a cream for the prevention and treatment of head lice; Pedilin - another drug for the fight against lice, produced in the form of a gel or emulsion; Para Plus is a spray that can be used to disinfect clothing and bedding. Preventing lice at home
Mom examines her daughter's hair
So, preventing lice at home is especially important for those children who already go to school or attend preschool educational institutions. You can reduce the risk of infection for your child by observing the following preventive rules: examine the child’s head daily for the presence of nits; girls with long hair need to have tight braids or buns; comb your hair thoroughly every day; trim your hair regularly; wash your hair regularly; change the child’s bedding and clothes in a timely manner; To prevent head lice, you can use a highly effective remedy such as tea tree oil - add a few drops to your shampoo or warm water in which you will wet your comb.
Doctor's advice: be sure to have explanatory conversations with your child, explain to him the danger of lice and ask him to never wear other people's clothes, hats, and use only his own personal hygiene items.
Prevention of head lice in kindergarten
Unfortunately, in preschool educational institutions, lice are not a rare phenomenon, and the reasons for this usually lie in the lack of awareness among parents regarding the effective prevention of head lice. In accordance with sanitary regulations, kindergarten medical personnel are required to examine each child upon admission and then conduct weekly checks on all children for lice. It is not difficult to identify lice in children by examining the scalp in a room with good lighting. When conducting an examination, medical professionals may use a fine comb and a magnifying glass. After each inspection, objects must be disinfected with an alcohol solution. It is very important that kindergarten managers take a responsible approach to the problem and do not accept infected children into the institution. If cases of morbidity are detected in an institution, the following measures must be taken:
isolation of infected children;
searching for the main source of infection;
examination of all children who may have been in contact with an infected child (several times during the month);
inform the clinic to which the infected child is assigned - this is necessary to ensure the necessary sanitary treatment of the patient and examination of his family members;
perform wet cleaning and disinfection;
check the sanitary and hygienic condition of all group premises of the kindergarten, as well as wardrobes for clothes and toys;
consulting parents on preventing lice at home;
After rehabilitation, children can be accepted back into kindergarten only if they have a medical certificate confirming the absence of head lice.
It is worth noting that today there are many effective remedies for lice that can be used, including in kindergartens. The source of the disease can be considered sanitized after children have been examined three times for the presence of lice with a negative result.
Prevention of head lice at school
To prevent head lice in schools, health workers are required to examine children at least four times a year (after each holiday), and there may also be monthly spot checks and checks a couple of weeks before the end of the school year. If any child is found to have lice, he must be removed from school until he has fully recovered. A recovered child will be able to return to the team if they have a certificate from a doctor confirming the absence of head lice.
Preventive measures to avoid lice infection
Memo for parents: if you become aware that cases of head lice have been identified at the school where your child is studying, urge your child to follow the following rules: under no circumstances exchange clothes with classmates, especially hats and scarves; do not use other people's hairpins and combs, and do not lend yours to anyone; when visiting the pool, wear a rubber cap; Do not use someone else's towel. After all of the above, we can draw a simple conclusion that timely detection and isolation of children infected with head lice is the most effective prevention of such an unpleasant disease.
Causes of pediculosis.
Reminder on the prevention of pediculosis
One of the problems that we have to face quite often nowadays is pediculosis.
The high level of head lice in the population suggests that this problem is quite relevant and requires increased attention. Lice, unfortunately, have always accompanied humans.
Even before our era, Herodotus wrote that Egyptian priests shaved their heads so carefully in order to protect themselves from unpleasant lice. Unlike a number of diseases that humanity has practically conquered, pediculosis has passed through the centuries, and its treatment continues to be relevant for our contemporaries.
Pediculosis (lice) is a parasitic skin disease caused by the human louse, a small insect that parasitizes the skin and clothing. Pediculosis manifests itself mainly as itching at the site of lice bites (itching of the scalp, itching in the genital area).
As a rule, pediculosis develops under unfavorable environmental conditions (large groups of people, lack of basic hygienic conditions, low cultural and economic level of society). Sometimes lice also occur in clean people when they come into contact with a person infected with lice.
- clothes, lives in the folds of linen and other clothes, especially in the seams. Lice eggs can also stick to hair on the human body, except the head.
- cephalic, lives and reproduces in the scalp, preferably on the temples, back of the head and crown.
- pubic, lives in the hair of the pubis, eyebrows, eyelashes, mustache, armpits.
Head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis) is the cause of head lice. Head lice live up to 40 days. Over the course of 35 days, the louse lays up to 10-12 eggs (nits) per day. Typically, nits are attached to the hair and look like transparent round sacs filled with liquid.
After emerging from the egg (nit), the young louse begins to feed on human blood and grow. Bright pigmentation is visible on the sides of head lice. The presence of head lice indicates a poor hygienic environment in the team, as well as the uncleanliness of people.
Head lice live on the scalp and are most common in girls and women, as they survive better in long hair. As a rule, lice infestation occurs through combs, hats, and hair brushes. It is also possible for the parasite to transfer from one person to another.
Head lice are extremely agile and capable of jumping high.
Main symptoms and signs of pediculosis.
It may take several weeks from the moment of infection with lice (pediculosis) to the first signs of the disease.
The main symptoms and signs of head lice are:
- Itchy skin at the site of the louse bite. With head lice, patients are most often bothered by itching of the scalp (behind the ears, in the temples and back of the head). With head lice, the itching in patients is of mild intensity; sometimes patients complain only of slight discomfort in the area of the lice bite.
- Rash as a symptom of lice. As a rule, a rash with lice appears a few days after lice bites. Head lice is characterized by red spots along the periphery of the scalp.
- Scratching (excoriation). With long-term lice, due to itching, the patient combs the areas of the skin bitten by lice. As a rule, purulent crusts appear at the site of scratching due to lice.
- The presence of nits in the hair. The presence of nits on the hair is one of the irrefutable signs of lice. Nits look like small (2-3 mm) silvery bubbles attached to the hair. Nits can be live or dead. Dead nits are usually dull in color.
- Secondary bacterial infection (pyoderma) on the scalp, behind-the-ear areas, face, impetigo (impetigo is a disease characterized by the presence of superficial vesicular-pustular rashes on the skin);
- Blepharitis, conjunctivitis;
- Lymphadenitis;
- Typhus – lice are carriers of typhus;
- Sepsis.
Prevention of head lice.
Prevention of head lice involves maintaining hygiene measures.
Maintain personal hygiene. It is necessary to change underwear and clothes regularly (at least 2 times a week). It is also important to regularly wash your bedding at a high temperature (you should avoid using other people's bedding). You should iron your clothes carefully (especially in the seam area). Preventive measures in some groups (kindergartens, schools, student dormitories) should be carried out by educators and doctors assigned to the children's institution.
For body lice, sanitization is carried out (the body is washed with hot water and soap) and at the same time disinsection of linen, outerwear, bedding and living quarters is carried out.
Individual prevention comes down to regular washing of the body with a change of underwear and bed linen, periodic examination of children at home, as well as in children's groups, control examination of linen for lice in unsatisfactory sanitary and living conditions (long stay on the road); prevention of contact with lice-infested people.
If you learn about a case of head lice at school, ask your child to:
- do not exchange clothes with your friends, especially scarves and hats;
- use only your own hair comb and hairpins;
- hide your hair under a cap in the pool;
- do not use someone else's towel.
If your child does become infected with lice, take personal preventive measures:
Information for parents about actions to take when identifying lice in a child.
- Buy any treatment for head lice at the pharmacy.
- Treat the child’s scalp with the product strictly in accordance with the attached instructions.
- Wash your baby using baby soap or shampoo. For boys, a haircut is possible.
- Remove dead insects and nits mechanically (pick with your hands or comb out with a fine-toothed comb). To remove nits, you need to wet strands of hair in a solution prepared from equal amounts of water and 9% table vinegar. Rinse your hair with warm water.
- Put on clean underwear and clothes for your child.
- Wash bedding and baby's clothes separately from other things, iron them using steam.
- Examine and, if necessary, treat all family members. Don't forget about yourself.
- Report the situation to the doctor (nurse) of the children's institution that your child visits, so that a set of anti-pediculosis measures can be carried out.
- Repeat examinations of the child and all family members after 7, 14, 21 days and, if necessary, carry out repeated treatments until insects and nits are completely eradicated.
Monitoring
Prevention of lice - how to protect your child from lice at school, kindergarten and at home
Currently, head lice in children is very common, however, it has always been so, because when visiting preschool educational institutions and schools, as well as summer camps and sanatoriums, it is very difficult to protect a child from this trouble. Pediculosis can spread simply at lightning speed, and the causative agents of the disease - lice - can cause a number of other skin diseases. That is why the importance of preventing head lice at home, in kindergarten and school should not be underestimated.
Content
· 1
Signs of lice in children
· 2
Drug prevention of head lice in children
· 3
Preventing lice at home
· 4
Prevention of head lice in kindergarten
· 5
Prevention of head lice at school
· 6
Video about head lice prevention
Signs of lice in children
It can take up to several weeks from the moment of direct contact with the source of infection until the first clinical signs of the disease appear in the child. As a rule, diseases can be recognized by their characteristic symptoms:
· itching at the sites of lice bites;
· rash on the skin, red spots in the scalp area covered with hair;
· scratching in places where parasites bite;
· the presence of nits in the hair - in most cases they can be seen with the naked eye or using a magnifying glass.
If it was not possible to protect the child from lice, the first thing to do is to isolate him from the group, that is, to temporarily stop attending classes at school and kindergarten. Treatment must be carried out very, very carefully and only after consultation with a doctor, and after recovery, special attention should be paid to the prevention of head lice in order to prevent re-infection. You should know: at home, you can prevent lice on your own, using shampoos and lice prevention products, as well as observing a number of hygiene rules. In educational institutions, disease prevention should be carried out by medical workers.
Drug prevention of head lice in children
Today you can choose any product to prevent lice, because there are a lot of different sprays, shampoos and lotions for lice. The most popular means include:
· Hygia is an effective lice remedy, the use of which is not recommended for children under two years of age;
· Nittifof – cream for the prevention and treatment of pediculosis;
· Pedilin is another drug to combat lice, available in the form of a gel or emulsion;
· Para plus is a spray that can be used to disinfect clothing and bedding.
When using any shampoo to prevent head lice or one of the above remedies, be sure to thoroughly comb the child’s hair, first using a wide-tooth comb, and then a fine-tooth comb.
Preventing lice at home
So, preventing lice at home is especially important for those children who already go to school or attend preschool educational institutions. You can reduce your child's risk of infection by following these preventative rules:
· examine the child’s head daily for the presence of nits;
· girls with long hair need to braid tight braids or make buns;
· Comb your hair thoroughly every day;
· regularly trim your hair;
Wash your hair regularly;
· change the child’s bedding and clothes in a timely manner;
· to prevent head lice, you can use a highly effective remedy such as tea tree oil - add a few drops to your shampoo or warm water in which you will wet your comb.
Doctor's advice:
Be sure to have explanatory conversations with your child, explain to him the danger of lice and ask him to never wear other people’s clothes, hats, and use only his own personal hygiene items.
Prevention of head lice in kindergarten
Unfortunately, in preschool educational institutions, lice are not a rare phenomenon, and the reasons for this usually lie in the lack of awareness among parents regarding the effective prevention of head lice. In accordance with sanitary regulations, kindergarten medical personnel are required to examine each child upon admission and then conduct weekly checks on all children for lice. It is not difficult to identify lice in children by examining the scalp in a room with good lighting. When conducting an examination, medical professionals may use a fine comb and a magnifying glass. After each inspection, items must be disinfected with an alcohol solution.
It is very important that kindergarten managers take the problem responsibly and do not accept infected children into the institution. If cases of morbidity are detected in an institution, the following measures must be taken:
· isolation of infected children;
· search for the main source of infection;
· examination of all children who may have been in contact with an infected child (several times during the month);
· inform the clinic to which the infected child is assigned - this is necessary to ensure the necessary sanitary treatment of the patient and examination of his family members;
· Perform wet cleaning and disinfection;
· check the sanitary and hygienic condition of all group premises of the kindergarten, as well as wardrobes for clothes and toys;
· consulting parents on the prevention of lice at home;
· After rehabilitation, children can be accepted back into kindergarten only if they have a medical certificate confirming the absence of head lice.
It is worth noting that today there are many effective remedies for lice that can be used, including in kindergartens. The source of the disease can be considered sanitized after children have been examined three times for the presence of lice with a negative result.
Prevention of head lice at school
To prevent head lice in schools, health workers are required to examine children at least four times a year (after each holiday), and there may also be monthly spot checks and checks a couple of weeks before the end of the school year. If any child is found to have lice, he must be removed from school until he has fully recovered. A recovered child will be able to return to the team if they have a certificate from a doctor confirming the absence of head lice.
Memo for parents:
If you become aware that cases of head lice have been identified at your child’s school, urge your child to follow these rules:
· under no circumstances exchange clothes with classmates, especially hats and scarves;
· do not use other people’s hairpins and combs, and do not lend yours to anyone;
· wear a rubber cap when visiting the pool;
· Do not use someone else's towel.
After all of the above, we can draw a simple conclusion that timely detection and isolation of children infected with head lice is the most effective prevention of such an unpleasant disease.
(https://med-look.ru/profilaktika-pedikulyoza-kak-uberech-rebyonka-ot-vshej.html)