What does a spider bite look like?
All representatives of spiders have poisonous glands. The toxic substance is necessary to immobilize the victim and liquefy the insides. In some spiders, the dose of poison is enough to kill fruit flies and mosquitoes, while others paralyze rodents and amphibians. The latter are usually called poisonous; it is their bites that can be fatal for a person.
Spiders bite with special fangs called chelicerae. They are located in the front part of the cephalothorax and have different shapes. The strength of the power is different for all predators. Some barely bite through the skin, others pierce the “tusks” to the very base. Bites differ in the severity of pain - an immediate burning pain or discomfort appears after some time.
On a note!
Spiders do not attack people on purpose; they bite to protect their own lives. Most bites occur due to a person’s carelessness, when he does not notice the predator, or out of excessive curiosity, as well as due to improper handling of an exotic pet.
How a spider bites, external symptoms:
- the presence of two wounds located in close proximity, or a continuous inflamed spot;
- swelling;
- redness;
- edema;
- blisters on the skin filled with fluid inside around the inflamed area;
- After a few days, suppuration may appear.
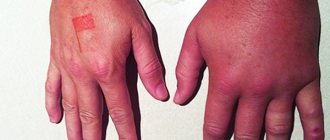
Externally, spider bites often resemble the bites of bees, wasps, hornets, and sometimes mosquitoes. It all depends on what species carried out the attack. A photo of a spider bite on a person is located below.
Spider bite
The entry of pathogenic microorganisms into an open wound leads to severe inflammation, swelling, increased redness, suppuration, the appearance of ulcers, and weeping eczema. Photos of skin lesions of secondary infection can be seen below.
Who are spiders?
A spider is an arthropod insect belonging to the class of arachnids. Modern science has more than 40,000 varieties. Almost all are predators and feed on a variety of fauna (from midges to small birds).
The territory, which previously included all countries of the USSR, is inhabited by more than 3,000 species of arthropods. How can you tell which spiders bite and which don't?
Spiders weave webs to catch their prey. Some types of spider webs are used to produce silk. When food falls into the trap, the arthropod hunter releases poison into the body. Almost all species are poisonous, but differ in the strength and nature of the poisonous substance, as well as the power of the bite. Small individuals cannot bite through human skin and are included in the “non-dangerous” group, while others easily release toxic substances into the body. How a spider bites depends on the type and size of the insect. Almost all patients report sharp pain like a pin prick.
Scientists divide spider poisonous substances into two types:
The first has an effect on blood cells and the epidermis, causing necrosis in various locations. The second type is the most common, since the main goal of the predator is to immobilize the prey, causing dysfunction of the central nervous system.
Spider bite - symptoms in humans
The development of general symptoms depends on how the spider bites, what species it is, and how much poison it injects. In most cases, people get away with discomfort and painful sensations on the skin, and some of the victims do not notice anything at all; the bite goes away on its own.
The strength of the immune system and the individual characteristics of the body play a huge role. However, in the event of a poisonous spider bite, even the strongest defensive reaction may not work. The effect of a toxic substance depends on qualitative and quantitative indicators. The spider bites once and rarely attacks again. After the first attack, he tries to quickly hide in a secluded place. The poison enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body; what the consequences will be depends on the quality indicators and the mechanism of action of the toxic substance.
- Neurotoxic poison affects the functioning of the central nervous system and peripheral. It provokes muscle spasms, which disrupts the functioning of internal organs - heart, lungs, stomach, brain, etc.
- The spider's hemolytic venom destroys red blood cells, leading to changes in the composition and quality of the blood. The bite can cause internal bleeding.
Spiders in Russia are the owners of a neurotoxic substance. The consequences depend on the composition of the poison. With a potent substance, deterioration in well-being is observed within 15 minutes after the incident.
- weakness;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- difficulty breathing;
- swelling of the larynx;
- shortness of breath, lack of oxygen;
- tremor of the limbs;
- muscle pain;
- profuse sweating;
- violation of movement coordination;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased blood pressure, body temperature;
- pale skin;
- slowing heart rate.
Consequences of a bite
Without timely medical care, a person may die from suffocation or cardiac arrest.
On a note!
The consequences of a spider bite are always more pronounced in children, the elderly, and people with reduced or pathologically weak immunity. In this case, even the bite of an ordinary cross can threaten a person’s life.
The human body's reaction to a karakurt bite
As already mentioned, the spider bite itself at first seems like a light prick. Therefore, many people think that they have been pricked by a thorn and are not particularly worried. But in vain! If you look closely at the bite site, it darkens within a few minutes. Then there is a lull. The insidious poison is absorbed into the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
An hour and a half after the bite, the body’s violent reaction to the action of the toxins contained in the poison begins. During this time, first aid should be provided.
- A tumor appears at the site of the bite, which grows and spreads throughout the victim’s body.
- Very strong painful sensations appear, which increase with the growth of the tumor.
- The person becomes increasingly nauseous, even to the point of vomiting.
- Strong mental arousal occurs, breathing quickens.
- Numbness and cramps appear in the limbs.
- Mental excitement is followed by lethargy and apathy.
- As a result of cardiac arrhythmia, suffocation appears, and blueness appears on the face.
- In the most severe cases, cardiac arrest and death of the victim may occur.
- In milder cases, recovery occurs in two to three days.
What spiders bite
Experts say that spiders that live in Russia do not attack themselves and do not rush to attack a person. They do not have an aggressive disposition; they prefer to quickly hide in a secluded place without unnecessary incidents. If the situation develops in such a way that the predator feels a threat to its own life, it bites and injects poison. Absolutely all arachnids bite, but the consequences are different.
You can meet a predator at home. In the warm season, spiders settle in residential buildings and apartments, entering through open windows, doors, and cracks in the wall. Small spiders hide in corners and behind furniture during the day, and at night they are active - they spin webs. A house spider bite is a rare occurrence and not dangerous. Small children under 1 year of age who show excessive curiosity and are left without parental supervision suffer. House spiders are dangerous only for people suffering from arachnophobia.
The most dangerous species of arachnids in Russia live in the wild, but in search of food, in the process of migration, they can end up in the possessions of a person, his home. Often predators bite people in nature, after they have quietly climbed into things, shoes, and clothes. They bite unnoticeably.
Why are spiders so dangerous?
Spiders live literally everywhere: in forests, gardens, steppes and even arid deserts. Their history goes back hundreds of millions of years: spiders caught dinosaurs and other creatures that are not now found on the planet.
There are several thousand species of arachnids in the world, only one of which feeds exclusively on plants. Other individuals do not disdain even their relatives, preferring living flesh to leaves. Their diet mainly consists of flies, mosquitoes and other insects, but sometimes larger prey is also found.
In this video you will learn about 10 deadly insects:
The danger of spiders is that they can take root in almost any habitat. At the same time, they are guided solely by instincts, and it is almost impossible to predict their behavior and defend themselves - even a house spider can bite. One thing is for sure: if in relation to other spiders and insects he behaves like a real predator, then when meeting a person he prefers to simply defend himself. Some individuals live in grass or bushes, so it can be very difficult to notice them.
The spider kills in the following way: it bites and injects a special poison, which instantly paralyzes the victim and leaves him no chance to escape from the trap. Fortunately, spider fangs are intended exclusively for killing insects, so only some large individuals, which are very rare in Russia, can bite through human skin.
Spider venom has a neuroparalytic effect on the victim.
Spider venom and its properties
The most dangerous spiders live as close as possible to the equator - they prefer a warm and humid climate. The further north you go, the smaller the arachnids living there become. Since in nature there is only one species of herbivorous spiders, the rest can one way or another be called predators. Another thing is that most of them do not pose any threat to humans. For example, from a house spider bite, a person will most likely feel only a burning sensation and a slight tingling sensation.
Read on topic:
Where are funnel-web spiders found and are they dangerous?
14.11.2020
Why signs of arachnophobia appear and what to do about it
14.11.2020
The most popular types of Australian spiders
14.11.2020
The main types of spiders living in a house or apartment
02/05/2020
The main problem is that with a spider bite, a person does not feel the poison penetrating his body , but an allergic reaction that this poison can cause. In addition, dirt can get into the wound and cause an infection, which can also worsen the condition and cause complications.
Consequences of a bite
The spider's venom glands affect two vital systems: the nervous and circulatory systems. Once in the blood, the poison causes necrosis - the death of the affected tissues. Damage to the nervous system causes paralysis of the victim: acting as a neurotoxin, the poison disrupts neuromuscular mechanisms, as a result of which the victim becomes completely helpless.
Symptoms of a spider bite can be very different, it all depends on the individual and the location of the wound. A spider bite looks different from bites from insects and other creatures. The first symptoms begin to appear only after 15-20 minutes (in some cases you will have to wait a whole day), while a wasp or bee sting immediately begins to hurt and itch.
Spider venom causes tissue necrosis, it is important to consult a doctor in time
Main symptoms:
- A small white spot appears at the site of the bite. There may be slight redness around it.
- Gradually, a small blister will appear in place of the spot, the skin around it will swell and turn red. It is not recommended to tear off the film from the blister or puncture it. Depending on the type of spider, the color of the central area may vary. For example, when bitten by a recluse spider, the wound will have a bluish-blue tint.
- Since when it enters the bloodstream, the poison begins to spread throughout the body, an allergic reaction in the form of swelling can appear not only near the wound itself, but also on the face and hands.
- After some time, the bite site may become numb - the poison affects the nervous system.
The venom in the spider's glands is not enough for more than one bite in a row - The venom in the spider's glands is designed for only one bite. Therefore, if there are more wounds, most likely the bite belongs to someone else. Or there were several spiders, which in itself is difficult not to notice, since usually poisonous spiders are large in size.
- Over time, unpleasant pain may appear at the site of the bite, but not as strong as from bee or wasp venom. There may also be a burning sensation and itching at the wound site.
- As the body begins to fight the ingested toxin, allergic effects such as nausea, vomiting, upset stomach, and loose stools may gradually occur. Often there is the appearance of drowsiness, weakness throughout the body, and aching joints.
- Often there is an increase in temperature, fever, chills. The color of urine may change to pinkish or red, as well as a rapid increase in pressure (as a result of the effect of spider venom on the blood).
- With partial paralysis, convulsions in some parts of the body, muscle spasms and pain may occur.
Dizziness and fainting are often possible, so if symptoms appear, it is better to immediately consult a doctor and try to reduce physical activity and physical activity as much as possible.
Dangerous spiders in our area
Due to global warming and dry summers, there is a migration of southern individuals to the northern regions. In Russia, poisonous creatures have become common, the bite of which leads to death if timely medical care is not provided.
Karakurt
The most dangerous spider in our area. The bite of a poisonous spider provokes instant pain, a local allergic reaction, and after 15 minutes the general symptoms of poisoning described in the section above develop.
Medium sized predator. The female reaches 2 cm, males - 70 mm. Long black legs, 13 red spots on the abdomen. With age, the color becomes more uniform, the spots disappear. Karakurts live in arid places and build burrows underground.
Karakurt and tarantula
South Russian tarantula
The most common poisonous specimen in our area. A bite on a person’s skin causes an immediate allergy, and after 20 minutes a deterioration in well-being is observed. If timely medical care is not provided, death may occur. Tarantulas are the most dangerous for children.
The size of the female, together with the leg span, reaches 35 mm; males are half that size. Color: beige, brown, white with dark streaks.
On a note!
A distinctive feature of the poisonous South Russian tarantula is its dark head. The limbs are long, powerful, the whole body is covered with hairs.
Sak
An exotic, bright creature with a memorable appearance. Other names: heyracantium, yellow. The predator is a medium-sized sak, the female is about 1 cm, the males are even smaller. The legs and abdomen are amber-yellow, the cephalothorax is red or orange.
On a note!
Powerful jaws, chelicerae in the form of curved fangs. Quietly bites through a person's nail plate.
The animal is timid and does not have an aggressive disposition; if a yellow sak bites, this means that it had to defend its own life. An instant, burning pain appears, followed by redness and swelling. After a bite, children, people with weak immunity, and a tendency to allergies develop weakness, malaise, and symptoms of intoxication. Medical attention required.
Black fathead
A bite with an allergic reaction of varying degrees of intensity is dangerous. It is classified as poisonous. Marks on the skin disappear within 2 weeks. General malaise is present for the first few days. If a severe allergic reaction occurs, medical attention is required. A red spider bite does not lead to death.
Males have a bright color - the legs and cephalothorax are black, velvety, the abdomen is red with four black spots. Females are larger in size - 1 cm, the whole body is black.
Spiders whose bites are dangerous
Black widow, false black widow
It is the most poisonous creature on earth. Black widows belong to the karakurt family.
Important!
The poison is 15 times stronger than the bite of a rattlesnake. Life-threatening symptoms develop within 15 minutes. The introduction of a special substance is required to neutralize the poison. If a child is bitten by a spider, death can occur within half an hour.
The false black widow is slightly different in appearance and its venom is not as strong. Provokes allergies.
The appearance is memorable - long black legs, cephalothorax, abdomen with a glossy sheen. On the lower part there is a characteristic red hourglass pattern; in false black widows it is pink, white and brown.
Poisonous spiders also include wolves, cross spiders, and hermits. They bite hard, but not fatally. In most cases, the consequences are limited to an allergic reaction.
Clinical signs of bites from different individuals
Karakurt
The enzymatic composition of the poison, which is produced by the domestic tarantula spider, cannot cause significant harm to humans. In this case, swelling and redness are possible only in the area of the bite. Karakurt (black widow) is a relatively small spider, but its bite can cause pain, general deterioration and a local allergic reaction. Signs of severe intoxication of the body may persist for several days.
A tarantula bite causes intense pain, numbness of the limbs and heart rhythm disturbances. The venom of this spider often causes severe allergic reactions. For children and people with weakened bodies, a bite from this arthropod can be fatal.
The cross is relatively common in Russia and the CIS countries. Spiders often coexist with people, spinning large webs even in apartment buildings, but they attack only in rare cases. The crosstail can bite only if the person poses a danger. The poison of the cross is hemolytic and leads to disruption of oxygen delivery to all tissues of the human body. This causes the condition to worsen. Adverse effects may persist for 24 hours and then subside. Even large individuals of this type of spider cannot produce enough venom to be lethal.
Recluse spider
The bite of the recluse spider (brown and brown) poses a mortal danger to humans. These arthropods are small in size. People's limbs are often affected; in most cases, bites occur on them. Without targeted treatment, tissue necrosis begins after a spider bite in the affected area of the arm or leg. The general condition also worsens due to increasing intoxication. Without the timely help of doctors, there is a high probability of death even for adults leading a healthy lifestyle.
What to do if bitten by a spider
It all depends on what type of spider bit. If this is a small non-venomous creature, first aid is sufficient. If the spider bites hard, an allergic reaction on the skin begins; local antihistamines are used. In the event of an attack by an unknown specimen or a general deterioration in health, you should immediately contact a specialist.
- A house spider bite is treated with antibacterial and antiseptic drugs. The pain goes away within a day, the skin is completely restored within a week.
- A green spider bite is not dangerous. Symptoms are limited to local allergies.
- If you are bitten by a white spider, you need to wash the wound and treat it with an antiseptic. If you have allergies, use antihistamine ointment.
If spiders live at home as a pet, if handled carelessly, they can bite. Further actions depend on how poisonous the pet is.
First aid to the victim
The only right step is to call an ambulance. However, while the doctor is traveling, you can try to alleviate the symptoms of intoxication as much as possible:
- Rinse the bite area with clean water and apply an antiseptic to remove dirt from the wound.
- Constantly observing how the symptoms appear is how you can assess how dangerous the bite is.
This is interesting: what does a spider in the house mean?
Observing the symptoms of a bite will help determine the degree of danger of the poison and the type of spider that bit the person.- If possible, take a photo of the spider or remember what it looked like so that it will be easier for the doctor to identify it and prescribe the necessary treatment.
- Apply ice or a cold compress to the wound to relieve pain.
- Reduce physical activity as much as possible to prevent the poison from spreading throughout the body.
- If the bite is on a limb, you can apply a loose elastic bandage or tourniquet above the wound.
- Drink more and do not scratch the bite site.
The doctor will do the rest of the work. You should not take medications or take other actions on your own. If possible, it is better to go to the hospital yourself before it is too late.
First aid for a spider bite
The initial task is to wash away the remnants of the poison, prevent it from spreading through the blood, and reduce the symptoms of an allergic reaction. The choice of first aid depends on the location where the event occurred. If a spider bites you at home or in the immediate vicinity, you can use a home first aid kit; in the wild, improvised materials are used.
First aid for a bite
- You need to wash the bite. Use running water, mineral, spring. At home, you need to use laundry soap.
- Disinfect the wound after a bite. They use folk remedies, alcohol tincture, hydrogen peroxide, menovazine solution, ammonia, etc.
- If the bite hurts a lot, or swelling appears, apply a cold object, compress, ice cubes wrapped in gauze.
To prevent the spread of poison through the blood after a bite from a poisonous predator, a tourniquet is applied over the wound or a bandage is made from a bandage or improvised materials.
Important!
You should not squeeze out the poison, since this procedure promotes the spread of the toxic substance through the blood, increasing the risk of developing a secondary infection and necrosis of cells around the affected area.
How is a bite treated?
What to do if you get a spider bite? Treatment is carried out symptomatically. Below are different treatment options depending on the types of reactions.
Local reactions
First aid for a spider bite is to clean the injury with soap and water, apply dry ice to reduce swelling, and monitor the patient for a period of time for signs of systemic reactions. Immobilizing the bite site (for example, splinting the affected limb) slows the lymphatic spread of the venom. In addition, a tetanus shot may be given. Necrotic lesions are treated with surgical removal of dead tissue, painkillers, sterile dressings, and rest.
Systemic reactions
Includes treatment of target organ damage:
- maintaining adequate fluid status;
- blood transfusion with extensive breakdown of blood cells;
- pain relief;
- injections of calcium gluconate to relieve intoxication.
Allergic reactions
Treatment, as for any other type I hypersensitivity reaction, includes:
- antihistamines;
- steroids;
- adrenaline for life-threatening reactions such as angioedema and anaphylaxis.
Muscle spasms
Treated with an antivenom that targets specific spider bites. Side effects from this therapy include fever, joint pain, muscle pain, swollen lymph nodes, and skin rashes.
First aid for bites
At the slightest suspicion of a poisonous spider bite, you should call an ambulance and provide first aid to the victim. First of all, it is necessary to wash off the remnants of the toxic substance, slow down the spread of the poison through the bloodstream, and relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction. The choice of first aid depends on where the attack occurred. If you are at home, a home first aid kit will do; if you are outdoors, you will have to use improvised materials. So:
- Thoroughly rinse the bite from any remaining poison with running, mineral or spring water. Use laundry soap at home.
- Disinfect the wound with alcohol, ammonia, hydrogen peroxide, vodka or any alcohol infusion. Attention! Scratching the wound is strictly forbidden, as this can accelerate the spread of poison throughout the body.
- In case of a pronounced local reaction, apply any cold object, compress, ice cubes wrapped in gauze to the inflamed wound.
- To ease allergic manifestations, give the victim an antihistamine.
- If an arm or leg is injured, a tourniquet or tight bandage should be applied above the bite. This is necessary in order to slow down the blood flow and the spread of poison throughout the body.
- Give the victim more fluid so that the kidneys remove the poison from the body more quickly.
- In case of severe pain, give the victim an anesthetic.
Remember! If a predator bites you on the neck, face or mucous membrane, the slightest delay can cost the victim his life.
Reaction to a spider bite
A panicked attitude can accelerate the spread of toxic substances, which means it is important to remain calm. Then you need to carefully examine the site of the bite. If it turns slightly red, but there are no characteristic wounds or dots, the attack was carried out by a harmless spider (most likely, medical attention will not be required).
First aid
Despite the fact that local and systemic symptoms caused by a bite usually go away spontaneously after a few hours, it is still better to know and carry out a number of preventive measures to prevent the likelihood of complications. Remember that ambulance is especially necessary for elderly people, hypertensive patients, children and pregnant women.
What to do if bitten by a spider?
It is important for anyone to know what to do if they are bitten by a spider, because a few simple steps can help save a life:
- To be able to identify the spider, try to catch it or save its body if it was crushed;
- wash the bite site with soap and water and wipe with alcohol; in general, sterilization can be carried out by the same treatment as for an infected wound;
- immobilize the affected limb;
- do not apply pressure bandages, but apply something cold, such as ice;
- take an antihistamine to prevent an allergic reaction;
- According to some reports, if a karakurt is bitten, immediate cauterization of the bite site with a match head can help.
Folk remedies for bites
What to do if a spider bite happens far from civilization, when you can’t get to the nearest populated area even in a couple of days?
To relieve unpleasant symptoms and speed up wound healing, you can use traditional medicine methods:
- Rinse the affected area with a solution - 1 teaspoon of vinegar per glass of water.
- Dilute baking soda with water to a paste and apply to the inflamed area.
- Wipe with lemon juice.
- Apply shaving foam for 5 minutes and rinse with cold water.
- Apply aloe leaves.
Attention! Any folk remedy, especially herbal ones, can provoke an allergic reaction and aggravate the condition of the victim. Therefore, it is better for allergy sufferers to refrain from such experiments.
After reading the presented review, many will wonder: is it possible to avoid a spider bite? To reduce the likelihood of an attack to a minimum, it is enough to follow some recommendations:
- Do not try to catch or hit the arthropod.
- Keep your home clean, not bypassing the most hidden corners.
- Once in nature, check your shoes and clothes, and keep your sleeping bags and tents closed.
- When going out of town, stock up on repellent sprays and creams.
- In the summer, close doors tightly and equip windows with mosquito nets.
In most cases, everything is limited to a local reaction, which goes away within a few days. Although no one is safe from meeting a dangerous individual. In order to promptly and competently respond to the consequences of a bite, it is important to equip your home first aid kit with everything you need, and when going into nature, take an “alarm suitcase” with you.
How to protect your skin from mosquito and bee bites
To reduce the likelihood of attacks from flying insects, you should avoid their habitats and take personal protective measures. For example, it is important to know that mosquitoes love damp and shady areas of land. According to experts, they see almost nothing, however, they are attracted to dark-colored clothing, and for their attacks they prefer the evening and night time. To prevent mosquito bites, you can do the following:
- In summer, install mosquito nets on the windows.
- In the evening, especially near bodies of water or places with high humidity, wear clothes that cover the body as much as possible.
- If you are prone to allergies, limit your stay in the forest, near a river or lake, or near swampy areas in the evening.
- Before walking, apply repellent to clothing and exposed skin. In this case, it is necessary to strictly follow the instructions for the product used, which is especially important when it comes to children and pregnant women.
- Use essential oils of tea tree, eucalyptus, and coniferous trees to aromatize the air, the smell of which repels mosquitoes. Special scented candles are also suitable.
- At your dacha, drain areas with standing water where insects usually breed.
The following rules will help you avoid bee and wasp stings:
- Avoid wearing brightly colored clothing that attracts insects.
- During the daytime, do not use perfumes or other odorous cosmetics.
- Be careful when visiting markets and places where food waste is thrown away.
- Do not eat or prepare food outdoors.
Folk remedies for bites
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms and accelerate the healing of the epidermis, use:
- Vinegar solution. For a glass of water, 1 teaspoon of the product. Treat the bite site.
- Baking soda paste. Dilute with water to a paste.
- Juice of lemon, orange, cucumber, onion, parsley, potato, as well as dandelion, plantain, celandine.
- Toothpaste, shaving foam. Apply to the bite site for 5 minutes and wash off.
- Aloe vera leaves or juice.
They are used for minor manifestations of allergies or as an aid.
Symptoms
After a spider bite, a child may experience various symptoms. It all depends on the type of arthropod and the individual characteristics of the child’s immune system. Children, unlike adults, usually feel a bite, since their pain threshold is weaker. The skin puncture made by a spider feels like a needle prick. A white spot surrounded by a pink halo forms at the site of the bite. A pinpoint wound can itch, burn, and sometimes hurt. In children, the reaction to spider bites is usually pronounced: the bite site itches, a rash appears around, and allergic reactions often develop. If the spider is non-venomous, then only local symptoms appear, which after a couple of hours either weaken or disappear completely.
The bite of a poisonous spider can be identified by a number of characteristic signs. The clinical picture is complemented by the following symptoms:
- severe muscle pain;
- muscle cramps;
- purple dots or blisters at the site of the bite;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased sweating;
- signs of intoxication of the body (fever, headache, general weakness).
If symptoms characteristic of a poisonous spider bite are added to the local manifestations, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely provision of assistance will help avoid serious consequences.
Diagnosis of a spider bite in a child
A spider bite can only be accurately determined at the moment of the bite itself. Subsequently, diagnosis is carried out on the basis of complaints, clinical manifestations and differentiation with other conditions (for example, bites of various insects). Determining the type of poison plays an important role in diagnosing a poisonous spider bite. If a spider has bitten a child in front of the parents, then to facilitate subsequent diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy, it is necessary to pay attention to the characteristic features of the arthropod.
Treatment of a spider bite in humans with medications
To stop the pathological process and neutralize the effect of the poison, local, systemic antihistamines are used.
Allergy tablets
Tablets, drops for allergies:
- Suprastin;
- Claritin;
- El-cet;
- Eden;
- Diazolin;
- Tavegil;
- Zodak;
- Loratadine;
- Diphenhydramine.
If there is a sharp deterioration in health with difficulty breathing, arrhythmia, or increased blood pressure, it is prohibited to treat the bite yourself. For an antidote, doctors administer a special serum or a combination of several drugs with different effects.
Preparations for treating the skin after a bite:
- Fenistil-Gel;
- Psilo-Balm;
- Advantan;
- Betamethasone;
- Elokom;
- Dermovate.
You can use any cream or ointment with an antiallergic or antihistamine effect. For minor allergies, use Zvezdochka balm, Calendula ointment, Menovasin, Bepanten cream. Treat the bite 1-4 times a day.
Important!
If you are attacked by spiders and abscesses appear after the bite, you need to see a dermatologist or allergist. Treatment will be prescribed by a specialist. In the presence of abscesses and ulcers, therapy is carried out with local antibiotics or combined agents - Elokom S, Tetracycline ointment, Levomekol, etc. If a spider bites you in the neck, you need to immediately go to the hospital without waiting for alarming symptoms to appear. The body's reaction can be unpredictable.
According to the International Classification of Diseases - ICD 10, poisonous spider bites, their consequences, and treatment are discussed in section T63.3. Deadly poisonous spiders in our area include 2 species - karakurt and tarantula.
Causes
Meetings with dangerous poisonous spiders usually occur in nature: in the country, in the forest, and even in the park. Children, especially younger ones, are at risk. Having seen a spider, an inquisitive child may want to touch it or pick it up. The arthropod perceives such actions as a threat and bites.
A spider can bite a child even at home. Non-venomous spiders live in the house; their bite is not particularly dangerous. If the house is located in the habitat of poisonous spiders (for example, karakurt), then the arthropod can easily enter the home. Spiders can migrate, so poisonous specimens are often found in uncharacteristic environments.
Prevention measures
It is worth remembering that a spider bite is quite rare. During the warm period, there are only a few dozen such cases throughout the country. At the same time, about half a million people seek help every year if they are bitten by a tick. Therefore, you should not be afraid of an insect attack; it is enough to take a number of preventive measures.
The best way to avoid being bitten is to avoid the spider. These arthropods should not be handled so as not to provoke an attack. Regular cleaning and maintaining cleanliness will allow you to promptly get rid of insects that accidentally appear at home.
When going outdoors, you need to use special repellents that can repel spiders. Clothes must be closed. If you plan to spend the night in the forest, you should take with you a canopy or mosquito net, which will prevent insects from accidentally crawling inside.
What to do if you are bitten by a poisonous spider
Treatment and prevention
Treatment for spider bites depends on the type of spider. For mild bites, painkillers, antibiotics, and antihistamines may be prescribed. Antivenin is used for black widow and brown recluse bites. Antivenin should be used as soon as possible after the bite.
Black Widow Spider Bites: Clean the bite and apply an ice pack to it. Get a tetanus shot. Black widow bites can cause severe muscle spasms, which may require intravenous medications to relax the muscles. Hypertension may also require treatment.
Recluse spider bites: You should clean the wound, apply a sterile bandage and cold compress, and elevate the bitten part of the body. Get a tetanus shot. You may need to be hospitalized if complications occur. In particular, hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) may require kidney dialysis, and bites that develop into large areas of dead tissue may require surgery and skin grafts.
Hair or tarantula bites: The bite should be cleaned. A tetanus vaccination is recommended. If your skin is exposed to hair, treatment with antihistamines and glucocorticoids may help.
Complications
The most common consequences of a spider bite in children include allergic reactions. Against the background of an allergy, Quincke's edema, an attack of suffocation and other unpleasant symptoms can occur. Also common complications include secondary wound infection. If parents react to the bite in time, this can be avoided.
Bites from dangerous poisonous spiders are rare. However, if this happens, the consequences can be the most unpredictable: from a malfunction of various organs to death.