I was bitten by a tick: action plan
A tick attached to the skin is difficult to ignore. In addition to the fact that its bite causes pain and discomfort, it is very dangerous, because ticks carry dangerous diseases: viral encephalitis, Lyme disease, tularemia and others. In this article we will tell you how to properly remove a tick, what to do with it, how to treat the wound, what consequences to expect and what to do to prevent the bite from happening again.
Signs of a bite, what a sucking tick looks like
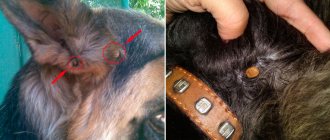
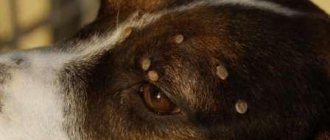
Most often we do not feel the moment of a tick bite. It is painless, as the tick secretes an anesthetic substance into the wound. Therefore, usually the only signs of a bite that can be seen are the bloodsucker itself (Fig. 1) or the area where it bit. Sometimes those bitten feel pain and difficulty breathing, and some develop rashes or blisters.
Figure 1. Attached tick. The longer a tick feeds on blood, the more it swells and the higher the likelihood of contracting a dangerous infection. Source: CC0 Public Domain
Where to look for a tick?
Ticks stick to places where they are difficult to notice and where the skin is thinner. After a walk in nature during tick season, be sure to inspect yourself, paying special attention to:
- areas covered with hair
- area behind the ears,
- armpits,
- abdominal area,
- inner thighs,
- areas under the knees.
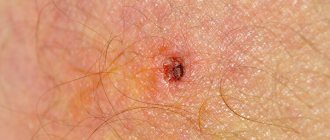
After the tick falls off, the site of its attachment bleeds slightly, gradually turning into a rounded red spot. It increases in size and itches. As it expands, the picture changes. The center of the bite becomes bright red or bluish, and a red spot forms around it due to inflammation.
If a parasite is detected, you need to remove it as quickly as possible and consult a doctor. It is worth going to the clinic if you find a suspicious wound on the skin.
How to get a tick and how to treat the bite site
If a tick has attached itself, it is best to consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will professionally remove the tick and treat the wound. However, a long search for a specialist can increase the likelihood of transmitting various infections from ticks. Therefore, it is often wiser to remove the tick yourself immediately after discovering it.
The first step is to treat the bite site with any antiseptic that you have on hand. Then use tweezers or strong thread to grab the tick as close to the surface of the skin as possible. This is necessary in order to remove the entire tick along with its oral apparatus. The tick must be removed with uniform, moderate force, strictly vertically, without sudden movements or twisting (Fig. 2). After removing the tick, treat the bite mark with an antiseptic again.
Figure 2. Removing the tick from the wound. 1 – Treat the tick wound with an antiseptic, take tweezers. 2 – Grab the tick firmly with tweezers or string. 3 – Gently pull the tick up, try to get the tick out of the skin entirely. 4 – Wash your hands and the bite site with soap and use an antiseptic. Source: cdc.gov
Be careful not to damage the tick while removing it from your body. If there are still fragments of it in the wound, do not be alarmed. After some time, the remains of the arthropod will come out of the skin on their own.
If you can't find tweezers, you can try to remove the tick with your fingers, but it is better not to crush the tick with your bare hands. To protect your skin, use a bandage or rubber gloves. You can first wrap the tick in gauze. After the tick is removed, do not forget to wash your hands with soap, or you can wipe your hands with alcohol.
Important! Some people are sure that the tick will crawl out of the wound on its own if you pour vegetable oil or other fat on it. The tick will simply have nothing to breathe. However, doctors do not recommend using this method. Due to blockage of the respiratory tract, the tick may die, having previously released substances into the wound, possibly containing the causative agent of the disease. A lit match is also useless; it will only cause the tick to burrow deeper.
Unfortunately, if you have not been vaccinated, once you have been bitten, it is no longer possible to prevent the disease. As a preventative measure for borreliosis, if the tick has been swollen with blood and there is a suspicion that it has been on the body for at least 24 hours, doctors advise adults and children over 8 years of age to take 4.4 mg/kg, but not more than 200 mg, of doxycycline.
What to do with a tick
Methods for diagnosing infections transmitted by ticks include examining the tick for the presence of pathogens (tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis).
A tick removed at home can be saved in case the doctor asks for it for examination. In this case, place the tick in a glass container with a lid and place a damp cotton wool in it to create increased humidity. Place the container in the refrigerator.
Important! Don't worry if you couldn't save the tick. Post-contact prophylaxis in the event of an infection in a tick is possible only for borreliosis, however, it is indicated for all patients, regardless of the result of the “dispensary examination” of the tick, provided that the tick was on the body for more than 36 hours (this is the time required for transmission of the infection).
Laboratories for testing ticks for the presence of the encephalitis virus are available only in the regional Centers for Hygiene and Epidemiology. The clinic doctor will tell you the address of the regional center. If necessary, you will have to transport the tick there yourself in a container with ice. If you first go to the clinic and take a referral to the Center, the analysis will be free for you. If you go without a direction, you will have to pay for the research.
How ticks are examined In the laboratory of the Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology, the presence of the encephalitis virus and the causative agent of tick-borne borreliosis in the tick contents is determined. The analysis is very accurate. It allows you to detect DNA or RNA of pathogens. If pathogens are not identified, you can rest assured. If pathogens are detected, you will have to undergo a blood test. It will show whether the infection occurred after contact with the insect.
Which doctor should I see and when?
After a bite, try to contact your local physician at the clinic as soon as possible. Typically, doctors do not prescribe any tests if the patient does not have alarming symptoms. You will need to carefully monitor your own health for 1-2 months in order to notify your doctor of possible illness. It may indicate infection with some kind of infection.
What tests should I take?
Immediately after a bite, no tests will help identify the presence of a tick-borne infection. DNA or RNA of the pathogen can be detected only after 10 days, and antibodies to pathogens begin to be produced in the body 10-14 days after the bite.
You should see a doctor and get a blood test if:
- the bite occurred in an area where tick-borne diseases are common,
- a study of the tick confirmed that it is contagious,
- a person exhibits symptoms of a disease transmitted through tick bites.
First aid for a tick bite
If a parasite has been detected on the body, then you need to act quickly and competently; the less contact with the insect, the lower the likelihood of infection with dangerous viruses or infections. Once an enemy has been detected, it should be removed. To do this, it is important to wear medical gloves to limit contact with the body of the arthropod, as it may contain viruses and dangerous microorganisms. You can remove the parasite using several tools:
- Any tweezers;
- Special pharmaceutical twister;
- Lasso made of thread, medical or self-made.
It is best to remove the arachnid in a medical facility, but you can do it yourself, taking all precautions. It is important to prevent crushing of the saprophage body in order to prevent infection of the wound. After removing the parasite, first aid for a tick bite is as follows:
- Disinfection of the wound using ethanol-based solutions or hydrogen peroxide;
- Carefully place the insect in a closed container with a damp cotton pad and submit it to the SES laboratory for research;
- Take a blood test and repeat it after 10 days to exclude infection with encephalitis, and 21 days.
If it is necessary to provide first aid to a child who has been bitten by a tick, you should remain calm and try to take the child to a doctor for a medical examination and qualified diagnosis. It is important to remember that you should not treat the insect or wound with oils or other substances.
What infections can you get from a tick?
A tick bite can cause infection:
- tick-borne encephalitis,
- tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease),
- tularemia,
- babesiosis,
- monocytic ehrlichiosis,
- tick-borne typhus,
- Q fever,
- spotted fever,
- hemorrhagic fevers, etc.
In Russia, the most common diseases are borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis. The peak incidence is observed in spring and summer. Other infections are much less common. Table 1 summarizes some of the infections listed.
Key warning signs associated with tick-borne infections include:
- drowsiness and weakness,
- temperature increase,
- chills,
- headache,
- pain in joints and muscles.
Tick-borne encephalitis is characterized by a fear of light and muscle weakness, and borreliosis is characterized by tension in the neck muscles, facial paralysis, inflammation of the joints and lymph nodes. Another telltale symptom of Lyme disease is erythema migrans. This is a red spot at the site of a tick bite, spreading out into a ring on the skin.
With tularemia and ehrlichiosis, digestive disorders (nausea, vomiting) are often observed, and babesiosis and Q fever may be accompanied by a dry cough.
What to do if you notice symptoms
If you notice any suspicious symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Currently, the effectiveness of post-exposure prophylaxis has been proven only for borreliosis (single dose of doxycycline), however, timely treatment helps to avoid many complications.
What happens if you don’t see a doctor: complications
Ignoring symptoms can lead to dire consequences, including death. In Table 1 we have listed the main complications associated with tick-borne diseases.
| Table 1. Complications caused by tick-borne infections. | |
| Disease | Complications |
| Tick-borne encephalitis | Inflammation of the brain substance, breathing disorders, damage to the circulatory system, mental disorders, paralysis, muscle atrophy, death |
| Lyme disease (borreliosis) | Arthritis, nervous system complications |
| Tularemia | With a generalized form of the course - death |
| Babesiosis | Anemia, acute renal failure |
| Ehrlichiosis | Aseptic meningitis, facial nerve paresis, liver damage, acute renal failure, toxic shock |
| Q fever | Pneumonia, tracheobronchitis |
If you notice any of the symptoms listed in the table, you should immediately consult a doctor. Currently, the effectiveness of post-exposure prophylaxis has been proven only for borreliosis (single dose of doxycycline), however, timely treatment helps to avoid many complications.
How dangerous are ticks?
Timely and correct first aid for a tick bite is the key to the health of any victim of blood-sucking parasites. Insects living in our country are not as dangerous as those living in countries with a warm and humid climate. Some types of saprophages can cause the development of such dangerous diseases as:
- Encephalitis is a viral infection in which brain damage is observed, accompanied by fever and severe intoxication of the body. The gray matter, cerebral cortex and even the spinal cord can be affected. This disease leads to complications in the functioning of the central nervous system, mental health problems, and in especially severe cases, death.
- Borreliosis or Lyme disease - the incubation period of this serious disease lasts about 3-6 weeks, after which signs of damage to the nervous system, including paralysis, can be observed. In the early stages, borreliosis can be determined by the presence of erythema, which forms at the site of attachment of the parasite.
When attacked by parasites from this class of arthropods, meningitis and poliomyelitis may develop.
Treatment
Treatment always depends on what disease struck the person bitten and how long it progressed before the person consulted a doctor and was diagnosed.
How are tick-borne diseases treated?
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed by the doctor. In the absence of severe symptoms, medications are taken at home, but if the disease is severe, the patient is sent to a hospital.
Most tick-borne infections can be cured with antibiotics, with the exception of encephalitis, the most severe disease that a tick can transmit. There is no targeted therapy against tick-borne viral encephalitis yet. Supporting agents include: medications containing interferon and interferon inducers, drugs to remove toxins from the body, antipyretics, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
On our website you can learn more about the course and treatment of tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis and tularemia.
Are they completely cured?
Tick-borne diseases can be cured, but some of their consequences, such as permanent paralysis or hearing loss caused by encephalitis, remain irreversible. Muscle pain and manifestations of arthritis after suffering from borreliosis may remain for a long time after treatment.
Chronic Lyme disease is referred to by some practitioners as post-Lyme disease syndrome. Although most patients with borreliosis can be cured with a 2-4 week course of antibiotics, some patients may continue to have symptoms (joint pain, fatigue, confusion) many years after the illness. This development of infection is usually associated with an autoimmune reaction of the body.
Source - article “Lyme disease or tick-borne borreliosis.”
How long does treatment take?
Antibiotic therapy aimed at eliminating the infection lasts about 7-14 days. The course of treatment for tick-borne encephalitis is usually 3-5 weeks. After discharge, survivors of encephalitis should be examined at intervals of 3-6 months for 1-3 years.
How long does a bite take to heal?
The rate of tissue regeneration depends on the individual characteristics of the person. Patients with accelerated recovery may no longer experience discomfort from the wound after 2-3 days. But there are also cases when the lump from the impact of the mite lasts for a month.
Normally, the bite should heal within a maximum of 2 weeks. In this case, there should not be increased redness of the affected area, suppuration, or heating. All these are signs of the development of an infection. At the first symptoms you should consult a doctor.
If the wound does not heal for more than two weeks, the matter may be due to one of the following reasons:
- Inflammation has developed. Against this background, regeneration processes slowed down. An ulcer or abscess may appear at the site of the wound, which takes a very long time to dry out.
- The patient constantly scratches the wound. Itching occurs due to an allergic reaction or infection.
- Healing is hampered by the part of the tick remaining in the body (head or proboscis).
In all cases, you should consult a doctor. He will either remove the remains of the parasite from under the skin and treat the wound with a healing composition, or prescribe therapy aimed against allergic reactions and inflammation.
Prevention
Prevention of diseases carried by ticks comes down to avoiding bites; in rare cases, vaccination will help protect you.
How to prevent ticks from biting you?
When going outdoors during tick season, the following preventive measures are necessary:
- use clothes with long sleeves and trousers that cover as much area of the body as possible, it is better if the clothes are light in color,
- wear hats,
- carefully inspect your body and clothes after a walk, comb your hair with a fine comb,
- also inspect your pets if they are walking outside (dogs often bring ticks into the house on their fur),
- use repellent before walking in the forest,
- do not tear off branches and try not to touch them, so beware of tall grass and bushes, stay in the middle of the path.
The effectiveness of vaccination, is it worth it?
You can protect yourself from tick-borne encephalitis and tularemia by getting vaccinated.
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis
In Russia, vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is indicated for residents of areas where encephalitis is endemic. You should receive a course of vaccinations in advance, at least 2 weeks before the start of the tick season. The vaccination regimen includes two doses of the drug with an interval of 1-3 months between doses and revaccination after a year. The completed course guarantees a stable immune response for 3 years.
If you missed the vaccination dates or unexpectedly went to a dangerous area, you can take an emergency course of 2 doses of the vaccine with an interval of 2 weeks. Revaccination will also need to be done after a year.
According to studies conducted in Russia, the frequency of development of stable immunity during vaccination according to the traditional scheme is up to 91%, and according to the emergency scheme – 88%.
Important! Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is the most effective measure to prevent this disease. Anyone who is in an area with an increased risk of contracting encephalitis or plans to stay in such a place should be vaccinated.
Vaccination against tularemia
In our country, people from foci of infection and workers in hazardous professions who have a high risk of infection are vaccinated against tularemia (for example, agricultural workers). Vaccination is allowed starting from 7 years of age.
For protection, one dose of a live vaccine administered subcutaneously or intradermally is sufficient. Revaccination is carried out every 5 years. The tularemia vaccine can significantly reduce the incidence of the disease and alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Important! Before vaccination, a doctor’s examination is necessary; the drugs have contraindications for administration. After vaccination, remain under the supervision of a specialist for at least half an hour in case of a sudden negative reaction.
Encephalitis insurance. Is it worth doing?
If you are not vaccinated and at the same time, due to the nature of your work, you are often in places where ticks live, it is advisable to conclude a voluntary health insurance contract in advance against tick-borne encephalitis. This will allow you not to think about the cost of treating this serious disease in the future.
The cost of the policy usually does not exceed 150-300 rubles. If you insure yourself and get sick, you will not be able to claim cash payments, but the insurance company will have to pay the costs of treatment and rehabilitation. The insured amount can range from 50 thousand to 1 million rubles, depending on the insurance company, insurance program and region. It is within these funds that you will be provided with the necessary medical care.
Typically it includes:
- examination of the victim and removal of the tick,
- laboratory testing of ticks for the presence of viruses,
- administration of immunoglobulin if indicated,
- hospitalization and treatment if the disease occurs,
- restorative therapy.
What to do to prevent a tick from biting
The tick becomes active during the warm season. He begins to look for his prey in warm, sunny weather. At high humidity, the parasite practically does not attack. But this does not mean that if a person visits the forest only in rainy weather, he will protect himself from the attack of the parasite. To prevent an insect bite, you need to take a whole range of measures.
Preventive measures need to be taken every time a person goes outdoors. Ticks are active in places where there is a lot of grass. They get onto the body from blades of grass, and much less often from the foliage of bushes and trees. If a person visits a forest park, a nature reserve, a nature reserve, a forest, or goes to a dacha or an overgrown park on the outskirts of the city, be sure to do the following:
- Cover areas of skin that are susceptible to tick bites. The parasite prefers the neck, area behind the ears, ankles, groin, elbow creases and back. Therefore, you should not wear T-shirts with a large neckline, rolled up jeans or shorts. During the warm season, when visiting the forest, you need to wear high boots with your pants wrapped in them, jackets with long sleeves and a high collar, caps or Panama hats.
- Use a pest repellent. Special sprays are available for application to the skin. It should be applied to the body immediately before going out into nature, following the instructions.
- Secure a summer cottage or house if a person goes there. Special concentrates are diluted in water and applied to plants and grass using a large spray bottle. Concentrates can also be used indoors. They repel ticks for 1.5 months.
You should not go through fields and forests unless necessary. It is much more difficult to encounter ticks in ordinary parks or in summer cottages. To prevent the parasite from clinging to the body, it is recommended to constantly mow the grass. Then the parasite will reach the maximum number of pets.
How to remove a tick
- If you notice an attached tick, you need to properly remove the insect and drink an antihistamine: Zyrtex or Suprastin.
- Fingers should be wrapped in a bandage or gauze; do not touch the bite site or tick with unprotected skin. An infectious tick can infect not only the person it bites, but also anyone who touches it.
shutterstock.com
- Clean your hands, tweezers, and the bite site with alcohol or chlorhexidine. You can “unscrew” the insect: the movements should be counterclockwise, and you need to keep the tick closer to the skin so as not to tear it into two parts. It is also extremely dangerous to crush a tick: then the contents of the abdomen will be squeezed out under the skin of the person it bit.
- You can use available tools: threads, tweezers or a special tool. It can be bought at a veterinary pharmacy or online store, the cost is 150-200 rubles.
If you take threads, wrap the proboscis as close to the skin as possible, and remove the tick with smooth rocking movements.
- After removing the insect, the wound must be treated with any solution containing alcohol.
You can also save the insect for future analysis. Place the removed tick in a small glass container and close tightly. If he died, it’s okay, the main thing is that he doesn’t dry out. To do this, place a moistened cotton pad next to the tick.
RIA News
- The cost of the analysis will be about 3000-4000 rubles. You can also take a PCR blood test for tick-borne infections; it will cost about 1,500-3,000 rubles. Blood is donated for tick-borne infections in case of complaints: elevated temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, rash.
- Mark the date of the bite on your calendar to help pinpoint when any symptoms began.
- Go to the emergency room immediately if you are afraid or cannot remove the tick yourself.
- After removing the tick, it is important to monitor yourself over the next few weeks.
Channel about healthy lifestyle in telegram! Subscribe
What are the symptoms of a tick bite?
To obtain food, ticks insert a special tube under the skin and begin the feeding process. At this stage, the symptoms are almost invisible. As soon as the tick begins to transfer special digestive enzymes under the skin, you will feel:
- Intense itching;
- Severe redness.
The insect needs to introduce components into the skin of the victim that will simplify the process of thinning the blood and speed up the rate of digestion of food. The affected area becomes like a blister and swells greatly. If a person is susceptible to allergic reactions, the bite will be very difficult to tolerate. Hives will appear, and the area of swelling will increase significantly.
If you notice bed mites at home and want to get rid of the pests as quickly as possible, then in parallel with treatment, it is necessary to take disinfestation measures. You can use professional products that are convenient to order in the online store. To quickly deal with the problem, you can use the services of a professional exterminator. When the premises are completely treated, the likelihood of re-infection is completely eliminated.
Self-treatment is highly undesirable when symptoms begin to worsen. After providing first aid, it is best to get tested to identify the likelihood of infection.