Human attitudes towards rats are ambiguous. Some are afraid of them, citing the example of the Middle Ages, when the rat became the culprit of epidemics. Others hate them and try in every possible way to eradicate them. Others have not encountered them in life, so they are neutral towards them.
There is also a 4th category - people who keep this animal as a pet. It doesn't matter what category you fall into. Anyone can encounter this rodent, and the result of this encounter can be a rat bite. Then the question arises - what to do if bitten by a rat, what are the complications and consequences?
Briefly about rats
Rats have been known to mankind for a long time. In many writings about them there are negative lines, descriptions of terrible diseases that caused the death of hundreds, even thousands of people. Man has been fighting this unwanted neighbor for centuries, but its population is not decreasing. Their numbers increase every year, and the reason for this is the man himself, who arranges city dumps.
This is an excellent place of residence for rodents: here they arrange housing for colonies and find food for themselves.
Note! Every year, about 2 thousand people die from a bite. It is not the bite itself that is dangerous, but the diseases that can be transmitted through saliva.
Rodents are divided into 2 categories: domestic and wild. A domestic animal is rarely dangerous. They are bought in pet stores, where a veterinary permit or license is required. Then a person takes care of him: cleans the cage, feeds him, plays. Contact with wild representatives is kept to a minimum. Wild individuals settle in close proximity to humans:
- in city landfills;
- in the entrances;
- near trash cans in the yard;
- close to agricultural fields.
It is much less common to find an animal at home. They not only cause great discomfort with their proximity, but are also dangerous.
What diseases does a rat carry?
Understanding how dangerous a rat bite is, a person will try to protect himself as much as possible from it. The most dangerous are wild rodents that live in garbage dumps, basements or warehouses, and catacombs.
Rat bites lead to infection with such dangerous diseases:
- leptospirosis. This pathology is transmitted from rats more often than other infections. The causative agent is a bacterium of the genus Leptospira. The disease is severe and in 16% of cases ends in death. Leptospirosis is accompanied by persistent fever. It affects capillaries, muscle fibers, liver, and kidneys. Complications of the pathology are myocarditis, paralysis or infectious-toxic shock.
- Sodoku. Infection occurs through bites, when spirilla enter the wound with the saliva of sick animals. The onset of the disease is sudden. The victim's temperature rises sharply, severe muscle pain and mental agitation appear. Untreated cases are fatal in 10% of victims.
- Listeriosis. The causative agent is the bacterium Listeria. It infects the central nervous system and can cause meningitis or encephalitis. In most cases it leads to death. Pregnant women, newborns, the elderly, or those with weakened immune systems are particularly at risk.
- Yersiniosis. An infectious disease characterized by damage to the gastrointestinal tract, joints, skin and other organs. The incubation period lasts from 15 hours to 15 days. In the vast majority of cases, the disease ends in recovery.
- Tetanus. This is a dangerous infectious disease that affects the nervous system and causes severe muscle cramps. The most common cause of death is asphyxia due to spasm of the respiratory muscles. This disease rarely develops from a rat bite, but such a risk cannot be excluded.
- Melioidosis. This infection occurs as a sepsis and is accompanied by the formation of metastatic abscesses and necrotic foci in many internal organs. If timely medical assistance is not provided, the probability of death is almost one hundred percent.
- Rabies. The rabies virus causes a specific encephalitis. It is transmitted through saliva when bitten by a sick animal. It is extremely rare for people to become infected with rabies from rats, but this possibility cannot be ruled out. Rabies in rats occurs in 2 stages. At first the animal hides in a dark place and then becomes aggressive. At the same time, viscous saliva is released from her mouth.
Along with the listed diseases, rodents are dangerous because they are carriers of fleas, bedbugs, and ticks. And if rats bite children, they often develop phobias.
Features of rat behavior
Rats are small animals with their own behavioral characteristics. Knowing them, you can minimize the risk of unwanted contact.
Reasons for attacks on people
This rodent, despite its close proximity to humans, prefers to avoid meeting him. An attack is possible if he feels hungry for a long time, but has nothing to eat. At risk are children, paralyzed patients, and adults who are heavily intoxicated by alcohol or drugs.
Note! A rat loses its sense of fear if it becomes infected with any viral disease. They become aggressive and stop hiding.
There are frequent cases of attack by an animal driven into a corner. Do not insist on playing with your pet if it has already refused once. Otherwise, the bite cannot be avoided. There are even known cases of rat bites in pet stores - they are under constant stress.
An adult female may show aggression if she sees that her offspring are in danger or the nest has been broken.
When rats bite
This animal rarely attacks first. But if, while next to him, you wave your arms or a stick, stomp, or perform other sudden actions, then he will take an attack pose. It looks like this:
- she stands on her hind legs;
- the body sways from side to side;
- a loud squeak is made, followed by an attack.
How a rat bites
The teeth of this rodent are quite long. They constantly sharpen them on all objects that come their way. In action are:
- crackers and other food products;
- paper;
- tree;
- plastic;
- concrete and other building materials.
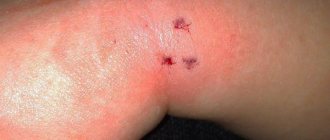
Human skin is very thin, it is quite easy to bite through it. The greatest danger is posed by the lower incisors - they are sharp and long. More often they bite fingers, arms, and legs. A rat bite looks like puncture wounds that bleed.
Differences between rat bites and bites of other animals
Sometimes it can be difficult to distinguish a rat bite from another animal bite. The injury can occur while sleeping or on the street. Particularly difficult is an injury sustained by a child or animal.
In this case, you need to carefully examine the affected area. If you can see marks from the upper and lower incisors close to each other, then this is often evidence of a rodent bite.
It doesn’t really matter whether it was a mouse, a vole, or a hamster. They are all equally dangerous to humans.
Precautionary measures
The best safety measure when dealing with dangerous rodents is to avoid contact with the predators. Rats usually run away from people, but in a life-threatening situation they attack. To avoid putting anyone at risk of being bitten, consider the following:
- trash cans must always be closed;
- leftover food should not be left in the public domain;
- installation of special ultrasonic repellers and traps eliminates rodents;
- specialized services fight rats more effectively than residents alone;
- The correct behavior when meeting a predatory animal is to avoid sudden movements, attempts to photograph rats, catch them, hit them with a stick, etc.
The only measure that helps in a critical situation of a collision with an aggressive animal is to spray the animal with cold water. This way you can scare away an evil predator.
Lovers of rats as pets should remember that the desire to photograph the animal while simultaneously feeding from hands often leads to a rat bite. The photo is not worth it to heal the deep marks from the teeth of a predator.
Rats have coexisted with humans for centuries, causing hostile feelings in chance encounters. An intelligent, hardy animal in the fight for territory, food supply, and to protect its offspring is always ready to engage in battle with the enemy. Only knowledge of the characteristics of the animal will help to avoid painful injuries.
What to do if bitten by a rat (ambulance)
First aid to the victim
If you have been bitten by a rat, you should immediately begin preventive action. Take your time to stop the bleeding - most of the pathogens will come out with the blood. It is recommended to apply additional pressure to the wound to help the blood flow out.
Rodents have sharp, long teeth. They penetrate deep under the skin. The top layers are drawn in quite quickly and prevent complete cleaning.
Rat bite.
First of all, you need to wash the wound with laundry soap. Then it is recommended to treat with hydrogen peroxide, iodine or brilliant green. If the wound is deep, try to push the solution inside as much as possible using a bulb or syringe. Then a bandage with levomekol is applied. Doctors sometimes prescribe antibiotics as a medical treatment.
Recognizing a rodent bite
Rats bite with their front incisors. Deep damage to the skin is accompanied by severe pain, and the wound can take a very long time to heal.
What do rat bites look like:
- severe bleeding appears;
- the appearance of the wound corresponds to the location of the rodent’s incisors, with which it makes a puncture (usually several holes);
- local increase in temperature in the damaged area of the skin;
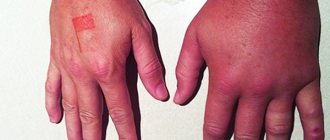
- spreading swelling and bluish color of the skin due to injury to the capillaries.
Most often, animals bite on the limbs, rarely on the face. After a bite, various signs may appear that indicate infection with dangerous diseases.
Possible consequences of rat bites
Abrasions, puncture and lacerations, hematomas, bruises are possible consequences of an encounter with a rodent. However, with well-planned treatment and care for the injury, the risk of complications is minimal.
Wound festering is the most common of these. The affected area is opened and drained. This complication can be avoided if you properly care for the wound. In advanced cases, soft tissue may be deeply affected, requiring amputation.
What infections do rats spread?
Rats have long been considered carriers of diseases, including viral ones. Of these, the most dangerous are the following:
- Sodoku is a rat bite disease that is fatal in 10% of known cases. It can be avoided if treatment is started on time;
- tetanus - the risk of death after infection reaches 20–30%. Tetanus ranks third among the most dangerous diseases after rabies and plague. Even after recovery, dangerous consequences are possible in the form of heart paralysis, pneumonia, sepsis;
- Leptospirosis is transmitted not only through saliva. If you notice that the animal has chewed the bread, then it is better not to eat it. The disease is dangerous due to paralysis, myocarditis, renal failure, infectious-toxic shock;
- pseudotuberculosis - dangerous for the development of meningitis, polyarthritis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis.
The risk of contracting rabies is minimal, however, it is a rather dangerous disease that requires prompt treatment.
Danger
Even shallow rat bites can be deadly. Rodents spread more than 60 pathogenic microorganisms, carry helminth eggs, and are carriers of dangerous diseases. When they bite, rats secrete saliva that contains viruses, bacteria, and other infections.
- Licorice. Or rat bite disease. Sad statistics show that if no measures are taken, 10% of cases end in death.
- Tetanus. People are vaccinated against this disease in childhood. This is enough to protect an adult from a dangerous infection. If vaccination has not been done, the risk of developing tetanus increases significantly. Complications of the disease are pneumonia, heart paralysis, blood poisoning. The fatality rate is quite high - about 23%.
- Leptospirosis. It is very often transmitted by the bite of a rat. In most cases, the patient ends up in intensive care. Complications are kidney failure, cardiac paralysis, anaphylactic shock, death.
- Pseudotuberculosis. Affects the respiratory organs and lungs. The danger is the development of pleurisy, myocarditis, and meningitis.
- Listeriosis. The causative agents of infectious diseases are pathogenic microorganisms. The risk of developing pathology increases in people with low immunity, children, and pregnant women. In pregnant women, it provokes miscarriage at any time.
- Toxoplasmosis. Infectious bacterial disease affecting the intestines. With a significant proliferation of pathological microflora, other internal organs are affected.
- Q fever. The disease is characterized by fever, chills, and severe intoxication. Dangerous complications that can affect any internal organs.
First actions after a rat bite
If you are bitten by a rat, do not panic. By adhering to a clear algorithm of actions, you can avoid harmful consequences.
- Rinse the wound under running water and then treat it with an antiseptic. Hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, Miramistin, iodine or brilliant green are suitable for this. Don't wait for the bleeding to stop. The bites are usually deep and bleed for a long time.
- To avoid dirt getting into the wound and other mechanical damage, the affected area is bandaged.
- Observe the wound, and if you have the slightest doubt, consult a doctor.
It would be a good idea to get a preventive vaccination against rabies and other diseases, which will be offered at the nearest emergency room. Saliva is a breeding ground for bacteria and viruses.
What to do after being bitten by a pet rat
Pets are not considered carriers of diseases. However, if there is a wound, it is necessary to provide first aid to the victim and treat it thoroughly.
Change the dressings regularly and continue to treat the wound until it heals. If your health worsens, then this is a reason to contact a medical facility.
What to do if rats bite children in kindergarten
If a child, coming from kindergarten, complains that he was bitten by a rat, then not only therapeutic measures should be taken. Such a violation of the Sanitary Rules and Norms is an administrative offense.
Note! The teacher is obliged to monitor not only the children under his care, but also the order. Such a complaint requires contacting the Administration. If the problem is not resolved, then parents should write a complaint to the Sanitary and Epidemiological Service requesting an inspection. It is better to draw up a collective appeal, and attach to it copies of certificates from the health care facility where the doctor examined the injury.
Are bites from decorative rats and animals in pet stores dangerous?
If you are bitten by a pet rat or injured in a pet store, do not panic. Pets rarely show aggression. Most likely, they will not even bite through the skin. However, if the wound still bleeds, then it must be treated to avoid suppuration.
Also, pets and pet store animals are rarely carriers of dangerous infectious diseases.
Are bites from rats and animals in pet stores dangerous?
Bites from domestic (decorative) rats are practically not dangerous. The risk of contracting an infection is minimal here, because ornamental animals are usually healthy and are not carriers of pathogens. And tame pets do not bite as violently as wild rats, and therefore the wounds left by them are rarely deep (usually the animal does not even bite through the skin).
However, if a decorative rat bites until it bleeds, suppuration of the wound can still occur, and therefore the bite must be fully treated in any case.
Likewise, if a rat bites a child in a pet store, the wound must be disinfected - for example, lubricated with iodine and bandaged. You don't need to do anything else. This is certainly not a reason to kill the animal and take its corpse for examination, since rats in pet stores are usually healthy (rabies, which parents usually start to worry about, is out of the question here).
If a rat bites your pet
An adult pet rarely needs help when treating a wound. They themselves carefully lick the wound. The saliva of cats and dogs contains an enzyme that acts like an antiseptic. Only rare supervision is required on the part of the owner.
If a young pet is bitten, regular antiseptic treatment and bandaging will be required.
If the owner notices a change in the behavior or activity of the animal, then a veterinarian should be called. Many diseases require emergency specialist care. You should not make decisions or prescribe medications on your own.
How to stop a rat from biting
If an animal has bitten its relatives or other pets, you should seriously think about the reasons for the rodent’s nervousness. Sometimes it can be:
- lack of water, food;
- lack of shelter in the cage for quiet rest;
- regular “torment” at the hands of people;
- disease.
Until the cause is determined, the animal should be placed in a separate cage for 10 days. If no illness has been identified, and the rodent does not lack communication and care, perhaps the bites were triggered by random stress or hormonal fluctuations.
Sometimes an animal bites out of habit, which was developed due to improper communication with it during the period of adaptation to a new place. This situation dictates the need to wean the rat from biting and to tame the pet again.
This process is best started by changing the cage. A new environment, fresh impressions and smells will help the animal change its behavior. The dwelling should be placed in a quiet corner of the room, dim lighting should be created, and a small “hole” should be built inside so that the rat can rest there from unnecessary attention and sleep peacefully.
For the first few days, the rodent is left alone. As soon as the animal begins to spend most of its time outside the burrow, you can begin to communicate with it. Rat training should be done regularly, but not for too long
It is important to observe the rodent, determine its inclinations, and not cause pain
If you try to bite, you should stop communicating. The animal will quickly understand that it is doing the wrong thing. Usually 1–2 months are enough to wean a rodent from a bad habit.
What symptoms indicate infection?
The incubation period for most diseases ranges from several days to a couple of weeks. Characteristic symptoms of infection:
- elevated temperature;
- chills;
- feeling of weakness;
- gastrointestinal disorders, namely vomiting, diarrhea, lack of appetite, abdominal pain;
- pain in the bite area, suppuration;
- uncontrolled muscle contractions;
- insomnia.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult your doctor for a diagnosis. It is important to tell the doctor when the bite occurred. This is the main difficulty: by the time they go to a medical facility, patients forget about the injury received from the rodent.
When is urgent medical attention needed?
If you are bitten by a rat, you should immediately go to the hospital if, 2-3 days after the incident, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- headaches;
- significant increase in temperature;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- chills;
- muscle pain;
- constant weakness;
- skin spasms around the injury;
- increase in liver size.
These symptoms indicate infection with a viral disease and require urgent medical attention.
Rodent control products
There are many repellent devices, and the operating principle is based on ultrasonic and electromagnetic waves. Such devices do not kill rodents, but force them to leave the room by affecting the nervous system. What types of repellers exist and what are the differences in operation:
- Electronic repellers. The essence of these devices is to distribute magnetic pulses through an electrical wire, which is a powerful irritant for rats and mice. The range of these repellers is enough to cover the entire area of the room.
- Ultrasonic repellers. These devices act on the nervous system of rodents with high-frequency sound vibrations with changing frequencies, due to which the rats do not have time to get used to the ultrasound and quickly flee.
- Combined repellers. These devices combine a dual effect on pests: high frequency sound and low range of electromagnetic waves. This variable component does not allow rodents to adapt.
The choice of a specific repellent device depends on a number of factors: the number of rats and mice, the area of residence, the level of human comfort, etc. Each device has a different radius of influence, so choosing a repeller for a specific case will not be difficult. Their undoubted advantage is that they quickly drive rodents out of the house.
What is known today about cannibal rats?
As noted above, there are quite well-known and frequent cases where rats gnaw off the hardened skin on a person’s heels. This usually happens when the victim is sleeping, and often the attack ends in serious trouble - the animals get to the soft tissues, and the wounds here do not heal for a very long time due to constant restlessness when walking.
When the rats realize that a person cannot harm them, they calmly gnaw off more and more pieces from his body. It was rats that killed a huge number of prisoners in prisons and captives in military camps in the Middle Ages: people were tied up, their ability to move was severely limited, and hungry rodents boldly (and competently) chewed on them, leaving bleeding wounds. A person usually died either from blood loss or from blood poisoning.
If a person is paralyzed or unconscious, they may suffer the same fate.
There is information about the terrible torture that guilty prisoners were subjected to in Stalin's labor camps: a person's hands and feet were tied, after which he was put in a large barrel, into which hungry rats were released. A few days later, corpses with their stomachs eaten away were taken out of the barrels. There were other options for torture...
And yet, we cannot talk about specialized cannibal rats. These animals are omnivores and eat any meat: whenever possible, the rat eats entrails and gnaws bones, and if it finds the corpse of any animal or person, it will bite off pieces of it too. The animal may not notice the difference between a corpse and an unconscious person.
That is, by and large, real cannibal rats are the most ordinary rats, eating everything, but by chance they simply found themselves next to the motionless body of a person and did not disdain to feast on it.
But rats that feed exclusively on human flesh are not known to science today. Moreover, there is no evidence that these animals can attack healthy people and bite them to death. Even an invasion of rats in certain areas never leads to human casualties. For example, from different Russian cities, rat infestations are reported with varying frequency, but no tragic cases follow these events.
Prevention
Treatment for flea bites will not bring any results if the insects remain indoors.
There is no point in delaying measures to eliminate bloodsuckers. Insects reproduce incredibly quickly. Zoologists know that 1 female produces 1 million offspring per month. During this time, the home will turn into a flea nest. The problem with fighting bloodsuckers is that only adult individuals live on pets. The source of reproduction - eggs, larvae and pupae, remain in floor cracks, carpets, bedding and animal care items.
When carrying out events, both the pet and the premises need to be treated.
Wet cleaning of the house does not protect against parasites and even promotes their survival. After all, fleas love moisture. The only effective way to kill insects is to treat pets. How to get rid of flea bites:
- use of insectoacaricidal shampoos for washing pets;
- wear flea collars;
- drops on the animal’s withers – Fleanet, Barrier, Celandine, Dana Ultra Neo;
- pills.
If the apartment is heavily infested with bloodsuckers, the right decision is to call specialists from the SES (sanitary and epidemiological station). They will disinfest clothing and furniture. They will destroy adult individuals, as well as their larvae, pupae and eggs.
When fleas are found on pets, timely treatment measures will prevent reproduction and prevent injury to family members. Compliance with basic sanitary standards in the house will protect against the appearance of bloodsuckers.