Origin of the species and description
Photo: Fireman Beetle
The fireman beetle is a medium-sized insect that got its name because of its original appearance, which includes red elements in its color. Quite often, this animal is confused with other beetles, called soldier bugs, onion rattles and bee moths by firemen. However, these are all completely different insects, with their own habits and external features.
Video: Fireman Beetle
Biologists also call firefighter beetles red-legged soft beetles. This is due to the bright burgundy color of the beetle’s legs and the absence of chitinous cover. The elytra of insects are very flexible and soft. Therefore, people believe that firefighters, like other representatives of soft-bodied animals, are more likely than others to be attacked by other animals and predators. But that's not true! These bugs can take care of themselves.
Interesting fact: Unfortunately, firefighting beetles have a very short lifespan. For this reason, such animals are able to reproduce within four weeks after their birth.
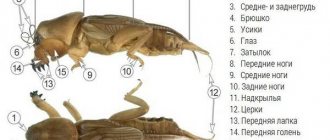
The fireman beetle is an insect of the soft-bodied family, order Coleoptera. It is quite easy to recognize this creature. His head is decorated with small antennae, very thin, resembling threads. These antennae are constantly in motion. There is a dark spot at the top of the head. It is by this that one can distinguish the fireman's beetle from other beetles. The body is rectangular, elongated. Adults rarely grow more than 1.5 centimeters in length. The belly is painted a bright burgundy color.
Firefighter beetles are usually found in gardens and are beneficial to humans. They effectively exterminate a huge number of insect pests. However, sometimes the population of such beetles grows very large and it becomes necessary to exterminate them. Firefighter beetles do not have to be poisoned, thereby polluting your own garden. Such insects can simply be collected by hand. But this method is relevant if the beetles have not yet had time to multiply very much. Otherwise, you can flavor the plants with a mixture of cheap tobacco and wood ash.
Reproduction and lifespan
In the hot summer, when the soil and air are thoroughly warmed up, the mating period of red-legged softies begins. This time falls in July, the zenith of summer.
The female lays eggs on some soft base: leaf litter, decomposed plant debris, wood debris, rotten stumps, branches, etc. After laying fertilized eggs, the female and male die after some time.
Incubation lasts 15-20 days - the period depends on the ambient temperature. A dark larva covered with hairs gradually appears. In appearance, it resembles fuzzy beads interconnected, somewhat similar to a necklace. The development of larvae is associated with active feeding and movement.
Larval development occurs in different ways. Some of them manage to pupate before the onset of winter, while others overwinter in rotten wood or rotten leaves. Pupation of the latter takes place in the spring, after warming.
This can be found in natural conditions somewhere under the bark of old trees. After two weeks, young red-legged softwings appear, and after a month they are ready to reproduce.
Rapid settlement and independent life do not last long. The total lifespan of a firefighter beetle is very short - about two months.
The study of garden inhabitants, firefighter beetles in particular, contributes to the correct line of behavior in the fight against garden pests. By conserving beneficial redlegged redwings, property owners are providing a natural environment in which crops will mature and survive.
External differences of the soldier bug
The body of the soldier bug is round, slightly flattened. The insect has a bright color: the body is black, the pronotum and elytra have a red pattern. Bedbugs have no wings. The eyes are red, the mustache and paws are black. The length of the soldiers is 8–11 mm. The oral apparatus is equipped with a piercing-sucking proboscis, which is in a horizontal position.
lenslenses adventurenaturetime dicdoc.macro
Red bugs often gather in groups in one place - adults and larvae, which is a distinctive feature of the species. The name “soldiers” comes from the property of being arranged into unique divisions and the colors of the chitinous cover.
Who is often confused with?
The red bug is often confused with two insects:
- Firefighter beetle, soft beetle (Cantharidae). In fact, insects have nothing in common with each other, except for confusion in names. The fire beetle belongs to the order Coleoptera. It has a long body 1–1.5 cm - twice as long as that of the soldier bug. The elytra and tarsi are black, with filamentous whiskers. The mouthparts are gnawing. Insects have wings with which they move through the air. The beetle's abdomen is orange or red.
a.koptyreva na_tasha.sh gita089
- Blackhead (Corizus hyoscyami). In appearance, the insects are very similar to each other. The differences are in the position of the head: triangular, slightly tilted, and the shape of the pattern on the back. The eyes are darker than those of the soldier bug - closer to brown. Insects live mainly on umbrella plants: onions, dill. The larvae feed on henbane and tobacco leaves.
Kinds
The soft-bodied family is numerous - almost 4000 species. There are 4 subfamilies. Despite the external defenselessness and small size of insects, they are not included in the bird diet due to toxic substances in the tissues of their body.
In addition to the well-known fireman beetles, or the red-legged soft beetle, the following are common in our latitudes:
- The brown softy beetle is an inhabitant of forests and forest-steppes. The length of the insect is 1.1 - 1.5 cm. The color is reddish-black. Legs are dark. Larvae of a brown softy beetle with 3 pairs of legs. Flat head with 2 eyes. The larvae feed on worms, small insects, and even eat each other. They live in the roots of trees, on plant litter, under stones, and take refuge in the soil;
- flower beetle (red) - the black tips of the soft elytra and the square shape of the pronotum distinguish this species from other relatives. The color is predominantly red. The length of the body is no more than 1 cm. It lives in flowering meadows and thickets of plants. The beetle is distributed throughout Europe. You can see it in nature from May to September.
Among soft beetles there are many predatory beetles, but there are vegetarians who are satisfied with exclusively plant foods.
In addition to beetles that are similar in essence, we can distinguish a rather rare relative - the common firefly, which is also part of the family of beetles with soft elytra (elytra).
Lantern fireflies live in the subtropics and tropics. They have the amazing ability to glow in the dark. Not all fireflies have luminous organs; some species glow according to gender: only females or exclusively males.
Where does the fireman beetle live?
Photo: Firefighter Beetle in Russia
The appearance of the fireman's beetle always attracts the eye and arouses genuine interest among adults and children. Such an insect cannot be ignored during the warm season. It is usually found in gardens, orchards, and other places where garden plants grow. Their population is especially huge where raspberries and currants grow. Firefighter beetles don't particularly like attention. When a person approaches, they try to quickly leave their place.
Interesting fact: Firefighting beetles provide invaluable benefits. They exterminate a huge number of pests. But there is also harm from such insects. Firefighters can damage some types of fruit and vegetable crops and garden plants.
The firefighter beetle is a ubiquitous insect. It is found wherever there is a cold or temperate climate. But the main requirement of these beetles is the availability of food suitable for them. There are large numbers of firefighter beetles in Europe, Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Georgia and many other countries.
Softworms reproduce quickly, but do not live long. These insects choose cultivated places to live. They can be found wherever there are plantings of fruit trees, raspberry bushes, currants, and gooseberries. They also prefer to live in vegetable gardens. Small populations of such insects are even welcomed by gardeners. This is not surprising, because firefighters help get rid of caterpillars, aphids, mosquitoes, midges and other pests.
Interesting fact: The fireman beetle is a safe and highly effective means of getting rid of cockroaches. In order for the Prussians to leave the living quarters, it is necessary to send several firefighters there and leave them for a while.
Now you know where the fireman beetle is found. Let's see what he eats.
Population and species status
The soft-bellied family is one of the most numerous. Today it numbers about four thousand beetles, among which fire beetles are considered one of the most common. The “red” beetle is widely represented in various parts of the planet. It is found wherever the climate remains temperate or even cool. It is impossible to determine the exact number of such beetles. However, according to the latest data, the population of this insect species is not at risk of extinction.
The number of firefighters in the natural habitat is unstable, but numerous. Instability usually occurs when people eradicate these insects from large agricultural areas. However, even this does not threaten the total number of firefighters. These beetles do not live long, but they reproduce successfully. From year to year they are rapidly increasing their numbers.
Firefighter beetles are dangerous only if the area is overpopulated. When their population in one place is small, such an insect can be of great benefit. It effectively destroys small garden pests. Firefighters eat caterpillars, aphids, various beetles, and mosquitoes. This is a safe and absolutely free “remedy” for protecting trees, bushes and plants.
The fireman beetle is a prominent representative of a large family of soft beetles. This is a unique creation that looks very much like a fire truck. This insect, provided its population is normal, can be of great benefit to gardeners. It eats almost all the most common pests, while itself does not cause significant harm to plants.
What does the fireman beetle eat?
Photo: Red Beetle Fireman
The fireman beetle, despite its “softness,” is a rather formidable predator. This insect has very powerful jaws. It is these jaws that enable the beetle to deftly absorb small insects.
A firefighter's daily diet includes:
- aphids;
- small caterpillars;
- sleepy flies;
- larvae of various insects;
- small chafers (those species that feed on leaves).
Looking at the beetle's diet, it is easy to realize that it prefers to eat only those insects that are much smaller than its own size. In addition, firefighter victims often have a soft body structure. This predator cannot cope with too hard chitinous cover, even with the help of its powerful jaws. The beetle avoids such insects.
The fireman's beetle's hunting process begins in the air. He looks out for his next victim during the flight. Having found a suitable insect, the fireman lands in close proximity to it or even directly on the animal. Next comes the jaws. The fire beetle stabs them into its prey, releasing a toxic substance as it does so. One portion of poison can significantly soften tissue, so the further process of food absorption is quite easy.
In the larval stage, the firefighter beetle eats a little differently. Its diet consists mainly of small worms and centipedes. Beetle larvae find such food right in their habitat - in rotten stumps, in old trees. For this reason, it is highly not recommended to remove stumps and old wood from the garden. Firefighting beetles could be of great benefit in the future.
Description and features
The fireman beetle insect belongs to the family of soft beetles, the name of which reflects their main feature - soft bodily integument that does not have a hard chitinous cover.
In scientific sources, the full name of the beetle is found - the red-legged soft beetle. Lives in temperate and cold zones, the fireman is distributed over a vast territory of Eurasia.
The insect is only 1.5-2 cm in length. The body has an elongated and flattened shape. The abdomen is composed of 7 rings of red or orange color. The big head is retracted. There is no upper lip. The filamentous antennae consist of 11 joints.
The elytra are black or dark gray. The upper part of the body has villi. In the front part of the back, near the head, you can see a dark spot in the shape of a heart, but the outline of the pattern changes for each representative of the species.
The fireman beetle in the photo always amazes with its slender shape and long antennae, like antennas, turned in different directions.
Female firefighter beetles are larger than males. They can also be distinguished by their claws. In females they are larger.
Birds and large insects do not bother firefighters because of their ability to defend themselves. The beetles' tissues contain a substance called cataridin, which is poisonous to enemies. When hunting, a small predator attacks caterpillars, flies, and other small insects, bites them and injects poison, like a snake.
After immobilizing the prey, they release a special liquid that liquefies the tissues of the prey to absorb food.
If you catch a softie and take it in your hand, it will release a blood-colored liquid with an unpleasant odor from its abdomen. There is no point in checking whether fireman beetles bite or not. It is known that it can bite with its dagger-shaped jaws, reminiscent of the teeth of poisonous snakes.
Such a grip often saves the beetle from the invader, who only needs to unclench his palm. The fire beetle usually quickly flies away or pretends to be dead by tucking its limbs. Even in flight, it is not difficult to catch an insect - the beetle’s movement speed is low due to confidence in its own safety.
They have extraintestinal digestion. The larvae release digestive juice into the victim’s body, destroying tissue, and then suck the resulting liquid.
In spring, meltwater forces the larvae to crawl out onto the snow, which is why they are called snowworms. The development of larvae lasts for 2-3 years; they pupate in the soil.
The red fireman's beetle serves as an environmentally friendly defense against garden pests. To attract beneficial insects, it is recommended to keep fallen leaves near the trees, not to use pesticides, and not to dig up the area, especially the tree trunks. Soft beetles are natural agricultural assistants.
To restore natural balance, firefighters can be carefully collected by hand and given to neighbors if they agree. Gloves will not be superfluous in this work, since the beetles bite
Another method is to spray the area with a mixture containing tobacco dust or crushed cigarettes. The pungent odor repels insects. But this method of scaring helps only until the first rain.
Radical methods of application are to use Mashenka chalk, which is crushed and sprinkled on the borders of a certain area.
It is recommended to catch insects by hand, since getting rid of firefighter beetles in the house using chemicals will not be environmentally friendly.
Humane methods of control
Of course, it is not very pleasant to destroy an insect that helps get rid of pests in your favorite garden. But sometimes you have to make sacrifices for your own good. How to deal with the fireman beetle so that your heart doesn’t hurt and your conscience doesn’t torment you? There are several humane ways:
- Share insects with gardening friends who are “fighting” an aphid infestation. The beetles are carefully collected in a small container and passed from hand to hand as a “precious trophy”.
- Using a special mixture consisting of tobacco, ash, red pepper, and aromatic herbs. Powder is generously sprinkled on damaged crops to repel annoying insects.
- Use of chemicals. Some gardeners use chalk to control cockroaches. They grind it into powder and then sprinkle it on the damaged area.
Instead of tobacco, you can take the cheapest cigarettes, such as Prima, and prepare a repellent.
Fire bug and fire bug. How to distinguish them?
As soon as the spring sun warms up, small, rather pleasant-looking insects wake up - soldier bugs. People often call them firefighter beetles, but toy soldiers have nothing in common with beetles; they belong to different orders.
First, let's take a closer look at the soldiers. The soldier bug, or wingless red bug, or cossack bug, is a terrestrial insect of the Red bug family of the order Hemiptera. They live in temperate climates throughout Eurasia, northern Africa, and North America.
These bugs measure 9-11 mm and cannot fly. The body is painted black, the elytra and pronotum are painted red, which makes their appearance bright and attractive. Like all bedbugs, the mouthparts are piercing-sucking. Unlike house bugs, soldier bugs do not bite and are not dangerous to people.
Red bugs in early spring and late summer like to gather in dense clusters on stumps, tree trunks, woodpiles and fences, always on the sunny side. They can remain in this state for hours, basking in the sun. At this time they most often catch our eye.
They have no natural enemies - the red color, warning of danger, scares away birds and other insects.
Redbug Pyrrhocoris apterusPhoto: Depositphotos
The red bug feeds on fallen seeds, plant juices, and dead invertebrates. Cannibalism is also observed in the colonies of these cute insects - they eat dead relatives.
In the spring, the female lays two to three dozen pearly white eggs, from which larvae appear within 7-10 days. Usually the body of the larvae is colored red, with dark spots scattered throughout it, this makes them look like adult insects.
Soldiers overwinter under fallen leaves or tree bark.
Red bugs are not considered pests of agricultural crops, but recently there has been evidence that they damage seedlings of green crops, cabbage, beets and other cultivated plants.
You don’t have to use insecticides - they don’t cause that much harm compared to officially recognized pests. It is enough to use folk remedies: sprinkle the plants with an infusion of onion peels, wormwood, and wood ash. You can also treat cultivated plantings with a solution of mustard powder (100 g per bucket of water).
You can also plant a black cohosh plant on your plot, which will not only repel soldier bugs from the beds, but will also decorate your garden with original bushes, and during the flowering period, with exquisite silver-white inflorescences.
Fireman BeetlePhoto: Depositphotos
The fireman beetle, or soft beetle, the rustic soft beetle, is twice as long as the soldier bug, its size ranges from one and a half to two centimeters, it belongs to the Soft Beetle family from the order Coleoptera.
The fireman's abdomen is colored red or orange, the elytra are black or dark gray, the paws are black, and the filamentous antennae are dark. Because of its bright abdomen, associated with the uniform of the Royal Guards, the British call the soft-bodied beetle the soldier beetle.
You can see soft beetles in the grass or on the leaves of plants. They feed on small insects and plant leaves. If the bug is disturbed, it will fly away or, with its paws tucked in, pretend to be dead.
The larvae of fire beetles live in leaf litter, under the bark of trees, in rotten wood, and feed on eggs and insect larvae, which makes them useful to humans.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Insect fireman beetle
Soft cows mate only when warm weather arrives. The sun should warm the air and soil well. Typically, the period of procreation occurs in the summer - July. First, females and males split into pairs, then mate. After some time, the female lays eggs in the substrate. It should be soft and warm. Leaf litter on the soil, decaying plants, stumps, wood debris, and rotten branches are ideal for this.
To mature, eggs need some time - from fifteen to twenty days. The incubation period largely depends on the air temperature. After maturation, larvae are born. Outwardly, they very much resemble beads. The larvae are completely covered with hairs. They are small and have three pairs of legs. The larvae of fire beetles are very cute and interesting. The beetle larvae develop quickly, but at this stage they live for quite a long time.
Firefighter larvae, like adults, are predators. They eat small worms and centipedes as food. Also very interesting is the fact that larvae are characterized by digestion outside the intestine. How does this happen? Extraintestinal digestion involves the use of a special substance, poison. The larva injects this poison directly into the body of the victim, it almost instantly dissolves the tissues of the prey. Then the larva just needs to suck up the liquid food.
Closer to winter, pupation of larvae occurs. But only some of the larvae turn into pupae. The other part simply spends the winter in their shelter. In spring, the pupae turn into caterpillars and crawl out. People nicknamed the furry caterpillars “snow worms.” Then, with the onset of warmth, young firefighter beetles appear.
Amazing birth
Like any insect, the firefighter beetle is born from eggs that the female hides inside rotten stumps or loose soil.
Although it dies after a while, cute larvae emerge from the clutch. From the outside, the “babies” look like miniature black beads strung on a thin thread. While in such a shelter, the larvae are constantly moving, which has a beneficial effect on their development. Here they feed and live until they transform into a pupa. After 14 days, a magnificent creation emerges from it - the fireman beetle.
Habits and habitat
A detailed description and photo of the fireman's beetle arouses genuine interest in this insect. It can be seen in the warm season on raspberry and currant bushes. He “walks” majestically among the petals of flowering plants. But as soon as a person approaches him, he spreads his wings and flies away.
Unfortunately, this is not always the case. Nimble gardeners manage to catch the predatory beetle in their hands. To protect itself, it releases a fragrant red liquid, and when held for a long time, it bites. Feeling pain, the person unclenches his hand, and the insect instantly disappears.
Some people are interested to know: why is the fireman beetle called that? Interestingly, the insect has nothing to do with extinguishing fire. Except for his appearance. The body and legs are painted red. And the surface of the wings is black. Truly a unique uniform for protectors of garden plants in a country house.
To get rid of annoying cockroaches, just throw a few firefighter beetles into the room and the Prussians will leave the residential abode forever.
Interaction with people
In most cases, red soft beetles are beneficial insects. Throughout the summer, they destroy garden and vegetable pests, as well as their eggs and larvae. Beetles are able to cleanse the house of such unpleasant neighbors as cockroaches. The softies themselves do not penetrate human habitation; they will have to be caught and brought indoors. During the dry season, when the beetles multiply significantly, they damage the buds of berry and fruit crops. Adults always feed on pollen and flowers of plants, but in small numbers their influence is unnoticeable.
Signs of appearance
The appearance of a red soldier in your garden can be signaled by such phenomena as:
- drying of leaves of umbrella crops;
- the appearance of yellow spots on cabbage leaves;
- falling of buds and flowers;
- curling and drying of root crop tops;
- developmental lag of young seedlings;
- drying of berries.
The easiest way to find signs of damage is in crops such as cabbage (you should pay attention to large yellow spots on the leaves), coriander or dill (they begin to dry out quickly, since these varieties belong to the umbrella family), carrots and beets are inhibited in their development, leaf blades become deformed and wither.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the benefits and harms of dried dates for the human body: how and why to use them
Severely affected crops that cannot be saved must be removed and destroyed. They may contain larvae, which may soon infect surrounding crops.
How to attract soft beetles to the garden?
Since firebug beetles actively feed on aphids, caterpillars, locust eggs, mites and other small pests, they are very welcome guests in our gardens. Encouraging the presence of soft beetles on the site is quite easy. It has been observed that fire beetles prefer flowers from members of the Asteraceae and Apiaceae families, as well as some plants that bloom in clusters of small flowers, such as spurge.
They give particular preference to yellow-colored inflorescences (yarrow, sulfur-yellow cosmos, fennel, goldenrod and others). Pollination by beetles, known as cantharophily, is also carried out with the help of soft beetles. Thus, to attract fire beetles to the garden, you need to select suitable plants that will bloom throughout the summer season.
In addition, there should be a source of water in the garden, since fire beetles choose moist habitats. For the life cycle of these beetles (and many other beneficial organisms), it is important that there is mulched soil around them, untouched by digging and loosening, since these are the places the larvae choose for pupation. Avoid raking fallen leaves and add organic material to the surface of the beds as needed.
The fire beetle actively destroys aphids on currants
Interesting Facts
In addition to its bright color, the insect is interesting because:
- The venom of the soft belly has a specific odor;
- the red spot on the pronotum is individual for each beetle, like fingerprints or the auricle of a person;
- the insect is not afraid of temperature changes; in temperate latitudes the beetle feels great;
- not afraid of insects and birds of prey, the main defense is poison;
- The saving grace for a firefighter can be the ability to pretend to be dead in case of danger;
- the insect is an excellent analogue to the chemical treatment of garden plants against pests;
- the beetle has no upper lip;
- It is not difficult to catch a beetle in flight; its movement speed is not high.
The fireman beetle will bring a lot of benefits in the garden and on the plot: it will rid plants of aphids and help cope with caterpillars and flies. However, large numbers of insects can destroy the harvest of some stone fruits; it is advisable to monitor their numbers.
What names do people come up with for beetles? There is a rhinoceros beetle, a stag beetle and even a fireman beetle. This insect, of course, has nothing to do with fire violence, and the beetle received its name because of its bright color, which resembles the shape of fire fighters.
Fireman beetle on a leaf in summer
Its legs and body are red, but the wings with which it tightly covers its body are black. Scientists decided to classify this beetle as a soft beetle. And in fact, the fireman’s body is soft, slightly flattened and weak, and its length reaches 1.5 cm.
And even though at the slightest danger it pulls its head into its body, this beetle cannot be called a coward. If, for example, cockroaches are rampant in the house, you should bring a couple of firefighter beetles, and the cockroaches will disappear. And no amount will frighten him.
This beetle is also not afraid of cool weather, and in summer it can be seen in all areas of temperate and cold climates. Most often, these soft-bodied animals prefer to settle next to cultivated trees, because there is a rich “table” for them. This is why gardeners consider the fireman beetle to be their assistant.
Very often in the photo the fireman beetle is shown on a person’s hand. But in reality, the beetle tries to avoid close contact with humans. And he succeeds very well, because he senses the approach of a person too well and manages to fly away, because his wings are well developed.
Pleasant fellowship in the fight against a common enemy
Everything that has been created around us occupies its own special place in the Creator’s plan.
Every insect and beetle occupy an important place in the existence of real nature. What is the benefit of the fireman's beetle and is this insect harmful to humans?
Considering what it feeds on, it becomes clear that without such a predator the garden would be lost. Infestations of very small caterpillars and aphids can quickly destroy a hard-won crop. However, for an amazing creation in a red and black robe, this is only tasty and nutritious food. Thanks to this, some gardeners lure beetles into their own property. To do this, they try to adhere to similar rules:
- do not dig up the soil on specific plots of land;
- do not burn fallen leaves;
- leave it under wintering bushes and trees;
- do not use harmful chemicals.
Unfortunately, sometimes such a useful community causes harm. If entire colonies of insects appear in the garden, they add plant foods to their diet.
Nutrition
The predatory nature of firefighter beetles manifests itself in the hunt for a variety of insects: aphids, caterpillars, small leaf beetles, and the larvae of other soft beetles. Organisms protected by a chitinous covering are too tough for the firefighter beetle.
Red-legged softies approach their prey closely or sit on it. They press with their jaws from all sides until the resistance stops. Sharp and strong sickle-shaped jaws, which are designed specifically for holding, not chewing, help preserve prey.
Injecting poison and digestive juice into the victim’s body helps convert what they catch into food. The diet includes insects whose size is smaller than the predator itself.
Many gardeners do not know about the benefits of firefighter and try to get rid of it, classifying it as a plant pest. It has been proven that the presence of red-legged softies on the site contributes to a good harvest.
Firefighter beetle larvae also follow the diet of predators. It is interesting that the number of garden pests destroyed by softfly larvae exceeds the imago, i.e. developed beetles. The larvae eat various centipedes, worms, and small insects.
What do firefighter beetles eat, besides small animals? If an excessive number of red-legged soft-bodied animals have gathered in one area, then the lack of animal food is compensated for by plant food.
Beetles bite off flowering buds and greenery of fruit crops, causing harm to gardeners and gardeners. This does not happen so often, so experts unanimously believe that the benefits of firefighter beetles are disproportionately greater than the harm.
Gravedigger beetles (lat. Nicrophorus)
Oh, and they were named! Although... there is nothing terrible about it, quite the contrary. These beetles from the family of carnivores are of great benefit. They are the best and most conscientious orderlies of the animal world. Gravediggers, in the literal sense of the word, bury the corpses of small animals. But they do this not for others, but first of all, for themselves. These corpses will serve as an excellent food base for their larvae in the future.
Gravedigger beetles (lat. Nicrophorus) (eng. Sexton Beetle)
Burying beetles have also become famous for their intelligence (if this concept is generally applicable to insects) and incredible care for their offspring. But before revealing all their secrets, let’s take a closer look at the physiology and habitat of this unique creature.
Photo by JC Schou
There are 68 species of gravediggers in the world. They are distributed almost everywhere, with the exception of tropical Africa and Australia. 20 of them live here in Russia.
Outwardly, they are very cute creatures. These are large black beetles with orange or yellow spots on the elytra. Their body length, depending on the species, can range from 1 to 4 centimeters. The large head is “decorated” with antennae with clubs at the ends. It is thanks to them that beetles, even with weak breaths of air, are able to “smell” the smell of decaying flesh, even if it is several hundred meters away.
Having reached the corpse, the gravediggers, like real foremen, begin to assess the scope of the upcoming work. This is done in order to bury the dead body as quickly as possible, before other scavengers, such as carrion flies or other carrion eaters, get to it first. The beetle climbs under the body of its “prey” and begins to dig the ground underneath it until it settles deeper under its own weight.
If the corpse lies on too hard ground, then the beetle with its whole body tries to move it to the side with softer soil. If plant stems get in his way, he gnaws them at the very base. It is practically impossible for one beetle to do this, so several insects work on one animal corpse. After some time, an earthen ridge forms around the dead animal, and the body itself settles under its own weight and is then covered with earth.
Photo by Eigenes Werk
But...several insects took part in the work, most often several males and a female, and as a result, only two remain near the “grave” - a male and a female, who, after mating, tries to drive away the male. But this is done not because of greed or the desire for sole ownership of a large sum, but purely because of “maternal” instincts. By the way, adult beetles practically do not eat carrion; all good things are intended exclusively for their offspring.
Then the female alone begins to dig a small underground niche, which opens to the carcass of the buried animal. Having laid a couple of dozen eggs there, the female returns to the corpse and begins to gnaw several funnel holes in it, into which she regurgitates her digestive juice. What are all these tricks for? All for the same thing, for his beloved and beloved offspring.
Photo by Thomas Walton
No matter how surprising it may sound. Burying beetles are one of the few representatives of the order Coleoptera, which are characterized by caring for their offspring. Having stuffed the corpse with her digestive juice, the female gets out of these underground catacombs and disappears for a couple of days to go about her business. A few days before the hatching of the larvae, the female, who somehow knew that this moment would soon come, returns back and clears the passage for her larvae.
After some time, the larvae hatch - white, blind, with a lanceolate body shape and 6 underdeveloped legs. But they have strong black jaws. Having reached the “parental” gift, each of them chooses the funnel he likes and begins to eat from it the corpse tissue dissolved by the mother’s digestive enzymes. On such nutritious food supplies they grow very quickly and literally after 10-12 days they are ready to pupate. The larvae burrow deeper into the ground and after 2 weeks a young gravedigger bug appears.
To prevent the animal's carcass from deteriorating prematurely and future babies from starving, the male and female of one of the species of gravediggers - Nicrophorus vespilloides - cover the fur or plumage of their find with a special secretion that has antibacterial properties. This enzyme, lysozyme, destroys the bacterial cell wall. Thus, burying beetles demonstrate one of the most unusual ways of caring for offspring among other insects for which social behavior is not typical (ants, termites, bees, etc.)