Photos of the wasp can be seen in any biology textbook, on Internet sites, and information publications. The common wasp is found everywhere, characterized by a bright striped yellow-black color, small antennae, and long transparent wings. Wild wasps often settle on a person’s dacha plot of land. They build nests in the ground, in trees, under the roof, in attics, and on balconies. However, there is a huge variety of wasps in the world, differing in color, body structure, strength of poison, and behavior.
Anatomy of a wasp
Hymenoptera is the most numerous, evolutionarily developed group of insects. Includes 155 thousand species.
A characteristic feature of insects of this species is the presence of a thin stalk between the abdomen and sternum. The concept of “wasp waist” even appeared among the people. The body is standardly divided into 3 parts - head, chest, abdomen. The color varies among different species, but black, yellow, and orange colors are almost always present.
Another distinctive feature is the special wings. Thin, transparent, with clearly visible veins. The rear ones are always smaller than the front ones. They shimmer in different colors or are colorless. A beautiful purple tint is more common. The wasp's legs consist of 5 segments. Perform walking, grasping, digging functions.
On the head there are mustaches of different shapes and lengths. They serve as a landmark, detect sounds and smells. Well visible eyes. The powerful jaws do not contain teeth, but are so hard that they can bite through the chitinous cover of an insect.
Common wasp
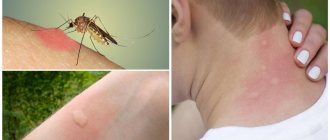
The wasp insect has a sting, which is hidden in the lower part of the abdomen and is a modified ovipositor. Only females have the ability to sting. The needle-shaped sting is connected to a gland where poison of varying toxicity is synthesized. It is used by insects in defense, protecting the nest, young, and immobilizing the victim.
Interesting!
Individuals of different sexes differ in body size and organ structure. The largest wasp in the world is female and reaches a size of 55 mm. It belongs to the Scolia species, lives in countries with a warm, tropical climate, some species are found in Russia and the countries of the former CIS.
You can see what a wasp looks like in the photo below. The larvae differ significantly in appearance from the imago. These are worm-like caterpillars of off-white color. They feed on protein foods and are predators.
Benefits and harms
Hoverflies can be classified as predatory insects, as they feed on plant foods and insect pests. Adults feed on pollen and plant nectar. Therefore, hover flies can be classified as pollinating insects. Insects give the greatest preference to umbelliferous and asteraceous plants. They do not disdain a variety of meadow grasses, fruit trees and shrubs.
The basis of insect nutrition is sugar, which is contained in nectar. It is he who gives the hoverflies energy. And pollen provides the protein necessary for the growth and development of eggs.
The hatched larvae differ in their feeding habits. Some feed on rotting wood, while others live and develop in water. There are exotic species that eat and process manure. Most of the larvae prefer aphids. Therefore, they can be considered true protectors of gardens. Many amateur gardeners specially plant the trunk circles of berry and fruit trees with umbrella crops in order to attract hoverflies to the garden to prevent aphid attacks.
But there are varieties of hover flies that feed on lily crops. It is these specimens that can cause damage to the crop by eating the bulbs of flower crops and damaging onions and garlic.
An interesting insect is the hoverfly. Despite the fact that some species can eat cultivated plants, in general they are assistants to humans. In remote mountainous areas, where there is a shortage of bees and wasps, they pollinate plants and increase their productivity. Great help is provided by eating aphids and spider mites in the garden. This protects the trees from pests. And it’s just interesting to watch them move in the air.
Many people have at least once in their lives seen a fly that visually resembles a bee or wasp. It differs from those of insects in its behavior. It is called the hoverfly. Insect larvae can be useful to humans. In the article we will consider the characteristics, behavioral features of the “pest” and methods of control.
There are about 6,000 species of hoverflies in nature, 800 of which live in the territory of the former USSR. In the adult state, the insect has a length from 4 to 25 mm. Body color is yellow-black. Externally, insects look like wasps. Thanks to its color and shape, the fly scares away enemies.
Important: mimicry is a natural property of animals that allows them to camouflage themselves by “taking on” the appearance of others. The female is capable of laying up to 200 eggs. It all depends on weather conditions and temperature conditions
Mucha places them on:
It all depends on weather conditions and temperature conditions. Mucha places them on:
The female is capable of laying up to 200 eggs. It all depends on weather conditions and temperature conditions. Mucha places them on:
- grass;
- plant stems;
- on buds and trees.
The location of the eggs directly depends on the type of insect. On the 5th day, larvae are born. Outwardly, they resemble maggots - the offspring of blowflies. The larvae feed depending on the species:
- dead plant tissue;
- detritus;
- aphids;
- bulbs (mostly flowers).
The larvae of some hoverflies are beneficial to humans. Therefore, before fighting them, it is recommended to carefully study the insects.
Types of wasps
The main classification divides these insects into 2 large groups.
Social wasps
They can be called differently, including paper. They form numerous families with up to 1 million individuals. They build nests of different sizes. A standard hive is the size of an apple, the largest being 60 cm in diameter. An image of the photograph can be seen below.
There is a clear division into castes. Individuals communicate with each other using sounds and signals. At the head of the family is the female queen, who is engaged in the reproduction of offspring. Some species of wasps provide several fertile females in one hive, but they do not pretend to be the queen, they simply help increase the number of members of the wasp society. Close-up of the wasp next.
Social wasps
Singles
They are distinguished by primitive behavior, each individual lives separately. There are no nests as such, there is no swarm. Most of them are predators. Eggs are laid on the abdomen of the larvae of large beetles, spiders, etc. The larva develops independently, eating the victim from the inside. At the end of the stage, it pupates and remains in this form for the winter. In spring, adults appear. Some solitary wasps are extremely poisonous, the bite is compared to piercing the skin with a hot nail. Photos with names can be seen below.
On a note!
Social wasps are often called paper wasps, wood wasps, because their nests look like a cocoon woven from toilet paper, and nests are built on a tree, under the roof of wooden buildings, attics, hollows, and old stumps. Solitary wasps include sand, burrowing, and road wasps. Among them there are quite harmless, useful creatures, parasites, killers.
Wasps are ubiquitous in Russia. Among them there are polystina, vespin, scoli, road, typhy, sand.
Single wasp
Description and features
The wasp is brightly colored. The pattern on her body is an alternation of black areas with yellow stripes on the body, as well as a pattern of the same color on the head and six legs.
Usually the bright color of insects in nature often indicates that this creature is poisonous. Wasps are often the name given to all stinging flying insects belonging to the suborder Stalk-bellied insects, with the exception of bees.
All wasps in the photo look the same, just like in real life, but they may differ in size. They have four transparent wings arranged in pairs. In addition, they have a very powerful mouthparts and faceted eyes, which provide the insect with excellent vision.
Coarse hairs can be observed on their paws, allowing such creatures to grip and hold on to a variety of surfaces.
This insect has two ways of fighting against the enemies that the wasp has in nature: mammals, birds, lizards and others.
First of all, the bright colors themselves provide powerful protection. It frightens the enemy, and hunters of various stripes, hungry for prey, lose their appetite when they look at the wasps. It’s just that their color causes unpleasant associations in many living creatures.
But even if one of the predators foolishly attempts to feast on such an insect, after the first misfire, their desires completely disappear. It's just that the sensations are not very pleasant. Therefore, subsequently, enemies stop making attempts to hunt wasps, having developed a warning reflex in themselves.
But in addition to passive methods of protection, these insects also have active methods. And their poisonous sting helps them in this - an autonomous organ, similar to a dagger blade in appearance and principle of action.
It freely penetrates under the skin of the animal, and also comes out without difficulty, having previously injected its portion of poison. This organ is located at the end of the abdomen, like a bee, because it is an insect very similar to a wasp , also capable of stinging.
But the bites of these two poisonous creatures have a number of differences, primarily for themselves. Unlike bees, who die after using their sharp weapon at least once and leaving it in the enemy’s body, wasps remain alive.
When a wasp stings, it does not leave a sting, unlike a bee.
Moreover, they feel great after a bite and are quite capable of making a new attack. In addition, wasps are endowed with the ability to use not only stings, but powerful jaws when attacking. But, like bees, these insects, sensing the smell of poison released by a fellow insect into the enemy’s body, will certainly enter into battle, collectively attacking the object that caused the alarm.
Externally, these insects are certainly similar, but it is not very difficult to distinguish them even by color. If the wasp is yellow and black, then the stripes on the bee’s body have a slightly different hue, with the addition of orange tones.
Pictured is a wasp and a bee
Lifespan
Life expectancy differs among different species and sexes. The male wasp performs the functions of a fertilizing male. Soon after mating it dies. On average, a male wasp lives 14 days.
Fertile females are called queens. Social queens lay the foundation of a future nest, choose a suitable place, and are exclusively engaged in the reproduction of offspring. The queen of ordinary wasps lives for a year. Dies with the onset of persistent cold weather. Young fertilized females overwinter in the wood and become more active in the spring. Representatives of other species in countries with warm climates can live for several years.
On a note!
The majority of the social wasp hive is made up of females who are not ready to mate—working individuals. They perform various functions such as building a nest, searching for food, feeding larvae, protecting the hive, etc. The working individual lives from 1 to 2 months.
How is a bee different from a wasp?
- Appearance. The bee has a round body, while the wasp has an elongated body shape.
- The bee has a brighter and more contrasting color, the wasp has a softer and more monotonous color.
- Like a fly, the average wasp is more parasitic and takes away than it gives. The bee, in turn, brings more benefits.
These are not all the differences, but they are the main ones, so distinguishing insects from each other is not difficult.
Life cycle - reproduction
Wasps lay eggs in a hive or a special hole underground, where they first drag the paralyzed victim.
Life cycle of public OS
The eggs are laid by the queen in separate combs. Initially, she takes care of the offspring herself and obtains food. After the appearance of the first generation of working individuals, all responsibilities for building the nest and caring for the larvae are transferred to them.
The wasp larva appears after a few days. Looks like a worm. It has a good appetite and grows quickly. It feeds on protein foods; insects carry beetles, spiders, flies, larvae, and pieces of meat to them. Over the course of 14 days, the young individual goes through several moults, increases in size, and finally pupates. It gnaws through the cocoon and emerges as an imago. The entire life cycle takes up to 20 days. The maximum activity of the family on our territory is observed in the summer.
Reproduction of wasps
Life cycle of solitary wasps
They are not so intensively engaged in the reproduction of offspring. The peak of activity occurs in the second half of summer. The female burrows into the ground, looks for a potential victim, and paralyzes. He pulls it into a special hole, lays an egg, climbs out, and buries the entrance. This is where her mission ends. For each larva, the female looks for a new victim and digs a separate hole. The larva overwinters in the cocoon and is born in early spring. The life of a wasp at the adult stage does not exceed 5 months.
Classification
Wasps are divided into two types - social and solitary.
Public
Social species live in nests and jointly care for their offspring. Females overwinter in cracks
bark or under stones. In the spring they begin building nests and laying eggs.
The emerging young take full care of the nest, and the queen is then exclusively engaged in egg laying. The nest is built from chewed tree bark mixed with saliva. This substance resembles paper. Hornets are the largest insects of this class; during construction they are capable of leaving small trees without bark. Eggs in social species produce sterile females in the summer. And only in the fall the queen lays eggs, from which a heterosexual brood emerges. Fertilized young females go into winter, and the old nest with all its inhabitants dies.
Singles
Solitary species lead a solitary lifestyle and are parasites dangerous to other insects. Females of solitary species catch spiders, flies and bedbugs. They are then paralyzed with poison and placed in their burrow, where eggs are laid in the body of the still living victim.
Usually the victim lives until pupation and only after that the parasitic wasp larvae destroy the host, completely drying out its internal organs. Hunting wasps more often attack different types of spiders. For example, their diet includes tarantulas. An interesting fact is the female’s indifference to her offspring. Very rarely, she can visit the nest and bring food to the larvae.
Predatory solitary wasp species help humans cope with agricultural pests. Some of them, on the contrary, cause harm by destroying bees in apiaries.
Where do insects live
Species of social representatives build nests and form a hive. They set up a place of residence in an area where there is building material and food. Abandoned nests, rodent burrows, and anthills are often favorable places. As well as ordinary grass, dense tree crowns, thickets of bushes, stones, mounds of soil. They can settle on the territory of human possessions - garden, vegetable garden, outbuildings, roof, attic, balcony. The wasps spend the entire summer in the hive and leave the nest with the onset of cold weather. Only young fertilized females survive, finding shelter for wintering under the bark of trees and crevices.
Solitary representatives live in the wild, spending the night with their jaws and paws hooked on the grass. They climb into a flower. It is impossible to determine their exact location, since it is constantly changing.
How wasps arrange their homes
The queen wasp begins building a nest; to begin with, she only needs a dwelling the size of a walnut - there she will lay her first clutch of eggs. She builds only one layer of the nest, then gradually builds on the next.
She will begin to build the nest herself until the worker wasps hatch from the first clutch, which will continue their work, completely freeing her for further procreation and increasing the number of livestock in the swarm.
By the size of the wasp nest, you can understand the size of the number of working individuals in the wasp family.
Wasps of a single species build their homes in their own way. This may be a small cell located in a place where prying eyes will not penetrate and precipitation will not fall.
For example, pottery wasps build dwellings from natural mud, shaped like a vase; structures are attached to tree branches or to the walls of human buildings.
Some wasps make homes in plant stems they have bitten through or dig holes in the soil. A single wasp can settle in any small crack located on a piece of thick cardboard, or in gardening gloves forgotten and lost in the garden.
The peculiarity of solitary wasps is that having laid a clutch, they seal it, and there is no interaction between adults and larvae.
There is an observation that from those cells that are smaller in size than the others, male larvae hatch, which means that the males are smaller in size than the females.
Everything about OSes - interesting facts
Varieties of wasps
Individual specialists study the life of wasps and continue to surprise ordinary people with interesting facts.
- Little wasps. They are representatives of social, ordinary species. The body length of the female reaches 20 mm. Drones, workers, males - about 18 mm.
- Tree wasp. Includes many varieties, has a bright black and orange color. The size range ranges from 10 to 60 mm. The most dangerous representative of this genus is the hornet, which can be distinguished by its large dimensions. An interesting representative is the synodica wasp, about which there is extremely little information.
- Asian hornet. The most dangerous wasp. In China and Japan, 50 people die from bites every year, according to official statistics. For an allergy sufferer, one bite from a giant killer pest can be fatal. The size of the hornet reaches 5.6 cm.
- Great spotted scolius. This species is the most beautiful representative of large wasps. The female’s body size is 55 mm, the male’s is 32 mm. Lays larvae on the body of larvae of cockchafers and rhinoceros. Leads a primitive, solitary lifestyle. Despite its impressive size, it is safe for humans. The consequences of the bite are numbness.
- German women. Externally, wingless, furry females resemble an ant. Body size does not exceed 30 mm. The female has a bright color, the males of this species are brown in color. They do not build their own nests; they parasitize in the hives of bees and other wasps.
There are extremely many representatives of this species of Hymenoptera in the world, each of them is unique and has its own characteristics.
Lifestyle and habitat
Wasps can be found almost everywhere, in almost every corner of the planet, with the exception of areas that are particularly unsuitable for life. They prefer to settle close to humans, because in the immediate vicinity of people and their homes there is always something to eat.
Now it's time to talk more about the social structure inherent in paper wasps. It is these representatives of the diversity of species already described that should be given special attention, because when they talk about wasps, they usually mean wild social wasps. Although this is not entirely correct.
The groups in which these insects gather to live together are close-knit families called colonies. They can have up to 20 thousand members. In such families there is a clearly established social structure and division into castes with a certain range of responsibilities.
Wasps and their honeycombs
The uterus is engaged in breeding offspring. Worker wasps look after the larvae, feed the rest of the family and guard the common home. The queen builds a nest out of a paper-like material.
It is produced naturally by wasps themselves, by grinding wood and mixing the material with their own saliva. Powerful jaws help these creatures build nests.
With these, the queen is capable of finely grinding hard wood. Worker wasps and drones are on average about 18 mm in size, but the queen of these insects is slightly larger. Males and females are approximately the same color, but females have a slightly larger abdomen. Single wasps may not build nests, but use burrows made by other insects and small rodents.
Wasp enemies
Despite the serious poisonous weapon in the form of a sting, wasps are often attacked by other insects and become victims of birds and mammals.
- Ants left without a queen destroy nests. Weak, sick individuals can become victims of these insects.
- The fan is paradoxical. The beetle makes its way into the hive, into the burrow of ground wasps, and lays eggs. Larvae develop on the body of young wasps.
- Hornets. The most formidable enemy of the wasp family is the killer wasps themselves, which have a significant advantage in size and number. Hornets completely devastate a family in one attack.
- Buzzard birds hunt wasps. The chicks are fed with adults and larvae.
In late autumn, the activity of the wasp family decreases; they become slow and inactive. They become victims of insects and many birds. In early spring, bears search for insects under stumps and bark.
Ways of coexistence of wasps with humans
People often become victims of stinging insects. Wasps in an apartment or house can find a decent source of food. Human dwellings attract large numbers of insects, which become prey. Flies are their favorite food, so these predators settle in places where cows are grazed or kept. Nature has endowed individual species with varying degrees of aggressiveness. For example, insects living on the forest floor sting any creature that is near their home.
Paper wasps
Paper wasps, which often settle near homes, do not attack humans unless someone tries to destroy their nest. The aggressive behavior of these insects towards humans in this case is usually a simple accident. For example, if the object on which it was sitting fell into your hands. Wasps often climb into a house to establish a colony for the purpose of self-defense, since their natural enemies, for example, dragonflies, are scared away into a person’s home. In addition, these insects can hide in the cracks of windows in order to overwinter in better conditions and not die.